Heyan Huang
DeepSurvey-Bench: Evaluating Academic Value of Automatically Generated Scientific Survey
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:The rapid development of automated scientific survey generation technology has made it increasingly important to establish a comprehensive benchmark to evaluate the quality of generated surveys.Nearly all existing evaluation benchmarks rely on flawed selection criteria such as citation counts and structural coherence to select human-written surveys as the ground truth survey datasets, and then use surface-level metrics such as structural quality and reference relevance to evaluate generated surveys.However, these benchmarks have two key issues: (1) the ground truth survey datasets are unreliable because of a lack academic dimension annotations; (2) the evaluation metrics only focus on the surface quality of the survey such as logical coherence. Both issues lead to existing benchmarks cannot assess to evaluate their deep "academic value", such as the core research objectives and the critical analysis of different studies. To address the above problems, we propose DeepSurvey-Bench, a novel benchmark designed to comprehensively evaluate the academic value of generated surveys. Specifically, our benchmark propose a comprehensive academic value evaluation criteria covering three dimensions: informational value, scholarly communication value, and research guidance value. Based on this criteria, we construct a reliable dataset with academic value annotations, and evaluate the deep academic value of the generated surveys. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our benchmark is highly consistent with human performance in assessing the academic value of generated surveys.
Beyond Literal Mapping: Benchmarking and Improving Non-Literal Translation Evaluation
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly advanced Machine Translation (MT), applying them to linguistically complex domains-such as Social Network Services, literature etc. In these scenarios, translations often require handling non-literal expressions, leading to the inaccuracy of MT metrics. To systematically investigate the reliability of MT metrics, we first curate a meta-evaluation dataset focused on non-literal translations, namely MENT. MENT encompasses four non-literal translation domains and features source sentences paired with translations from diverse MT systems, with 7,530 human-annotated scores on translation quality. Experimental results reveal the inaccuracies of traditional MT metrics and the limitations of LLM-as-a-Judge, particularly the knowledge cutoff and score inconsistency problem. To mitigate these limitations, we propose RATE, a novel agentic translation evaluation framework, centered by a reflective Core Agent that dynamically invokes specialized sub-agents. Experimental results indicate the efficacy of RATE, achieving an improvement of at least 3.2 meta score compared with current metrics. Further experiments demonstrate the robustness of RATE to general-domain MT evaluation. Code and dataset are available at: https://github.com/BITHLP/RATE.
MMWOZ: Building Multimodal Agent for Task-oriented Dialogue
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Task-oriented dialogue systems have garnered significant attention due to their conversational ability to accomplish goals, such as booking airline tickets for users. Traditionally, task-oriented dialogue systems are conceptualized as intelligent agents that interact with users using natural language and have access to customized back-end APIs. However, in real-world scenarios, the widespread presence of front-end Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) and the absence of customized back-end APIs create a significant gap for traditional task-oriented dialogue systems in practical applications. In this paper, to bridge the gap, we collect MMWOZ, a new multimodal dialogue dataset that is extended from MultiWOZ 2.3 dataset. Specifically, we begin by developing a web-style GUI to serve as the front-end. Next, we devise an automated script to convert the dialogue states and system actions from the original dataset into operation instructions for the GUI. Lastly, we collect snapshots of the web pages along with their corresponding operation instructions. In addition, we propose a novel multimodal model called MATE (Multimodal Agent for Task-oriEnted dialogue) as the baseline model for the MMWOZ dataset. Furthermore, we conduct comprehensive experimental analysis using MATE to investigate the construction of a practical multimodal agent for task-oriented dialogue.
PRIM: Towards Practical In-Image Multilingual Machine Translation
Sep 05, 2025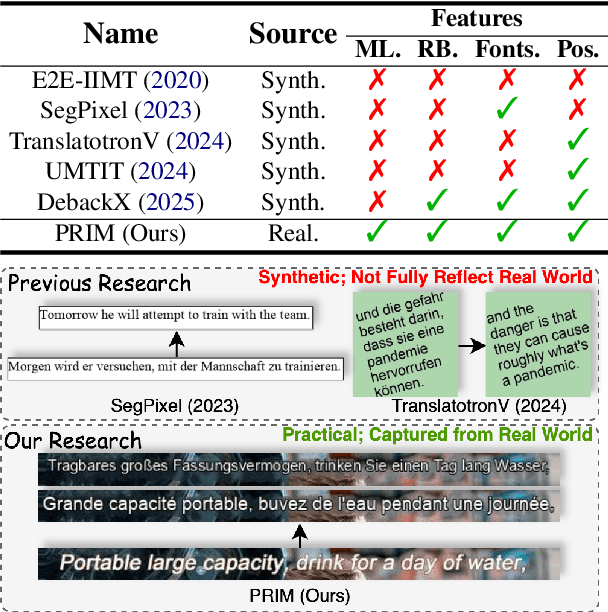
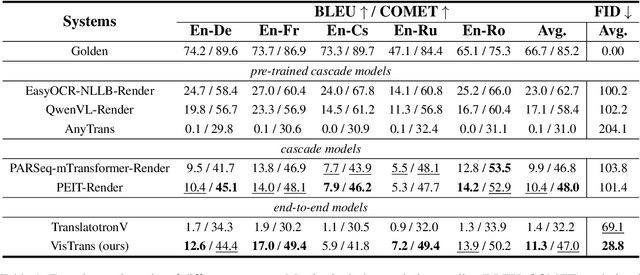
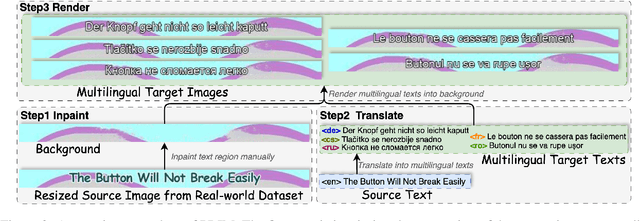
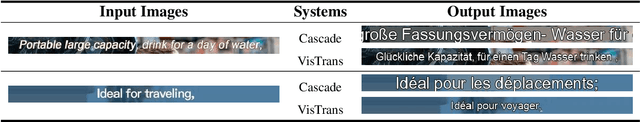
Abstract:In-Image Machine Translation (IIMT) aims to translate images containing texts from one language to another. Current research of end-to-end IIMT mainly conducts on synthetic data, with simple background, single font, fixed text position, and bilingual translation, which can not fully reflect real world, causing a significant gap between the research and practical conditions. To facilitate research of IIMT in real-world scenarios, we explore Practical In-Image Multilingual Machine Translation (IIMMT). In order to convince the lack of publicly available data, we annotate the PRIM dataset, which contains real-world captured one-line text images with complex background, various fonts, diverse text positions, and supports multilingual translation directions. We propose an end-to-end model VisTrans to handle the challenge of practical conditions in PRIM, which processes visual text and background information in the image separately, ensuring the capability of multilingual translation while improving the visual quality. Experimental results indicate the VisTrans achieves a better translation quality and visual effect compared to other models. The code and dataset are available at: https://github.com/BITHLP/PRIM.
A Survey of Automatic Evaluation Methods on Text, Visual and Speech Generations
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning have significantly enhanced generative AI capabilities across text, images, and audio. However, automatically evaluating the quality of these generated outputs presents ongoing challenges. Although numerous automatic evaluation methods exist, current research lacks a systematic framework that comprehensively organizes these methods across text, visual, and audio modalities. To address this issue, we present a comprehensive review and a unified taxonomy of automatic evaluation methods for generated content across all three modalities; We identify five fundamental paradigms that characterize existing evaluation approaches across these domains. Our analysis begins by examining evaluation methods for text generation, where techniques are most mature. We then extend this framework to image and audio generation, demonstrating its broad applicability. Finally, we discuss promising directions for future research in cross-modal evaluation methodologies.
DocMEdit: Towards Document-Level Model Editing
May 26, 2025Abstract:Model editing aims to correct errors and outdated knowledge in the Large language models (LLMs) with minimal cost. Prior research has proposed a variety of datasets to assess the effectiveness of these model editing methods. However, most existing datasets only require models to output short phrases or sentences, overlooks the widespread existence of document-level tasks in the real world, raising doubts about their practical usability. Aimed at addressing this limitation and promoting the application of model editing in real-world scenarios, we propose the task of document-level model editing. To tackle such challenges and enhance model capabilities in practical settings, we introduce \benchmarkname, a dataset focused on document-level model editing, characterized by document-level inputs and outputs, extrapolative, and multiple facts within a single edit. We propose a series of evaluation metrics and experiments. The results show that the difficulties in document-level model editing pose challenges for existing model editing methods.
T2I-Eval-R1: Reinforcement Learning-Driven Reasoning for Interpretable Text-to-Image Evaluation
May 23, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress in diffusion-based text-to-image (T2I) generation has created an urgent need for interpretable automatic evaluation methods that can assess the quality of generated images, therefore reducing the human annotation burden. To reduce the prohibitive cost of relying on commercial models for large-scale evaluation, and to improve the reasoning capabilities of open-source models, recent research has explored supervised fine-tuning (SFT) of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) as dedicated T2I evaluators. However, SFT approaches typically rely on high-quality critique datasets, which are either generated by proprietary LLMs-with potential issues of bias and inconsistency-or annotated by humans at high cost, limiting their scalability and generalization. To address these limitations, we propose T2I-Eval-R1, a novel reinforcement learning framework that trains open-source MLLMs using only coarse-grained quality scores, thereby avoiding the need for annotating high-quality interpretable evaluation rationale. Our approach integrates Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) into the instruction-tuning process, enabling models to generate both scalar scores and interpretable reasoning chains with only easy accessible annotated judgment scores or preferences. Furthermore, we introduce a continuous reward formulation that encourages score diversity and provides stable optimization signals, leading to more robust and discriminative evaluation behavior. Experimental results on three established T2I meta-evaluation benchmarks demonstrate that T2I-Eval-R1 achieves significantly higher alignment with human assessments and offers more accurate interpretable score rationales compared to strong baseline methods.
EduBench: A Comprehensive Benchmarking Dataset for Evaluating Large Language Models in Diverse Educational Scenarios
May 22, 2025Abstract:As large language models continue to advance, their application in educational contexts remains underexplored and under-optimized. In this paper, we address this gap by introducing the first diverse benchmark tailored for educational scenarios, incorporating synthetic data containing 9 major scenarios and over 4,000 distinct educational contexts. To enable comprehensive assessment, we propose a set of multi-dimensional evaluation metrics that cover 12 critical aspects relevant to both teachers and students. We further apply human annotation to ensure the effectiveness of the model-generated evaluation responses. Additionally, we succeed to train a relatively small-scale model on our constructed dataset and demonstrate that it can achieve performance comparable to state-of-the-art large models (e.g., Deepseek V3, Qwen Max) on the test set. Overall, this work provides a practical foundation for the development and evaluation of education-oriented language models. Code and data are released at https://github.com/ybai-nlp/EduBench.
SEOE: A Scalable and Reliable Semantic Evaluation Framework for Open Domain Event Detection
Mar 05, 2025Abstract:Automatic evaluation for Open Domain Event Detection (ODED) is a highly challenging task, because ODED is characterized by a vast diversity of un-constrained output labels from various domains. Nearly all existing evaluation methods for ODED usually first construct evaluation benchmarks with limited labels and domain coverage, and then evaluate ODED methods using metrics based on token-level label matching rules. However, this kind of evaluation framework faces two issues: (1) The limited evaluation benchmarks lack representatives of the real world, making it difficult to accurately reflect the performance of various ODED methods in real-world scenarios; (2) Evaluation metrics based on token-level matching rules fail to capture semantic similarity between predictions and golden labels. To address these two problems above, we propose a scalable and reliable Semantic-level Evaluation framework for Open domain Event detection (SEOE) by constructing a more representative evaluation benchmark and introducing a semantic evaluation metric. Specifically, our proposed framework first constructs a scalable evaluation benchmark that currently includes 564 event types covering 7 major domains, with a cost-effective supplementary annotation strategy to ensure the benchmark's representativeness. The strategy also allows for the supplement of new event types and domains in the future. Then, the proposed SEOE leverages large language models (LLMs) as automatic evaluation agents to compute a semantic F1-score, incorporating fine-grained definitions of semantically similar labels to enhance the reliability of the evaluation. Extensive experiments validate the representatives of the benchmark and the reliability of the semantic evaluation metric. Existing ODED methods are thoroughly evaluated, and the error patterns of predictions are analyzed, revealing several insightful findings.
CAMI: A Counselor Agent Supporting Motivational Interviewing through State Inference and Topic Exploration
Feb 05, 2025Abstract:Conversational counselor agents have become essential tools for addressing the rising demand for scalable and accessible mental health support. This paper introduces CAMI, a novel automated counselor agent grounded in Motivational Interviewing (MI) -- a client-centered counseling approach designed to address ambivalence and facilitate behavior change. CAMI employs a novel STAR framework, consisting of client's state inference, motivation topic exploration, and response generation modules, leveraging large language models (LLMs). These components work together to evoke change talk, aligning with MI principles and improving counseling outcomes for clients from diverse backgrounds. We evaluate CAMI's performance through both automated and manual evaluations, utilizing simulated clients to assess MI skill competency, client's state inference accuracy, topic exploration proficiency, and overall counseling success. Results show that CAMI not only outperforms several state-of-the-art methods but also shows more realistic counselor-like behavior. Additionally, our ablation study underscores the critical roles of state inference and topic exploration in achieving this performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge