Rong-Cheng Tu
SPA-Cache: Singular Proxies for Adaptive Caching in Diffusion Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:While Diffusion Language Models (DLMs) offer a flexible, arbitrary-order alternative to the autoregressive paradigm, their non-causal nature precludes standard KV caching, forcing costly hidden state recomputation at every decoding step. Existing DLM caching approaches reduce this cost by selective hidden state updates; however, they are still limited by (i) costly token-wise update identification heuristics and (ii) rigid, uniform budget allocation that fails to account for heterogeneous hidden state dynamics. To address these challenges, we present SPA-Cache that jointly optimizes update identification and budget allocation in DLM cache. First, we derive a low-dimensional singular proxy that enables the identification of update-critical tokens in a low-dimensional subspace, substantially reducing the overhead of update identification. Second, we introduce an adaptive strategy that allocates fewer updates to stable layers without degrading generation quality. Together, these contributions significantly improve the efficiency of DLMs, yielding up to an $8\times$ throughput improvement over vanilla decoding and a $2$--$4\times$ speedup over existing caching baselines.
A Survey on Efficient Large Language Model Training: From Data-centric Perspectives
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Post-training of Large Language Models (LLMs) is crucial for unlocking their task generalization potential and domain-specific capabilities. However, the current LLM post-training paradigm faces significant data challenges, including the high costs of manual annotation and diminishing marginal returns on data scales. Therefore, achieving data-efficient post-training has become a key research question. In this paper, we present the first systematic survey of data-efficient LLM post-training from a data-centric perspective. We propose a taxonomy of data-efficient LLM post-training methods, covering data selection, data quality enhancement, synthetic data generation, data distillation and compression, and self-evolving data ecosystems. We summarize representative approaches in each category and outline future research directions. By examining the challenges in data-efficient LLM post-training, we highlight open problems and propose potential research avenues. We hope our work inspires further exploration into maximizing the potential of data utilization in large-scale model training. Paper List: https://github.com/luo-junyu/Awesome-Data-Efficient-LLM
AD-FM: Multimodal LLMs for Anomaly Detection via Multi-Stage Reasoning and Fine-Grained Reward Optimization
Aug 06, 2025



Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate remarkable capabilities across diverse domains, their application to specialized anomaly detection (AD) remains constrained by domain adaptation challenges. Existing Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) based approaches suffer from two critical limitations: inadequate training data utilization when models produce uniform responses, and insufficient supervision over reasoning processes that encourage immediate binary decisions without deliberative analysis. We propose a comprehensive framework addressing these limitations through two synergistic innovations. First, we introduce a multi-stage deliberative reasoning process that guides models from region identification to focused examination, generating diverse response patterns essential for GRPO optimization while enabling structured supervision over analytical workflows. Second, we develop a fine-grained reward mechanism incorporating classification accuracy and localization supervision, transforming binary feedback into continuous signals that distinguish genuine analytical insight from spurious correctness. Comprehensive evaluation across multiple industrial datasets demonstrates substantial performance improvements in adapting general vision-language models to specialized anomaly detection. Our method achieves superior accuracy with efficient adaptation of existing annotations, effectively bridging the gap between general-purpose MLLM capabilities and the fine-grained visual discrimination required for detecting subtle manufacturing defects and structural irregularities.
Intra-Trajectory Consistency for Reward Modeling
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Reward models are critical for improving large language models (LLMs), particularly in reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) or inference-time verification. Current reward modeling typically relies on scores of overall responses to learn the outcome rewards for the responses. However, since the response-level scores are coarse-grained supervision signals, the reward model struggles to identify the specific components within a response trajectory that truly correlate with the scores, leading to poor generalization on unseen responses. In this paper, we propose to leverage generation probabilities to establish reward consistency between processes in the response trajectory, which allows the response-level supervisory signal to propagate across processes, thereby providing additional fine-grained signals for reward learning. Building on analysis under the Bayesian framework, we develop an intra-trajectory consistency regularization to enforce that adjacent processes with higher next-token generation probability maintain more consistent rewards. We apply the proposed regularization to the advanced outcome reward model, improving its performance on RewardBench. Besides, we show that the reward model trained with the proposed regularization induces better DPO-aligned policies and achieves better best-of-N (BON) inference-time verification results. Our code is provided in https://github.com/chaoyang101/ICRM.
A Survey of Automatic Evaluation Methods on Text, Visual and Speech Generations
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning have significantly enhanced generative AI capabilities across text, images, and audio. However, automatically evaluating the quality of these generated outputs presents ongoing challenges. Although numerous automatic evaluation methods exist, current research lacks a systematic framework that comprehensively organizes these methods across text, visual, and audio modalities. To address this issue, we present a comprehensive review and a unified taxonomy of automatic evaluation methods for generated content across all three modalities; We identify five fundamental paradigms that characterize existing evaluation approaches across these domains. Our analysis begins by examining evaluation methods for text generation, where techniques are most mature. We then extend this framework to image and audio generation, demonstrating its broad applicability. Finally, we discuss promising directions for future research in cross-modal evaluation methodologies.
Multimodal Reasoning Agent for Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval
May 26, 2025Abstract:Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval (ZS-CIR) aims to retrieve target images given a compositional query, consisting of a reference image and a modifying text-without relying on annotated training data. Existing approaches often generate a synthetic target text using large language models (LLMs) to serve as an intermediate anchor between the compositional query and the target image. Models are then trained to align the compositional query with the generated text, and separately align images with their corresponding texts using contrastive learning. However, this reliance on intermediate text introduces error propagation, as inaccuracies in query-to-text and text-to-image mappings accumulate, ultimately degrading retrieval performance. To address these problems, we propose a novel framework by employing a Multimodal Reasoning Agent (MRA) for ZS-CIR. MRA eliminates the dependence on textual intermediaries by directly constructing triplets, <reference image, modification text, target image>, using only unlabeled image data. By training on these synthetic triplets, our model learns to capture the relationships between compositional queries and candidate images directly. Extensive experiments on three standard CIR benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. On the FashionIQ dataset, our method improves Average R@10 by at least 7.5\% over existing baselines; on CIRR, it boosts R@1 by 9.6\%; and on CIRCO, it increases mAP@5 by 9.5\%.
MLLM-Guided VLM Fine-Tuning with Joint Inference for Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval
May 26, 2025Abstract:Existing Zero-Shot Composed Image Retrieval (ZS-CIR) methods typically train adapters that convert reference images into pseudo-text tokens, which are concatenated with the modifying text and processed by frozen text encoders in pretrained VLMs or LLMs. While this design leverages the strengths of large pretrained models, it only supervises the adapter to produce encoder-compatible tokens that loosely preserve visual semantics. Crucially, it does not directly optimize the composed query representation to capture the full intent of the composition or to align with the target semantics, thereby limiting retrieval performance, particularly in cases involving fine-grained or complex visual transformations. To address this problem, we propose MLLM-Guided VLM Fine-Tuning with Joint Inference (MVFT-JI), a novel approach that leverages a pretrained multimodal large language model (MLLM) to construct two complementary training tasks using only unlabeled images: target text retrieval taskand text-to-image retrieval task. By jointly optimizing these tasks, our method enables the VLM to inherently acquire robust compositional retrieval capabilities, supported by the provided theoretical justifications and empirical validation. Furthermore, during inference, we further prompt the MLLM to generate target texts from composed queries and compute retrieval scores by integrating similarities between (i) the composed query and candidate images, and (ii) the MLLM-generated target text and candidate images. This strategy effectively combines the VLM's semantic alignment strengths with the MLLM's reasoning capabilities.
VORTA: Efficient Video Diffusion via Routing Sparse Attention
May 24, 2025Abstract:Video Diffusion Transformers (VDiTs) have achieved remarkable progress in high-quality video generation, but remain computationally expensive due to the quadratic complexity of attention over high-dimensional video sequences. Recent attention acceleration methods leverage the sparsity of attention patterns to improve efficiency; however, they often overlook inefficiencies of redundant long-range interactions. To address this problem, we propose \textbf{VORTA}, an acceleration framework with two novel components: 1) a sparse attention mechanism that efficiently captures long-range dependencies, and 2) a routing strategy that adaptively replaces full 3D attention with specialized sparse attention variants throughout the sampling process. It achieves a $1.76\times$ end-to-end speedup without quality loss on VBench. Furthermore, VORTA can seamlessly integrate with various other acceleration methods, such as caching and step distillation, reaching up to $14.41\times$ speedup with negligible performance degradation. VORTA demonstrates its efficiency and enhances the practicality of VDiTs in real-world settings.
T2I-Eval-R1: Reinforcement Learning-Driven Reasoning for Interpretable Text-to-Image Evaluation
May 23, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress in diffusion-based text-to-image (T2I) generation has created an urgent need for interpretable automatic evaluation methods that can assess the quality of generated images, therefore reducing the human annotation burden. To reduce the prohibitive cost of relying on commercial models for large-scale evaluation, and to improve the reasoning capabilities of open-source models, recent research has explored supervised fine-tuning (SFT) of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) as dedicated T2I evaluators. However, SFT approaches typically rely on high-quality critique datasets, which are either generated by proprietary LLMs-with potential issues of bias and inconsistency-or annotated by humans at high cost, limiting their scalability and generalization. To address these limitations, we propose T2I-Eval-R1, a novel reinforcement learning framework that trains open-source MLLMs using only coarse-grained quality scores, thereby avoiding the need for annotating high-quality interpretable evaluation rationale. Our approach integrates Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) into the instruction-tuning process, enabling models to generate both scalar scores and interpretable reasoning chains with only easy accessible annotated judgment scores or preferences. Furthermore, we introduce a continuous reward formulation that encourages score diversity and provides stable optimization signals, leading to more robust and discriminative evaluation behavior. Experimental results on three established T2I meta-evaluation benchmarks demonstrate that T2I-Eval-R1 achieves significantly higher alignment with human assessments and offers more accurate interpretable score rationales compared to strong baseline methods.
Robust Distribution Alignment for Industrial Anomaly Detection under Distribution Shift
Mar 19, 2025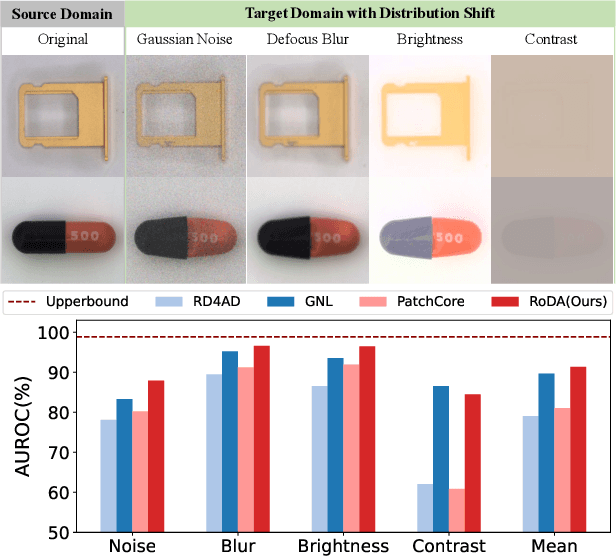
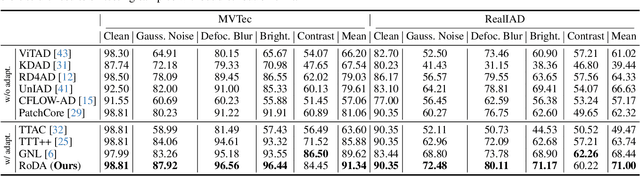
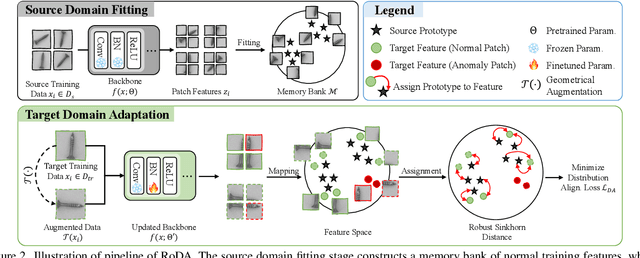

Abstract:Anomaly detection plays a crucial role in quality control for industrial applications. However, ensuring robustness under unseen domain shifts such as lighting variations or sensor drift remains a significant challenge. Existing methods attempt to address domain shifts by training generalizable models but often rely on prior knowledge of target distributions and can hardly generalise to backbones designed for other data modalities. To overcome these limitations, we build upon memory-bank-based anomaly detection methods, optimizing a robust Sinkhorn distance on limited target training data to enhance generalization to unseen target domains. We evaluate the effectiveness on both 2D and 3D anomaly detection benchmarks with simulated distribution shifts. Our proposed method demonstrates superior results compared with state-of-the-art anomaly detection and domain adaptation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge