Siqi Li
New York University
Can LLMs Discern the Traits Influencing Your Preferences? Evaluating Personality-Driven Preference Alignment in LLMs
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:User preferences are increasingly used to personalize Large Language Model (LLM) responses, yet how to reliably leverage preference signals for answer generation remains under-explored. In practice, preferences can be noisy, incomplete, or even misleading, which can degrade answer quality when applied naively. Motivated by the observation that stable personality traits shape everyday preferences, we study personality as a principled ''latent'' signal behind preference statements. Through extensive experiments, we find that conditioning on personality-aligned preferences substantially improves personalized question answering: selecting preferences consistent with a user's inferred personality increases answer-choice accuracy from 29.25% to 76%, compared to using randomly selected preferences. Based on these findings, we introduce PACIFIC (Preference Alignment Choices Inference for Five-factor Identity Characterization), a personality-labeled preference dataset containing 1200 preference statements spanning diverse domains (e.g., travel, movies, education), annotated with Big-Five (OCEAN) trait directions. Finally, we propose a framework that enables an LLM model to automatically retrieve personality-aligned preferences and incorporate them during answer generation.
Communication-Efficient Federated Risk Difference Estimation for Time-to-Event Clinical Outcomes
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Privacy-preserving model co-training in medical research is often hindered by server-dependent architectures incompatible with protected hospital data systems and by the predominant focus on relative effect measures (hazard ratios) which lack clinical interpretability for absolute survival risk assessment. We propose FedRD, a communication-efficient framework for federated risk difference estimation in distributed survival data. Unlike typical federated learning frameworks (e.g., FedAvg) that require persistent server connections and extensive iterative communication, FedRD is server-independent with minimal communication: one round of summary statistics exchange for the stratified model and three rounds for the unstratified model. Crucially, FedRD provides valid confidence intervals and hypothesis testing--capabilities absent in FedAvg-based frameworks. We provide theoretical guarantees by establishing the asymptotic properties of FedRD and prove that FedRD (unstratified) is asymptotically equivalent to pooled individual-level analysis. Simulation studies and real-world clinical applications across different countries demonstrate that FedRD outperforms local and federated baselines in both estimation accuracy and prediction performance, providing an architecturally feasible solution for absolute risk assessment in privacy-restricted, multi-site clinical studies.
Benchmarking and Enhancing VLM for Compressed Image Understanding
Dec 24, 2025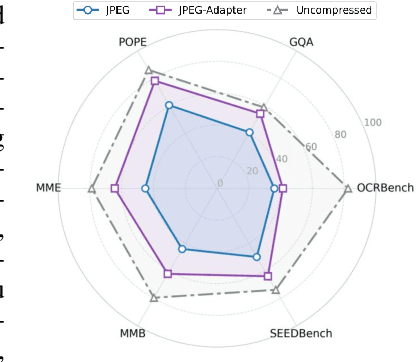
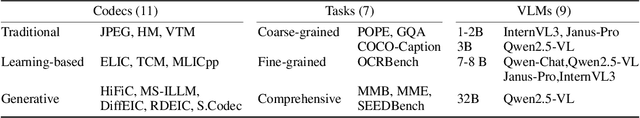

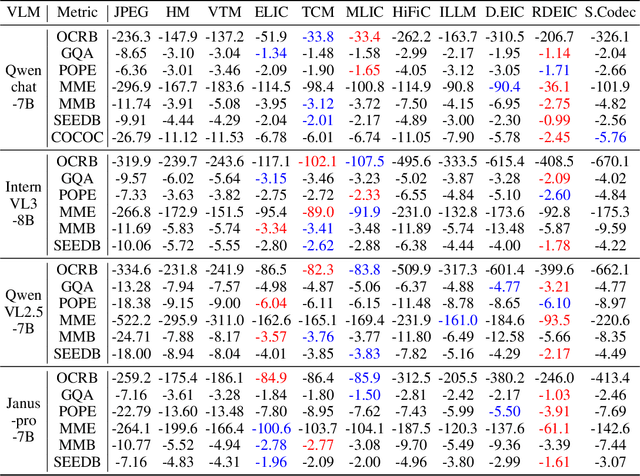
Abstract:With the rapid development of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and the growing demand for their applications, efficient compression of the image inputs has become increasingly important. Existing VLMs predominantly digest and understand high-bitrate compressed images, while their ability to interpret low-bitrate compressed images has yet to be explored by far. In this paper, we introduce the first comprehensive benchmark to evaluate the ability of VLM against compressed images, varying existing widely used image codecs and diverse set of tasks, encompassing over one million compressed images in our benchmark. Next, we analyse the source of performance gap, by categorising the gap from a) the information loss during compression and b) generalisation failure of VLM. We visualize these gaps with concrete examples and identify that for compressed images, only the generalization gap can be mitigated. Finally, we propose a universal VLM adaptor to enhance model performance on images compressed by existing codecs. Consequently, we demonstrate that a single adaptor can improve VLM performance across images with varying codecs and bitrates by 10%-30%. We believe that our benchmark and enhancement method provide valuable insights and contribute toward bridging the gap between VLMs and compressed images.
Patlak Parametric Image Estimation from Dynamic PET Using Diffusion Model Prior
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Dynamic PET enables the quantitative estimation of physiology-related parameters and is widely utilized in research and increasingly adopted in clinical settings. Parametric imaging in dynamic PET requires kinetic modeling to estimate voxel-wise physiological parameters based on specific kinetic models. However, parametric images estimated through kinetic model fitting often suffer from low image quality due to the inherently ill-posed nature of the fitting process and the limited counts resulting from non-continuous data acquisition across multiple bed positions in whole-body PET. In this work, we proposed a diffusion model-based kinetic modeling framework for parametric image estimation, using the Patlak model as an example. The score function of the diffusion model was pre-trained on static total-body PET images and served as a prior for both Patlak slope and intercept images by leveraging their patch-wise similarity. During inference, the kinetic model was incorporated as a data-consistency constraint to guide the parametric image estimation. The proposed framework was evaluated on total-body dynamic PET datasets with different dose levels, demonstrating the feasibility and promising performance of the proposed framework in improving parametric image quality.
TRACER: Transfer Learning based Real-time Adaptation for Clinical Evolving Risk
Dec 14, 2025Abstract:Clinical decision support tools built on electronic health records often experience performance drift due to temporal population shifts, particularly when changes in the clinical environment initially affect only a subset of patients, resulting in a transition to mixed populations. Such case-mix changes commonly arise following system-level operational updates or the emergence of new diseases, such as COVID-19. We propose TRACER (Transfer Learning-based Real-time Adaptation for Clinical Evolving Risk), a framework that identifies encounter-level transition membership and adapts predictive models using transfer learning without full retraining. In simulation studies, TRACER outperformed static models trained on historical or contemporary data. In a real-world application predicting hospital admission following emergency department visits across the COVID-19 transition, TRACER improved both discrimination and calibration. TRACER provides a scalable approach for maintaining robust predictive performance under evolving and heterogeneous clinical conditions.
H3Former: Hypergraph-based Semantic-Aware Aggregation via Hyperbolic Hierarchical Contrastive Loss for Fine-Grained Visual Classification
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Fine-Grained Visual Classification (FGVC) remains a challenging task due to subtle inter-class differences and large intra-class variations. Existing approaches typically rely on feature-selection mechanisms or region-proposal strategies to localize discriminative regions for semantic analysis. However, these methods often fail to capture discriminative cues comprehensively while introducing substantial category-agnostic redundancy. To address these limitations, we propose H3Former, a novel token-to-region framework that leverages high-order semantic relations to aggregate local fine-grained representations with structured region-level modeling. Specifically, we propose the Semantic-Aware Aggregation Module (SAAM), which exploits multi-scale contextual cues to dynamically construct a weighted hypergraph among tokens. By applying hypergraph convolution, SAAM captures high-order semantic dependencies and progressively aggregates token features into compact region-level representations. Furthermore, we introduce the Hyperbolic Hierarchical Contrastive Loss (HHCL), which enforces hierarchical semantic constraints in a non-Euclidean embedding space. The HHCL enhances inter-class separability and intra-class consistency while preserving the intrinsic hierarchical relationships among fine-grained categories. Comprehensive experiments conducted on four standard FGVC benchmarks validate the superiority of our H3Former framework.
FineSkiing: A Fine-grained Benchmark for Skiing Action Quality Assessment
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Action Quality Assessment (AQA) aims to evaluate and score sports actions, which has attracted widespread interest in recent years. Existing AQA methods primarily predict scores based on features extracted from the entire video, resulting in limited interpretability and reliability. Meanwhile, existing AQA datasets also lack fine-grained annotations for action scores, especially for deduction items and sub-score annotations. In this paper, we construct the first AQA dataset containing fine-grained sub-score and deduction annotations for aerial skiing, which will be released as a new benchmark. For the technical challenges, we propose a novel AQA method, named JudgeMind, which significantly enhances performance and reliability by simulating the judgment and scoring mindset of professional referees. Our method segments the input action video into different stages and scores each stage to enhance accuracy. Then, we propose a stage-aware feature enhancement and fusion module to boost the perception of stage-specific key regions and enhance the robustness to visual changes caused by frequent camera viewpoints switching. In addition, we propose a knowledge-based grade-aware decoder to incorporate possible deduction items as prior knowledge to predict more accurate and reliable scores. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
KoALA: KL-L0 Adversarial Detector via Label Agreement
Oct 14, 2025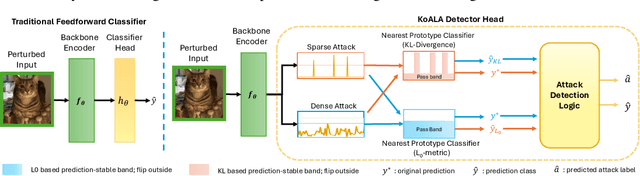
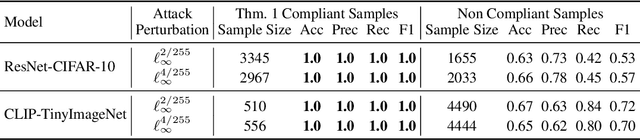
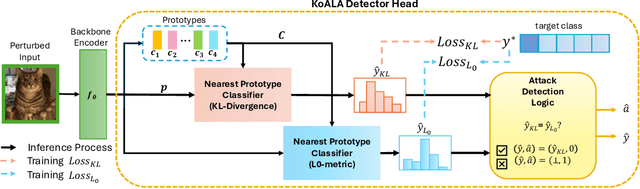
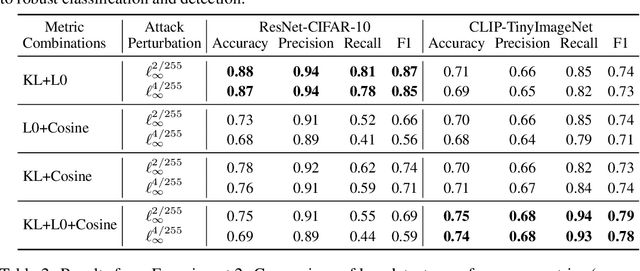
Abstract:Deep neural networks are highly susceptible to adversarial attacks, which pose significant risks to security- and safety-critical applications. We present KoALA (KL-L0 Adversarial detection via Label Agreement), a novel, semantics-free adversarial detector that requires no architectural changes or adversarial retraining. KoALA operates on a simple principle: it detects an adversarial attack when class predictions from two complementary similarity metrics disagree. These metrics-KL divergence and an L0-based similarity-are specifically chosen to detect different types of perturbations. The KL divergence metric is sensitive to dense, low-amplitude shifts, while the L0-based similarity is designed for sparse, high-impact changes. We provide a formal proof of correctness for our approach. The only training required is a simple fine-tuning step on a pre-trained image encoder using clean images to ensure the embeddings align well with both metrics. This makes KOALA a lightweight, plug-and-play solution for existing models and various data modalities. Our extensive experiments on ResNet/CIFAR-10 and CLIP/Tiny-ImageNet confirm our theoretical claims. When the theorem's conditions are met, KoALA consistently and effectively detects adversarial examples. On the full test sets, KoALA achieves a precision of 0.94 and a recall of 0.81 on ResNet/CIFAR-10, and a precision of 0.66 and a recall of 0.85 on CLIP/Tiny-ImageNet.
Shift-Invariant Attribute Scoring for Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks via Shapley Value
Oct 02, 2025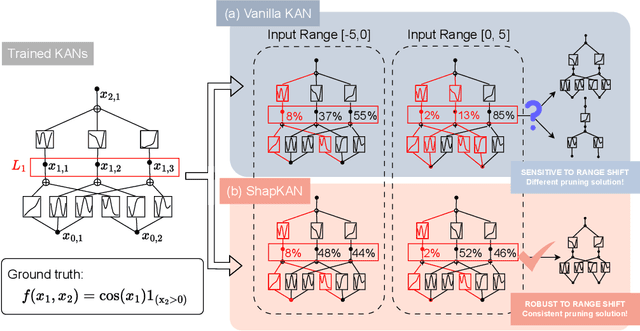
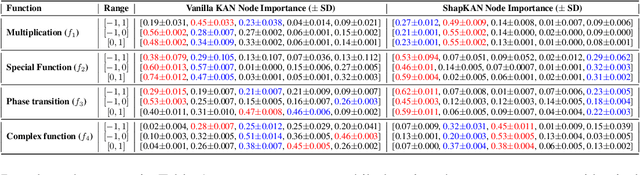
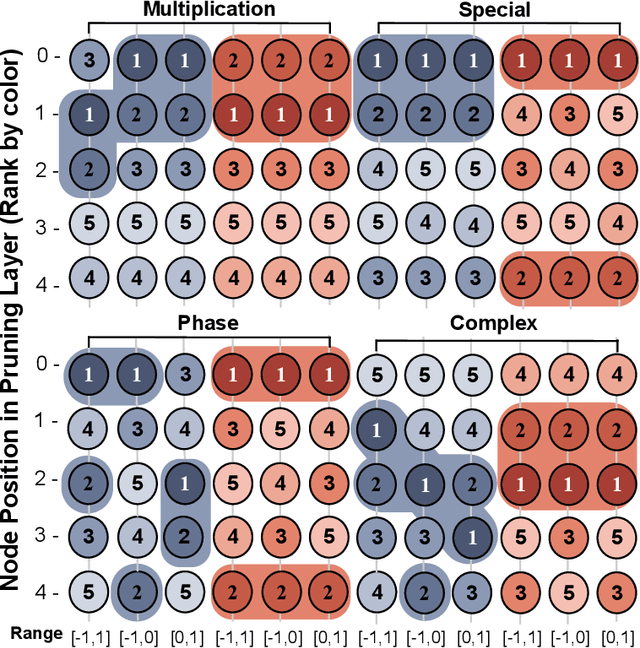
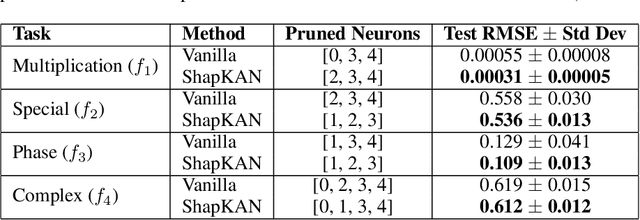
Abstract:For many real-world applications, understanding feature-outcome relationships is as crucial as achieving high predictive accuracy. While traditional neural networks excel at prediction, their black-box nature obscures underlying functional relationships. Kolmogorov--Arnold Networks (KANs) address this by employing learnable spline-based activation functions on edges, enabling recovery of symbolic representations while maintaining competitive performance. However, KAN's architecture presents unique challenges for network pruning. Conventional magnitude-based methods become unreliable due to sensitivity to input coordinate shifts. We propose \textbf{ShapKAN}, a pruning framework using Shapley value attribution to assess node importance in a shift-invariant manner. Unlike magnitude-based approaches, ShapKAN quantifies each node's actual contribution, ensuring consistent importance rankings regardless of input parameterization. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that ShapKAN preserves true node importance while enabling effective network compression. Our approach improves KAN's interpretability advantages, facilitating deployment in resource-constrained environments.
CodeBoost: Boosting Code LLMs by Squeezing Knowledge from Code Snippets with RL
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Code large language models (LLMs) have become indispensable tools for building efficient and automated coding pipelines. Existing models are typically post-trained using reinforcement learning (RL) from general-purpose LLMs using "human instruction-final answer" pairs, where the instructions are usually from manual annotations. However, collecting high-quality coding instructions is both labor-intensive and difficult to scale. On the other hand, code snippets are abundantly available from various sources. This imbalance presents a major bottleneck in instruction-based post-training. We propose CodeBoost, a post-training framework that enhances code LLMs purely from code snippets, without relying on human-annotated instructions. CodeBoost introduces the following key components: (1) maximum-clique curation, which selects a representative and diverse training corpus from code; (2) bi-directional prediction, which enables the model to learn from both forward and backward prediction objectives; (3) error-aware prediction, which incorporates learning signals from both correct and incorrect outputs; (4) heterogeneous augmentation, which diversifies the training distribution to enrich code semantics; and (5) heterogeneous rewarding, which guides model learning through multiple reward types including format correctness and execution feedback from both successes and failures. Extensive experiments across several code LLMs and benchmarks verify that CodeBoost consistently improves performance, demonstrating its effectiveness as a scalable and effective training pipeline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge