Tao Hu
Human Video Generation from a Single Image with 3D Pose and View Control
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Recent diffusion methods have made significant progress in generating videos from single images due to their powerful visual generation capabilities. However, challenges persist in image-to-video synthesis, particularly in human video generation, where inferring view-consistent, motion-dependent clothing wrinkles from a single image remains a formidable problem. In this paper, we present Human Video Generation in 4D (HVG), a latent video diffusion model capable of generating high-quality, multi-view, spatiotemporally coherent human videos from a single image with 3D pose and view control. HVG achieves this through three key designs: (i) Articulated Pose Modulation, which captures the anatomical relationships of 3D joints via a novel dual-dimensional bone map and resolves self-occlusions across views by introducing 3D information; (ii) View and Temporal Alignment, which ensures multi-view consistency and alignment between a reference image and pose sequences for frame-to-frame stability; and (iii) Progressive Spatio-Temporal Sampling with temporal alignment to maintain smooth transitions in long multi-view animations. Extensive experiments on image-to-video tasks demonstrate that HVG outperforms existing methods in generating high-quality 4D human videos from diverse human images and pose inputs.
Traceable Latent Variable Discovery Based on Multi-Agent Collaboration
Feb 16, 2026Abstract:Revealing the underlying causal mechanisms in the real world is crucial for scientific and technological progress. Despite notable advances in recent decades, the lack of high-quality data and the reliance of traditional causal discovery algorithms (TCDA) on the assumption of no latent confounders, as well as their tendency to overlook the precise semantics of latent variables, have long been major obstacles to the broader application of causal discovery. To address this issue, we propose a novel causal modeling framework, TLVD, which integrates the metadata-based reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) with the data-driven modeling capabilities of TCDA for inferring latent variables and their semantics. Specifically, we first employ a data-driven approach to construct a causal graph that incorporates latent variables. Then, we employ multi-LLM collaboration for latent variable inference, modeling this process as a game with incomplete information and seeking its Bayesian Nash Equilibrium (BNE) to infer the possible specific latent variables. Finally, to validate the inferred latent variables across multiple real-world web-based data sources, we leverage LLMs for evidence exploration to ensure traceability. We comprehensively evaluate TLVD on three de-identified real patient datasets provided by a hospital and two benchmark datasets. Extensive experimental results confirm the effectiveness and reliability of TLVD, with average improvements of 32.67% in Acc, 62.21% in CAcc, and 26.72% in ECit across the five datasets.
Low-Light Video Enhancement with An Effective Spatial-Temporal Decomposition Paradigm
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Low-Light Video Enhancement (LLVE) seeks to restore dynamic or static scenes plagued by severe invisibility and noise. In this paper, we present an innovative video decomposition strategy that incorporates view-independent and view-dependent components to enhance the performance of LLVE. The framework is called View-aware Low-light Video Enhancement (VLLVE). We leverage dynamic cross-frame correspondences for the view-independent term (which primarily captures intrinsic appearance) and impose a scene-level continuity constraint on the view-dependent term (which mainly describes the shading condition) to achieve consistent and satisfactory decomposition results. To further ensure consistent decomposition, we introduce a dual-structure enhancement network featuring a cross-frame interaction mechanism. By supervising different frames simultaneously, this network encourages them to exhibit matching decomposition features. This mechanism can seamlessly integrate with encoder-decoder single-frame networks, incurring minimal additional parameter costs. Building upon VLLVE, we propose a more comprehensive decomposition strategy by introducing an additive residual term, resulting in VLLVE++. This residual term can simulate scene-adaptive degradations, which are difficult to model using a decomposition formulation for common scenes, thereby further enhancing the ability to capture the overall content of videos. In addition, VLLVE++ enables bidirectional learning for both enhancement and degradation-aware correspondence refinement (end-to-end manner), effectively increasing reliable correspondences while filtering out incorrect ones. Notably, VLLVE++ demonstrates strong capability in handling challenging cases, such as real-world scenes and videos with high dynamics. Extensive experiments are conducted on widely recognized LLVE benchmarks.
When Classes Evolve: A Benchmark and Framework for Stage-Aware Class-Incremental Learning
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) aims to sequentially learn new classes while mitigating catastrophic forgetting of previously learned knowledge. Conventional CIL approaches implicitly assume that classes are morphologically static, focusing primarily on preserving previously learned representations as new classes are introduced. However, this assumption neglects intra-class evolution: a phenomenon wherein instances of the same semantic class undergo significant morphological transformations, such as a larva turning into a butterfly. Consequently, a model must both discriminate between classes and adapt to evolving appearances within a single class. To systematically address this challenge, we formalize Stage-Aware CIL (Stage-CIL), a paradigm in which each class is learned progressively through distinct morphological stages. To facilitate rigorous evaluation within this paradigm, we introduce the Stage-Bench, a 10-domain, 2-stages dataset and protocol that jointly measure inter- and intra-class forgetting. We further propose STAGE, a novel method that explicitly learns abstract and transferable evolution patterns within a fixed-size memory pool. By decoupling semantic identity from transformation dynamics, STAGE enables accurate prediction of future morphologies based on earlier representations. Extensive empirical evaluation demonstrates that STAGE consistently and substantially outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, highlighting its effectiveness in simultaneously addressing inter-class discrimination and intra-class morphological adaptation.
SenseNova-MARS: Empowering Multimodal Agentic Reasoning and Search via Reinforcement Learning
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) can solve complex tasks through agentic reasoning, their capabilities remain largely constrained to text-oriented chain-of-thought or isolated tool invocation. They fail to exhibit the human-like proficiency required to seamlessly interleave dynamic tool manipulation with continuous reasoning, particularly in knowledge-intensive and visually complex scenarios that demand coordinated external tools such as search and image cropping. In this work, we introduce SenseNova-MARS, a novel Multimodal Agentic Reasoning and Search framework that empowers VLMs with interleaved visual reasoning and tool-use capabilities via reinforcement learning (RL). Specifically, SenseNova-MARS dynamically integrates the image search, text search, and image crop tools to tackle fine-grained and knowledge-intensive visual understanding challenges. In the RL stage, we propose the Batch-Normalized Group Sequence Policy Optimization (BN-GSPO) algorithm to improve the training stability and advance the model's ability to invoke tools and reason effectively. To comprehensively evaluate the agentic VLMs on complex visual tasks, we introduce the HR-MMSearch benchmark, the first search-oriented benchmark composed of high-resolution images with knowledge-intensive and search-driven questions. Experiments demonstrate that SenseNova-MARS achieves state-of-the-art performance on open-source search and fine-grained image understanding benchmarks. Specifically, on search-oriented benchmarks, SenseNova-MARS-8B scores 67.84 on MMSearch and 41.64 on HR-MMSearch, surpassing proprietary models such as Gemini-3-Flash and GPT-5. SenseNova-MARS represents a promising step toward agentic VLMs by providing effective and robust tool-use capabilities. To facilitate further research in this field, we will release all code, models, and datasets.
GMODiff: One-Step Gain Map Refinement with Diffusion Priors for HDR Reconstruction
Dec 18, 2025

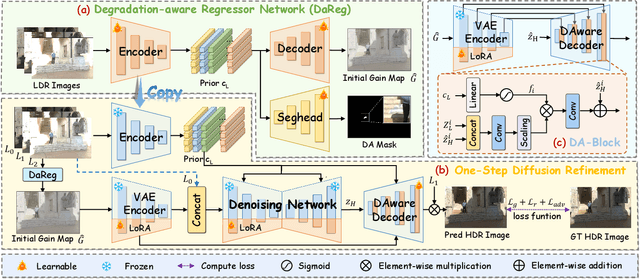

Abstract:Pre-trained Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) have recently shown strong perceptual priors for low-level vision tasks, making them a promising direction for multi-exposure High Dynamic Range (HDR) reconstruction. However, directly applying LDMs to HDR remains challenging due to: (1) limited dynamic-range representation caused by 8-bit latent compression, (2) high inference cost from multi-step denoising, and (3) content hallucination inherent to generative nature. To address these challenges, we introduce GMODiff, a gain map-driven one-step diffusion framework for multi-exposure HDR reconstruction. Instead of reconstructing full HDR content, we reformulate HDR reconstruction as a conditionally guided Gain Map (GM) estimation task, where the GM encodes the extended dynamic range while retaining the same bit depth as LDR images. We initialize the denoising process from an informative regression-based estimate rather than pure noise, enabling the model to generate high-quality GMs in a single denoising step. Furthermore, recognizing that regression-based models excel in content fidelity while LDMs favor perceptual quality, we leverage regression priors to guide both the denoising process and latent decoding of the LDM, suppressing hallucinations while preserving structural accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our GMODiff performs favorably against several state-of-the-art methods and is 100 faster than previous LDM-based methods.
Hierarchical Semantic Tree Anchoring for CLIP-Based Class-Incremental Learning
Nov 19, 2025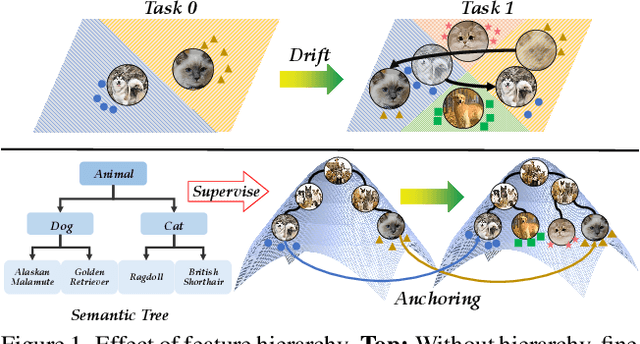
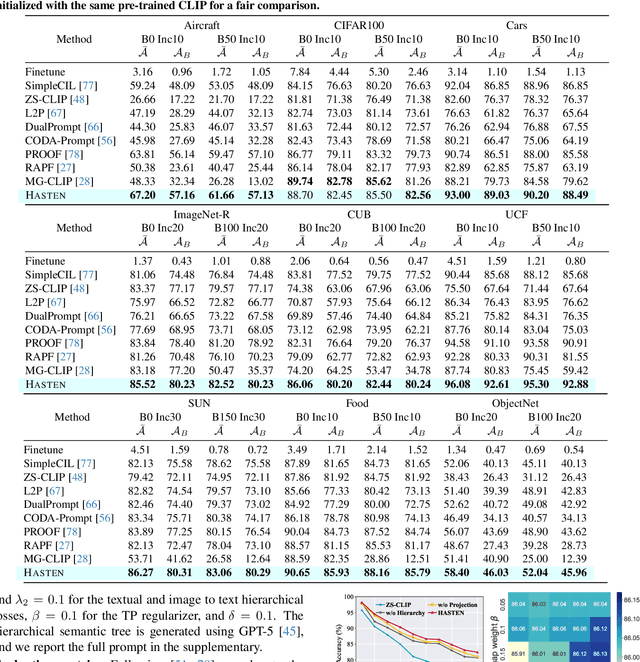
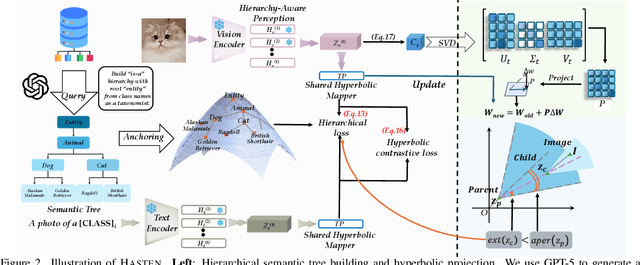
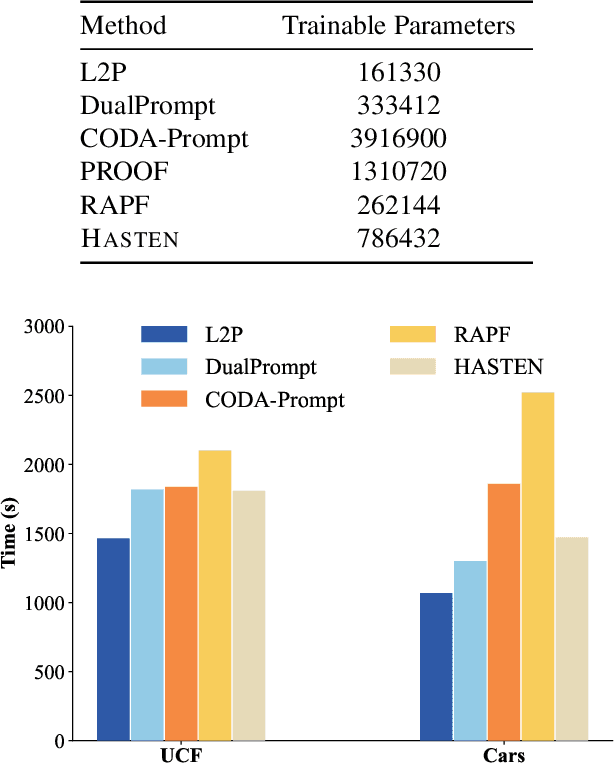
Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) enables models to learn new classes continually while preserving past knowledge. Recently, vision-language models like CLIP offer transferable features via multi-modal pre-training, making them well-suited for CIL. However, real-world visual and linguistic concepts are inherently hierarchical: a textual concept like "dog" subsumes fine-grained categories such as "Labrador" and "Golden Retriever," and each category entails its images. But existing CLIP-based CIL methods fail to explicitly capture this inherent hierarchy, leading to fine-grained class features drift during incremental updates and ultimately to catastrophic forgetting. To address this challenge, we propose HASTEN (Hierarchical Semantic Tree Anchoring) that anchors hierarchical information into CIL to reduce catastrophic forgetting. First, we employ an external knowledge graph as supervision to embed visual and textual features in hyperbolic space, effectively preserving hierarchical structure as data evolves. Second, to mitigate catastrophic forgetting, we project gradients onto the null space of the shared hyperbolic mapper, preventing interference with prior tasks. These two steps work synergistically to enable the model to resist forgetting by maintaining hierarchical relationships. Extensive experiments show that HASTEN consistently outperforms existing methods while providing a unified structured representation.
BOFA: Bridge-Layer Orthogonal Low-Rank Fusion for CLIP-Based Class-Incremental Learning
Nov 14, 2025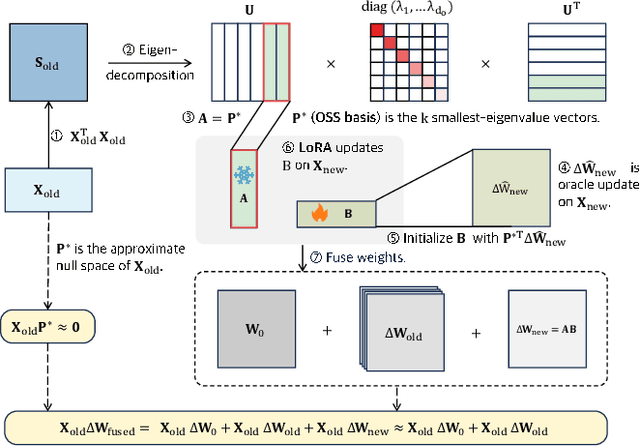
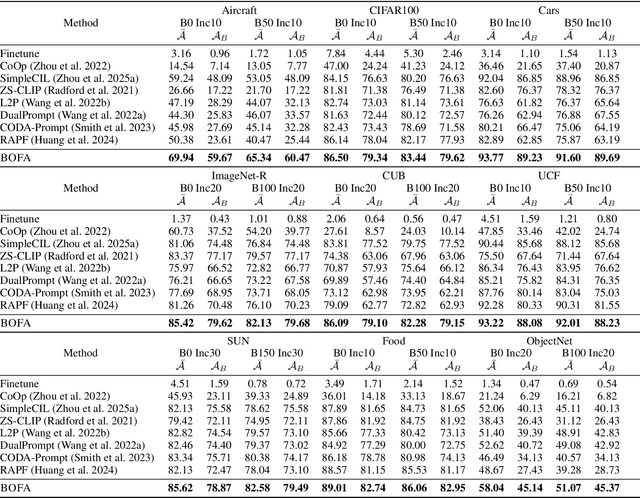
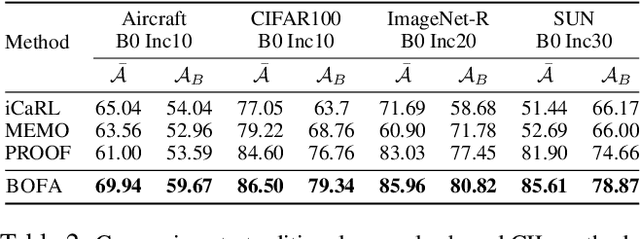
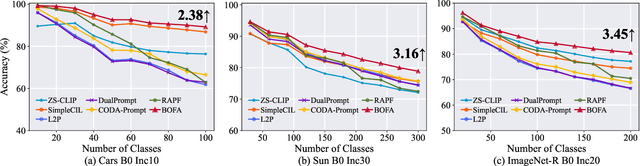
Abstract:Class-Incremental Learning (CIL) aims to continually learn new categories without forgetting previously acquired knowledge. Vision-language models such as CLIP offer strong transferable representations via multi-modal supervision, making them promising for CIL. However, applying CLIP to CIL poses two major challenges: (1) adapting to downstream tasks often requires additional learnable modules, increasing model complexity and susceptibility to forgetting; and (2) while multi-modal representations offer complementary strengths, existing methods have yet to fully realize their potential in effectively integrating visual and textual modalities. To address these issues, we propose BOFA (Bridge-layer Orthogonal Fusion for Adaptation), a novel framework for CIL. BOFA confines all model adaptation exclusively to CLIP's existing cross-modal bridge-layer, thereby adding no extra parameters or inference cost. To prevent forgetting within this layer, it leverages Orthogonal Low-Rank Fusion, a mechanism that constrains parameter updates to a low-rank ``safe subspace" mathematically constructed to be orthogonal to past task features. This ensures stable knowledge accumulation without data replay. Furthermore, BOFA employs a cross-modal hybrid prototype that synergizes stable textual prototypes with visual counterparts derived from our stably adapted bridge-layer, enhancing classification performance. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks show that BOFA achieves superior accuracy and efficiency compared to existing methods.
HVI-CIDNet+: Beyond Extreme Darkness for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Low-Light Image Enhancement (LLIE) aims to restore vivid content and details from corrupted low-light images. However, existing standard RGB (sRGB) color space-based LLIE methods often produce color bias and brightness artifacts due to the inherent high color sensitivity. While Hue, Saturation, and Value (HSV) color space can decouple brightness and color, it introduces significant red and black noise artifacts. To address this problem, we propose a new color space for LLIE, namely Horizontal/Vertical-Intensity (HVI), defined by the HV color map and learnable intensity. The HV color map enforces small distances for the red coordinates to remove red noise artifacts, while the learnable intensity compresses the low-light regions to remove black noise artifacts. Additionally, we introduce the Color and Intensity Decoupling Network+ (HVI-CIDNet+), built upon the HVI color space, to restore damaged content and mitigate color distortion in extremely dark regions. Specifically, HVI-CIDNet+ leverages abundant contextual and degraded knowledge extracted from low-light images using pre-trained vision-language models, integrated via a novel Prior-guided Attention Block (PAB). Within the PAB, latent semantic priors can promote content restoration, while degraded representations guide precise color correction, both particularly in extremely dark regions through the meticulously designed cross-attention fusion mechanism. Furthermore, we construct a Region Refinement Block that employs convolution for information-rich regions and self-attention for information-scarce regions, ensuring accurate brightness adjustments. Comprehensive results from benchmark experiments demonstrate that the proposed HVI-CIDNet+ outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on 10 datasets.
Conversational Intent-Driven GraphRAG: Enhancing Multi-Turn Dialogue Systems through Adaptive Dual-Retrieval of Flow Patterns and Context Semantics
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:We present CID-GraphRAG (Conversational Intent-Driven Graph Retrieval Augmented Generation), a novel framework that addresses the limitations of existing dialogue systems in maintaining both contextual coherence and goal-oriented progression in multi-turn customer service conversations. Unlike traditional RAG systems that rely solely on semantic similarity (Conversation RAG) or standard knowledge graphs (GraphRAG), CID-GraphRAG constructs dynamic intent transition graphs from goal achieved historical dialogues and implements a dual-retrieval mechanism that adaptively balances intent-based graph traversal with semantic search. This approach enables the system to simultaneously leverage both conversional intent flow patterns and contextual semantics, significantly improving retrieval quality and response quality. In extensive experiments on real-world customer service dialogues, we employ both automatic metrics and LLM-as-judge assessments, demonstrating that CID-GraphRAG significantly outperforms both semantic-based Conversation RAG and intent-based GraphRAG baselines across all evaluation criteria. Quantitatively, CID-GraphRAG demonstrates substantial improvements over Conversation RAG across automatic metrics, with relative gains of 11% in BLEU, 5% in ROUGE-L, 6% in METEOR, and most notably, a 58% improvement in response quality according to LLM-as-judge evaluations. These results demonstrate that the integration of intent transition structures with semantic retrieval creates a synergistic effect that neither approach achieves independently, establishing CID-GraphRAG as an effective framework for addressing the challenges of maintaining contextual coherence and goal-oriented progression in knowledge-intensive multi-turn dialogues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge