Weize Li
World In Your Hands: A Large-Scale and Open-source Ecosystem for Learning Human-centric Manipulation in the Wild
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Large-scale pre-training is fundamental for generalization in language and vision models, but data for dexterous hand manipulation remains limited in scale and diversity, hindering policy generalization. Limited scenario diversity, misaligned modalities, and insufficient benchmarking constrain current human manipulation datasets. To address these gaps, we introduce World In Your Hands (WiYH), a large-scale open-source ecosystem for human-centric manipulation learning. WiYH includes (1) the Oracle Suite, a wearable data collection kit with an auto-labeling pipeline for accurate motion capture; (2) the WiYH Dataset, featuring over 1,000 hours of multi-modal manipulation data across hundreds of skills in diverse real-world scenarios; and (3) extensive annotations and benchmarks supporting tasks from perception to action. Furthermore, experiments based on the WiYH ecosystem show that integrating WiYH's human-centric data significantly enhances the generalization and robustness of dexterous hand policies in tabletop manipulation tasks. We believe that World In Your Hands will bring new insights into human-centric data collection and policy learning to the community.
Taming VR Teleoperation and Learning from Demonstration for Multi-Task Bimanual Table Service Manipulation
Aug 21, 2025
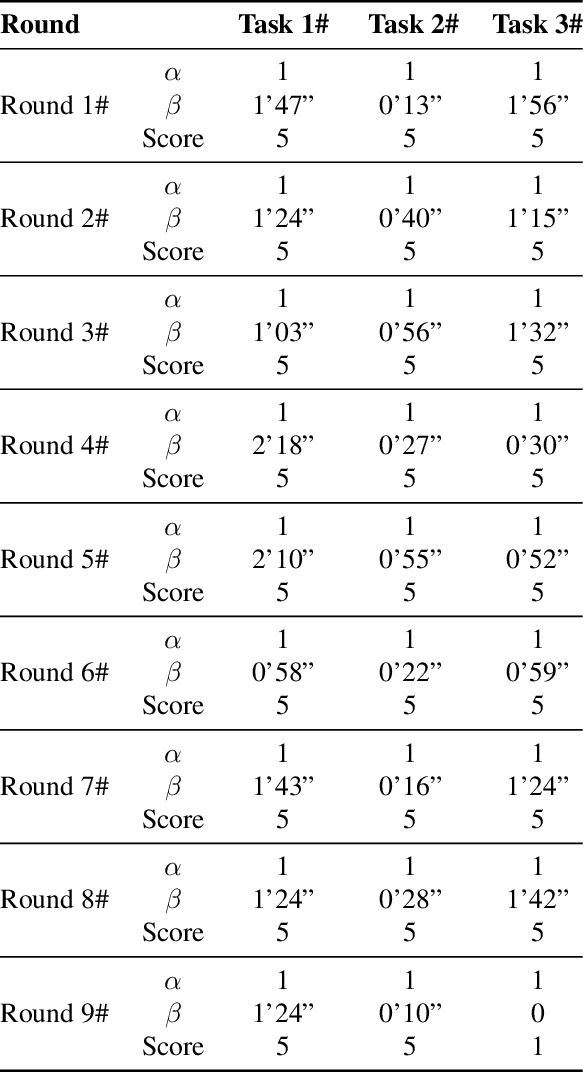
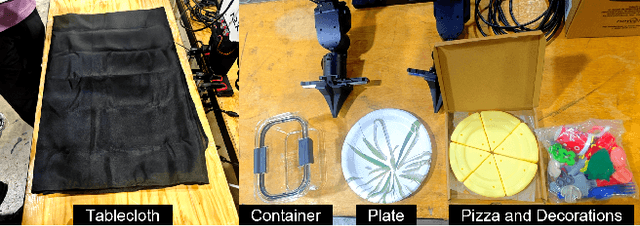

Abstract:This technical report presents the champion solution of the Table Service Track in the ICRA 2025 What Bimanuals Can Do (WBCD) competition. We tackled a series of demanding tasks under strict requirements for speed, precision, and reliability: unfolding a tablecloth (deformable-object manipulation), placing a pizza into the container (pick-and-place), and opening and closing a food container with the lid. Our solution combines VR-based teleoperation and Learning from Demonstrations (LfD) to balance robustness and autonomy. Most subtasks were executed through high-fidelity remote teleoperation, while the pizza placement was handled by an ACT-based policy trained from 100 in-person teleoperated demonstrations with randomized initial configurations. By carefully integrating scoring rules, task characteristics, and current technical capabilities, our approach achieved both high efficiency and reliability, ultimately securing the first place in the competition.
PosePilot: Steering Camera Pose for Generative World Models with Self-supervised Depth
May 03, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in autonomous driving (AD) systems have highlighted the potential of world models in achieving robust and generalizable performance across both ordinary and challenging driving conditions. However, a key challenge remains: precise and flexible camera pose control, which is crucial for accurate viewpoint transformation and realistic simulation of scene dynamics. In this paper, we introduce PosePilot, a lightweight yet powerful framework that significantly enhances camera pose controllability in generative world models. Drawing inspiration from self-supervised depth estimation, PosePilot leverages structure-from-motion principles to establish a tight coupling between camera pose and video generation. Specifically, we incorporate self-supervised depth and pose readouts, allowing the model to infer depth and relative camera motion directly from video sequences. These outputs drive pose-aware frame warping, guided by a photometric warping loss that enforces geometric consistency across synthesized frames. To further refine camera pose estimation, we introduce a reverse warping step and a pose regression loss, improving viewpoint precision and adaptability. Extensive experiments on autonomous driving and general-domain video datasets demonstrate that PosePilot significantly enhances structural understanding and motion reasoning in both diffusion-based and auto-regressive world models. By steering camera pose with self-supervised depth, PosePilot sets a new benchmark for pose controllability, enabling physically consistent, reliable viewpoint synthesis in generative world models.
CPAny: Couple With Any Encoder to Refer Multi-Object Tracking
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Referring Multi-Object Tracking (RMOT) aims to localize target trajectories specified by natural language expressions in videos. Existing RMOT methods mainly follow two paradigms, namely, one-stage strategies and two-stage ones. The former jointly trains tracking with referring but suffers from substantial computational overhead. Although the latter improves computational efficiency, its CLIP-inspired dual-tower architecture restricts compatibility with other visual/text backbones and is not future-proof. To overcome these limitations, we propose CPAny, a novel encoder-decoder framework for two-stage RMOT, which introduces two core components: (1) a Contextual Visual Semantic Abstractor (CVSA) performs context-aware aggregation on visual backbone features and projects them into a unified semantic space; (2) a Parallel Semantic Summarizer (PSS) decodes the visual and linguistic features at the semantic level in parallel and generates referring scores. By replacing the inherent feature alignment of encoders with a self-constructed unified semantic space, CPAny achieves flexible compatibility with arbitrary emerging visual / text encoders. Meanwhile, CPAny aggregates contextual information by encoding only once and processes multiple expressions in parallel, significantly reducing computational redundancy. Extensive experiments on the Refer-KITTI and Refer-KITTI-V2 datasets show that CPAny outperforms SOTA methods across diverse encoder combinations, with a particular 7.77\% HOTA improvement on Refer-KITTI-V2. Code will be available soon.
Bring Adaptive Binding Prototypes to Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation
May 24, 2024



Abstract:Referring Expression Segmentation (RES) has attracted rising attention, aiming to identify and segment objects based on natural language expressions. While substantial progress has been made in RES, the emergence of Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation (GRES) introduces new challenges by allowing expressions to describe multiple objects or lack specific object references. Existing RES methods, usually rely on sophisticated encoder-decoder and feature fusion modules, and are difficult to generate class prototypes that match each instance individually when confronted with the complex referent and binary labels of GRES. In this paper, reevaluating the differences between RES and GRES, we propose a novel Model with Adaptive Binding Prototypes (MABP) that adaptively binds queries to object features in the corresponding region. It enables different query vectors to match instances of different categories or different parts of the same instance, significantly expanding the decoder's flexibility, dispersing global pressure across all queries, and easing the demands on the encoder. Experimental results demonstrate that MABP significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in all three splits on gRefCOCO dataset. Meanwhile, MABP also surpasses state-of-the-art methods on RefCOCO+ and G-Ref datasets, and achieves very competitive results on RefCOCO. Code is available at https://github.com/buptLwz/MABP
TOD3Cap: Towards 3D Dense Captioning in Outdoor Scenes
Mar 28, 2024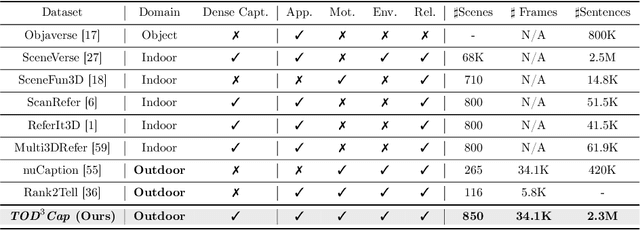
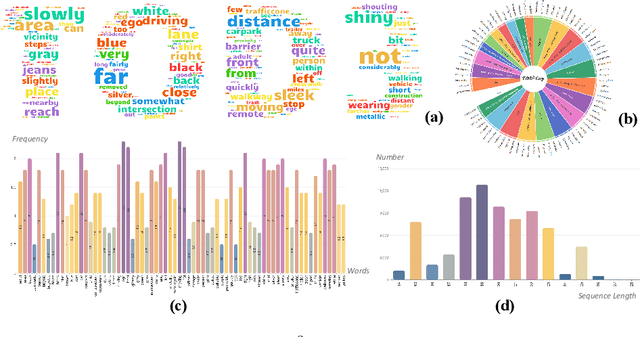

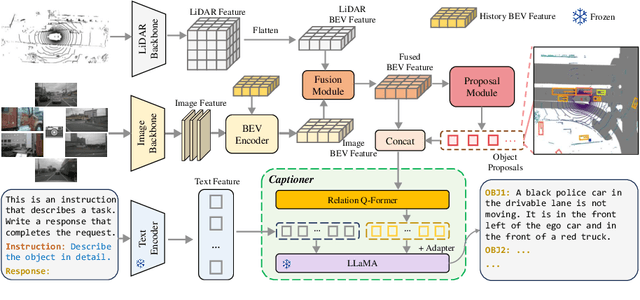
Abstract:3D dense captioning stands as a cornerstone in achieving a comprehensive understanding of 3D scenes through natural language. It has recently witnessed remarkable achievements, particularly in indoor settings. However, the exploration of 3D dense captioning in outdoor scenes is hindered by two major challenges: 1) the \textbf{domain gap} between indoor and outdoor scenes, such as dynamics and sparse visual inputs, makes it difficult to directly adapt existing indoor methods; 2) the \textbf{lack of data} with comprehensive box-caption pair annotations specifically tailored for outdoor scenes. To this end, we introduce the new task of outdoor 3D dense captioning. As input, we assume a LiDAR point cloud and a set of RGB images captured by the panoramic camera rig. The expected output is a set of object boxes with captions. To tackle this task, we propose the TOD3Cap network, which leverages the BEV representation to generate object box proposals and integrates Relation Q-Former with LLaMA-Adapter to generate rich captions for these objects. We also introduce the TOD3Cap dataset, the largest one to our knowledge for 3D dense captioning in outdoor scenes, which contains 2.3M descriptions of 64.3K outdoor objects from 850 scenes. Notably, our TOD3Cap network can effectively localize and caption 3D objects in outdoor scenes, which outperforms baseline methods by a significant margin (+9.6 CiDEr@0.5IoU). Code, data, and models are publicly available at https://github.com/jxbbb/TOD3Cap.
PAD: A Dataset and Benchmark for Pose-agnostic Anomaly Detection
Oct 11, 2023



Abstract:Object anomaly detection is an important problem in the field of machine vision and has seen remarkable progress recently. However, two significant challenges hinder its research and application. First, existing datasets lack comprehensive visual information from various pose angles. They usually have an unrealistic assumption that the anomaly-free training dataset is pose-aligned, and the testing samples have the same pose as the training data. However, in practice, anomaly may exist in any regions on a object, the training and query samples may have different poses, calling for the study on pose-agnostic anomaly detection. Second, the absence of a consensus on experimental protocols for pose-agnostic anomaly detection leads to unfair comparisons of different methods, hindering the research on pose-agnostic anomaly detection. To address these issues, we develop Multi-pose Anomaly Detection (MAD) dataset and Pose-agnostic Anomaly Detection (PAD) benchmark, which takes the first step to address the pose-agnostic anomaly detection problem. Specifically, we build MAD using 20 complex-shaped LEGO toys including 4K views with various poses, and high-quality and diverse 3D anomalies in both simulated and real environments. Additionally, we propose a novel method OmniposeAD, trained using MAD, specifically designed for pose-agnostic anomaly detection. Through comprehensive evaluations, we demonstrate the relevance of our dataset and method. Furthermore, we provide an open-source benchmark library, including dataset and baseline methods that cover 8 anomaly detection paradigms, to facilitate future research and application in this domain. Code, data, and models are publicly available at https://github.com/EricLee0224/PAD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge