Fei Zhao
Decouple Searching from Training: Scaling Data Mixing via Model Merging for Large Language Model Pre-training
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Determining an effective data mixture is a key factor in Large Language Model (LLM) pre-training, where models must balance general competence with proficiency on hard tasks such as math and code. However, identifying an optimal mixture remains an open challenge, as existing approaches either rely on unreliable tiny-scale proxy experiments or require prohibitively expensive large-scale exploration. To address this, we propose Decouple Searching from Training Mix (DeMix), a novel framework that leverages model merging to predict optimal data ratios. Instead of training proxy models for every sampled mixture, DeMix trains component models on candidate datasets at scale and derives data mixture proxies via weighted model merging. This paradigm decouples search from training costs, enabling evaluation of unlimited sampled mixtures without extra training burden and thus facilitating better mixture discovery through more search trials. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DeMix breaks the trade-off between sufficiency, accuracy and efficiency, obtaining the optimal mixture with higher benchmark performance at lower search cost. Additionally, we release the DeMix Corpora, a comprehensive 22T-token dataset comprising high-quality pre-training data with validated mixtures to facilitate open research. Our code and DeMix Corpora is available at https://github.com/Lucius-lsr/DeMix.
Robust Tool Use via Fission-GRPO: Learning to Recover from Execution Errors
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can call tools effectively, yet they remain brittle in multi-turn execution: following a tool call error, smaller models often degenerate into repetitive invalid re-invocations, failing to interpret error feedback and self-correct. This brittleness hinders reliable real-world deployment, where the execution errors are inherently inevitable during tool interaction procedures. We identify a key limitation of current approaches: standard reinforcement learning (RL) treats errors as sparse negative rewards, providing no guidance on how to recover, while pre-collected synthetic error-correction datasets suffer from distribution mismatch with the model's on-policy error modes. To bridge this gap, we propose Fission-GRPO, a framework that converts execution errors into corrective supervision within the RL training loop. Our core mechanism fissions each failed trajectory into a new training instance by augmenting it with diagnostic feedback from a finetuned Error Simulator, then resampling recovery rollouts on-policy. This enables the model to learn from the precise errors it makes during exploration, rather than from static, pre-collected error cases. On the BFCL v4 Multi-Turn, Fission-GRPO improves the error recovery rate of Qwen3-8B by 5.7% absolute, crucially, yielding a 4% overall accuracy gain (42.75% to 46.75%) over GRPO and outperforming specialized tool-use agents.
A Tri-Dynamic Preprocessing Framework for UGC Video Compression
Dec 18, 2025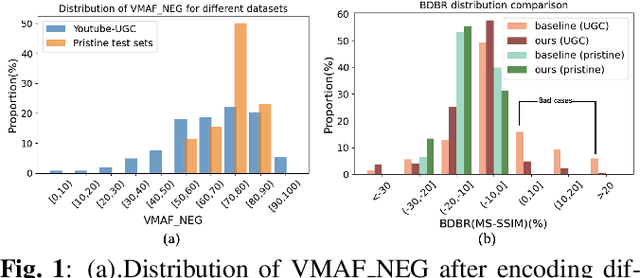
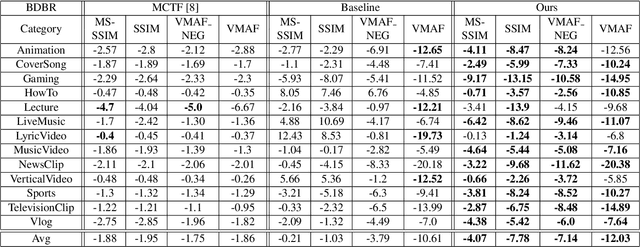
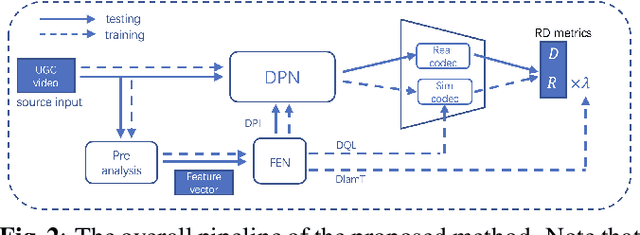
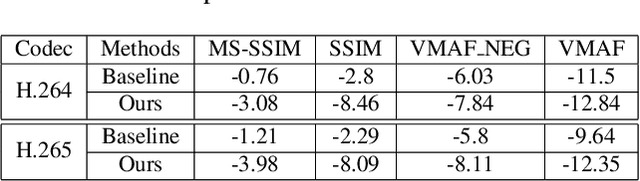
Abstract:In recent years, user generated content (UGC) has become the dominant force in internet traffic. However, UGC videos exhibit a higher degree of variability and diverse characteristics compared to traditional encoding test videos. This variance challenges the effectiveness of data-driven machine learning algorithms for optimizing encoding in the broader context of UGC scenarios. To address this issue, we propose a Tri-Dynamic Preprocessing framework for UGC. Firstly, we employ an adaptive factor to regulate preprocessing intensity. Secondly, an adaptive quantization level is employed to fine-tune the codec simulator. Thirdly, we utilize an adaptive lambda tradeoff to adjust the rate-distortion loss function. Experimental results on large-scale test sets demonstrate that our method attains exceptional performance.
A Preprocessing Framework for Video Machine Vision under Compression
Dec 17, 2025
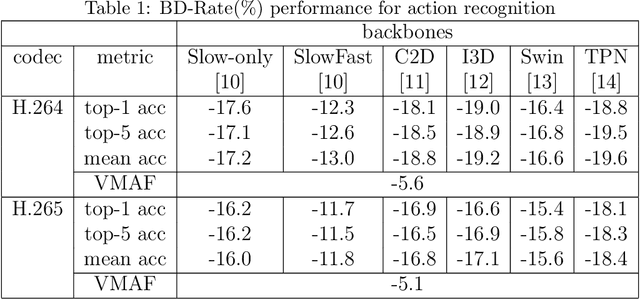
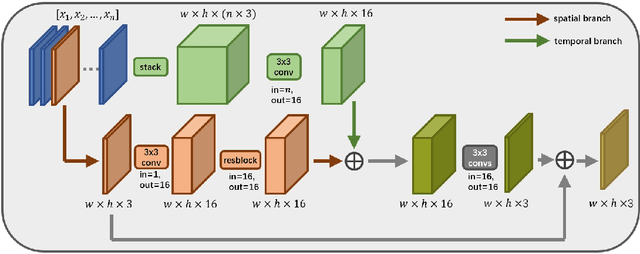
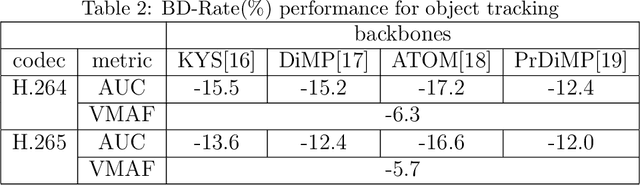
Abstract:There has been a growing trend in compressing and transmitting videos from terminals for machine vision tasks. Nevertheless, most video coding optimization method focus on minimizing distortion according to human perceptual metrics, overlooking the heightened demands posed by machine vision systems. In this paper, we propose a video preprocessing framework tailored for machine vision tasks to address this challenge. The proposed method incorporates a neural preprocessor which retaining crucial information for subsequent tasks, resulting in the boosting of rate-accuracy performance. We further introduce a differentiable virtual codec to provide constraints on rate and distortion during the training stage. We directly apply widely used standard codecs for testing. Therefore, our solution can be easily applied to real-world scenarios. We conducted extensive experiments evaluating our compression method on two typical downstream tasks with various backbone networks. The experimental results indicate that our approach can save over 15% of bitrate compared to using only the standard codec anchor version.
RedOne 2.0: Rethinking Domain-specific LLM Post-Training in Social Networking Services
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:As a key medium for human interaction and information exchange, social networking services (SNS) pose unique challenges for large language models (LLMs): heterogeneous workloads, fast-shifting norms and slang, and multilingual, culturally diverse corpora that induce sharp distribution shift. Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) can specialize models but often triggers a ``seesaw'' between in-distribution gains and out-of-distribution robustness, especially for smaller models. To address these challenges, we introduce RedOne 2.0, an SNS-oriented LLM trained with a progressive, RL-prioritized post-training paradigm designed for rapid and stable adaptation. The pipeline consist in three stages: (1) Exploratory Learning on curated SNS corpora to establish initial alignment and identify systematic weaknesses; (2) Targeted Fine-Tuning that selectively applies SFT to the diagnosed gaps while mixing a small fraction of general data to mitigate forgetting; and (3) Refinement Learning that re-applies RL with SNS-centric signals to consolidate improvements and harmonize trade-offs across tasks. Across various tasks spanning three categories, our 4B scale model delivers an average improvements about 2.41 over the 7B sub-optimal baseline. Additionally, RedOne 2.0 achieves average performance lift about 8.74 from the base model with less than half the data required by SFT-centric method RedOne, evidencing superior data efficiency and stability at compact scales. Overall, RedOne 2.0 establishes a competitive, cost-effective baseline for domain-specific LLMs in SNS scenario, advancing capability without sacrificing robustness.
Research on Audio-Visual Quality Assessment Dataset and Method for User-Generated Omnidirectional Video
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:In response to the rising prominence of the Metaverse, omnidirectional videos (ODVs) have garnered notable interest, gradually shifting from professional-generated content (PGC) to user-generated content (UGC). However, the study of audio-visual quality assessment (AVQA) within ODVs remains limited. To address this, we construct a dataset of UGC omnidirectional audio and video (A/V) content. The videos are captured by five individuals using two different types of omnidirectional cameras, shooting 300 videos covering 10 different scene types. A subjective AVQA experiment is conducted on the dataset to obtain the Mean Opinion Scores (MOSs) of the A/V sequences. After that, to facilitate the development of UGC-ODV AVQA fields, we construct an effective AVQA baseline model on the proposed dataset, of which the baseline model consists of video feature extraction module, audio feature extraction and audio-visual fusion module. The experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves optimal performance on the proposed dataset.
Towards Holistic Visual Quality Assessment of AI-Generated Videos: A LLM-Based Multi-Dimensional Evaluation Model
Jun 05, 2025



Abstract:The development of AI-Generated Video (AIGV) technology has been remarkable in recent years, significantly transforming the paradigm of video content production. However, AIGVs still suffer from noticeable visual quality defects, such as noise, blurriness, frame jitter and low dynamic degree, which severely impact the user's viewing experience. Therefore, an effective automatic visual quality assessment is of great importance for AIGV content regulation and generative model improvement. In this work, we decompose the visual quality of AIGVs into three dimensions: technical quality, motion quality, and video semantics. For each dimension, we design corresponding encoder to achieve effective feature representation. Moreover, considering the outstanding performance of large language models (LLMs) in various vision and language tasks, we introduce a LLM as the quality regression module. To better enable the LLM to establish reasoning associations between multi-dimensional features and visual quality, we propose a specially designed multi-modal prompt engineering framework. Additionally, we incorporate LoRA fine-tuning technology during the training phase, allowing the LLM to better adapt to specific tasks. Our proposed method achieved \textbf{second place} in the NTIRE 2025 Quality Assessment of AI-Generated Content Challenge: Track 2 AI Generated video, demonstrating its effectiveness. Codes can be obtained at https://github.com/QiZelu/AIGVEval.
Multi-Channel Acoustic Echo Cancellation Based on Direction-of-Arrival Estimation
May 26, 2025Abstract:Acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) is an important speech signal processing technology that can remove echoes from microphone signals to enable natural-sounding full-duplex speech communication. While single-channel AEC is widely adopted, multi-channel AEC can leverage spatial cues afforded by multiple microphones to achieve better performance. Existing multi-channel AEC approaches typically combine beamforming with deep neural networks (DNN). This work proposes a two-stage algorithm that enhances multi-channel AEC by incorporating sound source directional cues. Specifically, a lightweight DNN is first trained to predict the sound source directions, and then the predicted directional information, multi-channel microphone signals, and single-channel far-end signal are jointly fed into an AEC network to estimate the near-end signal. Evaluation results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms baseline approaches and exhibits robust generalization across diverse acoustic environments.
Room Impulse Response as a Prompt for Acoustic Echo Cancellation
May 26, 2025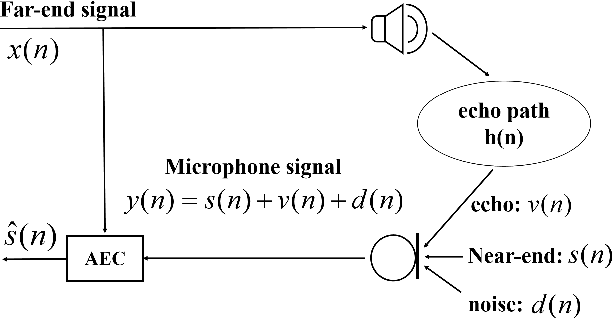
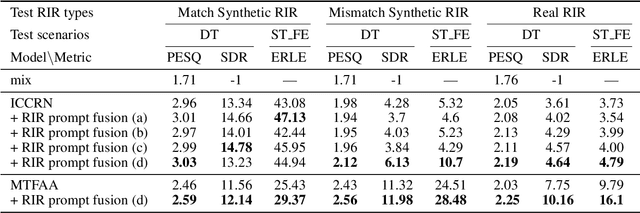
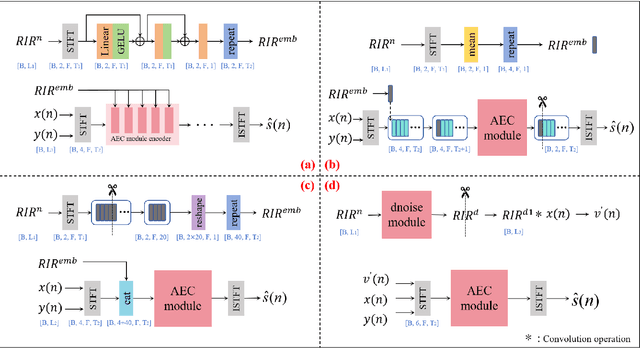
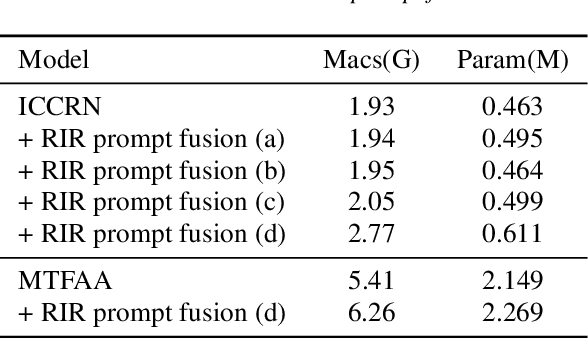
Abstract:Data-driven acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) methods, predominantly trained on synthetic or constrained real-world datasets, encounter performance declines in unseen echo scenarios, especially in real environments where echo paths are not directly observable. Our proposed method counters this limitation by integrating room impulse response (RIR) as a pivotal training prompt, aiming to improve the generalization of AEC models in such unforeseen conditions. We also explore four RIR prompt fusion methods. Comprehensive evaluations, including both simulated RIR under unknown conditions and recorded RIR in real, demonstrate that the proposed approach significantly improves performance compared to baseline models. These results substantiate the effectiveness of our RIR-guided approach in strengthening the model's generalization capabilities.
CompBench: Benchmarking Complex Instruction-guided Image Editing
May 18, 2025Abstract:While real-world applications increasingly demand intricate scene manipulation, existing instruction-guided image editing benchmarks often oversimplify task complexity and lack comprehensive, fine-grained instructions. To bridge this gap, we introduce, a large-scale benchmark specifically designed for complex instruction-guided image editing. CompBench features challenging editing scenarios that incorporate fine-grained instruction following, spatial and contextual reasoning, thereby enabling comprehensive evaluation of image editing models' precise manipulation capabilities. To construct CompBench, We propose an MLLM-human collaborative framework with tailored task pipelines. Furthermore, we propose an instruction decoupling strategy that disentangles editing intents into four key dimensions: location, appearance, dynamics, and objects, ensuring closer alignment between instructions and complex editing requirements. Extensive evaluations reveal that CompBench exposes fundamental limitations of current image editing models and provides critical insights for the development of next-generation instruction-guided image editing systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge