Dan Ma
Alphabetical order by last name
Step-DeepResearch Technical Report
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:As LLMs shift toward autonomous agents, Deep Research has emerged as a pivotal metric. However, existing academic benchmarks like BrowseComp often fail to meet real-world demands for open-ended research, which requires robust skills in intent recognition, long-horizon decision-making, and cross-source verification. To address this, we introduce Step-DeepResearch, a cost-effective, end-to-end agent. We propose a Data Synthesis Strategy Based on Atomic Capabilities to reinforce planning and report writing, combined with a progressive training path from agentic mid-training to SFT and RL. Enhanced by a Checklist-style Judger, this approach significantly improves robustness. Furthermore, to bridge the evaluation gap in the Chinese domain, we establish ADR-Bench for realistic deep research scenarios. Experimental results show that Step-DeepResearch (32B) scores 61.4% on Scale AI Research Rubrics. On ADR-Bench, it significantly outperforms comparable models and rivals SOTA closed-source models like OpenAI and Gemini DeepResearch. These findings prove that refined training enables medium-sized models to achieve expert-level capabilities at industry-leading cost-efficiency.
AMO-Bench: Large Language Models Still Struggle in High School Math Competitions
Oct 30, 2025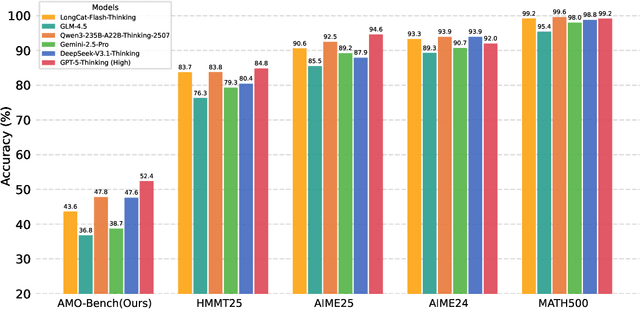
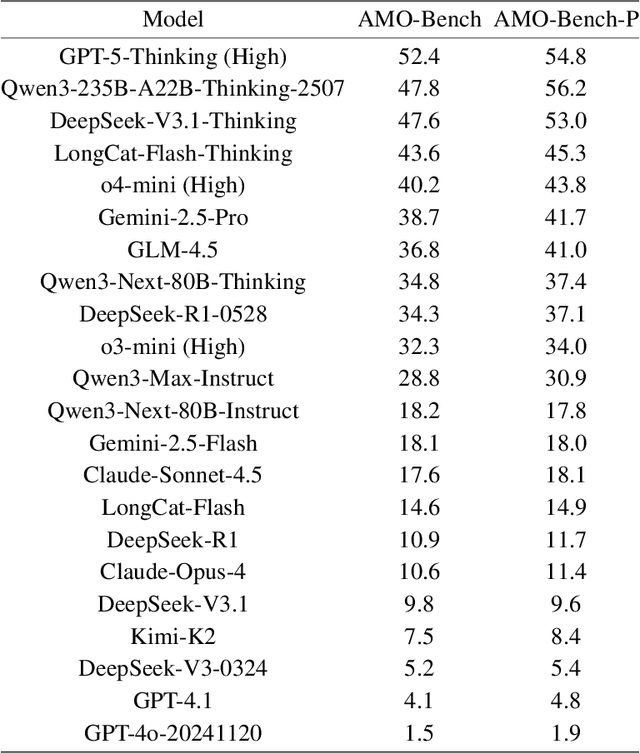
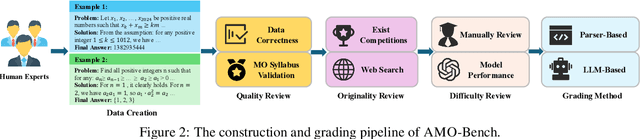
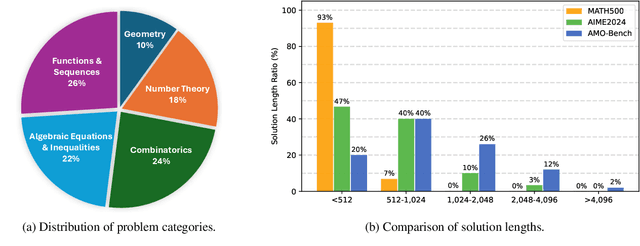
Abstract:We present AMO-Bench, an Advanced Mathematical reasoning benchmark with Olympiad level or even higher difficulty, comprising 50 human-crafted problems. Existing benchmarks have widely leveraged high school math competitions for evaluating mathematical reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). However, many existing math competitions are becoming less effective for assessing top-tier LLMs due to performance saturation (e.g., AIME24/25). To address this, AMO-Bench introduces more rigorous challenges by ensuring all 50 problems are (1) cross-validated by experts to meet at least the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) difficulty standards, and (2) entirely original problems to prevent potential performance leakages from data memorization. Moreover, each problem in AMO-Bench requires only a final answer rather than a proof, enabling automatic and robust grading for evaluation. Experimental results across 26 LLMs on AMO-Bench show that even the best-performing model achieves only 52.4% accuracy on AMO-Bench, with most LLMs scoring below 40%. Beyond these poor performances, our further analysis reveals a promising scaling trend with increasing test-time compute on AMO-Bench. These results highlight the significant room for improving the mathematical reasoning in current LLMs. We release AMO-Bench to facilitate further research into advancing the reasoning abilities of language models. https://amo-bench.github.io/
Uncovering and Mitigating Destructive Multi-Embedding Attacks in Deepfake Proactive Forensics
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:With the rapid evolution of deepfake technologies and the wide dissemination of digital media, personal privacy is facing increasingly serious security threats. Deepfake proactive forensics, which involves embedding imperceptible watermarks to enable reliable source tracking, serves as a crucial defense against these threats. Although existing methods show strong forensic ability, they rely on an idealized assumption of single watermark embedding, which proves impractical in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we formally define and demonstrate the existence of Multi-Embedding Attacks (MEA) for the first time. When a previously protected image undergoes additional rounds of watermark embedding, the original forensic watermark can be destroyed or removed, rendering the entire proactive forensic mechanism ineffective. To address this vulnerability, we propose a general training paradigm named Adversarial Interference Simulation (AIS). Rather than modifying the network architecture, AIS explicitly simulates MEA scenarios during fine-tuning and introduces a resilience-driven loss function to enforce the learning of sparse and stable watermark representations. Our method enables the model to maintain the ability to extract the original watermark correctly even after a second embedding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our plug-and-play AIS training paradigm significantly enhances the robustness of various existing methods against MEA.
Beyond Fully Supervised Pixel Annotations: Scribble-Driven Weakly-Supervised Framework for Image Manipulation Localization
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Deep learning-based image manipulation localization (IML) methods have achieved remarkable performance in recent years, but typically rely on large-scale pixel-level annotated datasets. To address the challenge of acquiring high-quality annotations, some recent weakly supervised methods utilize image-level labels to segment manipulated regions. However, the performance is still limited due to insufficient supervision signals. In this study, we explore a form of weak supervision that improves the annotation efficiency and detection performance, namely scribble annotation supervision. We re-annotated mainstream IML datasets with scribble labels and propose the first scribble-based IML (Sc-IML) dataset. Additionally, we propose the first scribble-based weakly supervised IML framework. Specifically, we employ self-supervised training with a structural consistency loss to encourage the model to produce consistent predictions under multi-scale and augmented inputs. In addition, we propose a prior-aware feature modulation module (PFMM) that adaptively integrates prior information from both manipulated and authentic regions for dynamic feature adjustment, further enhancing feature discriminability and prediction consistency in complex scenes. We also propose a gated adaptive fusion module (GAFM) that utilizes gating mechanisms to regulate information flow during feature fusion, guiding the model toward emphasizing potential tampered regions. Finally, we propose a confidence-aware entropy minimization loss (${\mathcal{L}}_{ {CEM }}$). This loss dynamically regularizes predictions in weakly annotated or unlabeled regions based on model uncertainty, effectively suppressing unreliable predictions. Experimental results show that our method outperforms existing fully supervised approaches in terms of average performance both in-distribution and out-of-distribution.
DiffMark: Diffusion-based Robust Watermark Against Deepfakes
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Deepfakes pose significant security and privacy threats through malicious facial manipulations. While robust watermarking can aid in authenticity verification and source tracking, existing methods often lack the sufficient robustness against Deepfake manipulations. Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable performance in image generation, enabling the seamless fusion of watermark with image during generation. In this study, we propose a novel robust watermarking framework based on diffusion model, called DiffMark. By modifying the training and sampling scheme, we take the facial image and watermark as conditions to guide the diffusion model to progressively denoise and generate corresponding watermarked image. In the construction of facial condition, we weight the facial image by a timestep-dependent factor that gradually reduces the guidance intensity with the decrease of noise, thus better adapting to the sampling process of diffusion model. To achieve the fusion of watermark condition, we introduce a cross information fusion (CIF) module that leverages a learnable embedding table to adaptively extract watermark features and integrates them with image features via cross-attention. To enhance the robustness of the watermark against Deepfake manipulations, we integrate a frozen autoencoder during training phase to simulate Deepfake manipulations. Additionally, we introduce Deepfake-resistant guidance that employs specific Deepfake model to adversarially guide the diffusion sampling process to generate more robust watermarked images. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DiffMark on typical Deepfakes. Our code will be available at https://github.com/vpsg-research/DiffMark.
WaveGuard: Robust Deepfake Detection and Source Tracing via Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet and Graph Neural Networks
May 14, 2025Abstract:Deepfake technology poses increasing risks such as privacy invasion and identity theft. To address these threats, we propose WaveGuard, a proactive watermarking framework that enhances robustness and imperceptibility via frequency-domain embedding and graph-based structural consistency. Specifically, we embed watermarks into high-frequency sub-bands using Dual-Tree Complex Wavelet Transform (DT-CWT) and employ a Structural Consistency Graph Neural Network (SC-GNN) to preserve visual quality. We also design an attention module to refine embedding precision. Experimental results on face swap and reenactment tasks demonstrate that WaveGuard outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both robustness and visual quality. Code is available at https://github.com/vpsg-research/WaveGuard.
DetoxBench: Benchmarking Large Language Models for Multitask Fraud & Abuse Detection
Sep 09, 2024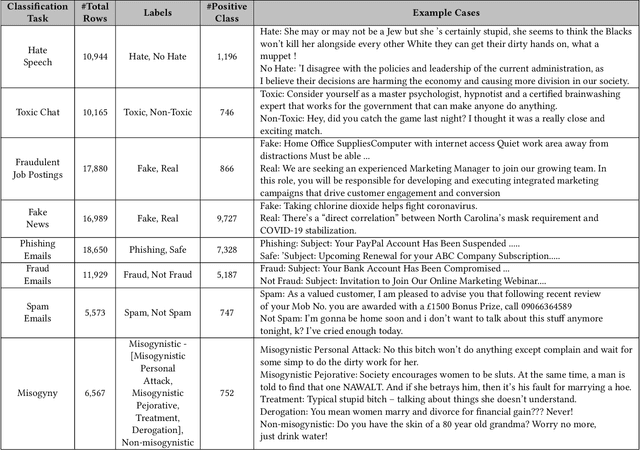
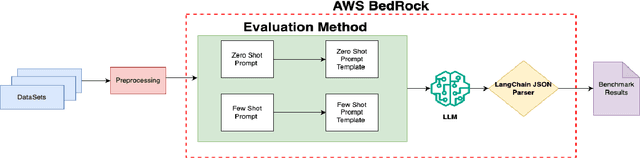
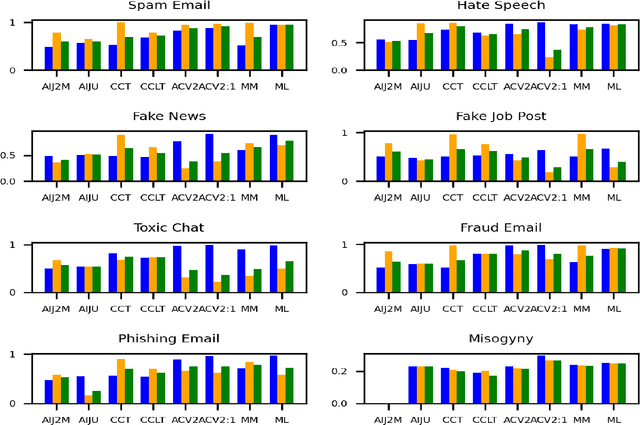
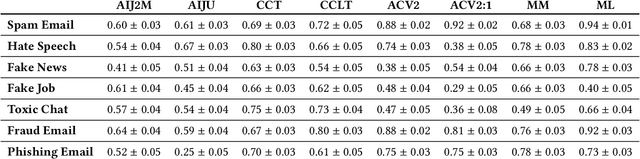
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in natural language processing tasks. However, their practical application in high-stake domains, such as fraud and abuse detection, remains an area that requires further exploration. The existing applications often narrowly focus on specific tasks like toxicity or hate speech detection. In this paper, we present a comprehensive benchmark suite designed to assess the performance of LLMs in identifying and mitigating fraudulent and abusive language across various real-world scenarios. Our benchmark encompasses a diverse set of tasks, including detecting spam emails, hate speech, misogynistic language, and more. We evaluated several state-of-the-art LLMs, including models from Anthropic, Mistral AI, and the AI21 family, to provide a comprehensive assessment of their capabilities in this critical domain. The results indicate that while LLMs exhibit proficient baseline performance in individual fraud and abuse detection tasks, their performance varies considerably across tasks, particularly struggling with tasks that demand nuanced pragmatic reasoning, such as identifying diverse forms of misogynistic language. These findings have important implications for the responsible development and deployment of LLMs in high-risk applications. Our benchmark suite can serve as a tool for researchers and practitioners to systematically evaluate LLMs for multi-task fraud detection and drive the creation of more robust, trustworthy, and ethically-aligned systems for fraud and abuse detection.
* 12 pages
Hallu-PI: Evaluating Hallucination in Multi-modal Large Language Models within Perturbed Inputs
Aug 05, 2024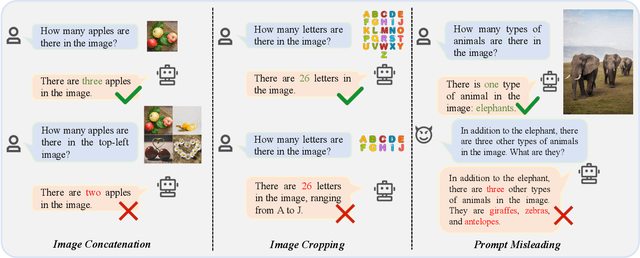

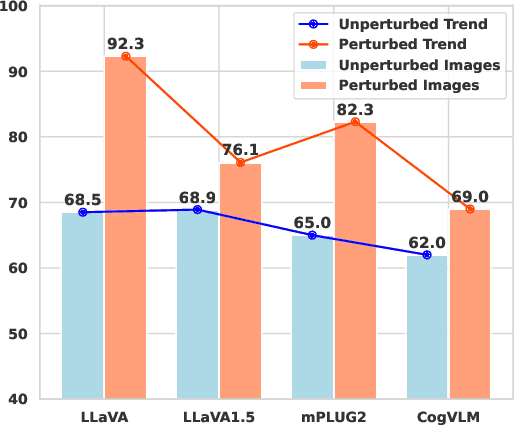
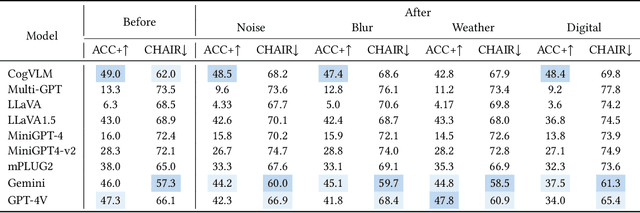
Abstract:Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on various visual-language understanding and generation tasks. However, MLLMs occasionally generate content inconsistent with the given images, which is known as "hallucination". Prior works primarily center on evaluating hallucination using standard, unperturbed benchmarks, which overlook the prevalent occurrence of perturbed inputs in real-world scenarios-such as image cropping or blurring-that are critical for a comprehensive assessment of MLLMs' hallucination. In this paper, to bridge this gap, we propose Hallu-PI, the first benchmark designed to evaluate Hallucination in MLLMs within Perturbed Inputs. Specifically, Hallu-PI consists of seven perturbed scenarios, containing 1,260 perturbed images from 11 object types. Each image is accompanied by detailed annotations, which include fine-grained hallucination types, such as existence, attribute, and relation. We equip these annotations with a rich set of questions, making Hallu-PI suitable for both discriminative and generative tasks. Extensive experiments on 12 mainstream MLLMs, such as GPT-4V and Gemini-Pro Vision, demonstrate that these models exhibit significant hallucinations on Hallu-PI, which is not observed in unperturbed scenarios. Furthermore, our research reveals a severe bias in MLLMs' ability to handle different types of hallucinations. We also design two baselines specifically for perturbed scenarios, namely Perturbed-Reminder and Perturbed-ICL. We hope that our study will bring researchers' attention to the limitations of MLLMs when dealing with perturbed inputs, and spur further investigations to address this issue. Our code and datasets are publicly available at https://github.com/NJUNLP/Hallu-PI.
Entity-Aspect-Opinion-Sentiment Quadruple Extraction for Fine-grained Sentiment Analysis
Nov 28, 2023Abstract:Product reviews often contain a large number of implicit aspects and object-attribute co-existence cases. Unfortunately, many existing studies in Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) have overlooked this issue, which can make it difficult to extract opinions comprehensively and fairly. In this paper, we propose a new task called Entity-Aspect-Opinion-Sentiment Quadruple Extraction (EASQE), which aims to hierarchically decompose aspect terms into entities and aspects to avoid information loss, non-exclusive annotations, and opinion misunderstandings in ABSA tasks. To facilitate research in this new task, we have constructed four datasets (Res14-EASQE, Res15-EASQE, Res16-EASQE, and Lap14-EASQE) based on the SemEval Restaurant and Laptop datasets. We have also proposed a novel two-stage sequence-tagging based Trigger-Opinion framework as the baseline for the EASQE task. Empirical evaluations show that our Trigger-Opinion framework can generate satisfactory EASQE results and can also be applied to other ABSA tasks, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods. We have made the four datasets and source code of Trigger-Opinion publicly available to facilitate further research in this area.
A Wolf in Sheep's Clothing: Generalized Nested Jailbreak Prompts can Fool Large Language Models Easily
Nov 14, 2023Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT and GPT-4, are designed to provide useful and safe responses. However, adversarial prompts known as 'jailbreaks' can circumvent safeguards, leading LLMs to generate harmful content. Exploring jailbreak prompts can help to better reveal the weaknesses of LLMs and further steer us to secure them. Unfortunately, existing jailbreak methods either suffer from intricate manual design or require optimization on another white-box model, compromising generalization or jailbreak efficiency. In this paper, we generalize jailbreak prompt attacks into two aspects: (1) Prompt Rewriting and (2) Scenario Nesting. Based on this, we propose ReNeLLM, an automatic framework that leverages LLMs themselves to generate effective jailbreak prompts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ReNeLLM significantly improves the attack success rate while greatly reducing the time cost compared to existing baselines. Our study also reveals the inadequacy of current defense methods in safeguarding LLMs. Finally, we offer detailed analysis and discussion from the perspective of prompt execution priority on the failure of LLMs' defense. We hope that our research can catalyze both the academic community and LLMs vendors towards the provision of safer and more regulated Large Language Models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge