Xinjie Zhang
PvNeXt: Rethinking Network Design and Temporal Motion for Point Cloud Video Recognition
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Point cloud video perception has become an essential task for the realm of 3D vision. Current 4D representation learning techniques typically engage in iterative processing coupled with dense query operations. Although effective in capturing temporal features, this approach leads to substantial computational redundancy. In this work, we propose a framework, named as PvNeXt, for effective yet efficient point cloud video recognition, via personalized one-shot query operation. Specially, PvNeXt consists of two key modules, the Motion Imitator and the Single-Step Motion Encoder. The former module, the Motion Imitator, is designed to capture the temporal dynamics inherent in sequences of point clouds, thus generating the virtual motion corresponding to each frame. The Single-Step Motion Encoder performs a one-step query operation, associating point cloud of each frame with its corresponding virtual motion frame, thereby extracting motion cues from point cloud sequences and capturing temporal dynamics across the entire sequence. Through the integration of these two modules, {PvNeXt} enables personalized one-shot queries for each frame, effectively eliminating the need for frame-specific looping and intensive query processes. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Pixel to Gaussian: Ultra-Fast Continuous Super-Resolution with 2D Gaussian Modeling
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Arbitrary-scale super-resolution (ASSR) aims to reconstruct high-resolution (HR) images from low-resolution (LR) inputs with arbitrary upsampling factors using a single model, addressing the limitations of traditional SR methods constrained to fixed-scale factors (\textit{e.g.}, $\times$ 2). Recent advances leveraging implicit neural representation (INR) have achieved great progress by modeling coordinate-to-pixel mappings. However, the efficiency of these methods may suffer from repeated upsampling and decoding, while their reconstruction fidelity and quality are constrained by the intrinsic representational limitations of coordinate-based functions. To address these challenges, we propose a novel ContinuousSR framework with a Pixel-to-Gaussian paradigm, which explicitly reconstructs 2D continuous HR signals from LR images using Gaussian Splatting. This approach eliminates the need for time-consuming upsampling and decoding, enabling extremely fast arbitrary-scale super-resolution. Once the Gaussian field is built in a single pass, ContinuousSR can perform arbitrary-scale rendering in just 1ms per scale. Our method introduces several key innovations. Through statistical ana
Large Images are Gaussians: High-Quality Large Image Representation with Levels of 2D Gaussian Splatting
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:While Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have demonstrated significant success in image representation, they are often hindered by large training memory and slow decoding speed. Recently, Gaussian Splatting (GS) has emerged as a promising solution in 3D reconstruction due to its high-quality novel view synthesis and rapid rendering capabilities, positioning it as a valuable tool for a broad spectrum of applications. In particular, a GS-based representation, 2DGS, has shown potential for image fitting. In our work, we present \textbf{L}arge \textbf{I}mages are \textbf{G}aussians (\textbf{LIG}), which delves deeper into the application of 2DGS for image representations, addressing the challenge of fitting large images with 2DGS in the situation of numerous Gaussian points, through two distinct modifications: 1) we adopt a variant of representation and optimization strategy, facilitating the fitting of a large number of Gaussian points; 2) we propose a Level-of-Gaussian approach for reconstructing both coarse low-frequency initialization and fine high-frequency details. Consequently, we successfully represent large images as Gaussian points and achieve high-quality large image representation, demonstrating its efficacy across various types of large images. Code is available at {\href{https://github.com/HKU-MedAI/LIG}{https://github.com/HKU-MedAI/LIG}}.
Rethinking Diffusion Posterior Sampling: From Conditional Score Estimator to Maximizing a Posterior
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in diffusion models have been leveraged to address inverse problems without additional training, and Diffusion Posterior Sampling (DPS) (Chung et al., 2022a) is among the most popular approaches. Previous analyses suggest that DPS accomplishes posterior sampling by approximating the conditional score. While in this paper, we demonstrate that the conditional score approximation employed by DPS is not as effective as previously assumed, but rather aligns more closely with the principle of maximizing a posterior (MAP). This assertion is substantiated through an examination of DPS on 512x512 ImageNet images, revealing that: 1) DPS's conditional score estimation significantly diverges from the score of a well-trained conditional diffusion model and is even inferior to the unconditional score; 2) The mean of DPS's conditional score estimation deviates significantly from zero, rendering it an invalid score estimation; 3) DPS generates high-quality samples with significantly lower diversity. In light of the above findings, we posit that DPS more closely resembles MAP than a conditional score estimator, and accordingly propose the following enhancements to DPS: 1) we explicitly maximize the posterior through multi-step gradient ascent and projection; 2) we utilize a light-weighted conditional score estimator trained with only 100 images and 8 GPU hours. Extensive experimental results indicate that these proposed improvements significantly enhance DPS's performance. The source code for these improvements is provided in https://github.com/tongdaxu/Rethinking-Diffusion-Posterior-Sampling-From-Conditional-Score-Estimator-to-Maximizing-a-Posterior.
MiniMax-01: Scaling Foundation Models with Lightning Attention
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:We introduce MiniMax-01 series, including MiniMax-Text-01 and MiniMax-VL-01, which are comparable to top-tier models while offering superior capabilities in processing longer contexts. The core lies in lightning attention and its efficient scaling. To maximize computational capacity, we integrate it with Mixture of Experts (MoE), creating a model with 32 experts and 456 billion total parameters, of which 45.9 billion are activated for each token. We develop an optimized parallel strategy and highly efficient computation-communication overlap techniques for MoE and lightning attention. This approach enables us to conduct efficient training and inference on models with hundreds of billions of parameters across contexts spanning millions of tokens. The context window of MiniMax-Text-01 can reach up to 1 million tokens during training and extrapolate to 4 million tokens during inference at an affordable cost. Our vision-language model, MiniMax-VL-01 is built through continued training with 512 billion vision-language tokens. Experiments on both standard and in-house benchmarks show that our models match the performance of state-of-the-art models like GPT-4o and Claude-3.5-Sonnet while offering 20-32 times longer context window. We publicly release MiniMax-01 at https://github.com/MiniMax-AI.
Dynamics-Aware Gaussian Splatting Streaming Towards Fast On-the-Fly Training for 4D Reconstruction
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:The recent development of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has led to great interest in 4D dynamic spatial reconstruction from multi-view visual inputs. While existing approaches mainly rely on processing full-length multi-view videos for 4D reconstruction, there has been limited exploration of iterative online reconstruction methods that enable on-the-fly training and per-frame streaming. Current 3DGS-based streaming methods treat the Gaussian primitives uniformly and constantly renew the densified Gaussians, thereby overlooking the difference between dynamic and static features and also neglecting the temporal continuity in the scene. To address these limitations, we propose a novel three-stage pipeline for iterative streamable 4D dynamic spatial reconstruction. Our pipeline comprises a selective inheritance stage to preserve temporal continuity, a dynamics-aware shift stage for distinguishing dynamic and static primitives and optimizing their movements, and an error-guided densification stage to accommodate emerging objects. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in online 4D reconstruction, demonstrating a 20% improvement in on-the-fly training speed, superior representation quality, and real-time rendering capability. Project page: https://www.liuzhening.top/DASS
MEGA: Memory-Efficient 4D Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scenes
Oct 17, 2024Abstract:4D Gaussian Splatting (4DGS) has recently emerged as a promising technique for capturing complex dynamic 3D scenes with high fidelity. It utilizes a 4D Gaussian representation and a GPU-friendly rasterizer, enabling rapid rendering speeds. Despite its advantages, 4DGS faces significant challenges, notably the requirement of millions of 4D Gaussians, each with extensive associated attributes, leading to substantial memory and storage cost. This paper introduces a memory-efficient framework for 4DGS. We streamline the color attribute by decomposing it into a per-Gaussian direct color component with only 3 parameters and a shared lightweight alternating current color predictor. This approach eliminates the need for spherical harmonics coefficients, which typically involve up to 144 parameters in classic 4DGS, thereby creating a memory-efficient 4D Gaussian representation. Furthermore, we introduce an entropy-constrained Gaussian deformation technique that uses a deformation field to expand the action range of each Gaussian and integrates an opacity-based entropy loss to limit the number of Gaussians, thus forcing our model to use as few Gaussians as possible to fit a dynamic scene well. With simple half-precision storage and zip compression, our framework achieves a storage reduction by approximately 190$\times$ and 125$\times$ on the Technicolor and Neural 3D Video datasets, respectively, compared to the original 4DGS. Meanwhile, it maintains comparable rendering speeds and scene representation quality, setting a new standard in the field.
HarmoniCa: Harmonizing Training and Inference for Better Feature Cache in Diffusion Transformer Acceleration
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) have gained prominence for outstanding scalability and extraordinary performance in generative tasks. However, their considerable inference costs impede practical deployment. The feature cache mechanism, which involves storing and retrieving redundant computations across timesteps, holds promise for reducing per-step inference time in diffusion models. Most existing caching methods for DiT are manually designed. Although the learning-based approach attempts to optimize strategies adaptively, it suffers from discrepancies between training and inference, which hampers both the performance and acceleration ratio. Upon detailed analysis, we pinpoint that these discrepancies primarily stem from two aspects: (1) Prior Timestep Disregard, where training ignores the effect of cache usage at earlier timesteps, and (2) Objective Mismatch, where the training target (align predicted noise in each timestep) deviates from the goal of inference (generate the high-quality image). To alleviate these discrepancies, we propose HarmoniCa, a novel method that Harmonizes training and inference with a novel learning-based Caching framework built upon Step-Wise Denoising Training (SDT) and Image Error Proxy-Guided Objective (IEPO). Compared to the traditional training paradigm, the newly proposed SDT maintains the continuity of the denoising process, enabling the model to leverage information from prior timesteps during training, similar to the way it operates during inference. Furthermore, we design IEPO, which integrates an efficient proxy mechanism to approximate the final image error caused by reusing the cached feature. Therefore, IEPO helps balance final image quality and cache utilization, resolving the issue of training that only considers the impact of cache usage on the predicted output at each timestep.
Bidirectional Stereo Image Compression with Cross-Dimensional Entropy Model
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:With the rapid advancement of stereo vision technologies, stereo image compression has emerged as a crucial field that continues to draw significant attention. Previous approaches have primarily employed a unidirectional paradigm, where the compression of one view is dependent on the other, resulting in imbalanced compression. To address this issue, we introduce a symmetric bidirectional stereo image compression architecture, named BiSIC. Specifically, we propose a 3D convolution based codec backbone to capture local features and incorporate bidirectional attention blocks to exploit global features. Moreover, we design a novel cross-dimensional entropy model that integrates various conditioning factors, including the spatial context, channel context, and stereo dependency, to effectively estimate the distribution of latent representations for entropy coding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed BiSIC outperforms conventional image/video compression standards, as well as state-of-the-art learning-based methods, in terms of both PSNR and MS-SSIM.
ESCoT: Towards Interpretable Emotional Support Dialogue Systems
Jun 16, 2024
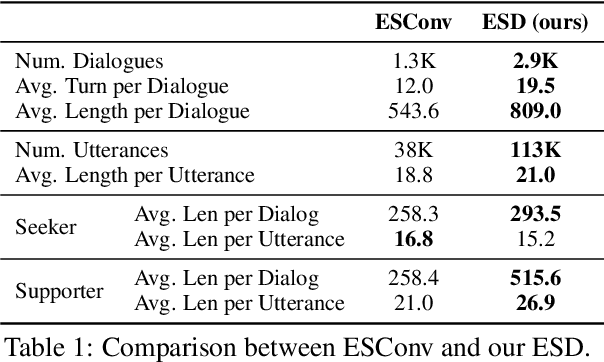

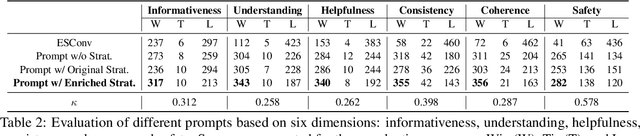
Abstract:Understanding the reason for emotional support response is crucial for establishing connections between users and emotional support dialogue systems. Previous works mostly focus on generating better responses but ignore interpretability, which is extremely important for constructing reliable dialogue systems. To empower the system with better interpretability, we propose an emotional support response generation scheme, named $\textbf{E}$motion-Focused and $\textbf{S}$trategy-Driven $\textbf{C}$hain-$\textbf{o}$f-$\textbf{T}$hought ($\textbf{ESCoT}$), mimicking the process of $\textit{identifying}$, $\textit{understanding}$, and $\textit{regulating}$ emotions. Specially, we construct a new dataset with ESCoT in two steps: (1) $\textit{Dialogue Generation}$ where we first generate diverse conversation situations, then enhance dialogue generation using richer emotional support strategies based on these situations; (2) $\textit{Chain Supplement}$ where we focus on supplementing selected dialogues with elements such as emotion, stimuli, appraisal, and strategy reason, forming the manually verified chains. Additionally, we further develop a model to generate dialogue responses with better interpretability. We also conduct extensive experiments and human evaluations to validate the effectiveness of the proposed ESCoT and generated dialogue responses. Our data and code are available at $\href{https://github.com/TeigenZhang/ESCoT}{https://github.com/TeigenZhang/ESCoT}$.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge