Xianghao Zhan
SAGE-FM: A lightweight and interpretable spatial transcriptomics foundation model
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics enables spatial gene expression profiling, motivating computational models that capture spatially conditioned regulatory relationships. We introduce SAGE-FM, a lightweight spatial transcriptomics foundation model based on graph convolutional networks (GCNs) trained with a masked central spot prediction objective. Trained on 416 human Visium samples spanning 15 organs, SAGE-FM learns spatially coherent embeddings that robustly recover masked genes, with 91% of masked genes showing significant correlations (p < 0.05). The embeddings generated by SAGE-FM outperform MOFA and existing spatial transcriptomics methods in unsupervised clustering and preservation of biological heterogeneity. SAGE-FM generalizes to downstream tasks, enabling 81% accuracy in pathologist-defined spot annotation in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and improving glioblastoma subtype prediction relative to MOFA. In silico perturbation experiments further demonstrate that the model captures directional ligand-receptor and upstream-downstream regulatory effects consistent with ground truth. These results demonstrate that simple, parameter-efficient GCNs can serve as biologically interpretable and spatially aware foundation models for large-scale spatial transcriptomics.
Sensor Drift Compensation in Electronic-Nose-Based Gas Recognition Using Knowledge Distillation
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Due to environmental changes and sensor aging, sensor drift challenges the performance of electronic nose systems in gas classification during real-world deployment. Previous studies using the UCI Gas Sensor Array Drift Dataset reported promising drift compensation results but lacked robust statistical experimental validation and may overcompensate for sensor drift, losing class-related variance.To address these limitations and improve sensor drift compensation with statistical rigor, we first designed two domain adaptation tasks based on the same electronic nose dataset: using the first batch to predict the remaining batches, simulating a controlled laboratory setting; and predicting the next batch using all prior batches, simulating continuous training data updates for online training. We then systematically tested three methods: our proposed novel Knowledge Distillation (KD) method, the benchmark method Domain Regularized Component Analysis (DRCA), and a hybrid method KD-DRCA, across 30 random test set partitions on the UCI dataset. We showed that KD consistently outperformed both DRCA and KD-DRCA, achieving up to an 18% improvement in accuracy and 15% in F1-score, demonstrating KD's superior effectiveness in drift compensation. This is the first application of KD for electronic nose drift mitigation, significantly outperforming the previous state-of-the-art DRCA method and enhancing the reliability of sensor drift compensation in real-world environments.
Benchmarking Chest X-ray Diagnosis Models Across Multinational Datasets
May 21, 2025Abstract:Foundation models leveraging vision-language pretraining have shown promise in chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation, yet their real-world performance across diverse populations and diagnostic tasks remains insufficiently evaluated. This study benchmarks the diagnostic performance and generalizability of foundation models versus traditional convolutional neural networks (CNNs) on multinational CXR datasets. We evaluated eight CXR diagnostic models - five vision-language foundation models and three CNN-based architectures - across 37 standardized classification tasks using six public datasets from the USA, Spain, India, and Vietnam, and three private datasets from hospitals in China. Performance was assessed using AUROC, AUPRC, and other metrics across both shared and dataset-specific tasks. Foundation models outperformed CNNs in both accuracy and task coverage. MAVL, a model incorporating knowledge-enhanced prompts and structured supervision, achieved the highest performance on public (mean AUROC: 0.82; AUPRC: 0.32) and private (mean AUROC: 0.95; AUPRC: 0.89) datasets, ranking first in 14 of 37 public and 3 of 4 private tasks. All models showed reduced performance on pediatric cases, with average AUROC dropping from 0.88 +/- 0.18 in adults to 0.57 +/- 0.29 in children (p = 0.0202). These findings highlight the value of structured supervision and prompt design in radiologic AI and suggest future directions including geographic expansion and ensemble modeling for clinical deployment. Code for all evaluated models is available at https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1B99yMQm7bB4h1sVMIBja0RfUu8gLktCE
Differences between Two Maximal Principal Strain Rate Calculation Schemes in Traumatic Brain Analysis with in-vivo and in-silico Datasets
Sep 12, 2024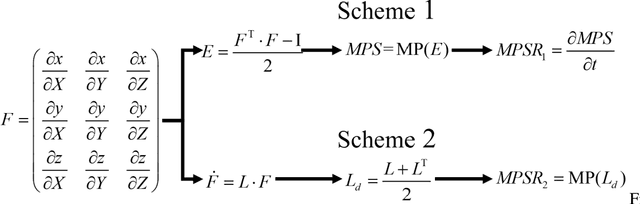
Abstract:Brain deformation caused by a head impact leads to traumatic brain injury (TBI). The maximum principal strain (MPS) was used to measure the extent of brain deformation and predict injury, and the recent evidence has indicated that incorporating the maximum principal strain rate (MPSR) and the product of MPS and MPSR, denoted as MPSxSR, enhances the accuracy of TBI prediction. However, ambiguities have arisen about the calculation of MPSR. Two schemes have been utilized: one (MPSR1) is to use the time derivative of MPS, and another (MPSR2) is to use the first eigenvalue of the strain rate tensor. Both MPSR1 and MPSR2 have been applied in previous studies to predict TBI. To quantify the discrepancies between these two methodologies, we conducted a comparison of these two MPSR methodologies across nine in-vivo and in-silico head impact datasets and found that 95MPSR1 was 5.87% larger than 95MPSR2, and 95MPSxSR1 was 2.55% larger than 95MPSxSR2. Across every element in all head impacts, MPSR1 was 8.28% smaller than MPSR2, and MPSxSR1 was 8.11% smaller than MPSxSR2. Furthermore, logistic regression models were trained to predict TBI based on the MPSR (or MPSxSR), and no significant difference was observed in the predictability across different variables. The consequence of misuse of MPSR and MPSxSR thresholds (i.e. compare threshold of 95MPSR1 with value from 95MPSR2 to determine if the impact is injurious) was investigated, and the resulting false rates were found to be around 1%. The evidence suggested that these two methodologies were not significantly different in detecting TBI.
Identification of head impact locations, speeds, and force based on head kinematics
Sep 12, 2024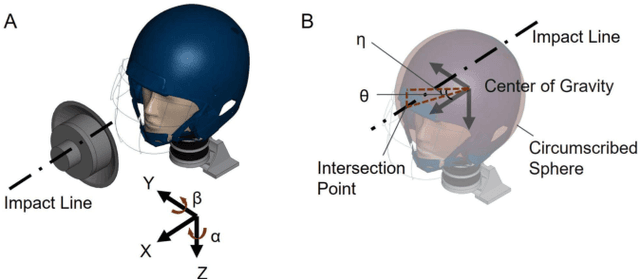
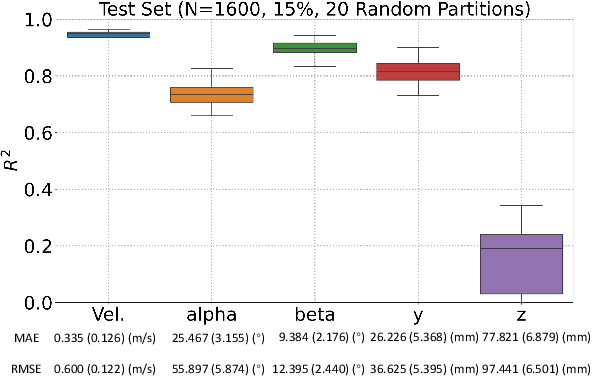
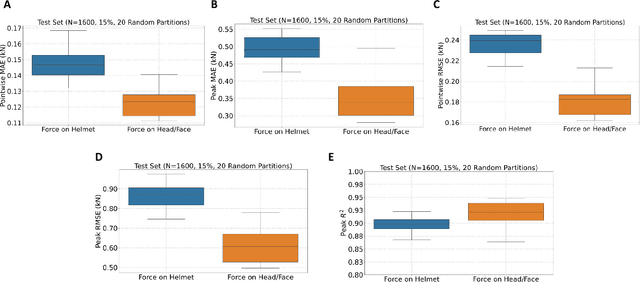
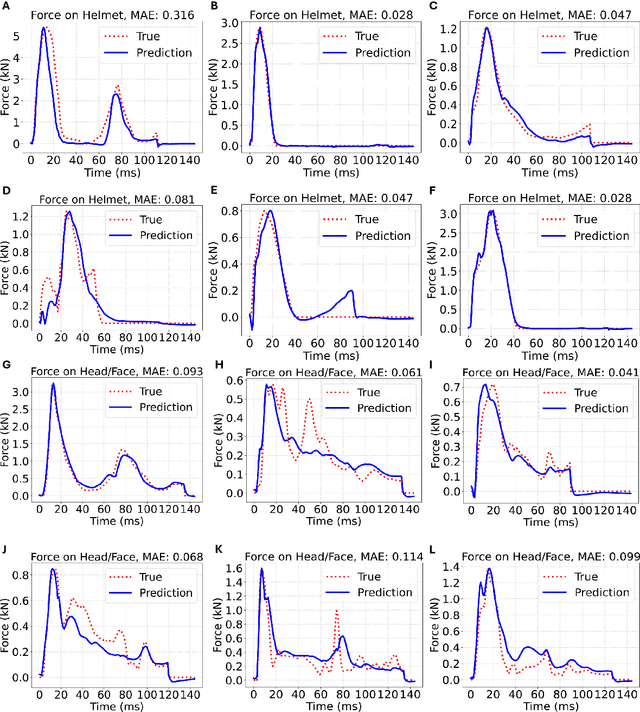
Abstract:Objective: Head impact information including impact directions, speeds and force are important to study traumatic brain injury, design and evaluate protective gears. This study presents a deep learning model developed to accurately predict head impact information, including location, speed, orientation, and force, based on head kinematics during helmeted impacts. Methods: Leveraging a dataset of 16,000 simulated helmeted head impacts using the Riddell helmet finite element model, we implemented a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network to process the head kinematics: tri-axial linear accelerations and angular velocities. Results: The models accurately predict the impact parameters describing impact location, direction, speed, and the impact force profile with R2 exceeding 70% for all tasks. Further validation was conducted using an on-field dataset recorded by instrumented mouthguards and videos, consisting of 79 head impacts in which the impact location can be clearly identified. The deep learning model significantly outperformed existing methods, achieving a 79.7% accuracy in identifying impact locations, compared to lower accuracies with traditional methods (the highest accuracy of existing methods is 49.4%). Conclusion: The precision underscores the model's potential in enhancing helmet design and safety in sports by providing more accurate impact data. Future studies should test the models across various helmets and sports on large in vivo datasets to validate the accuracy of the models, employing techniques like transfer learning to broaden its effectiveness.
Reliability-based cleaning of noisy training labels with inductive conformal prediction in multi-modal biomedical data mining
Sep 13, 2023Abstract:Accurately labeling biomedical data presents a challenge. Traditional semi-supervised learning methods often under-utilize available unlabeled data. To address this, we propose a novel reliability-based training data cleaning method employing inductive conformal prediction (ICP). This method capitalizes on a small set of accurately labeled training data and leverages ICP-calculated reliability metrics to rectify mislabeled data and outliers within vast quantities of noisy training data. The efficacy of the method is validated across three classification tasks within distinct modalities: filtering drug-induced-liver-injury (DILI) literature with title and abstract, predicting ICU admission of COVID-19 patients through CT radiomics and electronic health records, and subtyping breast cancer using RNA-sequencing data. Varying levels of noise to the training labels were introduced through label permutation. Results show significant enhancements in classification performance: accuracy enhancement in 86 out of 96 DILI experiments (up to 11.4%), AUROC and AUPRC enhancements in all 48 COVID-19 experiments (up to 23.8% and 69.8%), and accuracy and macro-average F1 score improvements in 47 out of 48 RNA-sequencing experiments (up to 74.6% and 89.0%). Our method offers the potential to substantially boost classification performance in multi-modal biomedical machine learning tasks. Importantly, it accomplishes this without necessitating an excessive volume of meticulously curated training data.
Toward more accurate and generalizable brain deformation estimators for traumatic brain injury detection with unsupervised domain adaptation
Jun 08, 2023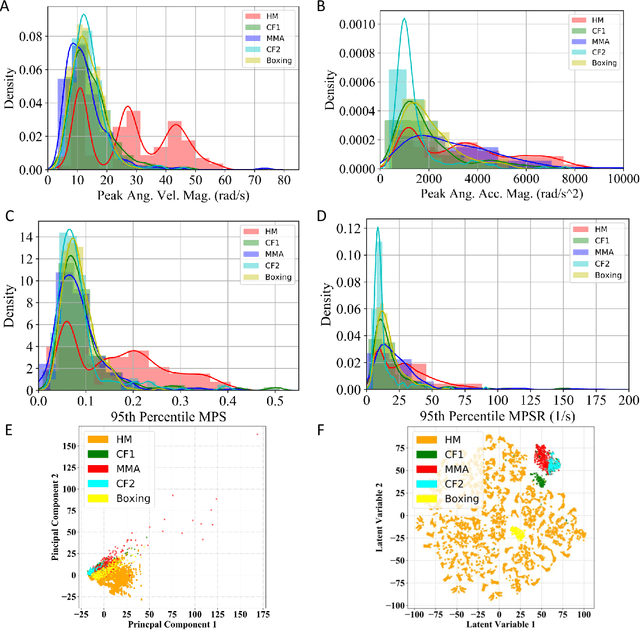
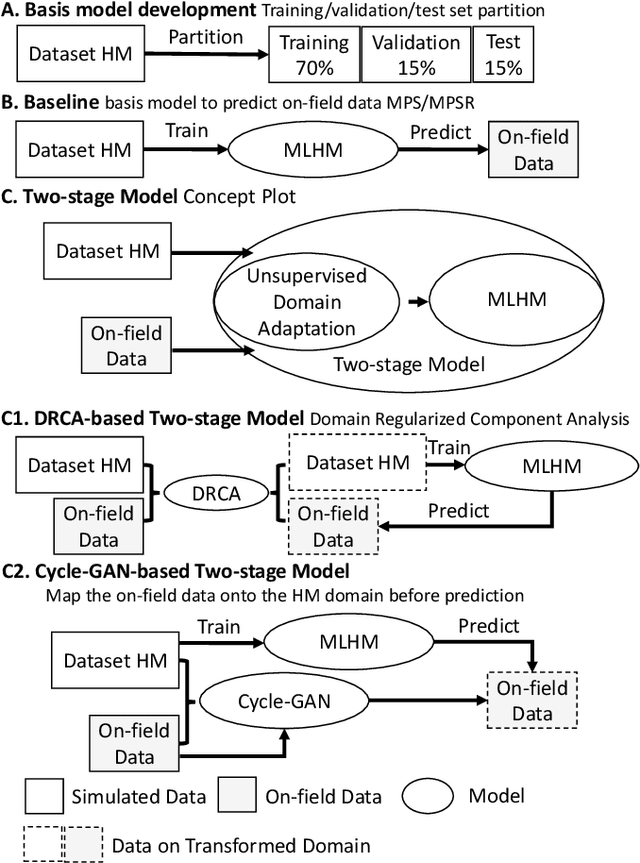
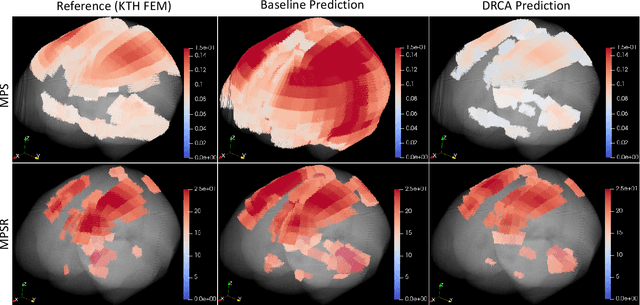
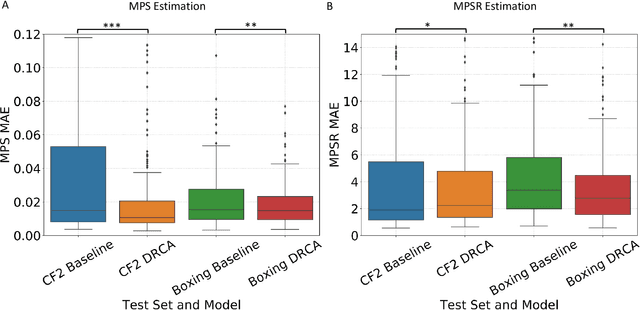
Abstract:Machine learning head models (MLHMs) are developed to estimate brain deformation for early detection of traumatic brain injury (TBI). However, the overfitting to simulated impacts and the lack of generalizability caused by distributional shift of different head impact datasets hinders the broad clinical applications of current MLHMs. We propose brain deformation estimators that integrates unsupervised domain adaptation with a deep neural network to predict whole-brain maximum principal strain (MPS) and MPS rate (MPSR). With 12,780 simulated head impacts, we performed unsupervised domain adaptation on on-field head impacts from 302 college football (CF) impacts and 457 mixed martial arts (MMA) impacts using domain regularized component analysis (DRCA) and cycle-GAN-based methods. The new model improved the MPS/MPSR estimation accuracy, with the DRCA method significantly outperforming other domain adaptation methods in prediction accuracy (p<0.001): MPS RMSE: 0.027 (CF) and 0.037 (MMA); MPSR RMSE: 7.159 (CF) and 13.022 (MMA). On another two hold-out test sets with 195 college football impacts and 260 boxing impacts, the DRCA model significantly outperformed the baseline model without domain adaptation in MPS and MPSR estimation accuracy (p<0.001). The DRCA domain adaptation reduces the MPS/MPSR estimation error to be well below TBI thresholds, enabling accurate brain deformation estimation to detect TBI in future clinical applications.
Denoising instrumented mouthguard measurements of head impact kinematics with a convolutional neural network
Dec 19, 2022
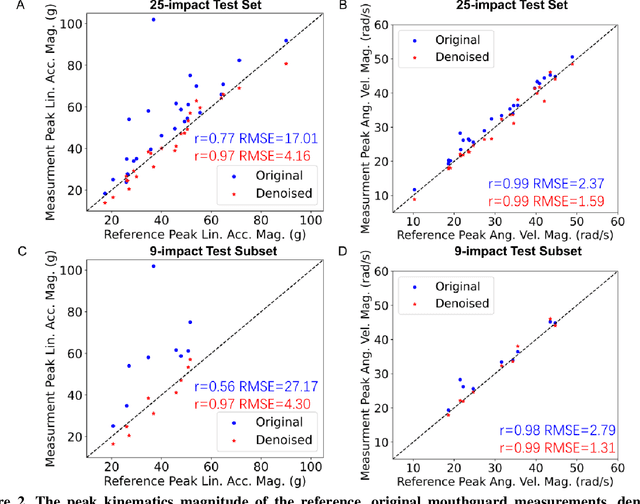
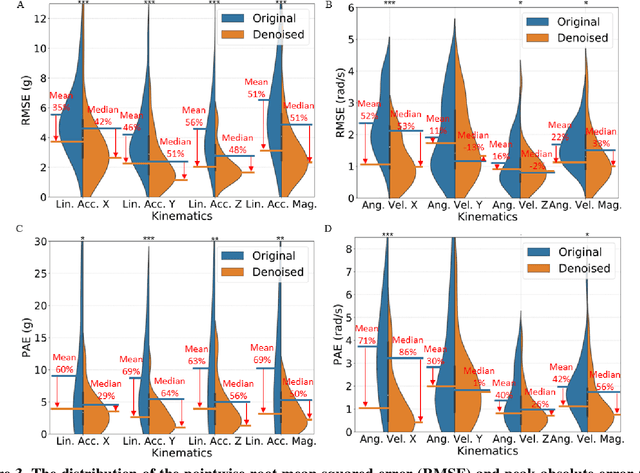
Abstract:Wearable sensors for measuring head kinematics can be noisy due to imperfect interfaces with the body. Mouthguards are used to measure head kinematics during impacts in traumatic brain injury (TBI) studies, but deviations from reference kinematics can still occur due to potential looseness. In this study, deep learning is used to compensate for the imperfect interface and improve measurement accuracy. A set of one-dimensional convolutional neural network (1D-CNN) models was developed to denoise mouthguard kinematics measurements along three spatial axes of linear acceleration and angular velocity. The denoised kinematics had significantly reduced errors compared to reference kinematics, and reduced errors in brain injury criteria and tissue strain and strain rate calculated via finite element modeling. The 1D-CNN models were also tested on an on-field dataset of college football impacts and a post-mortem human subject dataset, with similar denoising effects observed. The models can be used to improve detection of head impacts and TBI risk evaluation, and potentially extended to other sensors measuring kinematics.
Filter Drug-induced Liver Injury Literature with Natural Language Processing and Ensemble Learning
Mar 09, 2022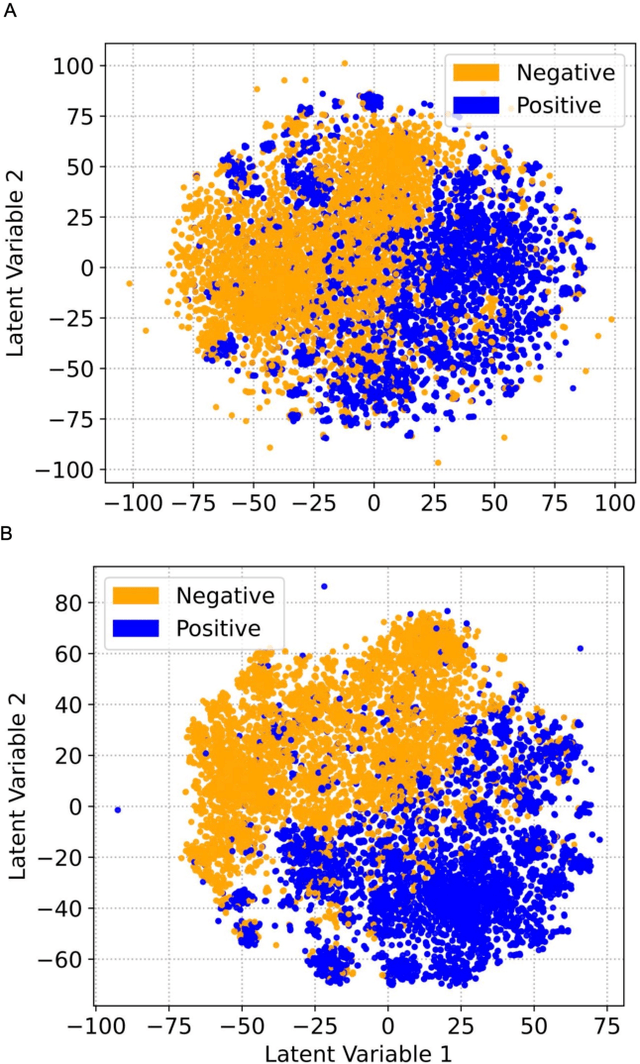
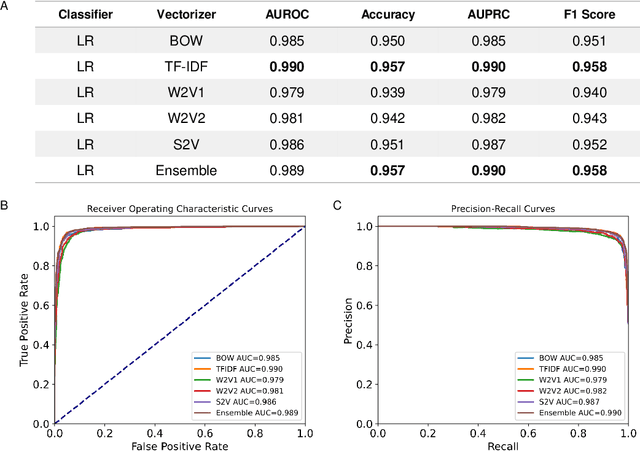
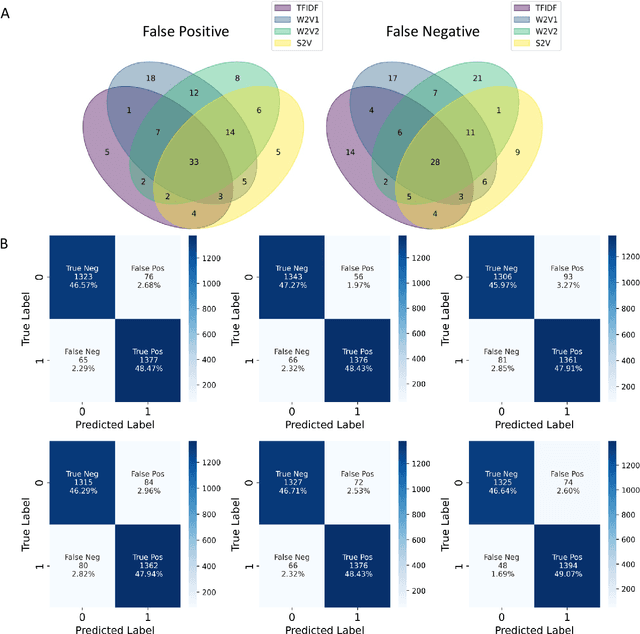
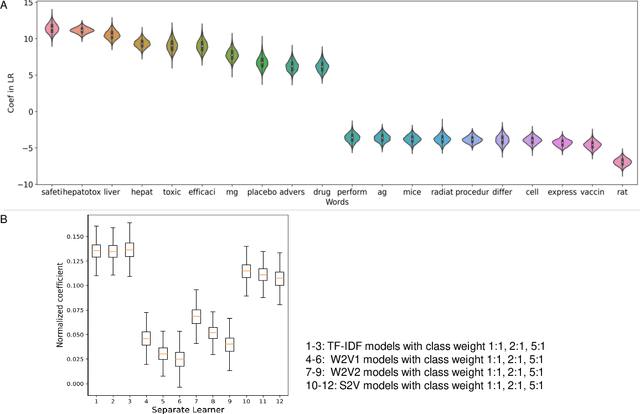
Abstract:Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) describes the adverse effects of drugs that damage liver. Life-threatening results including liver failure or death were also reported in severe DILI cases. Therefore, DILI-related events are strictly monitored for all approved drugs and the liver toxicity became important assessments for new drug candidates. These DILI-related reports are documented in hospital records, in clinical trial results, and also in research papers that contain preliminary in vitro and in vivo experiments. Conventionally, data extraction from previous publications relies heavily on resource-demanding manual labelling, which considerably decreased the efficiency of the information extraction process. The recent development of artificial intelligence, particularly, the rise of natural language processing (NLP) techniques, enabled the automatic processing of biomedical texts. In this study, based on around 28,000 papers (titles and abstracts) provided by the Critical Assessment of Massive Data Analysis (CAMDA) challenge, we benchmarked model performances on filtering out DILI literature. Among four word vectorization techniques, the model using term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) and logistic regression outperformed others with an accuracy of 0.957 with our in-house test set. Furthermore, an ensemble model with similar overall performances was implemented and was fine-tuned to lower the false-negative cases to avoid neglecting potential DILI reports. The ensemble model achieved a high accuracy of 0.954 and an F1 score of 0.955 in the hold-out validation data provided by the CAMDA committee. Moreover, important words in positive/negative predictions were identified via model interpretation. Overall, the ensemble model reached satisfactory classification results, which can be further used by researchers to rapidly filter DILI-related literature.
Data-driven decomposition of brain dynamics with principal component analysis in different types of head impacts
Oct 27, 2021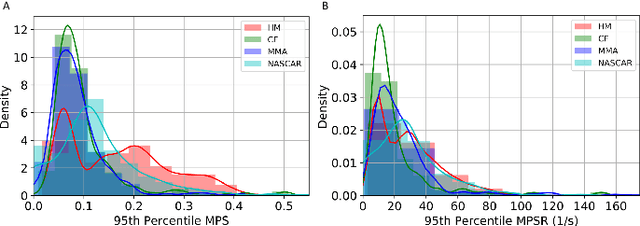
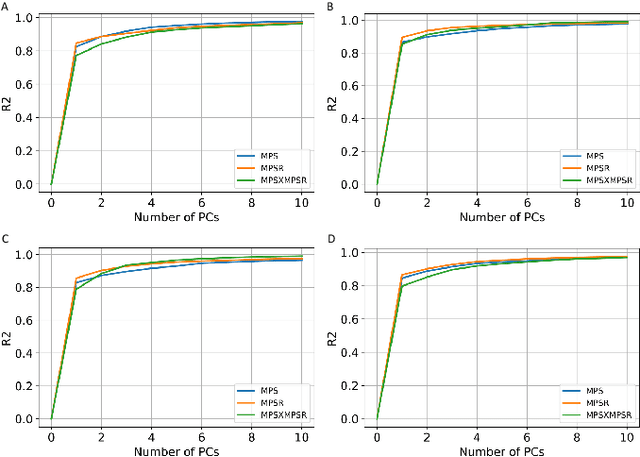
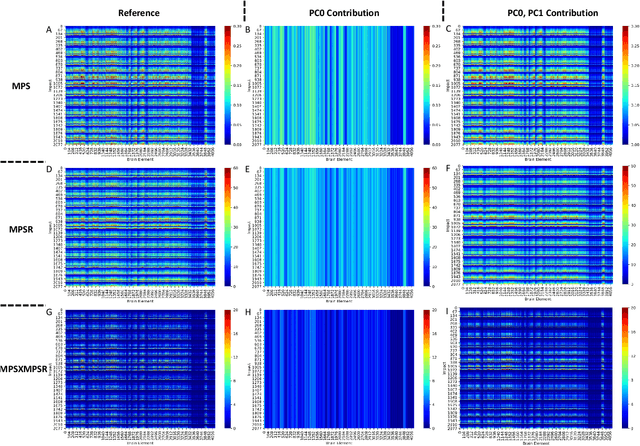
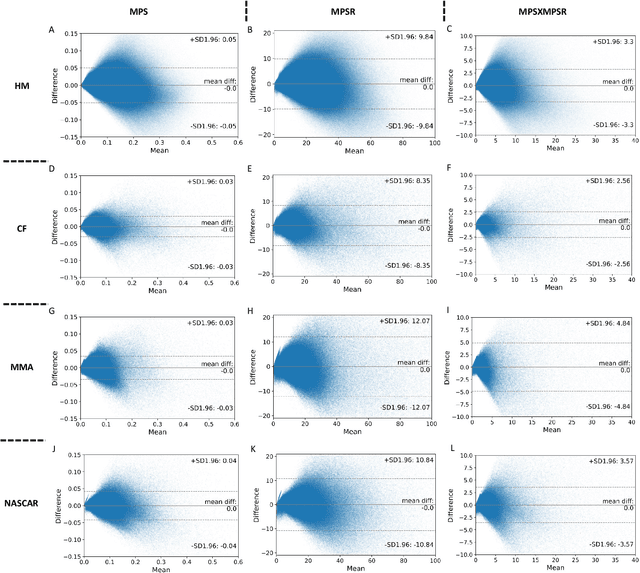
Abstract:Strain and strain rate are effective traumatic brain injury predictors. Kinematics-based models estimating these metrics suffer from significant different distributions of both kinematics and the injury metrics across head impact types. To address this, previous studies focus on the kinematics but not the injury metrics. We have previously shown the kinematic features vary largely across head impact types, resulting in different patterns of brain deformation. This study analyzes the spatial distribution of brain deformation and applies principal component analysis (PCA) to extract the representative patterns of injury metrics (maximum principal strain (MPS), MPS rate (MPSR) and MPSXMPSR) in four impact types (simulation, football, mixed martial arts and car crashes). We apply PCA to decompose the patterns of the injury metrics for all impacts in each impact type, and investigate the distributions among brain regions using the first principal component (PC1). Furthermore, we developed a deep learning head model (DLHM) to predict PC1 and then inverse-transform to predict for all brain elements. PC1 explained >80% variance on the datasets. Based on PC1 coefficients, the corpus callosum and midbrain exhibit high variance on all datasets. We found MPSXMPSR the most sensitive metric on which the top 5% of severe impacts further deviates from the mean and there is a higher variance among the severe impacts. Finally, the DLHM reached mean absolute errors of <0.018 for MPS, <3.7 (1/s) for MPSR and <1.1 (1/s) for MPSXMPSR, much smaller than the injury thresholds. The brain injury metric in a dataset can be decomposed into mean components and PC1 with high explained variance. The brain dynamics decomposition enables better interpretation of the patterns in brain injury metrics and the sensitivity of brain injury metrics across impact types. The decomposition also reduces the dimensionality of DLHM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge