Hongwei Feng
HUMANLLM: Benchmarking and Reinforcing LLM Anthropomorphism via Human Cognitive Patterns
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in reasoning and generation, serving as the foundation for advanced persona simulation and Role-Playing Language Agents (RPLAs). However, achieving authentic alignment with human cognitive and behavioral patterns remains a critical challenge for these agents. We present HUMANLLM, a framework treating psychological patterns as interacting causal forces. We construct 244 patterns from ~12,000 academic papers and synthesize 11,359 scenarios where 2-5 patterns reinforce, conflict, or modulate each other, with multi-turn conversations expressing inner thoughts, actions, and dialogue. Our dual-level checklists evaluate both individual pattern fidelity and emergent multi-pattern dynamics, achieving strong human alignment (r=0.91) while revealing that holistic metrics conflate simulation accuracy with social desirability. HUMANLLM-8B outperforms Qwen3-32B on multi-pattern dynamics despite 4x fewer parameters, demonstrating that authentic anthropomorphism requires cognitive modeling--simulating not just what humans do, but the psychological processes generating those behaviors.
CultureScope: A Dimensional Lens for Probing Cultural Understanding in LLMs
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in diverse cultural environments, evaluating their cultural understanding capability has become essential for ensuring trustworthy and culturally aligned applications. However, most existing benchmarks lack comprehensiveness and are challenging to scale and adapt across different cultural contexts, because their frameworks often lack guidance from well-established cultural theories and tend to rely on expert-driven manual annotations. To address these issues, we propose CultureScope, the most comprehensive evaluation framework to date for assessing cultural understanding in LLMs. Inspired by the cultural iceberg theory, we design a novel dimensional schema for cultural knowledge classification, comprising 3 layers and 140 dimensions, which guides the automated construction of culture-specific knowledge bases and corresponding evaluation datasets for any given languages and cultures. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can effectively evaluate cultural understanding. They also reveal that existing large language models lack comprehensive cultural competence, and merely incorporating multilingual data does not necessarily enhance cultural understanding. All code and data files are available at https://github.com/HoganZinger/Culture
AgentGroupChat-V2: Divide-and-Conquer Is What LLM-Based Multi-Agent System Need
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Large language model based multi-agent systems have demonstrated significant potential in social simulation and complex task resolution domains. However, current frameworks face critical challenges in system architecture design, cross-domain generalizability, and performance guarantees, particularly as task complexity and number of agents increases. We introduces AgentGroupChat-V2, a novel framework addressing these challenges through three core innovations: (1) a divide-and-conquer fully parallel architecture that decomposes user queries into hierarchical task forest structures enabling dependency management and distributed concurrent processing. (2) an adaptive collaboration engine that dynamically selects heterogeneous LLM combinations and interaction modes based on task characteristics. (3) agent organization optimization strategies combining divide-and-conquer approaches for efficient problem decomposition. Extensive experiments demonstrate AgentGroupChat-V2's superior performance across diverse domains, achieving 91.50% accuracy on GSM8K (exceeding the best baseline by 5.6 percentage points), 30.4% accuracy on competition-level AIME (nearly doubling other methods), and 79.20% pass@1 on HumanEval. Performance advantages become increasingly pronounced with higher task difficulty, particularly on Level 5 MATH problems where improvements exceed 11 percentage points compared to state-of-the-art baselines. These results confirm that AgentGroupChat-V2 provides a comprehensive solution for building efficient, general-purpose LLM multi-agent systems with significant advantages in complex reasoning scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/MikeGu721/AgentGroupChat-V2.
LITE: LLM-Impelled efficient Taxonomy Evaluation
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:This paper presents LITE, an LLM-based evaluation method designed for efficient and flexible assessment of taxonomy quality. To address challenges in large-scale taxonomy evaluation, such as efficiency, fairness, and consistency, LITE adopts a top-down hierarchical evaluation strategy, breaking down the taxonomy into manageable substructures and ensuring result reliability through cross-validation and standardized input formats. LITE also introduces a penalty mechanism to handle extreme cases and provides both quantitative performance analysis and qualitative insights by integrating evaluation metrics closely aligned with task objectives. Experimental results show that LITE demonstrates high reliability in complex evaluation tasks, effectively identifying semantic errors, logical contradictions, and structural flaws in taxonomies, while offering directions for improvement. Code is available at https://github.com/Zhang-l-i-n/TAXONOMY_DETECT .
ToReMi: Topic-Aware Data Reweighting for Dynamic Pre-Training Data Selection
Apr 01, 2025

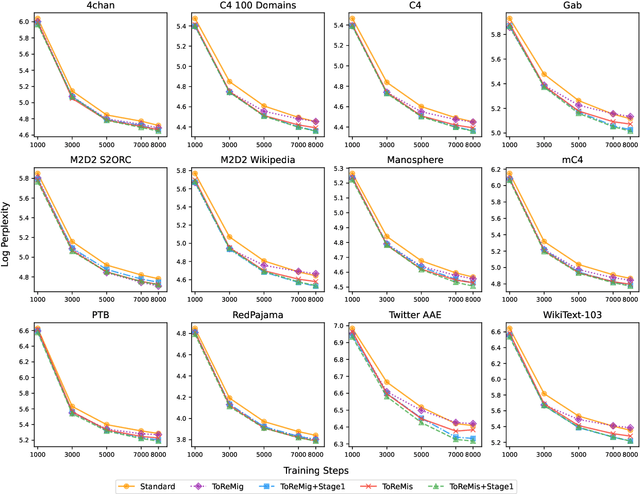

Abstract:Pre-training large language models (LLMs) necessitates enormous diverse textual corpora, making effective data selection a key challenge for balancing computational resources and model performance. Current methodologies primarily emphasize data quality metrics and mixing proportions, yet they fail to adequately capture the underlying semantic connections between training samples and quality disparities within individual domains. We introduce ToReMi (Topic-based Reweighting for Model improvement), a novel two-stage framework that dynamically adjusts training sample weights according to their topical associations and observed learning patterns. Our comprehensive experiments reveal that ToReMi variants consistently achieve superior performance over conventional pre-training approaches, demonstrating accelerated perplexity reduction across multiple domains and enhanced capabilities on downstream evaluation tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/zxx000728/ToReMi.
RECKON: Large-scale Reference-based Efficient Knowledge Evaluation for Large Language Model
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) advance, efficient knowledge evaluation becomes crucial to verifying their capabilities. Traditional methods, relying on benchmarks, face limitations such as high resource costs and information loss. We propose the Large-scale Reference-based Efficient Knowledge Evaluation for Large Language Model (RECKON), which directly uses reference data to evaluate models. RECKON organizes unstructured data into manageable units and generates targeted questions for each cluster, improving evaluation accuracy and efficiency. Experimental results show that RECKON reduces resource consumption by 56.5% compared to traditional methods while achieving over 97% accuracy across various domains, including world knowledge, code, legal, and biomedical datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/MikeGu721/reckon
GAPO: Learning Preferential Prompt through Generative Adversarial Policy Optimization
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have highlighted the critical need for precise control over model outputs through predefined constraints. While existing methods attempt to achieve this through either direct instruction-response synthesis or preferential response optimization, they often struggle with constraint understanding and adaptation. This limitation becomes particularly evident when handling fine-grained constraints, leading to either hallucination or brittle performance. We introduce Generative Adversarial Policy Optimization (GAPO), a novel framework that combines GAN-based training dynamics with an encoder-only reward model to progressively learn and adapt to increasingly complex constraints. GAPO leverages adversarial training to automatically generate training samples of varying difficulty while utilizing the encoder-only architecture to better capture prompt-response relationships. Extensive experiments demonstrate GAPO's superior performance across multiple benchmarks, particularly in scenarios requiring fine-grained constraint handling, where it significantly outperforms existing methods like PPO, DPO, and KTO. Our results suggest that GAPO's unique approach to preferential prompt learning offers a more robust and effective solution for controlling LLM outputs. Code is avaliable in https://github.com/MikeGu721/GAPO.
LLM-GAN: Construct Generative Adversarial Network Through Large Language Models For Explainable Fake News Detection
Sep 03, 2024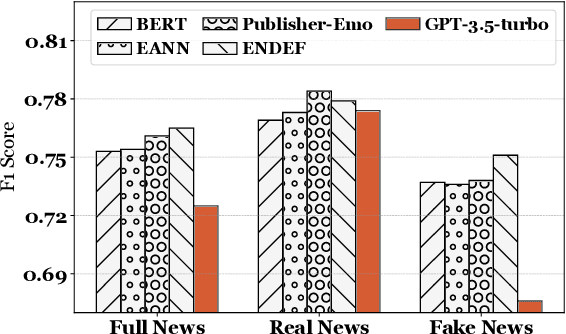
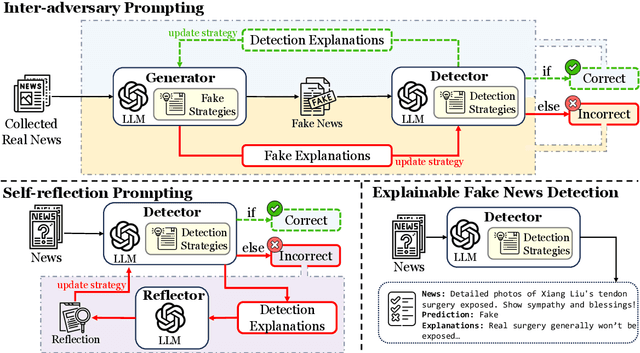
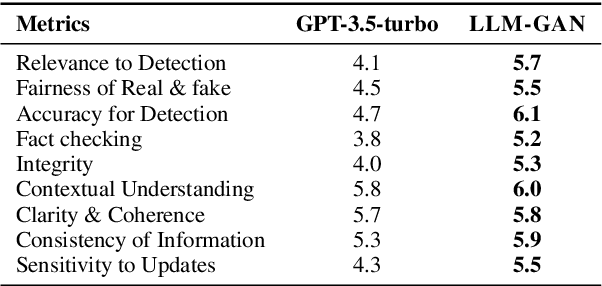
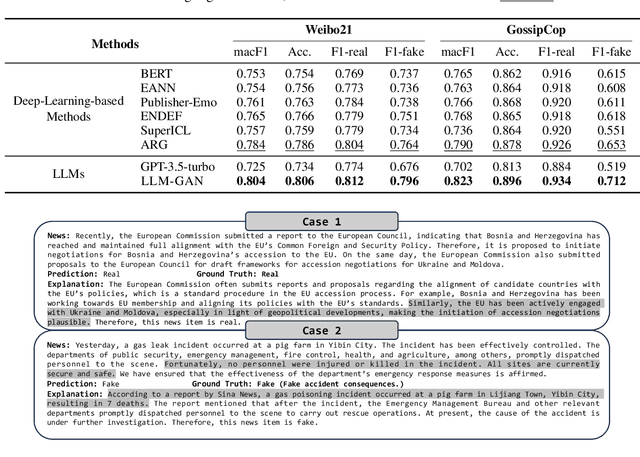
Abstract:Explainable fake news detection predicts the authenticity of news items with annotated explanations. Today, Large Language Models (LLMs) are known for their powerful natural language understanding and explanation generation abilities. However, presenting LLMs for explainable fake news detection remains two main challenges. Firstly, fake news appears reasonable and could easily mislead LLMs, leaving them unable to understand the complex news-faking process. Secondly, utilizing LLMs for this task would generate both correct and incorrect explanations, which necessitates abundant labor in the loop. In this paper, we propose LLM-GAN, a novel framework that utilizes prompting mechanisms to enable an LLM to become Generator and Detector and for realistic fake news generation and detection. Our results demonstrate LLM-GAN's effectiveness in both prediction performance and explanation quality. We further showcase the integration of LLM-GAN to a cloud-native AI platform to provide better fake news detection service in the cloud.
StrucText-Eval: An Autogenerated Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Model's Ability in Structure-Rich Text Understanding
Jun 30, 2024Abstract:Given the substantial volumes of structured data held by many companies, enabling Large Language Models (LLMs) to directly understand structured text in non-structured forms could significantly enhance their capabilities across various business scenarios. To this end, we propose evaluation data generation method for assessing LLM's ability in understanding the structure-rich text, which generates structured data of controllable complexity based on manually crafted question templates and generation rules. Building on this generation method, we introduce StrucText-Eval, a benchmark comprising 6,032 questions across 8 different structured languages and 29 specific tasks. Furthermore, considering human proficiency in rule-based tasks, we also present StrucText-Eval-Hard, which includes 3,016 questions designed to further examine the gap between LLMs and human performance. Results indicate that the best-performing LLM currently achieve an accuracy of 65.0\% on StrucText-Eval-Hard, while human accuracy reaches up to 95.7\%. Moreover, while fine-tuning using StrucText-Eval can enhance existing LLMs' understanding of all structured languages, it does not necessarily improve performance across all task types. The benchmark and generation codes are open sourced in https://github.com/MikeGu721/StrucText-Eval
DetectBench: Can Large Language Model Detect and Piece Together Implicit Evidence?
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Detecting evidence within the context is a key step in the process of reasoning task. Evaluating and enhancing the capabilities of LLMs in evidence detection will strengthen context-based reasoning performance. This paper proposes a benchmark called DetectBench for verifying the ability to detect and piece together implicit evidence within a long context. DetectBench contains 3,928 multiple-choice questions, with an average of 994 tokens per question. Each question contains an average of 4.55 pieces of implicit evidence, and solving the problem typically requires 7.62 logical jumps to find the correct answer. To enhance the performance of LLMs in evidence detection, this paper proposes Detective Reasoning Prompt and Finetune. Experiments demonstrate that the existing LLMs' abilities to detect evidence in long contexts are far inferior to humans. However, the Detective Reasoning Prompt effectively enhances the capability of powerful LLMs in evidence detection, while the Finetuning method shows significant effects in enhancing the performance of weaker LLMs. Moreover, when the abilities of LLMs in evidence detection are improved, their final reasoning performance is also enhanced accordingly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge