Yan Lu
Temperature as a Meta-Policy: Adaptive Temperature in LLM Reinforcement Learning
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Temperature is a crucial hyperparameter in large language models (LLMs), controlling the trade-off between exploration and exploitation during text generation. High temperatures encourage diverse but noisy outputs, while low temperatures produce focused outputs but may cause premature convergence. Yet static or heuristic temperature schedules fail to adapt to the dynamic demands of reinforcement learning (RL) throughout training, often limiting policy improvement. We propose Temperature Adaptive Meta Policy Optimization (TAMPO), a new framework that recasts temperature control as a learnable meta-policy. TAMPO operates through a hierarchical two-loop process. In the inner loop, the LLM policy is updated (e.g., using GRPO) with trajectories sampled at the temperature selected by the meta-policy. In the outer loop, meta-policy updates the distribution over candidate temperatures by rewarding those that maximize the likelihood of high-advantage trajectories. This trajectory-guided, reward-driven mechanism enables online adaptation without additional rollouts, directly aligning exploration with policy improvement. On five mathematical reasoning benchmarks, TAMPO outperforms baselines using fixed or heuristic temperatures, establishing temperature as an effective learnable meta-policy for adaptive exploration in LLM reinforcement learning. Accepted at ICLR 2026.
Efficient Autoregressive Video Diffusion with Dummy Head
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:The autoregressive video diffusion model has recently gained considerable research interest due to its causal modeling and iterative denoising. In this work, we identify that the multi-head self-attention in these models under-utilizes historical frames: approximately 25% heads attend almost exclusively to the current frame, and discarding their KV caches incurs only minor performance degradation. Building upon this, we propose Dummy Forcing, a simple yet effective method to control context accessibility across different heads. Specifically, the proposed heterogeneous memory allocation reduces head-wise context redundancy, accompanied by dynamic head programming to adaptively classify head types. Moreover, we develop a context packing technique to achieve more aggressive cache compression. Without additional training, our Dummy Forcing delivers up to 2.0x speedup over the baseline, supporting video generation at 24.3 FPS with less than 0.5% quality drop. Project page is available at https://csguoh.github.io/project/DummyForcing/.
Hierarchical Long Video Understanding with Audiovisual Entity Cohesion and Agentic Search
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Long video understanding presents significant challenges for vision-language models due to extremely long context windows. Existing solutions relying on naive chunking strategies with retrieval-augmented generation, typically suffer from information fragmentation and a loss of global coherence. We present HAVEN, a unified framework for long-video understanding that enables coherent and comprehensive reasoning by integrating audiovisual entity cohesion and hierarchical video indexing with agentic search. First, we preserve semantic consistency by integrating entity-level representations across visual and auditory streams, while organizing content into a structured hierarchy spanning global summary, scene, segment, and entity levels. Then we employ an agentic search mechanism to enable dynamic retrieval and reasoning across these layers, facilitating coherent narrative reconstruction and fine-grained entity tracking. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves good temporal coherence, entity consistency, and retrieval efficiency, establishing a new state-of-the-art with an overall accuracy of 84.1% on LVBench. Notably, it achieves outstanding performance in the challenging reasoning category, reaching 80.1%. These results highlight the effectiveness of structured, multimodal reasoning for comprehensive and context-consistent understanding of long-form videos.
A Unified Neural Codec Language Model for Selective Editable Text to Speech Generation
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Neural codec language models achieve impressive zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS) by fully imitating the acoustic characteristics of a short speech prompt, including timbre, prosody, and paralinguistic information. However, such holistic imitation limits their ability to isolate and control individual attributes. In this paper, we present a unified codec language model SpeechEdit that extends zero-shot TTS with a selective control mechanism. By default, SpeechEdit reproduces the complete acoustic profile inferred from the speech prompt, but it selectively overrides only the attributes specified by explicit control instructions. To enable controllable modeling, SpeechEdit is trained on our newly constructed LibriEdit dataset, which provides delta (difference-aware) training pairs derived from LibriHeavy. Experimental results show that our approach maintains naturalness and robustness while offering flexible and localized control over desired attributes. Audio samples are available at https://speech-editing.github.io/speech-editing/.
Breaking Coordinate Overfitting: Geometry-Aware WiFi Sensing for Cross-Layout 3D Pose Estimation
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:WiFi-based 3D human pose estimation offers a low-cost and privacy-preserving alternative to vision-based systems for smart interaction. However, existing approaches rely on visual 3D poses as supervision and directly regress CSI to a camera-based coordinate system. We find that this practice leads to coordinate overfitting: models memorize deployment-specific WiFi transceiver layouts rather than only learning activity-relevant representations, resulting in severe generalization failures. To address this challenge, we present PerceptAlign, the first geometry-conditioned framework for WiFi-based cross-layout pose estimation. PerceptAlign introduces a lightweight coordinate unification procedure that aligns WiFi and vision measurements in a shared 3D space using only two checkerboards and a few photos. Within this unified space, it encodes calibrated transceiver positions into high-dimensional embeddings and fuses them with CSI features, making the model explicitly aware of device geometry as a conditional variable. This design forces the network to disentangle human motion from deployment layouts, enabling robust and, for the first time, layout-invariant WiFi pose estimation. To support systematic evaluation, we construct the largest cross-domain 3D WiFi pose estimation dataset to date, comprising 21 subjects, 5 scenes, 18 actions, and 7 device layouts. Experiments show that PerceptAlign reduces in-domain error by 12.3% and cross-domain error by more than 60% compared to state-of-the-art baselines. These results establish geometry-conditioned learning as a viable path toward scalable and practical WiFi sensing.
From Off-Policy to On-Policy: Enhancing GUI Agents via Bi-level Expert-to-Policy Assimilation
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Vision-language models are increasingly deployed as computer-use agents (CUAs) that operate desktops and browsers. Top-performing CUAs are framework-based systems that decompose planning and execution, while end-to-end screenshot-to-action policies are easier to deploy but lag behind on benchmarks such as OSWorld-Verified. GUI datasets like OSWorld pose two bottlenecks: they expose only a few hundred interactive, verifiable tasks and environments, and expert trajectories must be gathered by interacting with these environments, making such data hard to scale. We therefore ask how reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) can best exploit a small pool of exist expert trajectories to train end-to-end policies. Naively mixing these off-policy traces into on-policy RLVR is brittle: even after format conversion, expert trajectories exhibit structural mismatch and distribution shift from the learner. We propose BEPA (Bi-Level Expert-to-Policy Assimilation), which turns static expert traces into policy-aligned guidance via self-rolled reachable trajectories under the base policy (LEVEL-1) and a per-task, dynamically updated cache used in RLVR (LEVEL-2). On OSWorld-Verified, BEPA improves UITARS1.5-7B success from 22.87% to 32.13% and raises a held-out split from 5.74% to 10.30%, with consistent gains on MMBench-GUI and Online-Mind2Web. Our code and data are available at: https://github.com/LEON-gittech/Verl_GUI.git
InfiniteWeb: Scalable Web Environment Synthesis for GUI Agent Training
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:GUI agents that interact with graphical interfaces on behalf of users represent a promising direction for practical AI assistants. However, training such agents is hindered by the scarcity of suitable environments. We present InfiniteWeb, a system that automatically generates functional web environments at scale for GUI agent training. While LLMs perform well on generating a single webpage, building a realistic and functional website with many interconnected pages faces challenges. We address these challenges through unified specification, task-centric test-driven development, and a combination of website seed with reference design image to ensure diversity. Our system also generates verifiable task evaluators enabling dense reward signals for reinforcement learning. Experiments show that InfiniteWeb surpasses commercial coding agents at realistic website construction, and GUI agents trained on our generated environments achieve significant performance improvements on OSWorld and Online-Mind2Web, demonstrating the effectiveness of proposed system.
Animate Any Character in Any World
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in world models have greatly enhanced interactive environment simulation. Existing methods mainly fall into two categories: (1) static world generation models, which construct 3D environments without active agents, and (2) controllable-entity models, which allow a single entity to perform limited actions in an otherwise uncontrollable environment. In this work, we introduce AniX, leveraging the realism and structural grounding of static world generation while extending controllable-entity models to support user-specified characters capable of performing open-ended actions. Users can provide a 3DGS scene and a character, then direct the character through natural language to perform diverse behaviors from basic locomotion to object-centric interactions while freely exploring the environment. AniX synthesizes temporally coherent video clips that preserve visual fidelity with the provided scene and character, formulated as a conditional autoregressive video generation problem. Built upon a pre-trained video generator, our training strategy significantly enhances motion dynamics while maintaining generalization across actions and characters. Our evaluation covers a broad range of aspects, including visual quality, character consistency, action controllability, and long-horizon coherence.
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
Spatia: Video Generation with Updatable Spatial Memory
Dec 17, 2025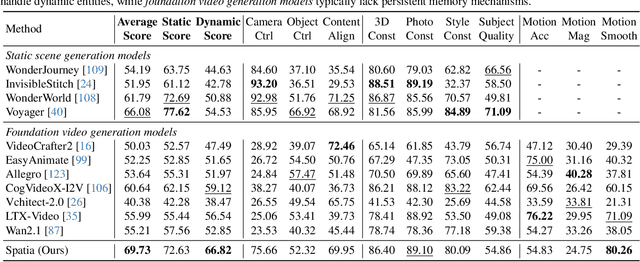
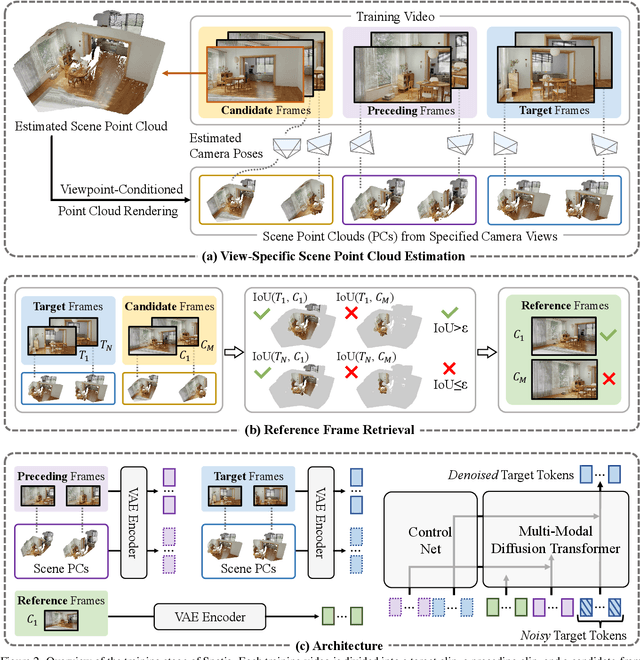

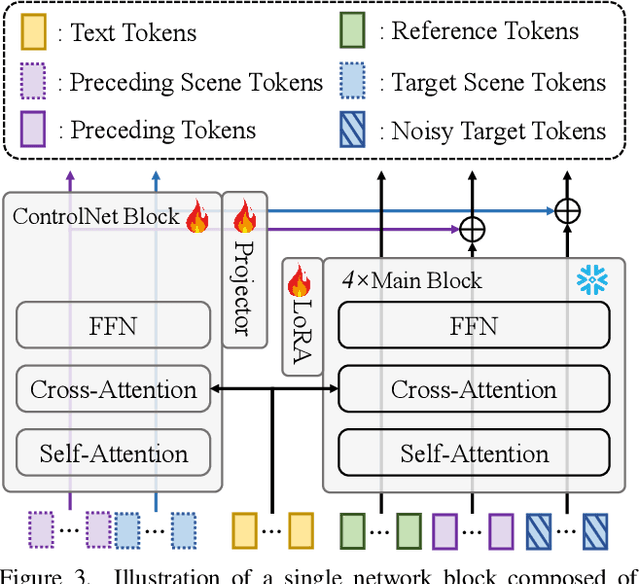
Abstract:Existing video generation models struggle to maintain long-term spatial and temporal consistency due to the dense, high-dimensional nature of video signals. To overcome this limitation, we propose Spatia, a spatial memory-aware video generation framework that explicitly preserves a 3D scene point cloud as persistent spatial memory. Spatia iteratively generates video clips conditioned on this spatial memory and continuously updates it through visual SLAM. This dynamic-static disentanglement design enhances spatial consistency throughout the generation process while preserving the model's ability to produce realistic dynamic entities. Furthermore, Spatia enables applications such as explicit camera control and 3D-aware interactive editing, providing a geometrically grounded framework for scalable, memory-driven video generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge