Yue Gao
SPICE: Submodular Penalized Information-Conflict Selection for Efficient Large Language Model Training
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Information-based data selection for instruction tuning is compelling: maximizing the log-determinant of the Fisher information yields a monotone submodular objective, enabling greedy algorithms to achieve a $(1-1/e)$ approximation under a cardinality budget. In practice, however, we identify alleviating gradient conflicts, misalignment between per-sample gradients, is a key factor that slows down the decay of marginal log-determinant information gains, thereby preventing significant loss of information. We formalize this via an $\varepsilon$-decomposition that quantifies the deviation from ideal submodularity as a function of conflict statistics, yielding data-dependent approximation factors that tighten as conflicts diminish. Guided by this analysis, we propose SPICE, a conflict-aware selector that maximizes information while penalizing misalignment, and that supports early stopping and proxy models for efficiency. Empirically, SPICE selects subsets with higher log-determinant information than original criteria, and these informational gains translate into performance improvements: across 8 benchmarks with LLaMA2-7B and Qwen2-7B, SPICE uses only 10% of the data, yet matches or exceeds 6 methods including full-data tuning. This achieves performance improvements with substantially lower training cost.
FocusNav: Spatial Selective Attention with Waypoint Guidance for Humanoid Local Navigation
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Robust local navigation in unstructured and dynamic environments remains a significant challenge for humanoid robots, requiring a delicate balance between long-range navigation targets and immediate motion stability. In this paper, we propose FocusNav, a spatial selective attention framework that adaptively modulates the robot's perceptual field based on navigational intent and real-time stability. FocusNav features a Waypoint-Guided Spatial Cross-Attention (WGSCA) mechanism that anchors environmental feature aggregation to a sequence of predicted collision-free waypoints, ensuring task-relevant perception along the planned trajectory. To enhance robustness in complex terrains, the Stability-Aware Selective Gating (SASG) module autonomously truncates distal information when detecting instability, compelling the policy to prioritize immediate foothold safety. Extensive experiments on the Unitree G1 humanoid robot demonstrate that FocusNav significantly improves navigation success rates in challenging scenarios, outperforming baselines in both collision avoidance and motion stability, achieving robust navigation in dynamic and complex environments.
SynergyWarpNet: Attention-Guided Cooperative Warping for Neural Portrait Animation
Dec 19, 2025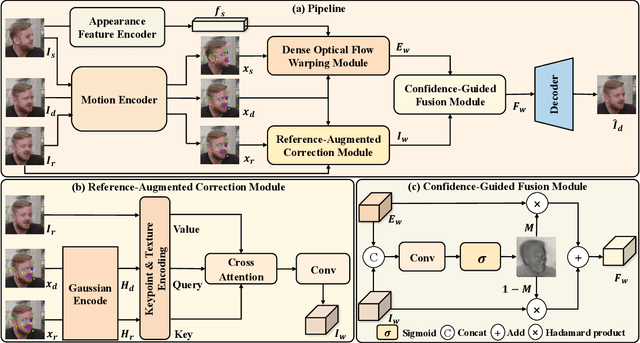
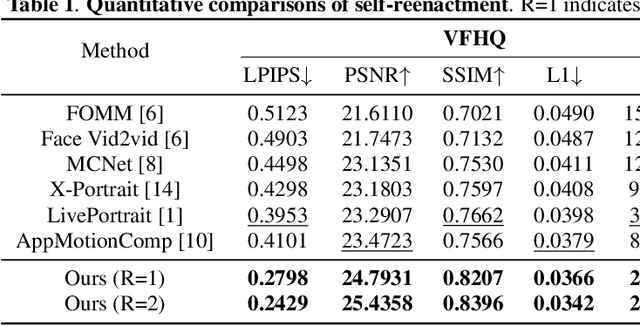

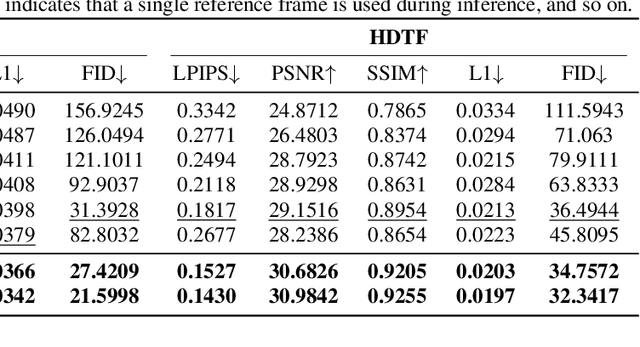
Abstract:Recent advances in neural portrait animation have demonstrated remarked potential for applications in virtual avatars, telepresence, and digital content creation. However, traditional explicit warping approaches often struggle with accurate motion transfer or recovering missing regions, while recent attention-based warping methods, though effective, frequently suffer from high complexity and weak geometric grounding. To address these issues, we propose SynergyWarpNet, an attention-guided cooperative warping framework designed for high-fidelity talking head synthesis. Given a source portrait, a driving image, and a set of reference images, our model progressively refines the animation in three stages. First, an explicit warping module performs coarse spatial alignment between the source and driving image using 3D dense optical flow. Next, a reference-augmented correction module leverages cross-attention across 3D keypoints and texture features from multiple reference images to semantically complete occluded or distorted regions. Finally, a confidence-guided fusion module integrates the warped outputs with spatially-adaptive fusing, using a learned confidence map to balance structural alignment and visual consistency. Comprehensive evaluations on benchmark datasets demonstrate state-of-the-art performance.
Cog-RAG: Cognitive-Inspired Dual-Hypergraph with Theme Alignment Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances the response quality and domain-specific performance of large language models (LLMs) by incorporating external knowledge to combat hallucinations. In recent research, graph structures have been integrated into RAG to enhance the capture of semantic relations between entities. However, it primarily focuses on low-order pairwise entity relations, limiting the high-order associations among multiple entities. Hypergraph-enhanced approaches address this limitation by modeling multi-entity interactions via hyperedges, but they are typically constrained to inter-chunk entity-level representations, overlooking the global thematic organization and alignment across chunks. Drawing inspiration from the top-down cognitive process of human reasoning, we propose a theme-aligned dual-hypergraph RAG framework (Cog-RAG) that uses a theme hypergraph to capture inter-chunk thematic structure and an entity hypergraph to model high-order semantic relations. Furthermore, we design a cognitive-inspired two-stage retrieval strategy that first activates query-relevant thematic content from the theme hypergraph, and then guides fine-grained recall and diffusion in the entity hypergraph, achieving semantic alignment and consistent generation from global themes to local details. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that Cog-RAG significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art baseline approaches.
* Accepted by AAAI 2026 main conference
H3Former: Hypergraph-based Semantic-Aware Aggregation via Hyperbolic Hierarchical Contrastive Loss for Fine-Grained Visual Classification
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Fine-Grained Visual Classification (FGVC) remains a challenging task due to subtle inter-class differences and large intra-class variations. Existing approaches typically rely on feature-selection mechanisms or region-proposal strategies to localize discriminative regions for semantic analysis. However, these methods often fail to capture discriminative cues comprehensively while introducing substantial category-agnostic redundancy. To address these limitations, we propose H3Former, a novel token-to-region framework that leverages high-order semantic relations to aggregate local fine-grained representations with structured region-level modeling. Specifically, we propose the Semantic-Aware Aggregation Module (SAAM), which exploits multi-scale contextual cues to dynamically construct a weighted hypergraph among tokens. By applying hypergraph convolution, SAAM captures high-order semantic dependencies and progressively aggregates token features into compact region-level representations. Furthermore, we introduce the Hyperbolic Hierarchical Contrastive Loss (HHCL), which enforces hierarchical semantic constraints in a non-Euclidean embedding space. The HHCL enhances inter-class separability and intra-class consistency while preserving the intrinsic hierarchical relationships among fine-grained categories. Comprehensive experiments conducted on four standard FGVC benchmarks validate the superiority of our H3Former framework.
FineSkiing: A Fine-grained Benchmark for Skiing Action Quality Assessment
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Action Quality Assessment (AQA) aims to evaluate and score sports actions, which has attracted widespread interest in recent years. Existing AQA methods primarily predict scores based on features extracted from the entire video, resulting in limited interpretability and reliability. Meanwhile, existing AQA datasets also lack fine-grained annotations for action scores, especially for deduction items and sub-score annotations. In this paper, we construct the first AQA dataset containing fine-grained sub-score and deduction annotations for aerial skiing, which will be released as a new benchmark. For the technical challenges, we propose a novel AQA method, named JudgeMind, which significantly enhances performance and reliability by simulating the judgment and scoring mindset of professional referees. Our method segments the input action video into different stages and scores each stage to enhance accuracy. Then, we propose a stage-aware feature enhancement and fusion module to boost the perception of stage-specific key regions and enhance the robustness to visual changes caused by frequent camera viewpoints switching. In addition, we propose a knowledge-based grade-aware decoder to incorporate possible deduction items as prior knowledge to predict more accurate and reliable scores. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Diff$^2$I2P: Differentiable Image-to-Point Cloud Registration with Diffusion Prior
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Learning cross-modal correspondences is essential for image-to-point cloud (I2P) registration. Existing methods achieve this mostly by utilizing metric learning to enforce feature alignment across modalities, disregarding the inherent modality gap between image and point data. Consequently, this paradigm struggles to ensure accurate cross-modal correspondences. To this end, inspired by the cross-modal generation success of recent large diffusion models, we propose Diff$^2$I2P, a fully Differentiable I2P registration framework, leveraging a novel and effective Diffusion prior for bridging the modality gap. Specifically, we propose a Control-Side Score Distillation (CSD) technique to distill knowledge from a depth-conditioned diffusion model to directly optimize the predicted transformation. However, the gradients on the transformation fail to backpropagate onto the cross-modal features due to the non-differentiability of correspondence retrieval and PnP solver. To this end, we further propose a Deformable Correspondence Tuning (DCT) module to estimate the correspondences in a differentiable way, followed by the transformation estimation using a differentiable PnP solver. With these two designs, the Diffusion model serves as a strong prior to guide the cross-modal feature learning of image and point cloud for forming robust correspondences, which significantly improves the registration. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that Diff$^2$I2P consistently outperforms SoTA I2P registration methods, achieving over 7% improvement in registration recall on the 7-Scenes benchmark.
Memory-Augmented Incomplete Multimodal Survival Prediction via Cross-Slide and Gene-Attentive Hypergraph Learning
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Multimodal pathology-genomic analysis is critical for cancer survival prediction. However, existing approaches predominantly integrate formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) slides with genomic data, while neglecting the availability of other preservation slides, such as Fresh Froze (FF) slides. Moreover, as the high-resolution spatial nature of pathology data tends to dominate the cross-modality fusion process, it hinders effective multimodal fusion and leads to modality imbalance challenges between pathology and genomics. These methods also typically require complete data modalities, limiting their clinical applicability with incomplete modalities, such as missing either pathology or genomic data. In this paper, we propose a multimodal survival prediction framework that leverages hypergraph learning to effectively integrate multi-WSI information and cross-modality interactions between pathology slides and genomics data while addressing modality imbalance. In addition, we introduce a memory mechanism that stores previously learned paired pathology-genomic features and dynamically compensates for incomplete modalities. Experiments on five TCGA datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms advanced methods by over 2.3% in C-Index. Under incomplete modality scenarios, our approach surpasses pathology-only (3.3%) and gene-only models (7.9%). Code: https://github.com/MCPathology/M2Surv
DyNaVLM: Zero-Shot Vision-Language Navigation System with Dynamic Viewpoints and Self-Refining Graph Memory
Jun 18, 2025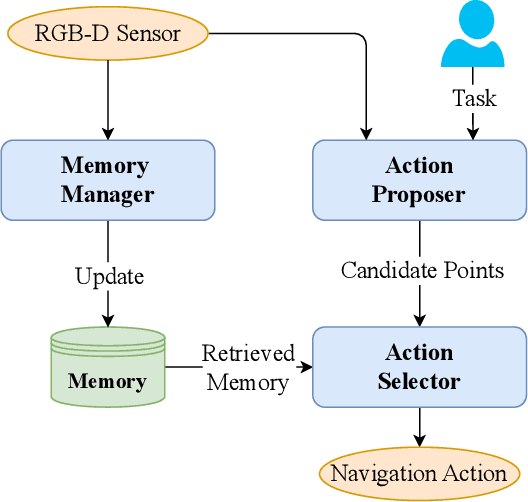
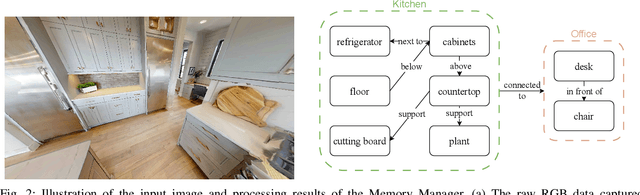


Abstract:We present DyNaVLM, an end-to-end vision-language navigation framework using Vision-Language Models (VLM). In contrast to prior methods constrained by fixed angular or distance intervals, our system empowers agents to freely select navigation targets via visual-language reasoning. At its core lies a self-refining graph memory that 1) stores object locations as executable topological relations, 2) enables cross-robot memory sharing through distributed graph updates, and 3) enhances VLM's decision-making via retrieval augmentation. Operating without task-specific training or fine-tuning, DyNaVLM demonstrates high performance on GOAT and ObjectNav benchmarks. Real-world tests further validate its robustness and generalization. The system's three innovations: dynamic action space formulation, collaborative graph memory, and training-free deployment, establish a new paradigm for scalable embodied robot, bridging the gap between discrete VLN tasks and continuous real-world navigation.
Stable CDE Autoencoders with Acuity Regularization for Offline Reinforcement Learning in Sepsis Treatment
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Effective reinforcement learning (RL) for sepsis treatment depends on learning stable, clinically meaningful state representations from irregular ICU time series. While previous works have explored representation learning for this task, the critical challenge of training instability in sequential representations and its detrimental impact on policy performance has been overlooked. This work demonstrates that Controlled Differential Equations (CDE) state representation can achieve strong RL policies when two key factors are met: (1) ensuring training stability through early stopping or stabilization methods, and (2) enforcing acuity-aware representations by correlation regularization with clinical scores (SOFA, SAPS-II, OASIS). Experiments on the MIMIC-III sepsis cohort reveal that stable CDE autoencoder produces representations strongly correlated with acuity scores and enables RL policies with superior performance (WIS return $> 0.9$). In contrast, unstable CDE representation leads to degraded representations and policy failure (WIS return $\sim$ 0). Visualizations of the latent space show that stable CDEs not only separate survivor and non-survivor trajectories but also reveal clear acuity score gradients, whereas unstable training fails to capture either pattern. These findings highlight practical guidelines for using CDEs to encode irregular medical time series in clinical RL, emphasizing the need for training stability in sequential representation learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge