Songlin Li
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Rubric-Based Benchmarking and Reinforcement Learning for Advancing LLM Instruction Following
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has led to impressive performance on a range of tasks, yet advanced instruction following (IF)-especially for complex, multi-turn, and system-prompted instructions-remains a significant challenge. Rigorous evaluation and effective training for such capabilities are hindered by the lack of high-quality, human-annotated benchmarks and reliable, interpretable reward signals. In this work, we introduce AdvancedIF (we will release this benchmark soon), a comprehensive benchmark featuring over 1,600 prompts and expert-curated rubrics that assess LLMs ability to follow complex, multi-turn, and system-level instructions. We further propose RIFL (Rubric-based Instruction-Following Learning), a novel post-training pipeline that leverages rubric generation, a finetuned rubric verifier, and reward shaping to enable effective reinforcement learning for instruction following. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RIFL substantially improves the instruction-following abilities of LLMs, achieving a 6.7% absolute gain on AdvancedIF and strong results on public benchmarks. Our ablation studies confirm the effectiveness of each component in RIFL. This work establishes rubrics as a powerful tool for both training and evaluating advanced IF in LLMs, paving the way for more capable and reliable AI systems.
Large Model Empowered Embodied AI: A Survey on Decision-Making and Embodied Learning
Aug 14, 2025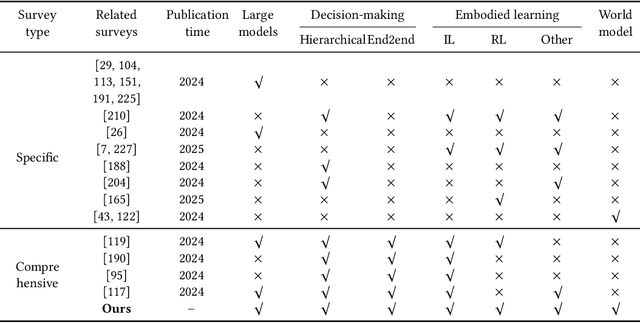
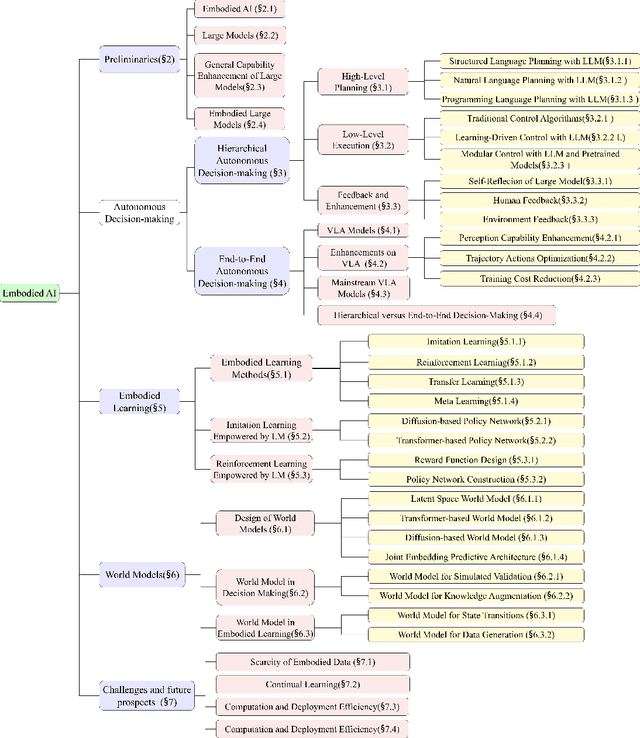
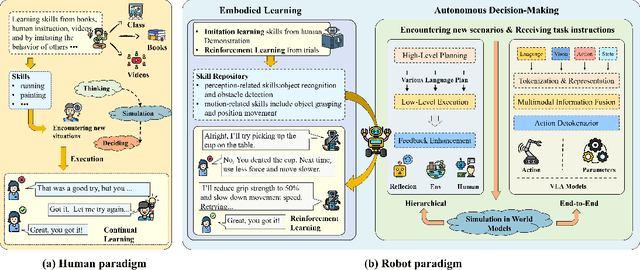
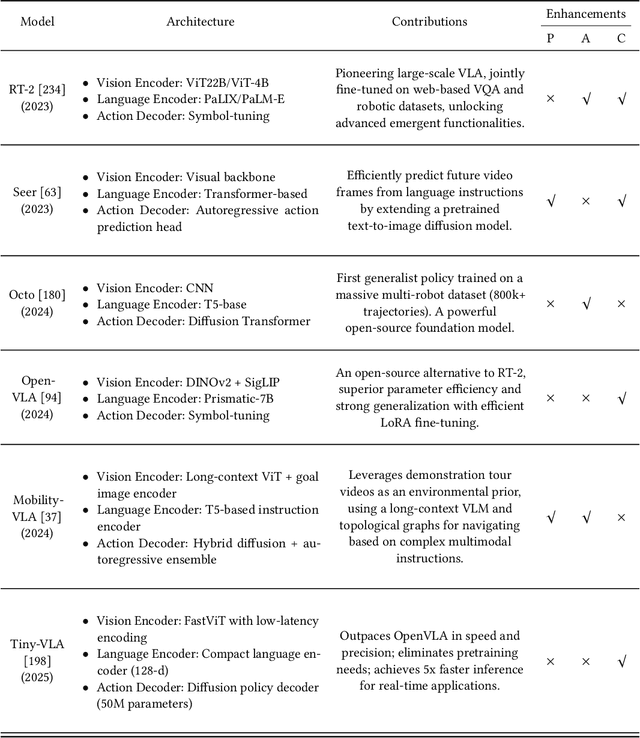
Abstract:Embodied AI aims to develop intelligent systems with physical forms capable of perceiving, decision-making, acting, and learning in real-world environments, providing a promising way to Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). Despite decades of explorations, it remains challenging for embodied agents to achieve human-level intelligence for general-purpose tasks in open dynamic environments. Recent breakthroughs in large models have revolutionized embodied AI by enhancing perception, interaction, planning and learning. In this article, we provide a comprehensive survey on large model empowered embodied AI, focusing on autonomous decision-making and embodied learning. We investigate both hierarchical and end-to-end decision-making paradigms, detailing how large models enhance high-level planning, low-level execution, and feedback for hierarchical decision-making, and how large models enhance Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models for end-to-end decision making. For embodied learning, we introduce mainstream learning methodologies, elaborating on how large models enhance imitation learning and reinforcement learning in-depth. For the first time, we integrate world models into the survey of embodied AI, presenting their design methods and critical roles in enhancing decision-making and learning. Though solid advances have been achieved, challenges still exist, which are discussed at the end of this survey, potentially as the further research directions.
Bridging Semantic Logic Gaps: A Cognition-Inspired Multimodal Boundary-Preserving Network for Image Manipulation Localization
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:The existing image manipulation localization (IML) models mainly relies on visual cues, but ignores the semantic logical relationships between content features. In fact, the content semantics conveyed by real images often conform to human cognitive laws. However, image manipulation technology usually destroys the internal relationship between content features, thus leaving semantic clues for IML. In this paper, we propose a cognition-inspired multimodal boundary-preserving network (CMB-Net). Specifically, CMB-Net utilizes large language models (LLMs) to analyze manipulated regions within images and generate prompt-based textual information to compensate for the lack of semantic relationships in the visual information. Considering that the erroneous texts induced by hallucination from LLMs will damage the accuracy of IML, we propose an image-text central ambiguity module (ITCAM). It assigns weights to the text features by quantifying the ambiguity between text and image features, thereby ensuring the beneficial impact of textual information. We also propose an image-text interaction module (ITIM) that aligns visual and text features using a correlation matrix for fine-grained interaction. Finally, inspired by invertible neural networks, we propose a restoration edge decoder (RED) that mutually generates input and output features to preserve boundary information in manipulated regions without loss. Extensive experiments show that CMB-Net outperforms most existing IML models.
Beyond Fully Supervised Pixel Annotations: Scribble-Driven Weakly-Supervised Framework for Image Manipulation Localization
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Deep learning-based image manipulation localization (IML) methods have achieved remarkable performance in recent years, but typically rely on large-scale pixel-level annotated datasets. To address the challenge of acquiring high-quality annotations, some recent weakly supervised methods utilize image-level labels to segment manipulated regions. However, the performance is still limited due to insufficient supervision signals. In this study, we explore a form of weak supervision that improves the annotation efficiency and detection performance, namely scribble annotation supervision. We re-annotated mainstream IML datasets with scribble labels and propose the first scribble-based IML (Sc-IML) dataset. Additionally, we propose the first scribble-based weakly supervised IML framework. Specifically, we employ self-supervised training with a structural consistency loss to encourage the model to produce consistent predictions under multi-scale and augmented inputs. In addition, we propose a prior-aware feature modulation module (PFMM) that adaptively integrates prior information from both manipulated and authentic regions for dynamic feature adjustment, further enhancing feature discriminability and prediction consistency in complex scenes. We also propose a gated adaptive fusion module (GAFM) that utilizes gating mechanisms to regulate information flow during feature fusion, guiding the model toward emphasizing potential tampered regions. Finally, we propose a confidence-aware entropy minimization loss (${\mathcal{L}}_{ {CEM }}$). This loss dynamically regularizes predictions in weakly annotated or unlabeled regions based on model uncertainty, effectively suppressing unreliable predictions. Experimental results show that our method outperforms existing fully supervised approaches in terms of average performance both in-distribution and out-of-distribution.
DGSense: A Domain Generalization Framework for Wireless Sensing
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Wireless sensing is of great benefits to our daily lives. However, wireless signals are sensitive to the surroundings. Various factors, e.g. environments, locations, and individuals, may induce extra impact on wireless propagation. Such a change can be regarded as a domain, in which the data distribution shifts. A vast majority of the sensing schemes are learning-based. They are dependent on the training domains, resulting in performance degradation in unseen domains. Researchers have proposed various solutions to address this issue. But these solutions leverage either semi-supervised or unsupervised domain adaptation techniques. They still require some data in the target domains and do not perform well in unseen domains. In this paper, we propose a domain generalization framework DGSense, to eliminate the domain dependence problem in wireless sensing. The framework is a general solution working across diverse sensing tasks and wireless technologies. Once the sensing model is built, it can generalize to unseen domains without any data from the target domain. To achieve the goal, we first increase the diversity of the training set by a virtual data generator, and then extract the domain independent features via episodic training between the main feature extractor and the domain feature extractors. The feature extractors employ a pre-trained Residual Network (ResNet) with an attention mechanism for spatial features, and a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (1DCNN) for temporal features. To demonstrate the effectiveness and generality of DGSense, we evaluated on WiFi gesture recognition, Millimeter Wave (mmWave) activity recognition, and acoustic fall detection. All the systems exhibited high generalization capability to unseen domains, including new users, locations, and environments, free of new data and retraining.
What You See Is What Matters: A Novel Visual and Physics-Based Metric for Evaluating Video Generation Quality
Nov 20, 2024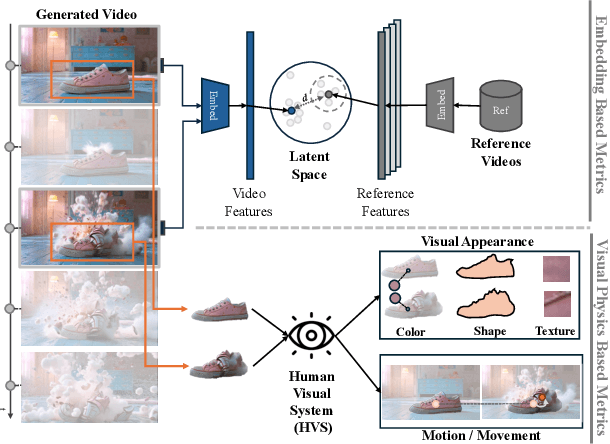
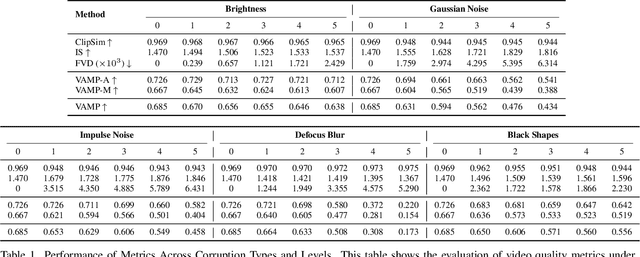
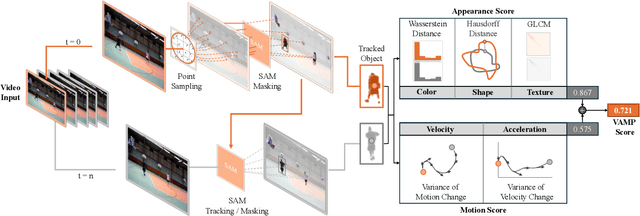
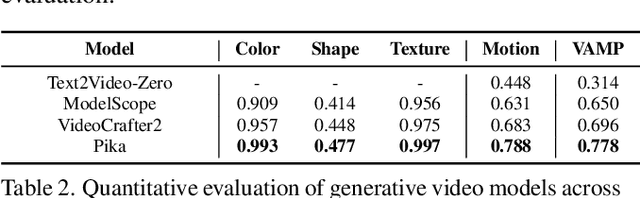
Abstract:As video generation models advance rapidly, assessing the quality of generated videos has become increasingly critical. Existing metrics, such as Fr\'echet Video Distance (FVD), Inception Score (IS), and ClipSim, measure quality primarily in latent space rather than from a human visual perspective, often overlooking key aspects like appearance and motion consistency to physical laws. In this paper, we propose a novel metric, VAMP (Visual Appearance and Motion Plausibility), that evaluates both the visual appearance and physical plausibility of generated videos. VAMP is composed of two main components: an appearance score, which assesses color, shape, and texture consistency across frames, and a motion score, which evaluates the realism of object movements. We validate VAMP through two experiments: corrupted video evaluation and generated video evaluation. In the corrupted video evaluation, we introduce various types of corruptions into real videos and measure the correlation between corruption severity and VAMP scores. In the generated video evaluation, we use state-of-the-art models to generate videos from carefully designed prompts and compare VAMP's performance to human evaluators' rankings. Our results demonstrate that VAMP effectively captures both visual fidelity and temporal consistency, offering a more comprehensive evaluation of video quality than traditional methods.
PASTA: Controllable Part-Aware Shape Generation with Autoregressive Transformers
Jul 18, 2024
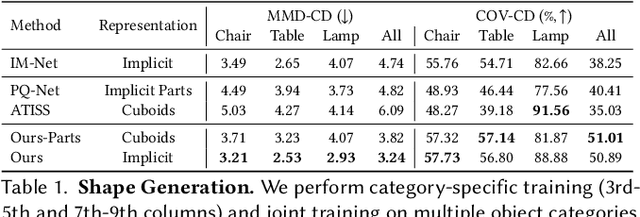


Abstract:The increased demand for tools that automate the 3D content creation process led to tremendous progress in deep generative models that can generate diverse 3D objects of high fidelity. In this paper, we present PASTA, an autoregressive transformer architecture for generating high quality 3D shapes. PASTA comprises two main components: An autoregressive transformer that generates objects as a sequence of cuboidal primitives and a blending network, implemented with a transformer decoder that composes the sequences of cuboids and synthesizes high quality meshes for each object. Our model is trained in two stages: First we train our autoregressive generative model using only annotated cuboidal parts as supervision and next, we train our blending network using explicit 3D supervision, in the form of watertight meshes. Evaluations on various ShapeNet objects showcase the ability of our model to perform shape generation from diverse inputs \eg from scratch, from a partial object, from text and images, as well size-guided generation, by explicitly conditioning on a bounding box that defines the object's boundaries. Moreover, as our model considers the underlying part-based structure of a 3D object, we are able to select a specific part and produce shapes with meaningful variations of this part. As evidenced by our experiments, our model generates 3D shapes that are both more realistic and diverse than existing part-based and non part-based methods, while at the same time is simpler to implement and train.
An Unsupervised Masking Objective for Abstractive Multi-Document News Summarization
Jan 07, 2022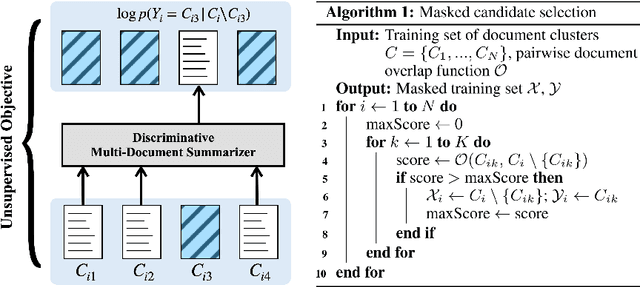

Abstract:We show that a simple unsupervised masking objective can approach near supervised performance on abstractive multi-document news summarization. Our method trains a state-of-the-art neural summarization model to predict the masked out source document with highest lexical centrality relative to the multi-document group. In experiments on the Multi-News dataset, our masked training objective yields a system that outperforms past unsupervised methods and, in human evaluation, surpasses the best supervised method without requiring access to any ground-truth summaries. Further, we evaluate how different measures of lexical centrality, inspired by past work on extractive summarization, affect final performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge