Haiyang Sun
FNF: Functional Network Fingerprint for Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The development of large language models (LLMs) is costly and has significant commercial value. Consequently, preventing unauthorized appropriation of open-source LLMs and protecting developers' intellectual property rights have become critical challenges. In this work, we propose the Functional Network Fingerprint (FNF), a training-free, sample-efficient method for detecting whether a suspect LLM is derived from a victim model, based on the consistency between their functional network activity. We demonstrate that models that share a common origin, even with differences in scale or architecture, exhibit highly consistent patterns of neuronal activity within their functional networks across diverse input samples. In contrast, models trained independently on distinct data or with different objectives fail to preserve such activity alignment. Unlike conventional approaches, our method requires only a few samples for verification, preserves model utility, and remains robust to common model modifications (such as fine-tuning, pruning, and parameter permutation), as well as to comparisons across diverse architectures and dimensionalities. FNF thus provides model owners and third parties with a simple, non-invasive, and effective tool for protecting LLM intellectual property. The code is available at https://github.com/WhatAboutMyStar/LLM_ACTIVATION.
DeepASMR: LLM-Based Zero-Shot ASMR Speech Generation for Anyone of Any Voice
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:While modern Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems achieve high fidelity for read-style speech, they struggle to generate Autonomous Sensory Meridian Response (ASMR), a specialized, low-intensity speech style essential for relaxation. The inherent challenges include ASMR's subtle, often unvoiced characteristics and the demand for zero-shot speaker adaptation. In this paper, we introduce DeepASMR, the first framework designed for zero-shot ASMR generation. We demonstrate that a single short snippet of a speaker's ordinary, read-style speech is sufficient to synthesize high-fidelity ASMR in their voice, eliminating the need for whispered training data from the target speaker. Methodologically, we first identify that discrete speech tokens provide a soft factorization of ASMR style from speaker timbre. Leveraging this insight, we propose a two-stage pipeline incorporating a Large Language Model (LLM) for content-style encoding and a flow-matching acoustic decoder for timbre reconstruction. Furthermore, we contribute DeepASMR-DB, a comprehensive 670-hour English-Chinese multi-speaker ASMR speech corpus, and introduce a novel evaluation protocol integrating objective metrics, human listening tests, LLM-based scoring and unvoiced speech analysis. Extensive experiments confirm that DeepASMR achieves state-of-the-art naturalness and style fidelity in ASMR generation for anyone of any voice, while maintaining competitive performance on normal speech synthesis.
OV-InstructTTS: Towards Open-Vocabulary Instruct Text-to-Speech
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Instruct Text-to-Speech (InstructTTS) leverages natural language descriptions as style prompts to guide speech synthesis. However, existing InstructTTS methods mainly rely on a direct combination of audio-related labels or their diverse rephrasings, making it difficult to handle flexible, high-level instructions. Such rigid control is insufficient for users such as content creators who wish to steer generation with descriptive instructions. To address these constraints, we introduce OV-InstructTTS, a new paradigm for open-vocabulary InstructTTS. We propose a comprehensive solution comprising a newly curated dataset, OV-Speech, and a novel reasoning-driven framework. The OV-Speech dataset pairs speech with open-vocabulary instructions, each augmented with a reasoning process that connects high-level instructions to acoustic features. The reasoning-driven framework infers emotional, acoustic, and paralinguistic information from open-vocabulary instructions before synthesizing speech. Evaluations show that this reasoning-driven approach significantly improves instruction-following fidelity and speech expressiveness. We believe this work can inspire the next user-friendly InstructTTS systems with stronger generalization and real-world applicability. The dataset and demos are publicly available on our project page.
ParkGaussian: Surround-view 3D Gaussian Splatting for Autonomous Parking
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Parking is a critical task for autonomous driving systems (ADS), with unique challenges in crowded parking slots and GPS-denied environments. However, existing works focus on 2D parking slot perception, mapping, and localization, 3D reconstruction remains underexplored, which is crucial for capturing complex spatial geometry in parking scenarios. Naively improving the visual quality of reconstructed parking scenes does not directly benefit autonomous parking, as the key entry point for parking is the slots perception module. To address these limitations, we curate the first benchmark named ParkRecon3D, specifically designed for parking scene reconstruction. It includes sensor data from four surround-view fisheye cameras with calibrated extrinsics and dense parking slot annotations. We then propose ParkGaussian, the first framework that integrates 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) for parking scene reconstruction. To further improve the alignment between reconstruction and downstream parking slot detection, we introduce a slot-aware reconstruction strategy that leverages existing parking perception methods to enhance the synthesis quality of slot regions. Experiments on ParkRecon3D demonstrate that ParkGaussian achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction quality and better preserves perception consistency for downstream tasks. The code and dataset will be released at: https://github.com/wm-research/ParkGaussian
DriveLaW:Unifying Planning and Video Generation in a Latent Driving World
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:World models have become crucial for autonomous driving, as they learn how scenarios evolve over time to address the long-tail challenges of the real world. However, current approaches relegate world models to limited roles: they operate within ostensibly unified architectures that still keep world prediction and motion planning as decoupled processes. To bridge this gap, we propose DriveLaW, a novel paradigm that unifies video generation and motion planning. By directly injecting the latent representation from its video generator into the planner, DriveLaW ensures inherent consistency between high-fidelity future generation and reliable trajectory planning. Specifically, DriveLaW consists of two core components: DriveLaW-Video, our powerful world model that generates high-fidelity forecasting with expressive latent representations, and DriveLaW-Act, a diffusion planner that generates consistent and reliable trajectories from the latent of DriveLaW-Video, with both components optimized by a three-stage progressive training strategy. The power of our unified paradigm is demonstrated by new state-of-the-art results across both tasks. DriveLaW not only advances video prediction significantly, surpassing best-performing work by 33.3% in FID and 1.8% in FVD, but also achieves a new record on the NAVSIM planning benchmark.
Mirage: One-Step Video Diffusion for Photorealistic and Coherent Asset Editing in Driving Scenes
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Vision-centric autonomous driving systems rely on diverse and scalable training data to achieve robust performance. While video object editing offers a promising path for data augmentation, existing methods often struggle to maintain both high visual fidelity and temporal coherence. In this work, we propose \textbf{Mirage}, a one-step video diffusion model for photorealistic and coherent asset editing in driving scenes. Mirage builds upon a text-to-video diffusion prior to ensure temporal consistency across frames. However, 3D causal variational autoencoders often suffer from degraded spatial fidelity due to compression, and directly passing 3D encoder features to decoder layers breaks temporal causality. To address this, we inject temporally agnostic latents from a pretrained 2D encoder into the 3D decoder to restore detail while preserving causal structures. Furthermore, because scene objects and inserted assets are optimized under different objectives, their Gaussians exhibit a distribution mismatch that leads to pose misalignment. To mitigate this, we introduce a two-stage data alignment strategy combining coarse 3D alignment and fine 2D refinement, thereby improving alignment and providing cleaner supervision. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Mirage achieves high realism and temporal consistency across diverse editing scenarios. Beyond asset editing, Mirage can also generalize to other video-to-video translation tasks, serving as a reliable baseline for future research. Our code is available at https://github.com/wm-research/mirage.
CorrectAD: A Self-Correcting Agentic System to Improve End-to-end Planning in Autonomous Driving
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:End-to-end planning methods are the de facto standard of the current autonomous driving system, while the robustness of the data-driven approaches suffers due to the notorious long-tail problem (i.e., rare but safety-critical failure cases). In this work, we explore whether recent diffusion-based video generation methods (a.k.a. world models), paired with structured 3D layouts, can enable a fully automated pipeline to self-correct such failure cases. We first introduce an agent to simulate the role of product manager, dubbed PM-Agent, which formulates data requirements to collect data similar to the failure cases. Then, we use a generative model that can simulate both data collection and annotation. However, existing generative models struggle to generate high-fidelity data conditioned on 3D layouts. To address this, we propose DriveSora, which can generate spatiotemporally consistent videos aligned with the 3D annotations requested by PM-Agent. We integrate these components into our self-correcting agentic system, CorrectAD. Importantly, our pipeline is an end-to-end model-agnostic and can be applied to improve any end-to-end planner. Evaluated on both nuScenes and a more challenging in-house dataset across multiple end-to-end planners, CorrectAD corrects 62.5% and 49.8% of failure cases, reducing collision rates by 39% and 27%, respectively.
Rethinking Driving World Model as Synthetic Data Generator for Perception Tasks
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in driving world models enable controllable generation of high-quality RGB videos or multimodal videos. Existing methods primarily focus on metrics related to generation quality and controllability. However, they often overlook the evaluation of downstream perception tasks, which are $\mathbf{really\ crucial}$ for the performance of autonomous driving. Existing methods usually leverage a training strategy that first pretrains on synthetic data and finetunes on real data, resulting in twice the epochs compared to the baseline (real data only). When we double the epochs in the baseline, the benefit of synthetic data becomes negligible. To thoroughly demonstrate the benefit of synthetic data, we introduce Dream4Drive, a novel synthetic data generation framework designed for enhancing the downstream perception tasks. Dream4Drive first decomposes the input video into several 3D-aware guidance maps and subsequently renders the 3D assets onto these guidance maps. Finally, the driving world model is fine-tuned to produce the edited, multi-view photorealistic videos, which can be used to train the downstream perception models. Dream4Drive enables unprecedented flexibility in generating multi-view corner cases at scale, significantly boosting corner case perception in autonomous driving. To facilitate future research, we also contribute a large-scale 3D asset dataset named DriveObj3D, covering the typical categories in driving scenarios and enabling diverse 3D-aware video editing. We conduct comprehensive experiments to show that Dream4Drive can effectively boost the performance of downstream perception models under various training epochs. Project: $\href{https://wm-research.github.io/Dream4Drive/}{this\ https\ URL}$
Pixel-Perfect Depth with Semantics-Prompted Diffusion Transformers
Oct 08, 2025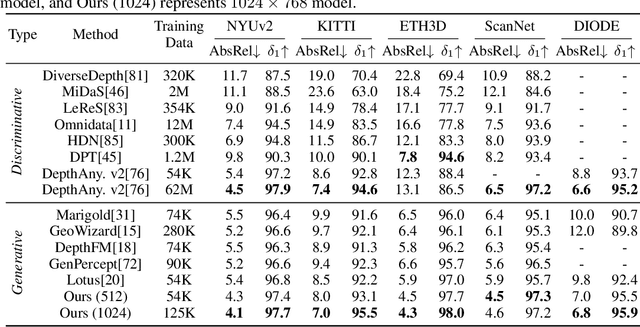

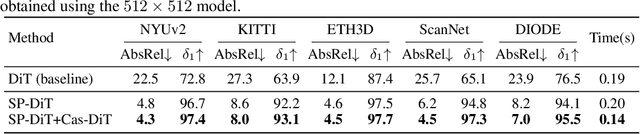
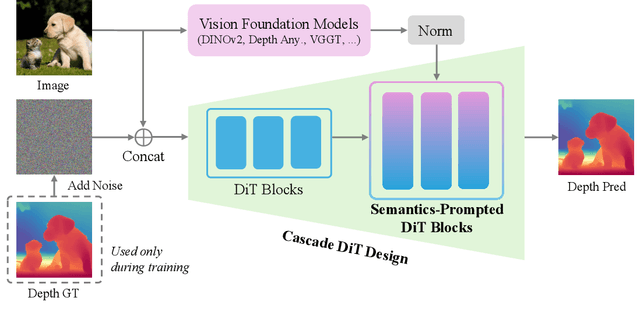
Abstract:This paper presents Pixel-Perfect Depth, a monocular depth estimation model based on pixel-space diffusion generation that produces high-quality, flying-pixel-free point clouds from estimated depth maps. Current generative depth estimation models fine-tune Stable Diffusion and achieve impressive performance. However, they require a VAE to compress depth maps into latent space, which inevitably introduces \textit{flying pixels} at edges and details. Our model addresses this challenge by directly performing diffusion generation in the pixel space, avoiding VAE-induced artifacts. To overcome the high complexity associated with pixel-space generation, we introduce two novel designs: 1) Semantics-Prompted Diffusion Transformers (SP-DiT), which incorporate semantic representations from vision foundation models into DiT to prompt the diffusion process, thereby preserving global semantic consistency while enhancing fine-grained visual details; and 2) Cascade DiT Design that progressively increases the number of tokens to further enhance efficiency and accuracy. Our model achieves the best performance among all published generative models across five benchmarks, and significantly outperforms all other models in edge-aware point cloud evaluation.
Uncovering and Mitigating Destructive Multi-Embedding Attacks in Deepfake Proactive Forensics
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:With the rapid evolution of deepfake technologies and the wide dissemination of digital media, personal privacy is facing increasingly serious security threats. Deepfake proactive forensics, which involves embedding imperceptible watermarks to enable reliable source tracking, serves as a crucial defense against these threats. Although existing methods show strong forensic ability, they rely on an idealized assumption of single watermark embedding, which proves impractical in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we formally define and demonstrate the existence of Multi-Embedding Attacks (MEA) for the first time. When a previously protected image undergoes additional rounds of watermark embedding, the original forensic watermark can be destroyed or removed, rendering the entire proactive forensic mechanism ineffective. To address this vulnerability, we propose a general training paradigm named Adversarial Interference Simulation (AIS). Rather than modifying the network architecture, AIS explicitly simulates MEA scenarios during fine-tuning and introduces a resilience-driven loss function to enforce the learning of sparse and stable watermark representations. Our method enables the model to maintain the ability to extract the original watermark correctly even after a second embedding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our plug-and-play AIS training paradigm significantly enhances the robustness of various existing methods against MEA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge