Hao Zhu
Do Transformers Have the Ability for Periodicity Generalization?
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) based on the Transformer have demonstrated strong performance across diverse tasks. However, current models still exhibit substantial limitations in out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization compared with humans. We investigate this gap through periodicity, one of the basic OOD scenarios. Periodicity captures invariance amid variation. Periodicity generalization represents a model's ability to extract periodic patterns from training data and generalize to OOD scenarios. We introduce a unified interpretation of periodicity from the perspective of abstract algebra and reasoning, including both single and composite periodicity, to explain why Transformers struggle to generalize periodicity. Then we construct Coper about composite periodicity, a controllable generative benchmark with two OOD settings, Hollow and Extrapolation. Experiments reveal that periodicity generalization in Transformers is limited, where models can memorize periodic data during training, but cannot generalize to unseen composite periodicity. We release the source code to support future research.
CooperBench: Why Coding Agents Cannot be Your Teammates Yet
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Resolving team conflicts requires not only task-specific competence, but also social intelligence to find common ground and build consensus. As AI agents increasingly collaborate on complex work, they must develop coordination capabilities to function as effective teammates. Yet we hypothesize that current agents lack these capabilities. To test this, we introduce CooperBench, a benchmark of over 600 collaborative coding tasks across 12 libraries in 4 programming languages. Each task assigns two agents different features that can be implemented independently but may conflict without proper coordination. Tasks are grounded in real open-source repositories with expert-written tests. Evaluating state-of-the-art coding agents, we observe the curse of coordination: agents achieve on average 30% lower success rates when working together compared to performing both tasks individually. This contrasts sharply with human teams, where adding teammates typically improves productivity. Our analysis reveals three key issues: (1) communication channels become jammed with vague, ill-timed, and inaccurate messages; (2) even with effective communication, agents deviate from their commitments; and (3) agents often hold incorrect expectations about others' plans and communication. Through large-scale simulation, we also observe rare but interesting emergent coordination behavior including role division, resource division, and negotiation. Our research presents a novel benchmark for collaborative coding and calls for a shift from pursuing individual agent capability to developing social intelligence.
MagicGUI-RMS: A Multi-Agent Reward Model System for Self-Evolving GUI Agents via Automated Feedback Reflux
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Graphical user interface (GUI) agents are rapidly progressing toward autonomous interaction and reliable task execution across diverse applications. However, two central challenges remain unresolved: automating the evaluation of agent trajectories and generating high-quality training data at scale to enable continual improvement. Existing approaches often depend on manual annotation or static rule-based verification, which restricts scalability and limits adaptability in dynamic environments. We present MagicGUI-RMS, a multi-agent reward model system that delivers adaptive trajectory evaluation, corrective feedback, and self-evolving learning capabilities. MagicGUI-RMS integrates a Domain-Specific Reward Model (DS-RM) with a General-Purpose Reward Model (GP-RM), enabling fine-grained action assessment and robust generalization across heterogeneous GUI tasks. To support reward learning at scale, we design a structured data construction pipeline that automatically produces balanced and diverse reward datasets, effectively reducing annotation costs while maintaining sample fidelity. During execution, the reward model system identifies erroneous actions, proposes refined alternatives, and continuously enhances agent behavior through an automated data-reflux mechanism. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MagicGUI-RMS yields substantial gains in task accuracy, behavioral robustness. These results establish MagicGUI-RMS as a principled and effective foundation for building self-improving GUI agents driven by reward-based adaptation.
KOCO-BENCH: Can Large Language Models Leverage Domain Knowledge in Software Development?
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel at general programming but struggle with domain-specific software development, necessitating domain specialization methods for LLMs to learn and utilize domain knowledge and data. However, existing domain-specific code benchmarks cannot evaluate the effectiveness of domain specialization methods, which focus on assessing what knowledge LLMs possess rather than how they acquire and apply new knowledge, lacking explicit knowledge corpora for developing domain specialization methods. To this end, we present KOCO-BENCH, a novel benchmark designed for evaluating domain specialization methods in real-world software development. KOCO-BENCH contains 6 emerging domains with 11 software frameworks and 25 projects, featuring curated knowledge corpora alongside multi-granularity evaluation tasks including domain code generation (from function-level to project-level with rigorous test suites) and domain knowledge understanding (via multiple-choice Q&A). Unlike previous benchmarks that only provide test sets for direct evaluation, KOCO-BENCH requires acquiring and applying diverse domain knowledge (APIs, rules, constraints, etc.) from knowledge corpora to solve evaluation tasks. Our evaluations reveal that KOCO-BENCH poses significant challenges to state-of-the-art LLMs. Even with domain specialization methods (e.g., SFT, RAG, kNN-LM) applied, improvements remain marginal. Best-performing coding agent, Claude Code, achieves only 34.2%, highlighting the urgent need for more effective domain specialization methods. We release KOCO-BENCH, evaluation code, and baselines to advance further research at https://github.com/jiangxxxue/KOCO-bench.
UIKA: Fast Universal Head Avatar from Pose-Free Images
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:We present UIKA, a feed-forward animatable Gaussian head model from an arbitrary number of unposed inputs, including a single image, multi-view captures, and smartphone-captured videos. Unlike the traditional avatar method, which requires a studio-level multi-view capture system and reconstructs a human-specific model through a long-time optimization process, we rethink the task through the lenses of model representation, network design, and data preparation. First, we introduce a UV-guided avatar modeling strategy, in which each input image is associated with a pixel-wise facial correspondence estimation. Such correspondence estimation allows us to reproject each valid pixel color from screen space to UV space, which is independent of camera pose and character expression. Furthermore, we design learnable UV tokens on which the attention mechanism can be applied at both the screen and UV levels. The learned UV tokens can be decoded into canonical Gaussian attributes using aggregated UV information from all input views. To train our large avatar model, we additionally prepare a large-scale, identity-rich synthetic training dataset. Our method significantly outperforms existing approaches in both monocular and multi-view settings. Project page: https://zijian-wu.github.io/uika-page/
TEA: Temporal Adaptive Satellite Image Semantic Segmentation
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Crop mapping based on satellite images time-series (SITS) holds substantial economic value in agricultural production settings, in which parcel segmentation is an essential step. Existing approaches have achieved notable advancements in SITS segmentation with predetermined sequence lengths. However, we found that these approaches overlooked the generalization capability of models across scenarios with varying temporal length, leading to markedly poor segmentation results in such cases. To address this issue, we propose TEA, a TEmporal Adaptive SITS semantic segmentation method to enhance the model's resilience under varying sequence lengths. We introduce a teacher model that encapsulates the global sequence knowledge to guide a student model with adaptive temporal input lengths. Specifically, teacher shapes the student's feature space via intermediate embedding, prototypes and soft label perspectives to realize knowledge transfer, while dynamically aggregating student model to mitigate knowledge forgetting. Finally, we introduce full-sequence reconstruction as an auxiliary task to further enhance the quality of representations across inputs of varying temporal lengths. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our method brings remarkable improvements across inputs of different temporal lengths on common benchmarks. Our code will be publicly available.
AIMS: An Adaptive Integration of Multi-Sensor Measurements for Quadrupedal Robot Localization
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of accurate localization for quadrupedal robots operating in narrow tunnel-like environments. Due to the long and homogeneous characteristics of such scenarios, LiDAR measurements often provide weak geometric constraints, making traditional sensor fusion methods susceptible to accumulated motion estimation errors. To address these challenges, we propose AIMS, an adaptive LiDAR-IMU-leg odometry fusion method for robust quadrupedal robot localization in degenerate environments. The proposed method is formulated within an error-state Kalman filtering framework, where LiDAR and leg odometry measurements are integrated with IMU-based state prediction, and measurement noise covariance matrices are adaptively adjusted based on online degeneracy-aware reliability assessment. Experimental results obtained in narrow corridor environments demonstrate that the proposed method improves localization accuracy and robustness compared with state-of-the-art approaches.
DECEPTICON: How Dark Patterns Manipulate Web Agents
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Deceptive UI designs, widely instantiated across the web and commonly known as dark patterns, manipulate users into performing actions misaligned with their goals. In this paper, we show that dark patterns are highly effective in steering agent trajectories, posing a significant risk to agent robustness. To quantify this risk, we introduce DECEPTICON, an environment for testing individual dark patterns in isolation. DECEPTICON includes 700 web navigation tasks with dark patterns -- 600 generated tasks and 100 real-world tasks, designed to measure instruction-following success and dark pattern effectiveness. Across state-of-the-art agents, we find dark patterns successfully steer agent trajectories towards malicious outcomes in over 70% of tested generated and real-world tasks -- compared to a human average of 31%. Moreover, we find that dark pattern effectiveness correlates positively with model size and test-time reasoning, making larger, more capable models more susceptible. Leading countermeasures against adversarial attacks, including in-context prompting and guardrail models, fail to consistently reduce the success rate of dark pattern interventions. Our findings reveal dark patterns as a latent and unmitigated risk to web agents, highlighting the urgent need for robust defenses against manipulative designs.
Perplexity-Aware Data Scaling Law: Perplexity Landscapes Predict Performance for Continual Pre-training
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Continual Pre-training (CPT) serves as a fundamental approach for adapting foundation models to domain-specific applications. Scaling laws for pre-training define a power-law relationship between dataset size and the test loss of an LLM. However, the marginal gains from simply increasing data for CPT diminish rapidly, yielding suboptimal data utilization and inefficient training. To address this challenge, we propose a novel perplexity-aware data scaling law to establish a predictive relationship between the perplexity landscape of domain-specific data and the test loss. Our approach leverages the perplexity derived from the pre-trained model on domain data as a proxy for estimating the knowledge gap, effectively quantifying the informational perplexity landscape of candidate training samples. By fitting this scaling law across diverse perplexity regimes, we enable adaptive selection of high-utility data subsets, prioritizing content that maximizes knowledge absorption while minimizing redundancy and noise. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently identifies near-optimal training subsets and achieves superior performance on both medical and general-domain benchmarks.
Transductive Visual Programming: Evolving Tool Libraries from Experience for Spatial Reasoning
Dec 24, 2025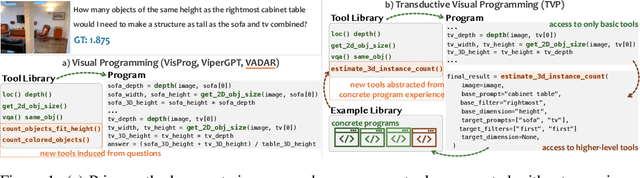
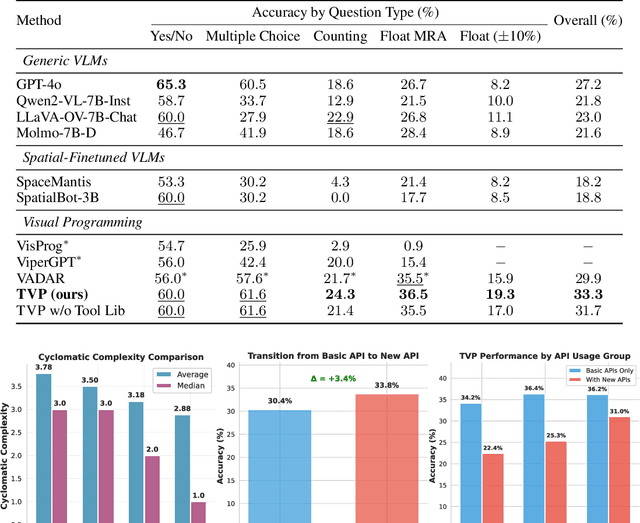
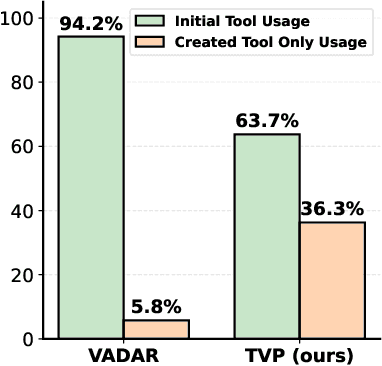
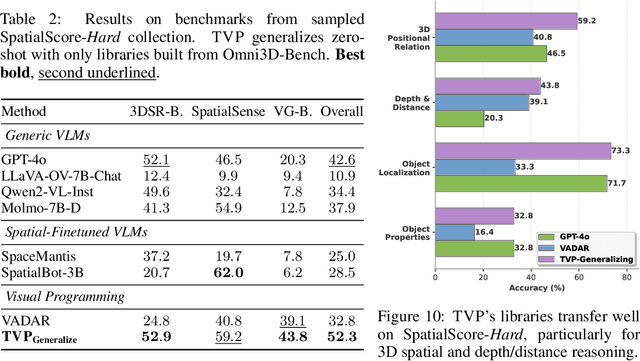
Abstract:Spatial reasoning in 3D scenes requires precise geometric calculations that challenge vision-language models. Visual programming addresses this by decomposing problems into steps calling specialized tools, yet existing methods rely on either fixed toolsets or speculative tool induction before solving problems, resulting in suboptimal programs and poor utilization of induced tools. We present Transductive Visual Programming (TVP), a novel framework that builds new tools from its own experience rather than speculation. TVP first solves problems using basic tools while accumulating experiential solutions into an Example Library, then abstracts recurring patterns from these programs into reusable higher-level tools for an evolving Tool Library. This allows TVP to tackle new problems with increasingly powerful tools learned from experience. On Omni3D-Bench, TVP achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming GPT-4o by 22% and the previous best visual programming system by 11%. Our transductively learned tools are used 5x more frequently as core program dependency than inductively created ones, demonstrating more effective tool discovery and reuse. The evolved tools also show strong generalization to unseen spatial tasks, achieving superior performance on benchmarks from SpatialScore-Hard collection without any testset-specific modification. Our work establishes experience-driven transductive tool creation as a powerful paradigm for building self-evolving visual programming agents that effectively tackle challenging spatial reasoning tasks. We release our code at https://transductive-visualprogram.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge