You Wang
GoLF-NRT: Integrating Global Context and Local Geometry for Few-Shot View Synthesis
May 26, 2025Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have transformed novel view synthesis by modeling scene-specific volumetric representations directly from images. While generalizable NeRF models can generate novel views across unknown scenes by learning latent ray representations, their performance heavily depends on a large number of multi-view observations. However, with limited input views, these methods experience significant degradation in rendering quality. To address this limitation, we propose GoLF-NRT: a Global and Local feature Fusion-based Neural Rendering Transformer. GoLF-NRT enhances generalizable neural rendering from few input views by leveraging a 3D transformer with efficient sparse attention to capture global scene context. In parallel, it integrates local geometric features extracted along the epipolar line, enabling high-quality scene reconstruction from as few as 1 to 3 input views. Furthermore, we introduce an adaptive sampling strategy based on attention weights and kernel regression, improving the accuracy of transformer-based neural rendering. Extensive experiments on public datasets show that GoLF-NRT achieves state-of-the-art performance across varying numbers of input views, highlighting the effectiveness and superiority of our approach. Code is available at https://github.com/KLMAV-CUC/GoLF-NRT.
Balancing Multi-Target Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation with Collaborative Generalist and Specialists
Apr 01, 2025Abstract:Despite the promising performance achieved by current semi-supervised models in segmenting individual medical targets, many of these models suffer a notable decrease in performance when tasked with the simultaneous segmentation of multiple targets. A vital factor could be attributed to the imbalanced scales among different targets: during simultaneously segmenting multiple targets, large targets dominate the loss, leading to small targets being misclassified as larger ones. To this end, we propose a novel method, which consists of a Collaborative Generalist and several Specialists, termed CGS. It is centered around the idea of employing a specialist for each target class, thus avoiding the dominance of larger targets. The generalist performs conventional multi-target segmentation, while each specialist is dedicated to distinguishing a specific target class from the remaining target classes and the background. Based on a theoretical insight, we demonstrate that CGS can achieve a more balanced training. Moreover, we develop cross-consistency losses to foster collaborative learning between the generalist and the specialists. Lastly, regarding their intrinsic relation that the target class of any specialized head should belong to the remaining classes of the other heads, we introduce an inter-head error detection module to further enhance the quality of pseudo-labels. Experimental results on three popular benchmarks showcase its superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
A Joint Prediction Method of Multi-Agent to Reduce Collision Rate
Nov 23, 2024



Abstract:Predicting future motions of road participants is an important task for driving autonomously. Most existing models excel at predicting the marginal trajectory of a single agent, but predicting joint trajectories for multiple agents that are consistent within a scene remains a challenge. Previous research has often focused on marginal predictions, but the importance of joint predictions has become increasingly apparent. Joint prediction aims to generate trajectories that are consistent across the entire scene. Our research builds upon the SIMPL baseline to explore methods for generating scene-consistent trajectories. We tested our algorithm on the Argoverse 2 dataset, and experimental results demonstrate that our approach can generate scene-consistent trajectories. Compared to the SIMPL baseline, our method significantly reduces the collision rate of joint trajectories within the scene.
A Simple Multi-agent Joint Prediction Method for Autonomous Driving
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:Predicting future motions of road participants is an important task for driving autonomously. Most existing models excel at predicting the marginal trajectory of a single agent, but predicting joint trajectories for multiple agents that are consistent within a scene remains a challenge. Previous research has often focused on marginal predictions, but the importance of joint predictions has become increasingly apparent. Joint prediction aims to generate trajectories that are consistent across the entire scene. Our research builds upon the SIMPL baseline to explore methods for generating scene-consistent trajectories. We tested our algorithm on the Argoverse 2 dataset, and experimental results demonstrate that our approach can generate scene-consistent trajectories. Compared to the SIMPL baseline, our method significantly reduces the collision rate of joint trajectories within the scene.
SOMTP: Self-Supervised Learning-Based Optimizer for MPC-Based Safe Trajectory Planning Problems in Robotics
May 15, 2024Abstract:Model Predictive Control (MPC)-based trajectory planning has been widely used in robotics, and incorporating Control Barrier Function (CBF) constraints into MPC can greatly improve its obstacle avoidance efficiency. Unfortunately, traditional optimizers are resource-consuming and slow to solve such non-convex constrained optimization problems (COPs) while learning-based methods struggle to satisfy the non-convex constraints. In this paper, we propose SOMTP algorithm, a self-supervised learning-based optimizer for CBF-MPC trajectory planning. Specifically, first, SOMTP employs problem transcription to satisfy most of the constraints. Then the differentiable SLPG correction is proposed to move the solution closer to the safe set and is then converted as the guide policy in the following training process. After that, inspired by the Augmented Lagrangian Method (ALM), our training algorithm integrated with guide policy constraints is proposed to enable the optimizer network to converge to a feasible solution. Finally, experiments show that the proposed algorithm has better feasibility than other learning-based methods and can provide solutions much faster than traditional optimizers with similar optimality.
Adaptive Model Prediction Control-Based Multi-Terrain Trajectory Tracking Framework for Mobile Spherical Robots
Mar 31, 2023



Abstract:Owing to uncertainties in both kinematics and dynamics, the current trajectory tracking framework for mobile robots like spherical robots cannot function effectively on multiple terrains, especially uneven and unknown ones. Since this is a prerequisite for robots to execute tasks in the wild, we enhance our previous hierarchical trajectory tracking framework to handle this issue. First, a modified adaptive RBF neural network (RBFNN) is proposed to represent all uncertainties in kinodynamics. Then the Lyapunov function is utilized to design its adaptive law, and a variable step-size algorithm is employed in the weights update procedure to accelerate convergence and improve stability. Hence, a new adaptive model prediction control-based instruction planner (VAN-MPC) is proposed. Without modifying the bottom controllers, we finally develop the multi-terrain trajectory tracking framework by employing the new instruction planner VAN-MPC. The practical experiments demonstrate its effectiveness and robustness.
An MPC-based Optimal Motion Control Framework for Pendulum-driven Spherical Robots
Feb 17, 2023



Abstract:Motion control is essential for all autonomous mobile robots, and even more so for spherical robots. Due to the uniqueness of the spherical robot, its motion control must not only ensure accurate tracking of the target commands, but also minimize fluctuations in the robot's attitude and motors' current while tracking. In this paper, model predictive control (MPC) is applied to the control of spherical robots and an MPC-based motion control framework is designed. There are two controllers in the framework, an optimal velocity controller ESO-MPC which combines extend states observers (ESO) and MPC, and an optimal orientation controller that uses multilayer perceptron (MLP) to generate accurate trajectories and MPC with changing weights to achieve optimal control. Finally, the performance of individual controllers and the whole control framework are verified by physical experiments. The experimental results show that the MPC-based motion control framework proposed in this work is much better than PID in terms of rapidity and accuracy, and has great advantages over sliding mode controller (SMC) for overshoot, attitude stability, current stability and energy consumption.
Discrete States-Based Trajectory Planning for Nonholonomic Robots
Feb 17, 2023



Abstract:Due to nonholonomic dynamics, the motion planning of nonholonomic robots is always a difficult problem. This letter presents a Discrete States-based Trajectory Planning(DSTP) algorithm for autonomous nonholonomic robots. The proposed algorithm represents the trajectory as x and y positions, orientation angle, longitude velocity and acceleration, angular velocity, and time intervals. More variables make the expression of optimization and constraints simpler, reduce the error caused by too many approximations, and also handle the gear shifting situation. L-BFGS-B is used to deal with the optimization of many variables and box constraints, thus speeding up the problem solving. Various simulation experiments compared with prior works have validated that our algorithm has an order-of-magnitude efficiency advantage and can generate a smoother trajectory with a high speed and low control effort. Besides, real-world experiments are also conducted to verify the feasibility of our algorithm in real scenes. We will release our codes as ros packages.
Direction and Trajectory Tracking Control for Nonholonomic Spherical Robot by Combining Sliding Mode Controller and Model Prediction Controller
May 27, 2022



Abstract:Spherical robot is a nonlinear, nonholonomic and unstable system which increases the difficulty of the direction and trajectory tracking problem. In this study, we propose a new direction controller HTSMC, an instruction planning controller MPC, and a trajectory tracking framework MHH. The HTSMC is designed by integrating a fast terminal algorithm, a hierarchical method, the motion features of a spherical robot, and its dynamics. In addition, the new direction controller has an excellent control effect with a quick response speed and strong stability. MPC can obtain optimal commands that are then transmitted to the velocity and direction controller. Since the two torque controllers in MHH are all Lyapunov-based sliding mode controllers, the MHH framework may achieve optimal control performance while assuring stability. Finally, the two controllers eliminate the requirement for MPC's stability and dynamic constraints. Finally, hardware experiments demonstrate the efficacy of the HTSMC, MPC, and MHH.
Unsupervised cross-user adaptation in taste sensationrecognition based on surface electromyography withconformal prediction and domain regularizedcomponent analysis
Oct 20, 2021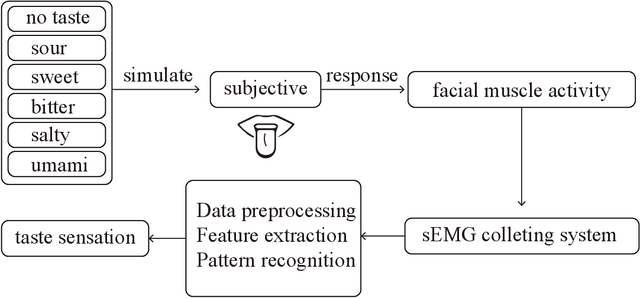
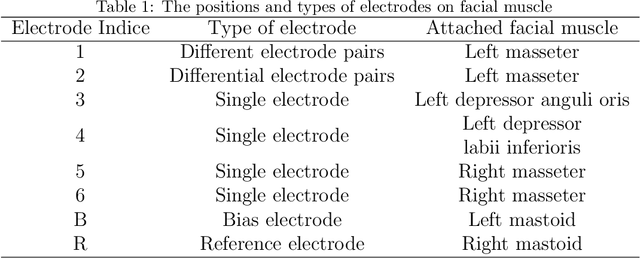
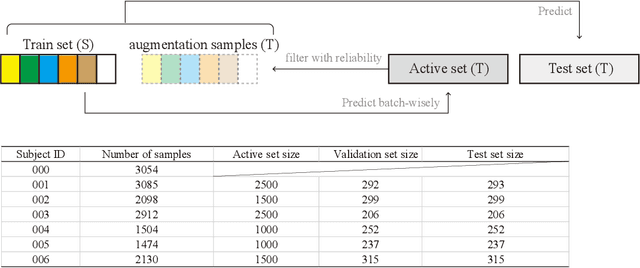
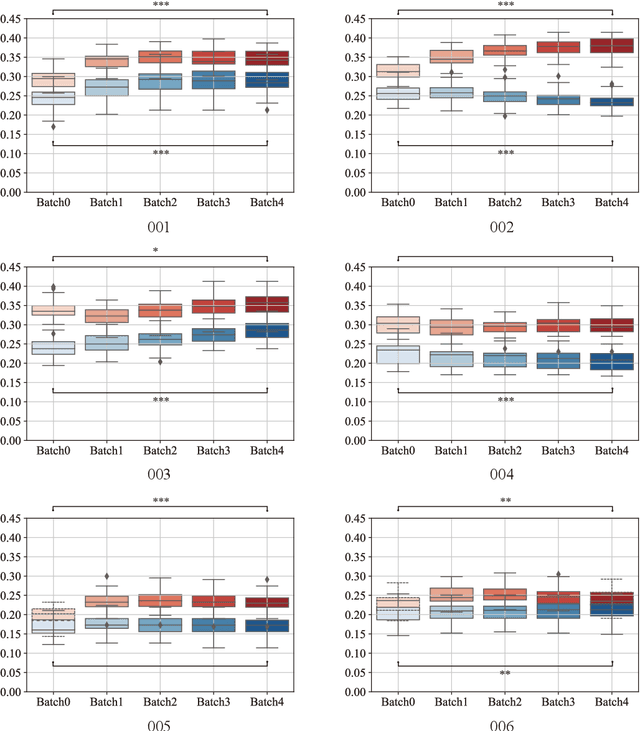
Abstract:Human taste sensation can be qualitatively described with surface electromyography. However, the pattern recognition models trained on one subject (the source domain) do not generalize well on other subjects (the target domain). To improve the generalizability and transferability of taste sensation models developed with sEMG data, two methods were innovatively applied in this study: domain regularized component analysis (DRCA) and conformal prediction with shrunken centroids (CPSC). The effectiveness of these two methods was investigated independently in an unlabeled data augmentation process with the unlabeled data from the target domain, and the same cross-user adaptation pipeline were conducted on six subjects. The results show that DRCA improved the classification accuracy on six subjects (p < 0.05), compared with the baseline models trained only with the source domain data;, while CPSC did not guarantee the accuracy improvement. Furthermore, the combination of DRCA and CPSC presented statistically significant improvement (p < 0.05) in classification accuracy on six subjects. The proposed strategy combining DRCA and CPSC showed its effectiveness in addressing the cross-user data distribution drift in sEMG-based taste sensation recognition application. It also shows the potential in more cross-user adaptation applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge