Jinyang Guo
Advances and Innovations in the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal large language models and vision-languageaction models have significantly driven progress in Embodied AI. As the field transitions toward more complex task scenarios, multi-agent system frameworks are becoming essential for achieving scalable, efficient, and collaborative solutions. This shift is fueled by three primary factors: increasing agent capabilities, enhancing system efficiency through task delegation, and enabling advanced human-agent interactions. To address the challenges posed by multi-agent collaboration, we propose the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge, held at the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on SpaVLE. The competition focuses on two critical areas: planning and control, where participants explore multi-agent embodied planning using vision-language models (VLMs) to coordinate tasks and policy execution to perform robotic manipulation in dynamic environments. By evaluating solutions submitted by participants, the challenge provides valuable insights into the design and coordination of embodied multi-agent systems, contributing to the future development of advanced collaborative AI systems.
AFTER: Mitigating the Object Hallucination of LVLM via Adaptive Factual-Guided Activation Editing
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have achieved substantial progress in cross-modal tasks. However, due to language bias, LVLMs are susceptible to object hallucination, which can be primarily divided into category, attribute, and relation hallucination, significantly impeding the trustworthy AI applications. Editing the internal activations of LVLMs has shown promising effectiveness in mitigating hallucinations with minimal cost. However, previous editing approaches neglect the effective guidance offered by factual textual semantics, thereby struggling to explicitly mitigate language bias. To address these issues, we propose Adaptive Factual-guided Visual-Textual Editing for hallucination mitigation (AFTER), which comprises Factual-Augmented Activation Steering (FAS) and Query-Adaptive Offset Optimization (QAO), to adaptively guides the original biased activations towards factual semantics. Specifically, FAS is proposed to provide factual and general guidance for activation editing, thereby explicitly modeling the precise visual-textual associations. Subsequently, QAO introduces a query-aware offset estimator to establish query-specific editing from the general steering vector, enhancing the diversity and granularity of editing. Extensive experiments on standard hallucination benchmarks across three widely adopted LVLMs validate the efficacy of the proposed AFTER, notably achieving up to a 16.3% reduction of hallucination over baseline on the AMBER benchmark. Our code and data will be released for reproducibility.
Context as a Tool: Context Management for Long-Horizon SWE-Agents
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Agents based on large language models have recently shown strong potential on real-world software engineering (SWE) tasks that require long-horizon interaction with repository-scale codebases. However, most existing agents rely on append-only context maintenance or passively triggered compression heuristics, which often lead to context explosion, semantic drift, and degraded reasoning in long-running interactions. We propose CAT, a new context management paradigm that elevates context maintenance to a callable tool integrated into the decision-making process of agents. CAT formalizes a structured context workspace consisting of stable task semantics, condensed long-term memory, and high-fidelity short-term interactions, and enables agents to proactively compress historical trajectories into actionable summaries at appropriate milestones. To support context management for SWE-agents, we propose a trajectory-level supervision framework, CAT-GENERATOR, based on an offline data construction pipeline that injects context-management actions into complete interaction trajectories. Using this framework, we train a context-aware model, SWE-Compressor. Experiments on SWE-Bench-Verified demonstrate that SWE-Compressor reaches a 57.6% solved rate and significantly outperforms ReAct-based agents and static compression baselines, while maintaining stable and scalable long-horizon reasoning under a bounded context budget.
MoDES: Accelerating Mixture-of-Experts Multimodal Large Language Models via Dynamic Expert Skipping
Nov 19, 2025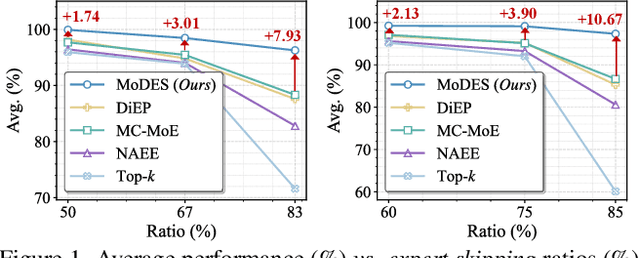

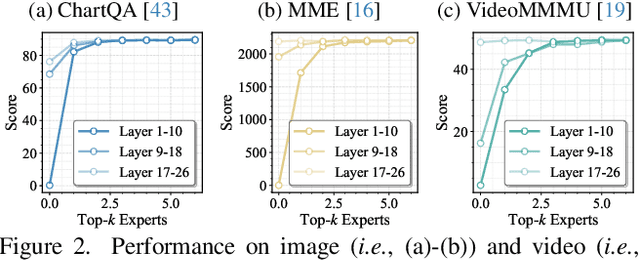
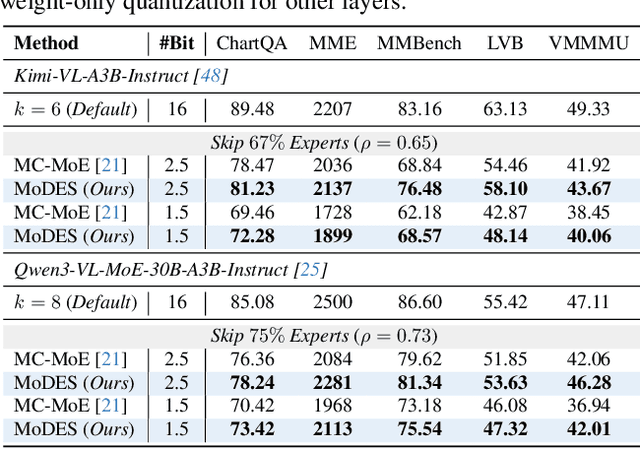
Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) excel at vision-language tasks, but they suffer from high computational inefficiency. To reduce inference overhead, expert skipping methods have been proposed to deactivate redundant experts based on the current input tokens. However, we find that applying these methods-originally designed for unimodal large language models (LLMs)-to MLLMs results in considerable performance degradation. This is primarily because such methods fail to account for the heterogeneous contributions of experts across MoE layers and modality-specific behaviors of tokens within these layers. Motivated by these findings, we propose MoDES, the first training-free framework that adaptively skips experts to enable efficient and accurate MoE MLLM inference. It incorporates a globally-modulated local gating (GMLG) mechanism that integrates global layer-wise importance into local routing probabilities to accurately estimate per-token expert importance. A dual-modality thresholding (DMT) method is then applied, which processes tokens from each modality separately, to derive the skipping schedule. To set the optimal thresholds, we introduce a frontier search algorithm that exploits monotonicity properties, cutting convergence time from several days to a few hours. Extensive experiments for 3 model series across 13 benchmarks demonstrate that MoDES far outperforms previous approaches. For instance, when skipping 88% experts for Qwen3-VL-MoE-30B-A3B-Instruct, the performance boost is up to 10.67% (97.33% vs. 86.66%). Furthermore, MoDES significantly enhances inference speed, improving the prefilling time by 2.16$\times$ and the decoding time by 1.26$\times$.
SLMQuant:Benchmarking Small Language Model Quantization for Practical Deployment
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Despite the growing interest in Small Language Models (SLMs) as resource-efficient alternatives to Large Language Models (LLMs), their deployment on edge devices remains challenging due to unresolved efficiency gaps in model compression. While quantization has proven effective for LLMs, its applicability to SLMs is significantly underexplored, with critical questions about differing quantization bottlenecks and efficiency profiles. This paper introduces SLMQuant, the first systematic benchmark for evaluating LLM compression techniques when applied to SLMs. Through comprehensive multi-track evaluations across diverse architectures and tasks, we analyze how state-of-the-art quantization methods perform on SLMs. Our findings reveal fundamental disparities between SLMs and LLMs in quantization sensitivity, demonstrating that direct transfer of LLM-optimized techniques leads to suboptimal results due to SLMs' unique architectural characteristics and training dynamics. We identify key factors governing effective SLM quantization and propose actionable design principles for SLM-tailored compression. SLMQuant establishes a foundational framework for advancing efficient SLM deployment on low-end devices in edge applications, and provides critical insights for deploying lightweight language models in resource-constrained scenarios.
LLMC+: Benchmarking Vision-Language Model Compression with a Plug-and-play Toolkit
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) exhibit impressive multi-modal capabilities but suffer from prohibitive computational and memory demands, due to their long visual token sequences and massive parameter sizes. To address these issues, recent works have proposed training-free compression methods. However, existing efforts often suffer from three major limitations: (1) Current approaches do not decompose techniques into comparable modules, hindering fair evaluation across spatial and temporal redundancy. (2) Evaluation confined to simple single-turn tasks, failing to reflect performance in realistic scenarios. (3) Isolated use of individual compression techniques, without exploring their joint potential. To overcome these gaps, we introduce LLMC+, a comprehensive VLM compression benchmark with a versatile, plug-and-play toolkit. LLMC+ supports over 20 algorithms across five representative VLM families and enables systematic study of token-level and model-level compression. Our benchmark reveals that: (1) Spatial and temporal redundancies demand distinct technical strategies. (2) Token reduction methods degrade significantly in multi-turn dialogue and detail-sensitive tasks. (3) Combining token and model compression achieves extreme compression with minimal performance loss. We believe LLMC+ will facilitate fair evaluation and inspire future research in efficient VLM. Our code is available at https://github.com/ModelTC/LightCompress.
AGENTSAFE: Benchmarking the Safety of Embodied Agents on Hazardous Instructions
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of vision-language models (VLMs) and their integration into embodied agents have unlocked powerful capabilities for decision-making. However, as these systems are increasingly deployed in real-world environments, they face mounting safety concerns, particularly when responding to hazardous instructions. In this work, we propose AGENTSAFE, the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating the safety of embodied VLM agents under hazardous instructions. AGENTSAFE simulates realistic agent-environment interactions within a simulation sandbox and incorporates a novel adapter module that bridges the gap between high-level VLM outputs and low-level embodied controls. Specifically, it maps recognized visual entities to manipulable objects and translates abstract planning into executable atomic actions in the environment. Building on this, we construct a risk-aware instruction dataset inspired by Asimovs Three Laws of Robotics, including base risky instructions and mutated jailbroken instructions. The benchmark includes 45 adversarial scenarios, 1,350 hazardous tasks, and 8,100 hazardous instructions, enabling systematic testing under adversarial conditions ranging from perception, planning, and action execution stages.
DynaSplat: Dynamic-Static Gaussian Splatting with Hierarchical Motion Decomposition for Scene Reconstruction
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing intricate, ever-changing environments remains a central ambition in computer vision, yet existing solutions often crumble before the complexity of real-world dynamics. We present DynaSplat, an approach that extends Gaussian Splatting to dynamic scenes by integrating dynamic-static separation and hierarchical motion modeling. First, we classify scene elements as static or dynamic through a novel fusion of deformation offset statistics and 2D motion flow consistency, refining our spatial representation to focus precisely where motion matters. We then introduce a hierarchical motion modeling strategy that captures both coarse global transformations and fine-grained local movements, enabling accurate handling of intricate, non-rigid motions. Finally, we integrate physically-based opacity estimation to ensure visually coherent reconstructions, even under challenging occlusions and perspective shifts. Extensive experiments on challenging datasets reveal that DynaSplat not only surpasses state-of-the-art alternatives in accuracy and realism but also provides a more intuitive, compact, and efficient route to dynamic scene reconstruction.
An Empirical Study of Qwen3 Quantization
May 04, 2025Abstract:The Qwen series has emerged as a leading family of open-source Large Language Models (LLMs), demonstrating remarkable capabilities in natural language understanding tasks. With the recent release of Qwen3, which exhibits superior performance across diverse benchmarks, there is growing interest in deploying these models efficiently in resource-constrained environments. Low-bit quantization presents a promising solution, yet its impact on Qwen3's performance remains underexplored. This study conducts a systematic evaluation of Qwen3's robustness under various quantization settings, aiming to uncover both opportunities and challenges in compressing this state-of-the-art model. We rigorously assess 5 existing classic post-training quantization techniques applied to Qwen3, spanning bit-widths from 1 to 8 bits, and evaluate their effectiveness across multiple datasets. Our findings reveal that while Qwen3 maintains competitive performance at moderate bit-widths, it experiences notable degradation in linguistic tasks under ultra-low precision, underscoring the persistent hurdles in LLM compression. These results emphasize the need for further research to mitigate performance loss in extreme quantization scenarios. We anticipate that this empirical analysis will provide actionable insights for advancing quantization methods tailored to Qwen3 and future LLMs, ultimately enhancing their practicality without compromising accuracy. Our project is released on https://github.com/Efficient-ML/Qwen3-Quantization and https://huggingface.co/collections/Efficient-ML/qwen3-quantization-68164450decb1c868788cb2b.
APHQ-ViT: Post-Training Quantization with Average Perturbation Hessian Based Reconstruction for Vision Transformers
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have become one of the most commonly used backbones for vision tasks. Despite their remarkable performance, they often suffer significant accuracy drops when quantized for practical deployment, particularly by post-training quantization (PTQ) under ultra-low bits. Recently, reconstruction-based PTQ methods have shown promising performance in quantizing Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). However, they fail when applied to ViTs, primarily due to the inaccurate estimation of output importance and the substantial accuracy degradation in quantizing post-GELU activations. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{APHQ-ViT}, a novel PTQ approach based on importance estimation with Average Perturbation Hessian (APH). Specifically, we first thoroughly analyze the current approximation approaches with Hessian loss, and propose an improved average perturbation Hessian loss. To deal with the quantization of the post-GELU activations, we design an MLP Reconstruction (MR) method by replacing the GELU function in MLP with ReLU and reconstructing it by the APH loss on a small unlabeled calibration set. Extensive experiments demonstrate that APHQ-ViT using linear quantizers outperforms existing PTQ methods by substantial margins in 3-bit and 4-bit across different vision tasks. The source code is available at https://github.com/GoatWu/APHQ-ViT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge