Yucheng Zhang
InterAct: Advancing Large-Scale Versatile 3D Human-Object Interaction Generation
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:While large-scale human motion capture datasets have advanced human motion generation, modeling and generating dynamic 3D human-object interactions (HOIs) remain challenging due to dataset limitations. Existing datasets often lack extensive, high-quality motion and annotation and exhibit artifacts such as contact penetration, floating, and incorrect hand motions. To address these issues, we introduce InterAct, a large-scale 3D HOI benchmark featuring dataset and methodological advancements. First, we consolidate and standardize 21.81 hours of HOI data from diverse sources, enriching it with detailed textual annotations. Second, we propose a unified optimization framework to enhance data quality by reducing artifacts and correcting hand motions. Leveraging the principle of contact invariance, we maintain human-object relationships while introducing motion variations, expanding the dataset to 30.70 hours. Third, we define six benchmarking tasks and develop a unified HOI generative modeling perspective, achieving state-of-the-art performance. Extensive experiments validate the utility of our dataset as a foundational resource for advancing 3D human-object interaction generation. To support continued research in this area, the dataset is publicly available at https://github.com/wzyabcas/InterAct, and will be actively maintained.
Semantic-decoupled Spatial Partition Guided Point-supervised Oriented Object Detection
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Recent remote sensing tech advancements drive imagery growth, making oriented object detection rapid development, yet hindered by labor-intensive annotation for high-density scenes. Oriented object detection with point supervision offers a cost-effective solution for densely packed scenes in remote sensing, yet existing methods suffer from inadequate sample assignment and instance confusion due to rigid rule-based designs. To address this, we propose SSP (Semantic-decoupled Spatial Partition), a unified framework that synergizes rule-driven prior injection and data-driven label purification. Specifically, SSP introduces two core innovations: 1) Pixel-level Spatial Partition-based Sample Assignment, which compactly estimates the upper and lower bounds of object scales and mines high-quality positive samples and hard negative samples through spatial partitioning of pixel maps. 2) Semantic Spatial Partition-based Box Extraction, which derives instances from spatial partitions modulated by semantic maps and reliably converts them into bounding boxes to form pseudo-labels for supervising the learning of downstream detectors. Experiments on DOTA-v1.0 and others demonstrate SSP\' s superiority: it achieves 45.78% mAP under point supervision, outperforming SOTA method PointOBB-v2 by 4.10%. Furthermore, when integrated with ORCNN and ReDet architectures, the SSP framework achieves mAP values of 47.86% and 48.50%, respectively. The code is available at https://github.com/antxinyuan/ssp.
HAIF-GS: Hierarchical and Induced Flow-Guided Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scene
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing dynamic 3D scenes from monocular videos remains a fundamental challenge in 3D vision. While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) achieves real-time rendering in static settings, extending it to dynamic scenes is challenging due to the difficulty of learning structured and temporally consistent motion representations. This challenge often manifests as three limitations in existing methods: redundant Gaussian updates, insufficient motion supervision, and weak modeling of complex non-rigid deformations. These issues collectively hinder coherent and efficient dynamic reconstruction. To address these limitations, we propose HAIF-GS, a unified framework that enables structured and consistent dynamic modeling through sparse anchor-driven deformation. It first identifies motion-relevant regions via an Anchor Filter to suppresses redundant updates in static areas. A self-supervised Induced Flow-Guided Deformation module induces anchor motion using multi-frame feature aggregation, eliminating the need for explicit flow labels. To further handle fine-grained deformations, a Hierarchical Anchor Propagation mechanism increases anchor resolution based on motion complexity and propagates multi-level transformations. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world benchmarks validate that HAIF-GS significantly outperforms prior dynamic 3DGS methods in rendering quality, temporal coherence, and reconstruction efficiency.
TopoPoint: Enhance Topology Reasoning via Endpoint Detection in Autonomous Driving
May 23, 2025Abstract:Topology reasoning, which unifies perception and structured reasoning, plays a vital role in understanding intersections for autonomous driving. However, its performance heavily relies on the accuracy of lane detection, particularly at connected lane endpoints. Existing methods often suffer from lane endpoints deviation, leading to incorrect topology construction. To address this issue, we propose TopoPoint, a novel framework that explicitly detects lane endpoints and jointly reasons over endpoints and lanes for robust topology reasoning. During training, we independently initialize point and lane query, and proposed Point-Lane Merge Self-Attention to enhance global context sharing through incorporating geometric distances between points and lanes as an attention mask . We further design Point-Lane Graph Convolutional Network to enable mutual feature aggregation between point and lane query. During inference, we introduce Point-Lane Geometry Matching algorithm that computes distances between detected points and lanes to refine lane endpoints, effectively mitigating endpoint deviation. Extensive experiments on the OpenLane-V2 benchmark demonstrate that TopoPoint achieves state-of-the-art performance in topology reasoning (48.8 on OLS). Additionally, we propose DET$_p$ to evaluate endpoint detection, under which our method significantly outperforms existing approaches (52.6 v.s. 45.2 on DET$_p$). The code is released at https://github.com/Franpin/TopoPoint.
KunPeng: A Global Ocean Environmental Model
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:Inspired by the similarity of the atmosphere-ocean physical coupling mechanism, this study innovatively migrates meteorological large-model techniques to the ocean domain, constructing the KunPeng global ocean environmental prediction model. Aimed at the discontinuous characteristics of marine space, we propose a terrain-adaptive mask constraint mechanism to mitigate effectively training divergence caused by abrupt gradients at land-sea boundaries. To fully integrate far-, medium-, and close-range marine features, a longitude-cyclic deformable convolution network (LC-DCN) is employed to enhance the dynamic receptive field, achieving refined modeling of multi-scale oceanic characteristics. A Deformable Convolution-enhanced Multi-Step Prediction module (DC-MTP) is employed to strengthen temporal dependency feature extraction capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that this model achieves an average ACC of 0.80 in 15-day global predictions at 0.25$^\circ$ resolution, outperforming comparative models by 0.01-0.08. The average mean squared error (MSE) is 0.41 (representing a 5%-31% reduction) and the average mean absolute error (MAE) is 0.44 (0.6%-21% reduction) compared to other models. Significant improvements are particularly observed in sea surface parameter prediction, deep-sea region characterization, and current velocity field forecasting. Through a horizontal comparison of the applicability of operators at different scales in the marine domain, this study reveals that local operators significantly outperform global operators under slow-varying oceanic processes, demonstrating the effectiveness of dynamic feature pyramid representations in predicting marine physical parameters.
TRIX: A More Expressive Model for Zero-shot Domain Transfer in Knowledge Graphs
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Fully inductive knowledge graph models can be trained on multiple domains and subsequently perform zero-shot knowledge graph completion (KGC) in new unseen domains. This is an important capability towards the goal of having foundation models for knowledge graphs. In this work, we introduce a more expressive and capable fully inductive model, dubbed TRIX, which not only yields strictly more expressive triplet embeddings (head entity, relation, tail entity) compared to state-of-the-art methods, but also introduces a new capability: directly handling both entity and relation prediction tasks in inductive settings. Empirically, we show that TRIX outperforms the state-of-the-art fully inductive models in zero-shot entity and relation predictions in new domains, and outperforms large-context LLMs in out-of-domain predictions. The source code is available at https://github.com/yuchengz99/TRIX.
Exact: Exploring Space-Time Perceptive Clues for Weakly Supervised Satellite Image Time Series Semantic Segmentation
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Automated crop mapping through Satellite Image Time Series (SITS) has emerged as a crucial avenue for agricultural monitoring and management. However, due to the low resolution and unclear parcel boundaries, annotating pixel-level masks is exceptionally complex and time-consuming in SITS. This paper embraces the weakly supervised paradigm (i.e., only image-level categories available) to liberate the crop mapping task from the exhaustive annotation burden. The unique characteristics of SITS give rise to several challenges in weakly supervised learning: (1) noise perturbation from spatially neighboring regions, and (2) erroneous semantic bias from anomalous temporal periods. To address the above difficulties, we propose a novel method, termed exploring space-time perceptive clues (Exact). First, we introduce a set of spatial clues to explicitly capture the representative patterns of different crops from the most class-relative regions. Besides, we leverage the temporal-to-class interaction of the model to emphasize the contributions of pivotal clips, thereby enhancing the model perception for crop regions. Build upon the space-time perceptive clues, we derive the clue-based CAMs to effectively supervise the SITS segmentation network. Our method demonstrates impressive performance on various SITS benchmarks. Remarkably, the segmentation network trained on Exact-generated masks achieves 95% of its fully supervised performance, showing the bright promise of weakly supervised paradigm in crop mapping scenario. Our code will be publicly available.
Using SlowFast Networks for Near-Miss Incident Analysis in Dashcam Videos
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:This paper classifies near-miss traffic videos using the SlowFast deep neural network that mimics the characteristics of the slow and fast visual information processed by two different streams from the M (Magnocellular) and P (Parvocellular) cells of the human brain. The approach significantly improves the accuracy of the traffic near-miss video analysis and presents insights into human visual perception in traffic scenarios. Moreover, it contributes to traffic safety enhancements and provides novel perspectives on the potential cognitive errors in traffic accidents.
* Best Research Paper Award for Asia-Pacific Region, The 30th ITS World Congress 2024
Electrically functionalized body surface for deep-tissue bioelectrical recording
Dec 04, 2024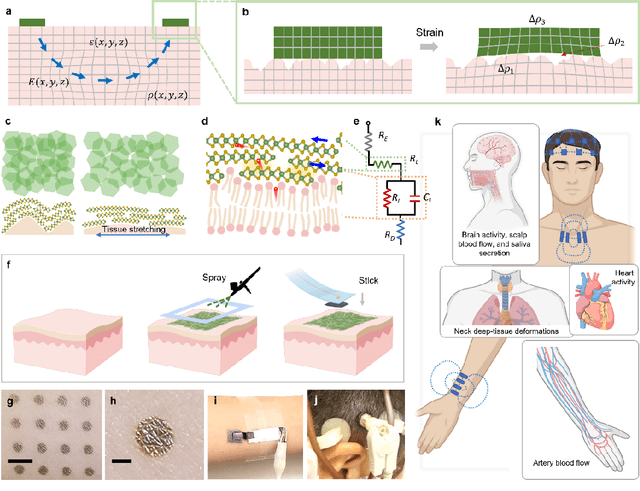
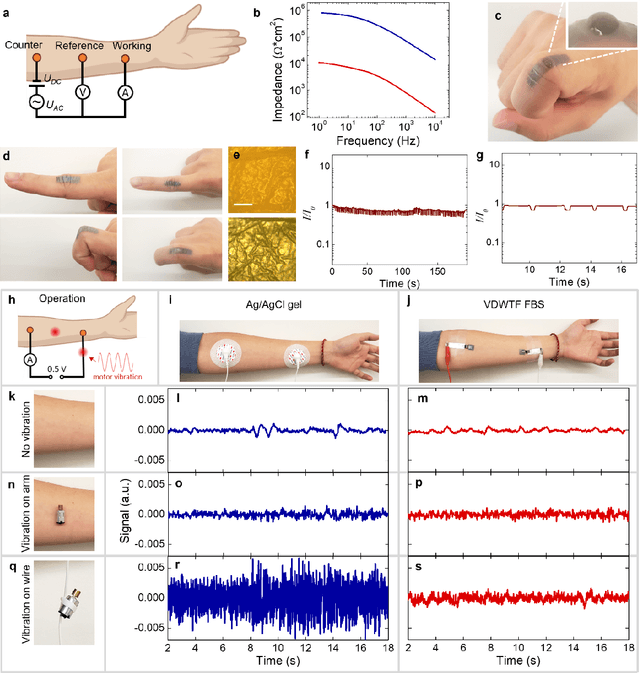
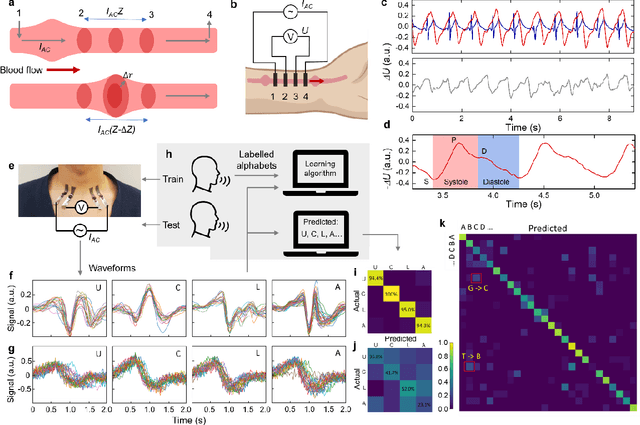
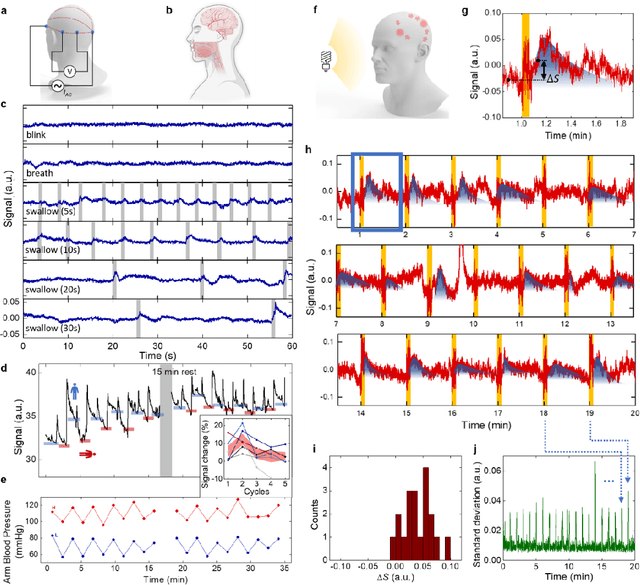
Abstract:Directly probing deep tissue activities from body surfaces offers a noninvasive approach to monitoring essential physiological processes1-3. However, this method is technically challenged by rapid signal attenuation toward the body surface and confounding motion artifacts4-6 primarily due to excessive contact impedance and mechanical mismatch with conventional electrodes. Herein, by formulating and directly spray coating biocompatible two-dimensional nanosheet ink onto the human body under ambient conditions, we create microscopically conformal and adaptive van der Waals thin films (VDWTFs) that seamlessly merge with non-Euclidean, hairy, and dynamically evolving body surfaces. Unlike traditional deposition methods, which often struggle with conformality and adaptability while retaining high electronic performance, this gentle process enables the formation of high-performance VDWTFs directly on the body surface under bio-friendly conditions, making it ideal for biological applications. This results in low-impedance electrically functionalized body surfaces (EFBS), enabling highly robust monitoring of biopotential and bioimpedance modulations associated with deep-tissue activities, such as blood circulation, muscle movements, and brain activities. Compared to commercial solutions, our VDWTF-EFBS exhibits nearly two-orders of magnitude lower contact impedance and substantially reduces the extrinsic motion artifacts, enabling reliable extraction of bioelectrical signals from irregular surfaces, such as unshaved human scalps. This advancement defines a technology for continuous, noninvasive monitoring of deep-tissue activities during routine body movements.
HijackRAG: Hijacking Attacks against Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems enhance large language models (LLMs) by integrating external knowledge, making them adaptable and cost-effective for various applications. However, the growing reliance on these systems also introduces potential security risks. In this work, we reveal a novel vulnerability, the retrieval prompt hijack attack (HijackRAG), which enables attackers to manipulate the retrieval mechanisms of RAG systems by injecting malicious texts into the knowledge database. When the RAG system encounters target questions, it generates the attacker's pre-determined answers instead of the correct ones, undermining the integrity and trustworthiness of the system. We formalize HijackRAG as an optimization problem and propose both black-box and white-box attack strategies tailored to different levels of the attacker's knowledge. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets show that HijackRAG consistently achieves high attack success rates, outperforming existing baseline attacks. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the attack is transferable across different retriever models, underscoring the widespread risk it poses to RAG systems. Lastly, our exploration of various defense mechanisms reveals that they are insufficient to counter HijackRAG, emphasizing the urgent need for more robust security measures to protect RAG systems in real-world deployments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge