Yingdong Hu
Mon3tr: Monocular 3D Telepresence with Pre-built Gaussian Avatars as Amortization
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Immersive telepresence aims to transform human interaction in AR/VR applications by enabling lifelike full-body holographic representations for enhanced remote collaboration. However, existing systems rely on hardware-intensive multi-camera setups and demand high bandwidth for volumetric streaming, limiting their real-time performance on mobile devices. To overcome these challenges, we propose Mon3tr, a novel Monocular 3D telepresence framework that integrates 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS) based parametric human modeling into telepresence for the first time. Mon3tr adopts an amortized computation strategy, dividing the process into a one-time offline multi-view reconstruction phase to build a user-specific avatar and a monocular online inference phase during live telepresence sessions. A single monocular RGB camera is used to capture body motions and facial expressions in real time to drive the 3DGS-based parametric human model, significantly reducing system complexity and cost. The extracted motion and appearance features are transmitted at < 0.2 Mbps over WebRTC's data channel, allowing robust adaptation to network fluctuations. On the receiver side, e.g., Meta Quest 3, we develop a lightweight 3DGS attribute deformation network to dynamically generate corrective 3DGS attribute adjustments on the pre-built avatar, synthesizing photorealistic motion and appearance at ~ 60 FPS. Extensive experiments demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our method, achieving a PSNR of > 28 dB for novel poses, an end-to-end latency of ~ 80 ms, and > 1000x bandwidth reduction compared to point-cloud streaming, while supporting real-time operation from monocular inputs across diverse scenarios. Our demos can be found at https://mon3tr3d.github.io.
Point What You Mean: Visually Grounded Instruction Policy
Dec 22, 2025
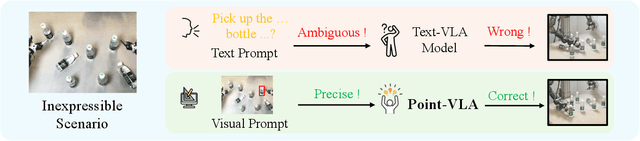
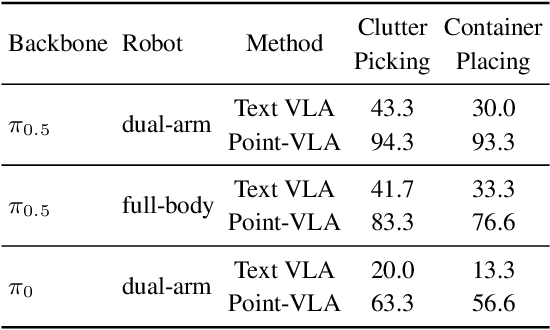
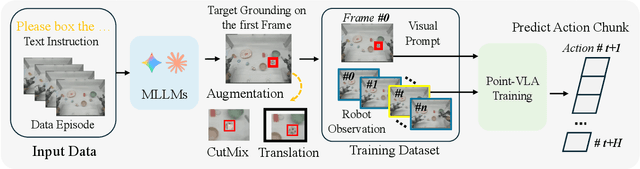
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models align vision and language with embodied control, but their object referring ability remains limited when relying solely on text prompt, especially in cluttered or out-of-distribution (OOD) scenes. In this study, we introduce the Point-VLA, a plug-and-play policy that augments language instructions with explicit visual cues (e.g., bounding boxes) to resolve referential ambiguity and enable precise object-level grounding. To efficiently scale visually grounded datasets, we further develop an automatic data annotation pipeline requiring minimal human effort. We evaluate Point-VLA on diverse real-world referring tasks and observe consistently stronger performance than text-only instruction VLAs, particularly in cluttered or unseen-object scenarios, with robust generalization. These results demonstrate that Point-VLA effectively resolves object referring ambiguity through pixel-level visual grounding, achieving more generalizable embodied control.
Maritime Communication in Evaporation Duct Environment with Ship Trajectory Optimization
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:In maritime wireless networks, the evaporation duct effect has been known as a preferable condition for long-range transmissions. However, how to effectively utilize the duct effect for efficient communication design is still open for investigation. In this paper, we consider a typical scenario of ship-to-shore data transmission, where a ship collects data from multiple oceanographic buoys, sails from one to another, and transmits the collected data back to a terrestrial base station during its voyage. A novel framework, which exploits priori information of the channel gain map in the presence of evaporation duct, is proposed to minimize the data transmission time and the sailing time by optimizing the ship's trajectory. To this end, a multi-objective optimization problem is formulated and is further solved by a dynamic population PSO-integrated NSGA-II algorithm. Through simulations, it is demonstrated that, compared to the benchmark scheme which ignores useful information of the evaporation duct, the proposed scheme can effectively reduce both the data transmission time and the sailing time.
PanoLAM: Large Avatar Model for Gaussian Full-Head Synthesis from One-shot Unposed Image
Sep 09, 2025



Abstract:We present a feed-forward framework for Gaussian full-head synthesis from a single unposed image. Unlike previous work that relies on time-consuming GAN inversion and test-time optimization, our framework can reconstruct the Gaussian full-head model given a single unposed image in a single forward pass. This enables fast reconstruction and rendering during inference. To mitigate the lack of large-scale 3D head assets, we propose a large-scale synthetic dataset from trained 3D GANs and train our framework using only synthetic data. For efficient high-fidelity generation, we introduce a coarse-to-fine Gaussian head generation pipeline, where sparse points from the FLAME model interact with the image features by transformer blocks for feature extraction and coarse shape reconstruction, which are then densified for high-fidelity reconstruction. To fully leverage the prior knowledge residing in pretrained 3D GANs for effective reconstruction, we propose a dual-branch framework that effectively aggregates the structured spherical triplane feature and unstructured point-based features for more effective Gaussian head reconstruction. Experimental results show the effectiveness of our framework towards existing work.
OneTwoVLA: A Unified Vision-Language-Action Model with Adaptive Reasoning
May 17, 2025Abstract:General-purpose robots capable of performing diverse tasks require synergistic reasoning and acting capabilities. However, recent dual-system approaches, which separate high-level reasoning from low-level acting, often suffer from challenges such as limited mutual understanding of capabilities between systems and latency issues. This paper introduces OneTwoVLA, a single unified vision-language-action model that can perform both acting (System One) and reasoning (System Two). Crucially, OneTwoVLA adaptively switches between two modes: explicitly reasoning at critical moments during task execution, and generating actions based on the most recent reasoning at other times. To further unlock OneTwoVLA's reasoning and generalization capabilities, we design a scalable pipeline for synthesizing embodied reasoning-centric vision-language data, used for co-training with robot data. We validate OneTwoVLA's effectiveness through extensive experiments, highlighting its superior performance across four key capabilities: long-horizon task planning, error detection and recovery, natural human-robot interaction, and generalizable visual grounding, enabling the model to perform long-horizon, highly dexterous manipulation tasks such as making hotpot or mixing cocktails.
HuB: Learning Extreme Humanoid Balance
May 12, 2025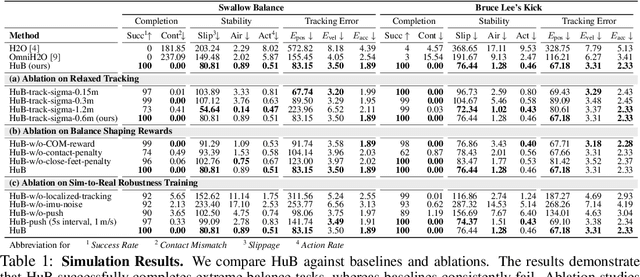
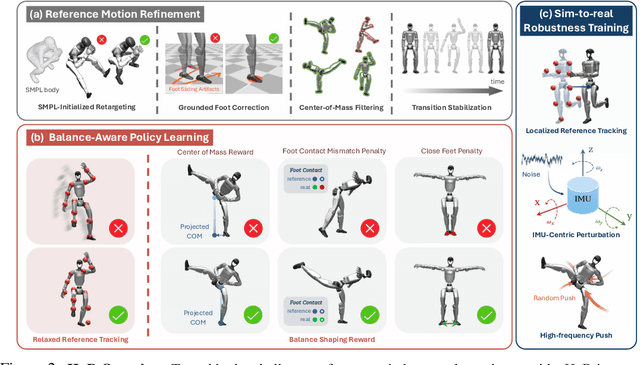
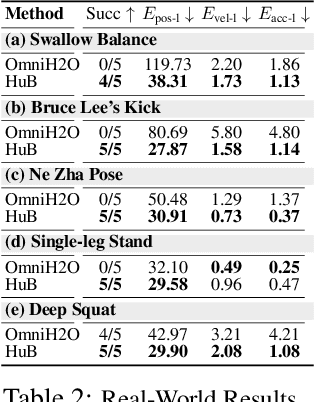
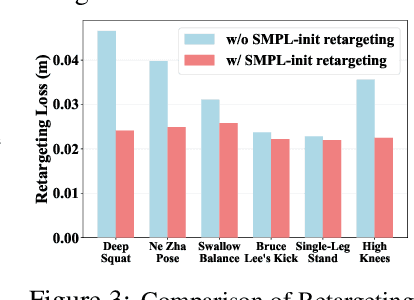
Abstract:The human body demonstrates exceptional motor capabilities-such as standing steadily on one foot or performing a high kick with the leg raised over 1.5 meters-both requiring precise balance control. While recent research on humanoid control has leveraged reinforcement learning to track human motions for skill acquisition, applying this paradigm to balance-intensive tasks remains challenging. In this work, we identify three key obstacles: instability from reference motion errors, learning difficulties due to morphological mismatch, and the sim-to-real gap caused by sensor noise and unmodeled dynamics. To address these challenges, we propose HuB (Humanoid Balance), a unified framework that integrates reference motion refinement, balance-aware policy learning, and sim-to-real robustness training, with each component targeting a specific challenge. We validate our approach on the Unitree G1 humanoid robot across challenging quasi-static balance tasks, including extreme single-legged poses such as Swallow Balance and Bruce Lee's Kick. Our policy remains stable even under strong physical disturbances-such as a forceful soccer strike-while baseline methods consistently fail to complete these tasks. Project website: https://hub-robot.github.io
WRF-GS: Wireless Radiation Field Reconstruction with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:Wireless channel modeling plays a pivotal role in designing, analyzing, and optimizing wireless communication systems. Nevertheless, developing an effective channel modeling approach has been a longstanding challenge. This issue has been escalated due to the denser network deployment, larger antenna arrays, and wider bandwidth in 5G and beyond networks. To address this challenge, we put forth WRF-GS, a novel framework for channel modeling based on wireless radiation field (WRF) reconstruction using 3D Gaussian splatting. WRF-GS employs 3D Gaussian primitives and neural networks to capture the interactions between the environment and radio signals, enabling efficient WRF reconstruction and visualization of the propagation characteristics. The reconstructed WRF can then be used to synthesize the spatial spectrum for comprehensive wireless channel characterization. Notably, with a small number of measurements, WRF-GS can synthesize new spatial spectra within milliseconds for a given scene, thereby enabling latency-sensitive applications. Experimental results demonstrate that WRF-GS outperforms existing methods for spatial spectrum synthesis, such as ray tracing and other deep-learning approaches. Moreover, WRF-GS achieves superior performance in the channel state information prediction task, surpassing existing methods by a significant margin of more than 2.43 dB.
Dynamics-Aware Gaussian Splatting Streaming Towards Fast On-the-Fly Training for 4D Reconstruction
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:The recent development of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has led to great interest in 4D dynamic spatial reconstruction from multi-view visual inputs. While existing approaches mainly rely on processing full-length multi-view videos for 4D reconstruction, there has been limited exploration of iterative online reconstruction methods that enable on-the-fly training and per-frame streaming. Current 3DGS-based streaming methods treat the Gaussian primitives uniformly and constantly renew the densified Gaussians, thereby overlooking the difference between dynamic and static features and also neglecting the temporal continuity in the scene. To address these limitations, we propose a novel three-stage pipeline for iterative streamable 4D dynamic spatial reconstruction. Our pipeline comprises a selective inheritance stage to preserve temporal continuity, a dynamics-aware shift stage for distinguishing dynamic and static primitives and optimizing their movements, and an error-guided densification stage to accommodate emerging objects. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in online 4D reconstruction, demonstrating a 20% improvement in on-the-fly training speed, superior representation quality, and real-time rendering capability. Project page: https://www.liuzhening.top/DASS
Data Scaling Laws in Imitation Learning for Robotic Manipulation
Oct 24, 2024Abstract:Data scaling has revolutionized fields like natural language processing and computer vision, providing models with remarkable generalization capabilities. In this paper, we investigate whether similar data scaling laws exist in robotics, particularly in robotic manipulation, and whether appropriate data scaling can yield single-task robot policies that can be deployed zero-shot for any object within the same category in any environment. To this end, we conduct a comprehensive empirical study on data scaling in imitation learning. By collecting data across numerous environments and objects, we study how a policy's generalization performance changes with the number of training environments, objects, and demonstrations. Throughout our research, we collect over 40,000 demonstrations and execute more than 15,000 real-world robot rollouts under a rigorous evaluation protocol. Our findings reveal several intriguing results: the generalization performance of the policy follows a roughly power-law relationship with the number of environments and objects. The diversity of environments and objects is far more important than the absolute number of demonstrations; once the number of demonstrations per environment or object reaches a certain threshold, additional demonstrations have minimal effect. Based on these insights, we propose an efficient data collection strategy. With four data collectors working for one afternoon, we collect sufficient data to enable the policies for two tasks to achieve approximately 90% success rates in novel environments with unseen objects.
EVA-Gaussian: 3D Gaussian-based Real-time Human Novel View Synthesis under Diverse Camera Settings
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:The feed-forward based 3D Gaussian Splatting method has demonstrated exceptional capability in real-time human novel view synthesis. However, existing approaches are restricted to dense viewpoint settings, which limits their flexibility in free-viewpoint rendering across a wide range of camera view angle discrepancies. To address this limitation, we propose a real-time pipeline named EVA-Gaussian for 3D human novel view synthesis across diverse camera settings. Specifically, we first introduce an Efficient cross-View Attention (EVA) module to accurately estimate the position of each 3D Gaussian from the source images. Then, we integrate the source images with the estimated Gaussian position map to predict the attributes and feature embeddings of the 3D Gaussians. Moreover, we employ a recurrent feature refiner to correct artifacts caused by geometric errors in position estimation and enhance visual fidelity.To further improve synthesis quality, we incorporate a powerful anchor loss function for both 3D Gaussian attributes and human face landmarks. Experimental results on the THuman2.0 and THumansit datasets showcase the superiority of our EVA-Gaussian approach in rendering quality across diverse camera settings. Project page: https://zhenliuzju.github.io/huyingdong/EVA-Gaussian.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge