Ping Shi
Research on Audio-Visual Quality Assessment Dataset and Method for User-Generated Omnidirectional Video
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:In response to the rising prominence of the Metaverse, omnidirectional videos (ODVs) have garnered notable interest, gradually shifting from professional-generated content (PGC) to user-generated content (UGC). However, the study of audio-visual quality assessment (AVQA) within ODVs remains limited. To address this, we construct a dataset of UGC omnidirectional audio and video (A/V) content. The videos are captured by five individuals using two different types of omnidirectional cameras, shooting 300 videos covering 10 different scene types. A subjective AVQA experiment is conducted on the dataset to obtain the Mean Opinion Scores (MOSs) of the A/V sequences. After that, to facilitate the development of UGC-ODV AVQA fields, we construct an effective AVQA baseline model on the proposed dataset, of which the baseline model consists of video feature extraction module, audio feature extraction and audio-visual fusion module. The experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves optimal performance on the proposed dataset.
DynaSplat: Dynamic-Static Gaussian Splatting with Hierarchical Motion Decomposition for Scene Reconstruction
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing intricate, ever-changing environments remains a central ambition in computer vision, yet existing solutions often crumble before the complexity of real-world dynamics. We present DynaSplat, an approach that extends Gaussian Splatting to dynamic scenes by integrating dynamic-static separation and hierarchical motion modeling. First, we classify scene elements as static or dynamic through a novel fusion of deformation offset statistics and 2D motion flow consistency, refining our spatial representation to focus precisely where motion matters. We then introduce a hierarchical motion modeling strategy that captures both coarse global transformations and fine-grained local movements, enabling accurate handling of intricate, non-rigid motions. Finally, we integrate physically-based opacity estimation to ensure visually coherent reconstructions, even under challenging occlusions and perspective shifts. Extensive experiments on challenging datasets reveal that DynaSplat not only surpasses state-of-the-art alternatives in accuracy and realism but also provides a more intuitive, compact, and efficient route to dynamic scene reconstruction.
Towards Holistic Visual Quality Assessment of AI-Generated Videos: A LLM-Based Multi-Dimensional Evaluation Model
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:The development of AI-Generated Video (AIGV) technology has been remarkable in recent years, significantly transforming the paradigm of video content production. However, AIGVs still suffer from noticeable visual quality defects, such as noise, blurriness, frame jitter and low dynamic degree, which severely impact the user's viewing experience. Therefore, an effective automatic visual quality assessment is of great importance for AIGV content regulation and generative model improvement. In this work, we decompose the visual quality of AIGVs into three dimensions: technical quality, motion quality, and video semantics. For each dimension, we design corresponding encoder to achieve effective feature representation. Moreover, considering the outstanding performance of large language models (LLMs) in various vision and language tasks, we introduce a LLM as the quality regression module. To better enable the LLM to establish reasoning associations between multi-dimensional features and visual quality, we propose a specially designed multi-modal prompt engineering framework. Additionally, we incorporate LoRA fine-tuning technology during the training phase, allowing the LLM to better adapt to specific tasks. Our proposed method achieved \textbf{second place} in the NTIRE 2025 Quality Assessment of AI-Generated Content Challenge: Track 2 AI Generated video, demonstrating its effectiveness. Codes can be obtained at https://github.com/QiZelu/AIGVEval.
Comprehensive Subjective and Objective Evaluation Method for Text-generated Video
Jan 15, 2025



Abstract:Recent text-to-video (T2V) technology advancements, as demonstrated by models such as Gen3, Pika, and Sora, have significantly broadened its applicability and popularity. This progress has created a growing demand for accurate quality assessment metrics to evaluate the perceptual quality of text-generated videos and optimize video generation models. However, assessing the quality of text-generated videos remains challenging due to the presence of highly complex distortions, such as unnatural actions and phenomena that defy human cognition. To address these challenges, we constructed a large-scale benchmark dataset for \textbf{T}ext-generated \textbf{V}ideo \textbf{eval}uation, \textbf{T2VEval-Bench}, comprising 148 textual words and 1,783 videos generated by 12 models. During the subjective evaluation, we collected five key scores: overall impression, video quality, aesthetic quality, realness, and text-video consistency. For objective evaluation, we developed the \textbf{T2VEval} model, which assesses videos across three branches: quality, authenticity, and consistency. Using an attention-based fusion module, T2VEval effectively integrates features from each branch and predicts scores with the aid of a large oracle model. Additionally, we implemented a progressive training strategy, enabling each branch to learn targeted knowledge while maintaining synergy with the others. Experimental results demonstrate that T2VEval achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple metrics. The dataset and code will be open-sourced upon completion of the follow-up work.
Elastic Net based Feature Ranking and Selection
Dec 30, 2020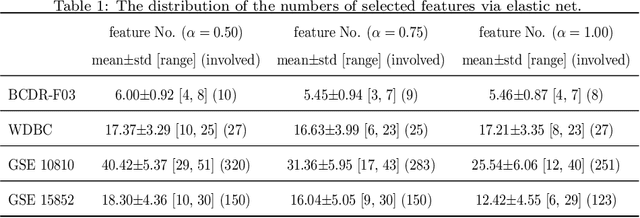
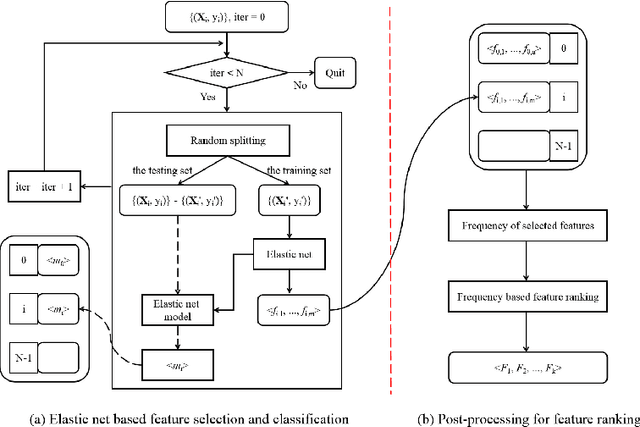
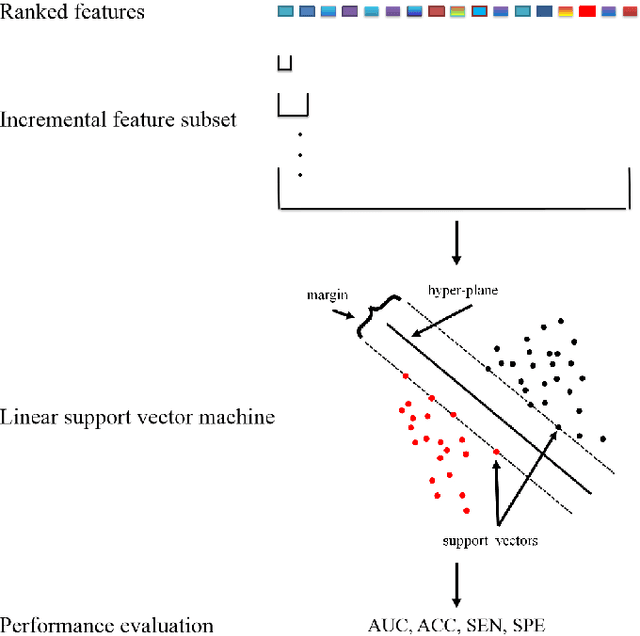
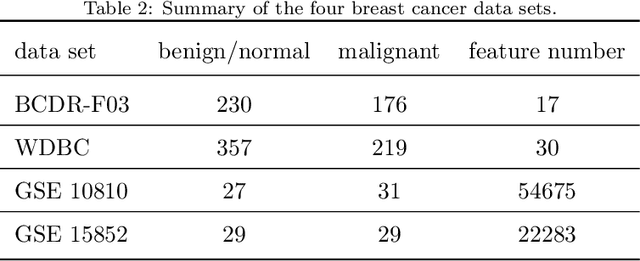
Abstract:Feature selection is important in data representation and intelligent diagnosis. Elastic net is one of the most widely used feature selectors. However, the features selected are dependant on the training data, and their weights dedicated for regularized regression are irrelevant to their importance if used for feature ranking, that degrades the model interpretability and extension. In this study, an intuitive idea is put at the end of multiple times of data splitting and elastic net based feature selection. It concerns the frequency of selected features and uses the frequency as an indicator of feature importance. After features are sorted according to their frequency, linear support vector machine performs the classification in an incremental manner. At last, a compact subset of discriminative features is selected by comparing the prediction performance. Experimental results on breast cancer data sets (BCDR-F03, WDBC, GSE 10810, and GSE 15852) suggest that the proposed framework achieves competitive or superior performance to elastic net and with consistent selection of fewer features. How to further enhance its consistency on high-dimension small-sample-size data sets should be paid more attention in our future work. The proposed framework is accessible online (https://github.com/NicoYuCN/elasticnetFR).
Blind Predicting Similar Quality Map for Image Quality Assessment
May 22, 2018



Abstract:A key problem in blind image quality assessment (BIQA) is how to effectively model the properties of human visual system in a data-driven manner. In this paper, we propose a simple and efficient BIQA model based on a novel framework which consists of a fully convolutional neural network (FCNN) and a pooling network to solve this problem. In principle, FCNN is capable of predicting a pixel-by-pixel similar quality map only from a distorted image by using the intermediate similarity maps derived from conventional full-reference image quality assessment methods. The predicted pixel-by-pixel quality maps have good consistency with the distortion correlations between the reference and distorted images. Finally, a deep pooling network regresses the quality map into a score. Experiments have demonstrated that our predictions outperform many state-of-the-art BIQA methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge