Pinlong Cai
The Agent's First Day: Benchmarking Learning, Exploration, and Scheduling in the Workplace Scenarios
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:The rapid evolution of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has advanced workflow automation; however, existing research mainly targets performance upper bounds in static environments, overlooking robustness for stochastic real-world deployment. We identify three key challenges: dynamic task scheduling, active exploration under uncertainty, and continuous learning from experience. To bridge this gap, we introduce \method{}, a dynamic evaluation environment that simulates a "trainee" agent continuously exploring a novel setting. Unlike traditional benchmarks, \method{} evaluates agents along three dimensions: (1) context-aware scheduling for streaming tasks with varying priorities; (2) prudent information acquisition to reduce hallucination via active exploration; and (3) continuous evolution by distilling generalized strategies from rule-based, dynamically generated tasks. Experiments show that cutting-edge agents have significant deficiencies in dynamic environments, especially in active exploration and continual learning. Our work establishes a framework for assessing agent reliability, shifting evaluation from static tests to realistic, production-oriented scenarios. Our codes are available at https://github.com/KnowledgeXLab/EvoEnv
SymDrive: Realistic and Controllable Driving Simulator via Symmetric Auto-regressive Online Restoration
Dec 25, 2025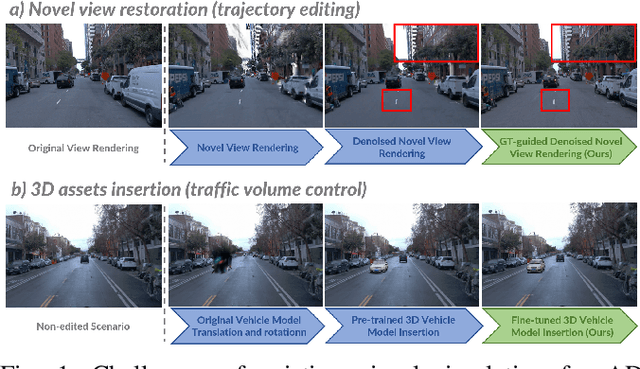
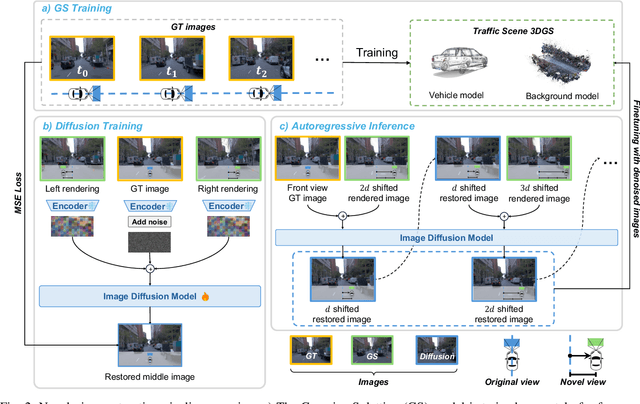

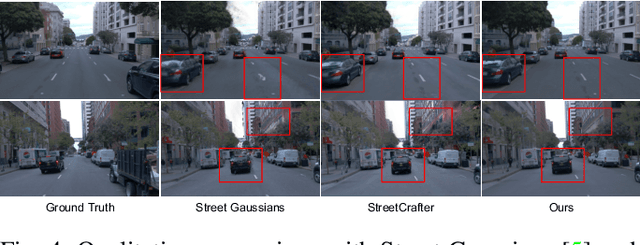
Abstract:High-fidelity and controllable 3D simulation is essential for addressing the long-tail data scarcity in Autonomous Driving (AD), yet existing methods struggle to simultaneously achieve photorealistic rendering and interactive traffic editing. Current approaches often falter in large-angle novel view synthesis and suffer from geometric or lighting artifacts during asset manipulation. To address these challenges, we propose SymDrive, a unified diffusion-based framework capable of joint high-quality rendering and scene editing. We introduce a Symmetric Auto-regressive Online Restoration paradigm, which constructs paired symmetric views to recover fine-grained details via a ground-truth-guided dual-view formulation and utilizes an auto-regressive strategy for consistent lateral view generation. Furthermore, we leverage this restoration capability to enable a training-free harmonization mechanism, treating vehicle insertion as context-aware inpainting to ensure seamless lighting and shadow consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SymDrive achieves state-of-the-art performance in both novel-view enhancement and realistic 3D vehicle insertion.
Learning on the Job: An Experience-Driven Self-Evolving Agent for Long-Horizon Tasks
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across diverse domains, yet significant challenges persist when deploying them as AI agents for real-world long-horizon tasks. Existing LLM agents suffer from a critical limitation: they are test-time static and cannot learn from experience, lacking the ability to accumulate knowledge and continuously improve on the job. To address this challenge, we propose MUSE, a novel agent framework that introduces an experience-driven, self-evolving system centered around a hierarchical Memory Module. MUSE organizes diverse levels of experience and leverages them to plan and execute long-horizon tasks across multiple applications. After each sub-task execution, the agent autonomously reflects on its trajectory, converting the raw trajectory into structured experience and integrating it back into the Memory Module. This mechanism enables the agent to evolve beyond its static pretrained parameters, fostering continuous learning and self-evolution. We evaluate MUSE on the long-horizon productivity benchmark TAC. It achieves new SOTA performance by a significant margin using only a lightweight Gemini-2.5 Flash model. Sufficient Experiments demonstrate that as the agent autonomously accumulates experience, it exhibits increasingly superior task completion capabilities, as well as robust continuous learning and self-evolution capabilities. Moreover, the accumulated experience from MUSE exhibits strong generalization properties, enabling zero-shot improvement on new tasks. MUSE establishes a new paradigm for AI agents capable of real-world productivity task automation.
LeanRAG: Knowledge-Graph-Based Generation with Semantic Aggregation and Hierarchical Retrieval
Aug 14, 2025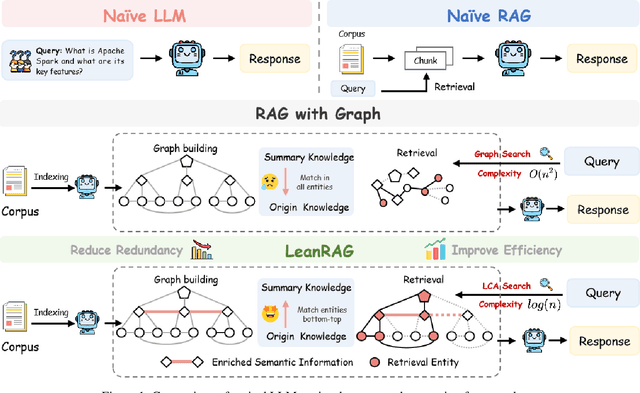
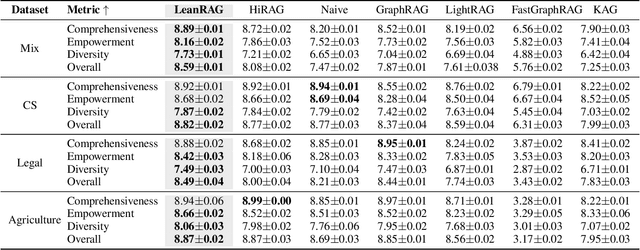
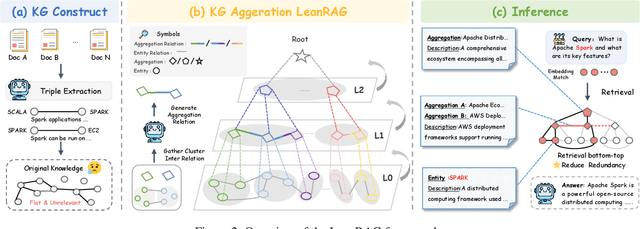
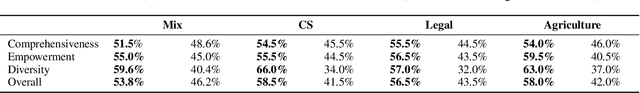
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) plays a crucial role in grounding Large Language Models by leveraging external knowledge, whereas the effectiveness is often compromised by the retrieval of contextually flawed or incomplete information. To address this, knowledge graph-based RAG methods have evolved towards hierarchical structures, organizing knowledge into multi-level summaries. However, these approaches still suffer from two critical, unaddressed challenges: high-level conceptual summaries exist as disconnected ``semantic islands'', lacking the explicit relations needed for cross-community reasoning; and the retrieval process itself remains structurally unaware, often degenerating into an inefficient flat search that fails to exploit the graph's rich topology. To overcome these limitations, we introduce LeanRAG, a framework that features a deeply collaborative design combining knowledge aggregation and retrieval strategies. LeanRAG first employs a novel semantic aggregation algorithm that forms entity clusters and constructs new explicit relations among aggregation-level summaries, creating a fully navigable semantic network. Then, a bottom-up, structure-guided retrieval strategy anchors queries to the most relevant fine-grained entities and then systematically traverses the graph's semantic pathways to gather concise yet contextually comprehensive evidence sets. The LeanRAG can mitigate the substantial overhead associated with path retrieval on graphs and minimizes redundant information retrieval. Extensive experiments on four challenging QA benchmarks with different domains demonstrate that LeanRAG significantly outperforming existing methods in response quality while reducing 46\% retrieval redundancy. Code is available at: https://github.com/RaZzzyz/LeanRAG
O$^2$-Searcher: A Searching-based Agent Model for Open-Domain Open-Ended Question Answering
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), despite their advancements, are fundamentally limited by their static parametric knowledge, hindering performance on tasks requiring open-domain up-to-date information. While enabling LLMs to interact with external knowledge environments is a promising solution, current efforts primarily address closed-end problems. Open-ended questions, which characterized by lacking a standard answer or providing non-unique and diverse answers, remain underexplored. To bridge this gap, we present O$^2$-Searcher, a novel search agent leveraging reinforcement learning to effectively tackle both open-ended and closed-ended questions in the open domain. O$^2$-Searcher leverages an efficient, locally simulated search environment for dynamic knowledge acquisition, effectively decoupling the external world knowledge from model's sophisticated reasoning processes. It employs a unified training mechanism with meticulously designed reward functions, enabling the agent to identify problem types and adapt different answer generation strategies. Furthermore, to evaluate performance on complex open-ended tasks, we construct O$^2$-QA, a high-quality benchmark featuring 300 manually curated, multi-domain open-ended questions with associated web page caches. Extensive experiments show that O$^2$-Searcher, using only a 3B model, significantly surpasses leading LLM agents on O$^2$-QA. It also achieves SOTA results on various closed-ended QA benchmarks against similarly-sized models, while performing on par with much larger ones.
GDI-Bench: A Benchmark for General Document Intelligence with Vision and Reasoning Decoupling
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) has profoundly impacted the document domain, creating a wide array of application scenarios. This progress highlights the need for a comprehensive benchmark to evaluate these models' capabilities across various document-specific tasks. However, existing benchmarks often fail to locate specific model weaknesses or guide systematic improvements. To bridge this gap, we introduce a General Document Intelligence Benchmark (GDI-Bench), featuring 1.9k images across 9 key scenarios and 19 document-specific tasks. By decoupling visual complexity and reasoning complexity, the GDI-Bench structures graded tasks that allow performance assessment by difficulty, aiding in model weakness identification and optimization guidance. We evaluate the GDI-Bench on various open-source and closed-source models, conducting decoupled analyses in the visual and reasoning domains. For instance, the GPT-4o model excels in reasoning tasks but exhibits limitations in visual capabilities. To address the diverse tasks and domains in the GDI-Bench, we propose a GDI Model that mitigates the issue of catastrophic forgetting during the supervised fine-tuning (SFT) process through a intelligence-preserving training strategy. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on previous benchmarks and the GDI-Bench. Both our benchmark and model will be open source.
RAKG:Document-level Retrieval Augmented Knowledge Graph Construction
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:With the rise of knowledge graph based retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) techniques such as GraphRAG and Pike-RAG, the role of knowledge graphs in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) has become increasingly prominent. However, traditional Knowledge Graph Construction (KGC) methods face challenges like complex entity disambiguation, rigid schema definition, and insufficient cross-document knowledge integration. This paper focuses on the task of automatic document-level knowledge graph construction. It proposes the Document-level Retrieval Augmented Knowledge Graph Construction (RAKG) framework. RAKG extracts pre-entities from text chunks and utilizes these pre-entities as queries for RAG, effectively addressing the issue of long-context forgetting in LLMs and reducing the complexity of Coreference Resolution. In contrast to conventional KGC methods, RAKG more effectively captures global information and the interconnections among disparate nodes, thereby enhancing the overall performance of the model. Additionally, we transfer the RAG evaluation framework to the KGC field and filter and evaluate the generated knowledge graphs, thereby avoiding incorrectly generated entities and relationships caused by hallucinations in LLMs. We further developed the MINE dataset by constructing standard knowledge graphs for each article and experimentally validated the performance of RAKG. The results show that RAKG achieves an accuracy of 95.91 % on the MINE dataset, a 6.2 % point improvement over the current best baseline, GraphRAG (89.71 %). The code is available at https://github.com/LMMApplication/RAKG.
Aligning Vision to Language: Text-Free Multimodal Knowledge Graph Construction for Enhanced LLMs Reasoning
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Multimodal reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs) struggles with incomplete knowledge and hallucination artifacts, challenges that textual Knowledge Graphs (KGs) only partially mitigate due to their modality isolation. While Multimodal Knowledge Graphs (MMKGs) promise enhanced cross-modal understanding, their practical construction is impeded by semantic narrowness of manual text annotations and inherent noise in visual-semantic entity linkages. In this paper, we propose Vision-align-to-Language integrated Knowledge Graph (VaLiK), a novel approach for constructing MMKGs that enhances LLMs reasoning through cross-modal information supplementation. Specifically, we cascade pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to align image features with text, transforming them into descriptions that encapsulate image-specific information. Furthermore, we developed a cross-modal similarity verification mechanism to quantify semantic consistency, effectively filtering out noise introduced during feature alignment. Even without manually annotated image captions, the refined descriptions alone suffice to construct the MMKG. Compared to conventional MMKGs construction paradigms, our approach achieves substantial storage efficiency gains while maintaining direct entity-to-image linkage capability. Experimental results on multimodal reasoning tasks demonstrate that LLMs augmented with VaLiK outperform previous state-of-the-art models. Our code is published at https://github.com/Wings-Of-Disaster/VaLiK.
DeepInnovation AI: A Global Dataset Mapping the AI innovation from Academic Research to Industrial Patents
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:In the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence (AI), mapping innovation patterns and understanding effective technology transfer from research to applications are essential for economic growth. However, existing data infrastructures suffer from fragmentation, incomplete coverage, and insufficient evaluative capacity. Here, we present DeepInnovationAI, a comprehensive global dataset containing three structured files. DeepPatentAI.csv: Contains 2,356,204 patent records with 8 field-specific attributes. DeepDiveAI.csv: Encompasses 3,511,929 academic publications with 13 metadata fields. These two datasets leverage large language models, multilingual text analysis and dual-layer BERT classifiers to accurately identify AI-related content, while utilizing hypergraph analysis to create robust innovation metrics. Additionally, DeepCosineAI.csv: By applying semantic vector proximity analysis, this file presents approximately one hundred million calculated paper-patent similarity pairs to enhance understanding of how theoretical advancements translate into commercial technologies. DeepInnovationAI enables researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders to anticipate trends and identify collaboration opportunities. With extensive temporal and geographical scope, it supports detailed analysis of technological development patterns and international competition dynamics, establishing a foundation for modeling AI innovation and technology transfer processes.
LimSim Series: An Autonomous Driving Simulation Platform for Validation and Enhancement
Feb 13, 2025Abstract:Closed-loop simulation environments play a crucial role in the validation and enhancement of autonomous driving systems (ADS). However, certain challenges warrant significant attention, including balancing simulation accuracy with duration, reconciling functionality with practicality, and establishing comprehensive evaluation mechanisms. This paper addresses these challenges by introducing the LimSim Series, a comprehensive simulation platform designed to support the rapid deployment and efficient iteration of ADS. The LimSim Series integrates multi-type information from road networks, employs human-like decision-making and planning algorithms for background vehicles, and introduces the concept of the Area of Interest (AoI) to optimize computational resources. The platform offers a variety of baseline algorithms and user-friendly interfaces, facilitating flexible validation of multiple technical pipelines. Additionally, the LimSim Series incorporates multi-dimensional evaluation metrics, delivering thorough insights into system performance, thus enabling researchers to promptly identify issues for further improvements. Experiments demonstrate that the LimSim Series is compatible with modular, end-to-end, and VLM-based knowledge-driven systems. It can assist in the iteration and updating of ADS by evaluating performance across various scenarios. The code of the LimSim Series is released at: https://github.com/PJLab-ADG/LimSim.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge