Yang Gao
Harry
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
OpenGuanDan: A Large-Scale Imperfect Information Game Benchmark
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:The advancement of data-driven artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning, heavily depends on large-scale benchmarks. Despite remarkable progress across domains ranging from pattern recognition to intelligent decision-making in recent decades, exemplified by breakthroughs in board games, card games, and electronic sports games, there remains a pressing need for more challenging benchmarks to drive further research. To this end, this paper proposes OpenGuanDan, a novel benchmark that enables both efficient simulation of GuanDan (a popular four-player, multi-round Chinese card game) and comprehensive evaluation of both learning-based and rule-based GuanDan AI agents. OpenGuanDan poses a suite of nontrivial challenges, including imperfect information, large-scale information set and action spaces, a mixed learning objective involving cooperation and competition, long-horizon decision-making, variable action spaces, and dynamic team composition. These characteristics make it a demanding testbed for existing intelligent decision-making methods. Moreover, the independent API for each player allows human-AI interactions and supports integration with large language models. Empirically, we conduct two types of evaluations: (1) pairwise competitions among all GuanDan AI agents, and (2) human-AI matchups. Experimental results demonstrate that while current learning-based agents substantially outperform rule-based counterparts, they still fall short of achieving superhuman performance, underscoring the need for continued research in multi-agent intelligent decision-making domain. The project is publicly available at https://github.com/GameAI-NJUPT/OpenGuanDan.
Residual Learning for Neural Ambisonics Encoders
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Emerging wearable devices such as smartglasses and extended reality headsets demand high-quality spatial audio capture from compact, head-worn microphone arrays. Ambisonics provides a device-agnostic spatial audio representation by mapping array signals to spherical harmonic (SH) coefficients. In practice, however, accurate encoding remains challenging. While traditional linear encoders are signal-independent and robust, they amplify low-frequency noise and suffer from high-frequency spatial aliasing. On the other hand, neural network approaches can outperform linear encoders but they often assume idealized microphones and may perform inconsistently in real-world scenarios. To leverage their complementary strengths, we introduce a residual-learning framework that refines a linear encoder with corrections from a neural network. Using measured array transfer functions from smartglasses, we compare a UNet-based encoder from the literature with a new recurrent attention model. Our analysis reveals that both neural encoders only consistently outperform the linear baseline when integrated within the residual learning framework. In the residual configuration, both neural models achieve consistent and significant improvements across all tested metrics for in-domain data and moderate gains for out-of-domain data. Yet, coherence analysis indicates that all neural encoder configurations continue to struggle with directionally accurate high-frequency encoding.
Beyond Text-to-SQL: Can LLMs Really Debug Enterprise ETL SQL?
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:SQL is central to enterprise data engineering, yet generating fully correct SQL code in a single attempt remains difficult, even for experienced developers and advanced text-to-SQL LLMs, often requiring multiple debugging iterations. We introduce OurBench, the first benchmark for enterprise-level SQL reasoning and debugging. Our benchmark is built on two key innovations: (1) an automated construction workflow that uses reverse engineering to systematically inject realistic bugs into large-scale SQL code, enabling scalable and diverse benchmark generation; and (2) an execution-free evaluation framework tailored to enterprise settings, providing fast, accurate, and resource-efficient assessment. OurBench comprises 469 OurBenchSyn queries featuring syntax errors with explicit error messages, and 516 OurBenchSem queries targeting semantic errors in which the code fails to meet user intent. The queries are highly complex, averaging over 140 lines and featuring deep and wide abstract syntax trees. Evaluation of nearly 30 LLMs reveals a substantial performance gap: the best-performing model, Claude-4-Sonnet, achieves only 36.46 percent accuracy on OurBenchSyn and 32.17 percent on OurBenchSem, while most models score below 20 percent. We further explore four solution strategies, identify key challenges, and outline promising directions for enterprise SQL debugging with LLMs.
SpatCode: Rotary-based Unified Encoding Framework for Efficient Spatiotemporal Vector Retrieval
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Spatiotemporal vector retrieval has emerged as a critical paradigm in modern information retrieval, enabling efficient access to massive, heterogeneous data that evolve over both time and space. However, existing spatiotemporal retrieval methods are often extensions of conventional vector search systems that rely on external filters or specialized indices to incorporate temporal and spatial constraints, leading to inefficiency, architectural complexity, and limited flexibility in handling heterogeneous modalities. To overcome these challenges, we present a unified spatiotemporal vector retrieval framework that integrates temporal, spatial, and semantic cues within a coherent similarity space while maintaining scalability and adaptability to continuous data streams. Specifically, we propose (1) a Rotary-based Unified Encoding Method that embeds time and location into rotational position vectors for consistent spatiotemporal representation; (2) a Circular Incremental Update Mechanism that supports efficient sliding-window updates without global re-encoding or index reconstruction; and (3) a Weighted Interest-based Retrieval Algorithm that adaptively balances modality weights for context-aware and personalized retrieval. Extensive experiments across multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that our framework substantially outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in both retrieval accuracy and efficiency, while maintaining robustness under dynamic data evolution. These results highlight the effectiveness and practicality of the proposed approach for scalable spatiotemporal information retrieval in intelligent systems.
Thinking-Based Non-Thinking: Solving the Reward Hacking Problem in Training Hybrid Reasoning Models via Reinforcement Learning
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) have attracted much attention due to their exceptional performance. However, their performance mainly stems from thinking, a long Chain of Thought (CoT), which significantly increase computational overhead. To address this overthinking problem, existing work focuses on using reinforcement learning (RL) to train hybrid reasoning models that automatically decide whether to engage in thinking or not based on the complexity of the query. Unfortunately, using RL will suffer the the reward hacking problem, e.g., the model engages in thinking but is judged as not doing so, resulting in incorrect rewards. To mitigate this problem, existing works either employ supervised fine-tuning (SFT), which incurs high computational costs, or enforce uniform token limits on non-thinking responses, which yields limited mitigation of the problem. In this paper, we propose Thinking-Based Non-Thinking (TNT). It does not employ SFT, and sets different maximum token usage for responses not using thinking across various queries by leveraging information from the solution component of the responses using thinking. Experiments on five mathematical benchmarks demonstrate that TNT reduces token usage by around 50% compared to DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B/7B and DeepScaleR-1.5B, while significantly improving accuracy. In fact, TNT achieves the optimal trade-off between accuracy and efficiency among all tested methods. Additionally, the probability of reward hacking problem in TNT's responses, which are classified as not using thinking, remains below 10% across all tested datasets.
Leveraging Flatness to Improve Information-Theoretic Generalization Bounds for SGD
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Information-theoretic (IT) generalization bounds have been used to study the generalization of learning algorithms. These bounds are intrinsically data- and algorithm-dependent so that one can exploit the properties of data and algorithm to derive tighter bounds. However, we observe that although the flatness bias is crucial for SGD's generalization, these bounds fail to capture the improved generalization under better flatness and are also numerically loose. This is caused by the inadequate leverage of SGD's flatness bias in existing IT bounds. This paper derives a more flatness-leveraging IT bound for the flatness-favoring SGD. The bound indicates the learned models generalize better if the large-variance directions of the final weight covariance have small local curvatures in the loss landscape. Experiments on deep neural networks show our bound not only correctly reflects the better generalization when flatness is improved, but is also numerically much tighter. This is achieved by a flexible technique called "omniscient trajectory". When applied to Gradient Descent's minimax excess risk on convex-Lipschitz-Bounded problems, it improves representative IT bounds' $Ω(1)$ rates to $O(1/\sqrt{n})$. It also implies a by-pass of memorization-generalization trade-offs.
* Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2025
FUSE-RSVLM: Feature Fusion Vision-Language Model for Remote Sensing
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) exhibit strong performance across various tasks. However, these VLMs encounter significant challenges when applied to the remote sensing domain due to the inherent differences between remote sensing images and natural images. Existing remote sensing VLMs often fail to extract fine-grained visual features and suffer from visual forgetting during deep language processing. To address this, we introduce MF-RSVLM, a Multi-Feature Fusion Remote Sensing Vision--Language Model that effectively extracts and fuses visual features for RS understanding. MF-RSVLM learns multi-scale visual representations and combines global context with local details, improving the capture of small and complex structures in RS scenes. A recurrent visual feature injection scheme ensures the language model remains grounded in visual evidence and reduces visual forgetting during generation. Extensive experiments on diverse RS benchmarks show that MF-RSVLM achieves state-of-the-art or highly competitive performance across remote sensing classification, image captioning, and VQA tasks. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Yunkaidang/RSVLM.
LibContinual: A Comprehensive Library towards Realistic Continual Learning
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:A fundamental challenge in Continual Learning (CL) is catastrophic forgetting, where adapting to new tasks degrades the performance on previous ones. While the field has evolved with diverse methods, this rapid surge in diverse methodologies has culminated in a fragmented research landscape. The lack of a unified framework, including inconsistent implementations, conflicting dependencies, and varying evaluation protocols, makes fair comparison and reproducible research increasingly difficult. To address this challenge, we propose LibContinual, a comprehensive and reproducible library designed to serve as a foundational platform for realistic CL. Built upon a high-cohesion, low-coupling modular architecture, LibContinual integrates 19 representative algorithms across five major methodological categories, providing a standardized execution environment. Meanwhile, leveraging this unified framework, we systematically identify and investigate three implicit assumptions prevalent in mainstream evaluation: (1) offline data accessibility, (2) unregulated memory resources, and (3) intra-task semantic homogeneity. We argue that these assumptions often overestimate the real-world applicability of CL methods. Through our comprehensive analysis using strict online CL settings, a novel unified memory budget protocol, and a proposed category-randomized setting, we reveal significant performance drops in many representative CL methods when subjected to these real-world constraints. Our study underscores the necessity of resource-aware and semantically robust CL strategies, and offers LibContinual as a foundational toolkit for future research in realistic continual learning. The source code is available from \href{https://github.com/RL-VIG/LibContinual}{https://github.com/RL-VIG/LibContinual}.
Point What You Mean: Visually Grounded Instruction Policy
Dec 22, 2025
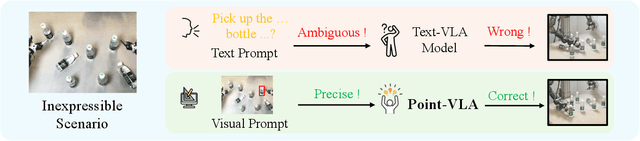
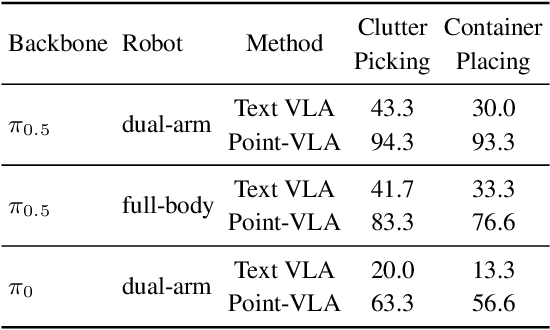
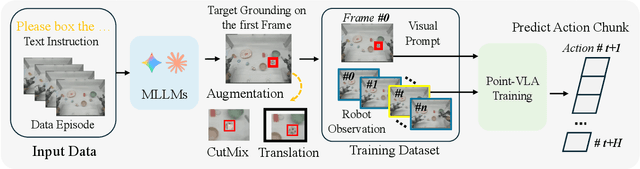
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models align vision and language with embodied control, but their object referring ability remains limited when relying solely on text prompt, especially in cluttered or out-of-distribution (OOD) scenes. In this study, we introduce the Point-VLA, a plug-and-play policy that augments language instructions with explicit visual cues (e.g., bounding boxes) to resolve referential ambiguity and enable precise object-level grounding. To efficiently scale visually grounded datasets, we further develop an automatic data annotation pipeline requiring minimal human effort. We evaluate Point-VLA on diverse real-world referring tasks and observe consistently stronger performance than text-only instruction VLAs, particularly in cluttered or unseen-object scenarios, with robust generalization. These results demonstrate that Point-VLA effectively resolves object referring ambiguity through pixel-level visual grounding, achieving more generalizable embodied control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge