Tianyu Li
Charlie
AI-enabled Satellite Edge Computing: A Single-Pixel Feature based Shallow Classification Model for Hyperspectral Imaging
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:As the important component of the Earth observation system, hyperspectral imaging satellites provide high-fidelity and enriched information for the formulation of related policies due to the powerful spectral measurement capabilities. However, the transmission speed of the satellite downlink has become a major bottleneck in certain applications, such as disaster monitoring and emergency mapping, which demand a fast response ability. We propose an efficient AI-enabled Satellite Edge Computing paradigm for hyperspectral image classification, facilitating the satellites to attain autonomous decision-making. To accommodate the resource constraints of satellite platforms, the proposed method adopts a lightweight, non-deep learning framework integrated with a few-shot learning strategy. Moreover, onboard processing on satellites could be faced with sensor failure and scan pattern errors, which result in degraded image quality with bad/misaligned pixels and mixed noise. To address these challenges, we develop a novel two-stage pixel-wise label propagation scheme that utilizes only intrinsic spectral features at the single pixel level without the necessity to consider spatial structural information as requested by deep neural networks. In the first stage, initial pixel labels are obtained by propagating selected anchor labels through the constructed anchor-pixel affinity matrix. Subsequently, a top-k pruned sparse graph is generated by directly computing pixel-level similarities. In the second stage, a closed-form solution derived from the sparse graph is employed to replace iterative computations. Furthermore, we developed a rank constraint-based graph clustering algorithm to determine the anchor labels.
PlannerRFT: Reinforcing Diffusion Planners through Closed-Loop and Sample-Efficient Fine-Tuning
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Diffusion-based planners have emerged as a promising approach for human-like trajectory generation in autonomous driving. Recent works incorporate reinforcement fine-tuning to enhance the robustness of diffusion planners through reward-oriented optimization in a generation-evaluation loop. However, they struggle to generate multi-modal, scenario-adaptive trajectories, hindering the exploitation efficiency of informative rewards during fine-tuning. To resolve this, we propose PlannerRFT, a sample-efficient reinforcement fine-tuning framework for diffusion-based planners. PlannerRFT adopts a dual-branch optimization that simultaneously refines the trajectory distribution and adaptively guides the denoising process toward more promising exploration, without altering the original inference pipeline. To support parallel learning at scale, we develop nuMax, an optimized simulator that achieves 10 times faster rollout compared to native nuPlan. Extensive experiments shows that PlannerRFT yields state-of-the-art performance with distinct behaviors emerging during the learning process.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
LatentVLA: Efficient Vision-Language Models for Autonomous Driving via Latent Action Prediction
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving models trained on largescale datasets perform well in common scenarios but struggle with rare, long-tail situations due to limited scenario diversity. Recent Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models leverage broad knowledge from pre-trained visionlanguage models to address this limitation, yet face critical challenges: (1) numerical imprecision in trajectory prediction due to discrete tokenization, (2) heavy reliance on language annotations that introduce linguistic bias and annotation burden, and (3) computational inefficiency from multi-step chain-of-thought reasoning hinders real-time deployment. We propose LatentVLA, a novel framework that employs self-supervised latent action prediction to train VLA models without language annotations, eliminating linguistic bias while learning rich driving representations from unlabeled trajectory data. Through knowledge distillation, LatentVLA transfers the generalization capabilities of VLA models to efficient vision-based networks, achieving both robust performance and real-time efficiency. LatentVLA establishes a new state-of-the-art on the NAVSIM benchmark with a PDMS score of 92.4 and demonstrates strong zeroshot generalization on the nuScenes benchmark.
EgoReAct: Egocentric Video-Driven 3D Human Reaction Generation
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Humans exhibit adaptive, context-sensitive responses to egocentric visual input. However, faithfully modeling such reactions from egocentric video remains challenging due to the dual requirements of strictly causal generation and precise 3D spatial alignment. To tackle this problem, we first construct the Human Reaction Dataset (HRD) to address data scarcity and misalignment by building a spatially aligned egocentric video-reaction dataset, as existing datasets (e.g., ViMo) suffer from significant spatial inconsistency between the egocentric video and reaction motion, e.g., dynamically moving motions are always paired with fixed-camera videos. Leveraging HRD, we present EgoReAct, the first autoregressive framework that generates 3D-aligned human reaction motions from egocentric video streams in real-time. We first compress the reaction motion into a compact yet expressive latent space via a Vector Quantised-Variational AutoEncoder and then train a Generative Pre-trained Transformer for reaction generation from the visual input. EgoReAct incorporates 3D dynamic features, i.e., metric depth, and head dynamics during the generation, which effectively enhance spatial grounding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EgoReAct achieves remarkably higher realism, spatial consistency, and generation efficiency compared with prior methods, while maintaining strict causality during generation. We will release code, models, and data upon acceptance.
Vision Transformers are Circulant Attention Learners
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:The self-attention mechanism has been a key factor in the advancement of vision Transformers. However, its quadratic complexity imposes a heavy computational burden in high-resolution scenarios, restricting the practical application. Previous methods attempt to mitigate this issue by introducing handcrafted patterns such as locality or sparsity, which inevitably compromise model capacity. In this paper, we present a novel attention paradigm termed \textbf{Circulant Attention} by exploiting the inherent efficient pattern of self-attention. Specifically, we first identify that the self-attention matrix in vision Transformers often approximates the Block Circulant matrix with Circulant Blocks (BCCB), a kind of structured matrix whose multiplication with other matrices can be performed in $\mathcal{O}(N\log N)$ time. Leveraging this interesting pattern, we explicitly model the attention map as its nearest BCCB matrix and propose an efficient computation algorithm for fast calculation. The resulting approach closely mirrors vanilla self-attention, differing only in its use of BCCB matrices. Since our design is inspired by the inherent efficient paradigm, it not only delivers $\mathcal{O}(N\log N)$ computation complexity, but also largely maintains the capacity of standard self-attention. Extensive experiments on diverse visual tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, establishing circulant attention as a promising alternative to self-attention for vision Transformer architectures. Code is available at https://github.com/LeapLabTHU/Circulant-Attention.
Optimization-Guided Diffusion for Interactive Scene Generation
Dec 11, 2025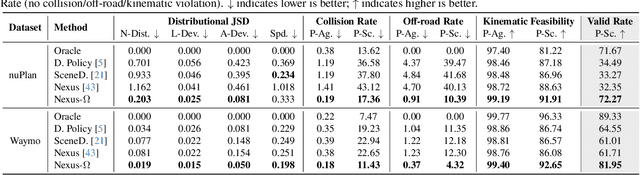
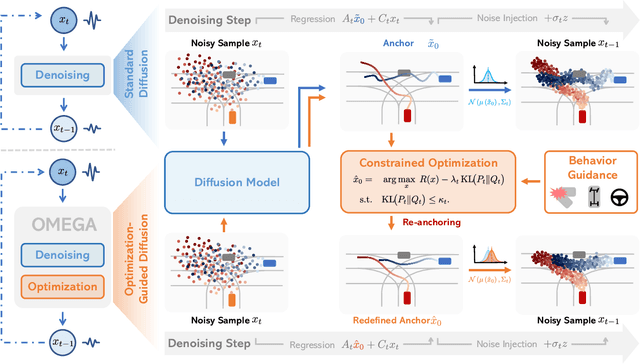
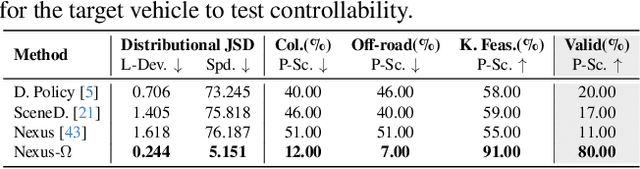
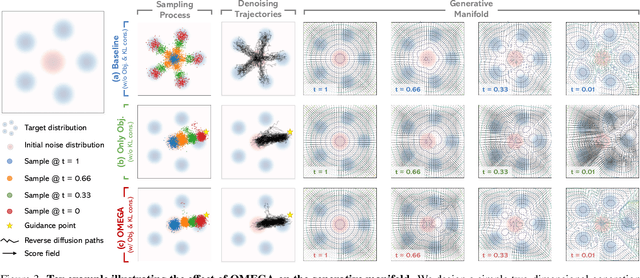
Abstract:Realistic and diverse multi-agent driving scenes are crucial for evaluating autonomous vehicles, but safety-critical events which are essential for this task are rare and underrepresented in driving datasets. Data-driven scene generation offers a low-cost alternative by synthesizing complex traffic behaviors from existing driving logs. However, existing models often lack controllability or yield samples that violate physical or social constraints, limiting their usability. We present OMEGA, an optimization-guided, training-free framework that enforces structural consistency and interaction awareness during diffusion-based sampling from a scene generation model. OMEGA re-anchors each reverse diffusion step via constrained optimization, steering the generation towards physically plausible and behaviorally coherent trajectories. Building on this framework, we formulate ego-attacker interactions as a game-theoretic optimization in the distribution space, approximating Nash equilibria to generate realistic, safety-critical adversarial scenarios. Experiments on nuPlan and Waymo show that OMEGA improves generation realism, consistency, and controllability, increasing the ratio of physically and behaviorally valid scenes from 32.35% to 72.27% for free exploration capabilities, and from 11% to 80% for controllability-focused generation. Our approach can also generate $5\times$ more near-collision frames with a time-to-collision under three seconds while maintaining the overall scene realism.
Geo-R1: Improving Few-Shot Geospatial Referring Expression Understanding with Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Sep 26, 2025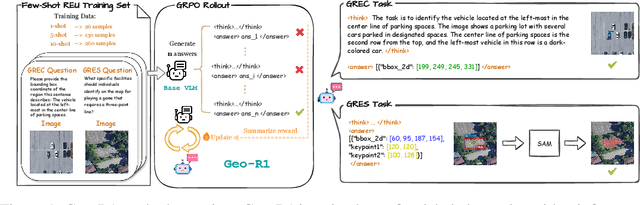


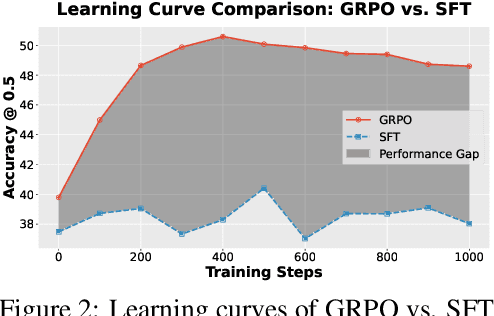
Abstract:Referring expression understanding in remote sensing poses unique challenges, as it requires reasoning over complex object-context relationships. While supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on multimodal large language models achieves strong performance with massive labeled datasets, they struggle in data-scarce scenarios, leading to poor generalization. To address this limitation, we propose Geo-R1, a reasoning-centric reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) paradigm for few-shot geospatial referring. Geo-R1 enforces the model to first generate explicit, interpretable reasoning chains that decompose referring expressions, and then leverage these rationales to localize target objects. This "reason first, then act" process enables the model to make more effective use of limited annotations, enhances generalization, and provides interpretability. We validate Geo-R1 on three carefully designed few-shot geospatial referring benchmarks, where our model consistently and substantially outperforms SFT baselines. It also demonstrates strong cross-dataset generalization, highlighting its robustness. Code and data will be released at http://geo-r1.github.io.
MoE-CE: Enhancing Generalization for Deep Learning based Channel Estimation via a Mixture-of-Experts Framework
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Reliable channel estimation (CE) is fundamental for robust communication in dynamic wireless environments, where models must generalize across varying conditions such as signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs), the number of resource blocks (RBs), and channel profiles. Traditional deep learning (DL)-based methods struggle to generalize effectively across such diverse settings, particularly under multitask and zero-shot scenarios. In this work, we propose MoE-CE, a flexible mixture-of-experts (MoE) framework designed to enhance the generalization capability of DL-based CE methods. MoE-CE provides an appropriate inductive bias by leveraging multiple expert subnetworks, each specialized in distinct channel characteristics, and a learned router that dynamically selects the most relevant experts per input. This architecture enhances model capacity and adaptability without a proportional rise in computational cost while being agnostic to the choice of the backbone model and the learning algorithm. Through extensive experiments on synthetic datasets generated under diverse SNRs, RB numbers, and channel profiles, including multitask and zero-shot evaluations, we demonstrate that MoE-CE consistently outperforms conventional DL approaches, achieving significant performance gains while maintaining efficiency.
FCPE: A Fast Context-based Pitch Estimation Model
Sep 18, 2025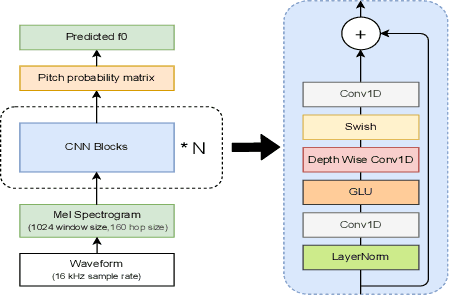
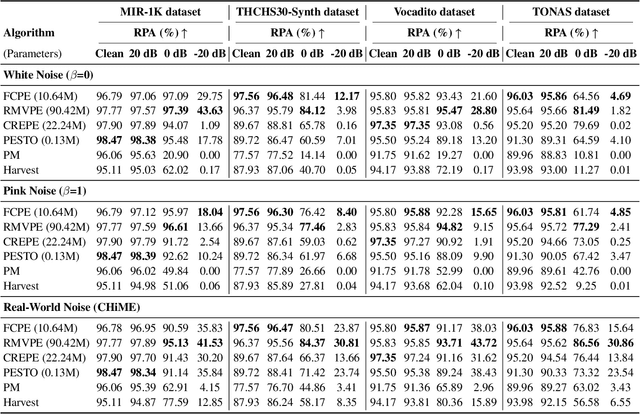
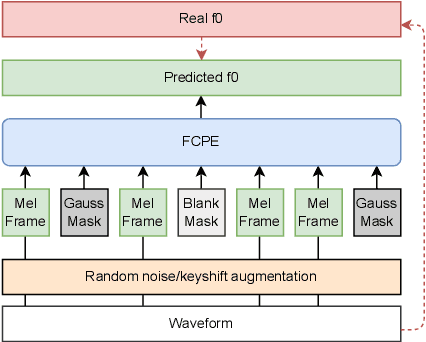

Abstract:Pitch estimation (PE) in monophonic audio is crucial for MIDI transcription and singing voice conversion (SVC), but existing methods suffer significant performance degradation under noise. In this paper, we propose FCPE, a fast context-based pitch estimation model that employs a Lynx-Net architecture with depth-wise separable convolutions to effectively capture mel spectrogram features while maintaining low computational cost and robust noise tolerance. Experiments show that our method achieves 96.79\% Raw Pitch Accuracy (RPA) on the MIR-1K dataset, on par with the state-of-the-art methods. The Real-Time Factor (RTF) is 0.0062 on a single RTX 4090 GPU, which significantly outperforms existing algorithms in efficiency. Code is available at https://github.com/CNChTu/FCPE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge