Zheyu Ye
RedOne 2.0: Rethinking Domain-specific LLM Post-Training in Social Networking Services
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:As a key medium for human interaction and information exchange, social networking services (SNS) pose unique challenges for large language models (LLMs): heterogeneous workloads, fast-shifting norms and slang, and multilingual, culturally diverse corpora that induce sharp distribution shift. Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) can specialize models but often triggers a ``seesaw'' between in-distribution gains and out-of-distribution robustness, especially for smaller models. To address these challenges, we introduce RedOne 2.0, an SNS-oriented LLM trained with a progressive, RL-prioritized post-training paradigm designed for rapid and stable adaptation. The pipeline consist in three stages: (1) Exploratory Learning on curated SNS corpora to establish initial alignment and identify systematic weaknesses; (2) Targeted Fine-Tuning that selectively applies SFT to the diagnosed gaps while mixing a small fraction of general data to mitigate forgetting; and (3) Refinement Learning that re-applies RL with SNS-centric signals to consolidate improvements and harmonize trade-offs across tasks. Across various tasks spanning three categories, our 4B scale model delivers an average improvements about 2.41 over the 7B sub-optimal baseline. Additionally, RedOne 2.0 achieves average performance lift about 8.74 from the base model with less than half the data required by SFT-centric method RedOne, evidencing superior data efficiency and stability at compact scales. Overall, RedOne 2.0 establishes a competitive, cost-effective baseline for domain-specific LLMs in SNS scenario, advancing capability without sacrificing robustness.
AgentGroupChat-V2: Divide-and-Conquer Is What LLM-Based Multi-Agent System Need
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Large language model based multi-agent systems have demonstrated significant potential in social simulation and complex task resolution domains. However, current frameworks face critical challenges in system architecture design, cross-domain generalizability, and performance guarantees, particularly as task complexity and number of agents increases. We introduces AgentGroupChat-V2, a novel framework addressing these challenges through three core innovations: (1) a divide-and-conquer fully parallel architecture that decomposes user queries into hierarchical task forest structures enabling dependency management and distributed concurrent processing. (2) an adaptive collaboration engine that dynamically selects heterogeneous LLM combinations and interaction modes based on task characteristics. (3) agent organization optimization strategies combining divide-and-conquer approaches for efficient problem decomposition. Extensive experiments demonstrate AgentGroupChat-V2's superior performance across diverse domains, achieving 91.50% accuracy on GSM8K (exceeding the best baseline by 5.6 percentage points), 30.4% accuracy on competition-level AIME (nearly doubling other methods), and 79.20% pass@1 on HumanEval. Performance advantages become increasingly pronounced with higher task difficulty, particularly on Level 5 MATH problems where improvements exceed 11 percentage points compared to state-of-the-art baselines. These results confirm that AgentGroupChat-V2 provides a comprehensive solution for building efficient, general-purpose LLM multi-agent systems with significant advantages in complex reasoning scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/MikeGu721/AgentGroupChat-V2.
Act-as-Pet: Benchmarking the Abilities of Large Language Models as E-Pets in Social Network Services
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:As interest in using Large Language Models (LLMs) for interactive and emotionally rich experiences grows, virtual pet companionship emerges as a novel yet underexplored application. Existing approaches focus on basic pet role-playing interactions without systematically benchmarking LLMs for comprehensive companionship. In this paper, we introduce Pet-Bench, a dedicated benchmark that evaluates LLMs across both self-interaction and human-interaction dimensions. Unlike prior work, Pet-Bench emphasizes self-evolution and developmental behaviors alongside interactive engagement, offering a more realistic reflection of pet companionship. It features diverse tasks such as intelligent scheduling, memory-based dialogues, and psychological conversations, with over 7,500 interaction instances designed to simulate complex pet behaviors. Evaluation of 28 LLMs reveals significant performance variations linked to model size and inherent capabilities, underscoring the need for specialized optimization in this domain. Pet-Bench serves as a foundational resource for benchmarking pet-related LLM abilities and advancing emotionally immersive human-pet interactions.
PaRT: Enhancing Proactive Social Chatbots with Personalized Real-Time Retrieval
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:Social chatbots have become essential intelligent companions in daily scenarios ranging from emotional support to personal interaction. However, conventional chatbots with passive response mechanisms usually rely on users to initiate or sustain dialogues by bringing up new topics, resulting in diminished engagement and shortened dialogue duration. In this paper, we present PaRT, a novel framework enabling context-aware proactive dialogues for social chatbots through personalized real-time retrieval and generation. Specifically, PaRT first integrates user profiles and dialogue context into a large language model (LLM), which is initially prompted to refine user queries and recognize their underlying intents for the upcoming conversation. Guided by refined intents, the LLM generates personalized dialogue topics, which then serve as targeted queries to retrieve relevant passages from RedNote. Finally, we prompt LLMs with summarized passages to generate knowledge-grounded and engagement-optimized responses. Our approach has been running stably in a real-world production environment for more than 30 days, achieving a 21.77\% improvement in the average duration of dialogues.
Vision-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in Multimodal Large Language Models
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:DeepSeek-R1-Zero has successfully demonstrated the emergence of reasoning capabilities in LLMs purely through Reinforcement Learning (RL). Inspired by this breakthrough, we explore how RL can be utilized to enhance the reasoning capability of MLLMs. However, direct training with RL struggles to activate complex reasoning capabilities such as questioning and reflection in MLLMs, due to the absence of substantial high-quality multimodal reasoning data. To address this issue, we propose the reasoning MLLM, Vision-R1, to improve multimodal reasoning capability. Specifically, we first construct a high-quality multimodal CoT dataset without human annotations by leveraging an existing MLLM and DeepSeek-R1 through modality bridging and data filtering to obtain a 200K multimodal CoT dataset, Vision-R1-cold dataset. It serves as cold-start initialization data for Vision-R1. To mitigate the optimization challenges caused by overthinking after cold start, we propose Progressive Thinking Suppression Training (PTST) strategy and employ Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with the hard formatting result reward function to gradually refine the model's ability to learn correct and complex reasoning processes on a 10K multimodal math dataset. Comprehensive experiments show our model achieves an average improvement of $\sim$6% across various multimodal math reasoning benchmarks. Vision-R1-7B achieves a 73.5% accuracy on the widely used MathVista benchmark, which is only 0.4% lower than the leading reasoning model, OpenAI O1. The datasets and code will be released in: https://github.com/Osilly/Vision-R1 .
Dynamic-LLaVA: Efficient Multimodal Large Language Models via Dynamic Vision-language Context Sparsification
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable success in vision understanding, reasoning, and interaction. However, the inference computation and memory increase progressively with the generation of output tokens during decoding, directly affecting the efficacy of MLLMs. Existing methods attempt to reduce the vision context redundancy to achieve efficient MLLMs. Unfortunately, the efficiency benefits of the vision context reduction in the prefill stage gradually diminish during the decoding stage. To address this problem, we proposed a dynamic vision-language context sparsification framework Dynamic-LLaVA, which dynamically reduces the redundancy of vision context in the prefill stage and decreases the memory and computation overhead of the generated language context during decoding. Dynamic-LLaVA designs a tailored sparsification inference scheme for different inference modes, i.e., prefill, decoding with and without KV cache, to achieve efficient inference of MLLMs. In practice, Dynamic-LLaVA can reduce computation consumption by $\sim$75\% in the prefill stage. Meanwhile, throughout the entire generation process of MLLMs, Dynamic-LLaVA reduces the $\sim$50\% computation consumption under decoding without KV cache, while saving $\sim$50\% GPU memory overhead when decoding with KV cache, due to the vision-language context sparsification. Extensive experiments also demonstrate that Dynamic-LLaVA achieves efficient inference for MLLMs with negligible understanding and generation ability degradation or even performance gains compared to the full-context inference baselines. Code is available at https://github.com/Osilly/dynamic_llava .
MoDification: Mixture of Depths Made Easy
Oct 18, 2024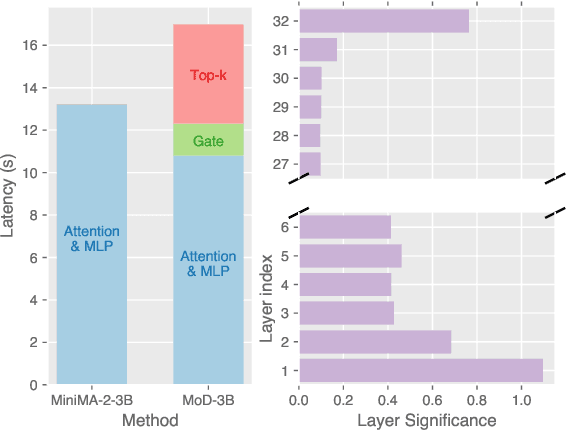
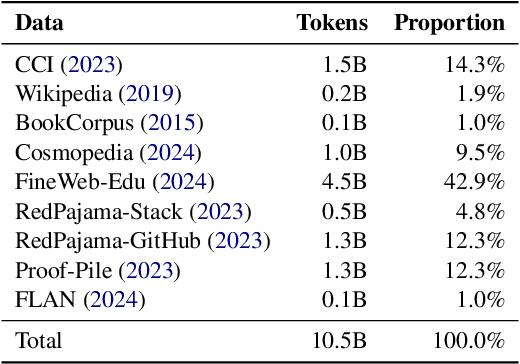
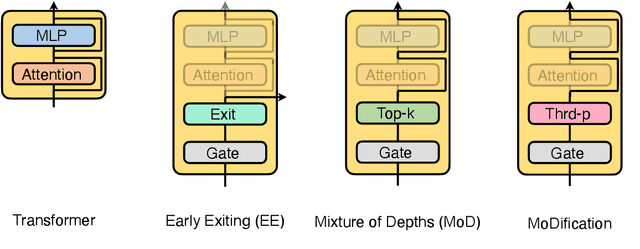
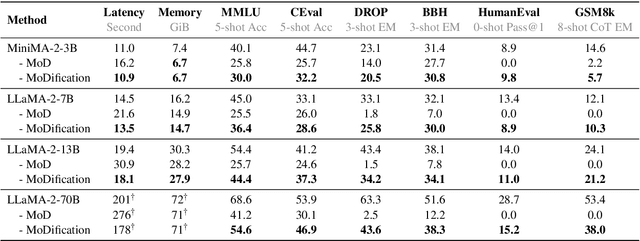
Abstract:Long-context efficiency has recently become a trending topic in serving large language models (LLMs). And mixture of depths (MoD) is proposed as a perfect fit to bring down both latency and memory. In this paper, however, we discover that MoD can barely transform existing LLMs without costly training over an extensive number of tokens. To enable the transformations from any LLMs to MoD ones, we showcase top-k operator in MoD should be promoted to threshold-p operator, and refinement to architecture and data should also be crafted along. All these designs form our method termed MoDification. Through a comprehensive set of experiments covering model scales from 3B to 70B, we exhibit MoDification strikes an excellent balance between efficiency and effectiveness. MoDification can achieve up to ~1.2x speedup in latency and ~1.8x reduction in memory compared to original LLMs especially in long-context applications.
DetectBench: Can Large Language Model Detect and Piece Together Implicit Evidence?
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Detecting evidence within the context is a key step in the process of reasoning task. Evaluating and enhancing the capabilities of LLMs in evidence detection will strengthen context-based reasoning performance. This paper proposes a benchmark called DetectBench for verifying the ability to detect and piece together implicit evidence within a long context. DetectBench contains 3,928 multiple-choice questions, with an average of 994 tokens per question. Each question contains an average of 4.55 pieces of implicit evidence, and solving the problem typically requires 7.62 logical jumps to find the correct answer. To enhance the performance of LLMs in evidence detection, this paper proposes Detective Reasoning Prompt and Finetune. Experiments demonstrate that the existing LLMs' abilities to detect evidence in long contexts are far inferior to humans. However, the Detective Reasoning Prompt effectively enhances the capability of powerful LLMs in evidence detection, while the Finetuning method shows significant effects in enhancing the performance of weaker LLMs. Moreover, when the abilities of LLMs in evidence detection are improved, their final reasoning performance is also enhanced accordingly.
Agent Group Chat: An Interactive Group Chat Simulacra For Better Eliciting Collective Emergent Behavior
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:To investigate the role of language in human collective behaviors, we developed the Agent Group Chat simulation to simulate linguistic interactions among multi-agent in different settings. Agents are asked to free chat in this simulation for their own purposes based on their character setting, aiming to see agents exhibit emergent behaviours that are both unforeseen and significant. Four narrative scenarios, Inheritance Disputes, Law Court Debates, Philosophical Discourses, Movie Casting Contention, are integrated into Agent Group Chat to evaluate its support for diverse storylines. By configuring specific environmental settings within Agent Group Chat, we are able to assess whether agents exhibit behaviors that align with human expectations. We evaluate the disorder within the environment by computing the n-gram Shannon entropy of all the content speak by characters. Our findings reveal that under the premise of agents possessing substantial alignment with human expectations, facilitating more extensive information exchange within the simulation ensures greater orderliness amidst diversity, which leads to the emergence of more unexpected and meaningful emergent behaviors. The code is open source in https://github.com/MikeGu721/AgentGroup, and online platform will be open soon.
Towards the Law of Capacity Gap in Distilling Language Models
Nov 13, 2023



Abstract:Language model (LM) distillation is a trending area that aims to distil the knowledge resided in a large teacher LM to a small student one. While various methods have been proposed to push the distillation to its limits, it is still a pain distilling LMs when a large capacity gap is exhibited between the teacher and the student LMs. The pain is mainly resulted by the curse of capacity gap, which describes that a larger teacher LM cannot always lead to a better student LM than one distilled from a smaller teacher LM due to the affect of capacity gap increment. That is, there is likely an optimal point yielding the best student LM along the scaling course of the teacher LM. Even worse, the curse of capacity gap can be only partly yet not fully lifted as indicated in previous studies. However, the tale is not ever one-sided. Although a larger teacher LM has better performance than a smaller teacher LM, it is much more resource-demanding especially in the context of recent large LMs (LLMs). Consequently, instead of sticking to lifting the curse, leaving the curse as is should be arguably fine. Even better, in this paper, we reveal that the optimal capacity gap is almost consistent across different student scales and architectures, fortunately turning the curse into the law of capacity gap. The law later guides us to distil a 3B student LM (termed MiniMA) from a 7B teacher LM (adapted LLaMA2-7B). MiniMA is demonstrated to yield a new compute-performance pareto frontier among existing 3B LMs on commonly used benchmarks, and its instruction-tuned version (termed MiniChat) outperforms a wide range of 3B competitors in GPT4 evaluation and could even compete with several 7B chat models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge