Sixu Yan
ReCogDrive: A Reinforced Cognitive Framework for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Jun 09, 2025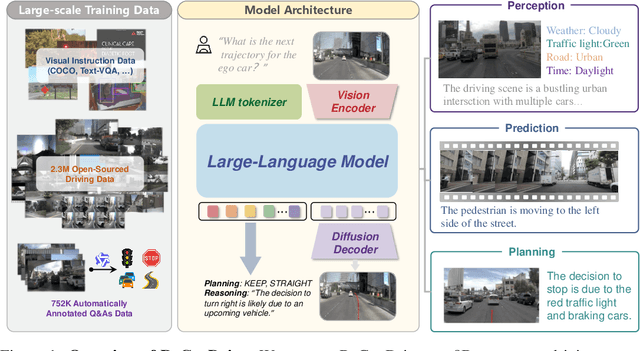
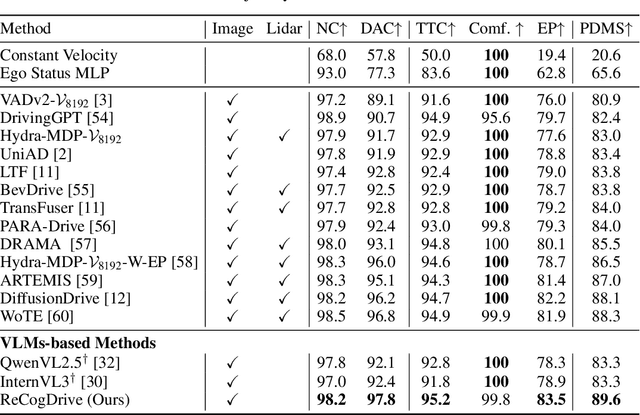
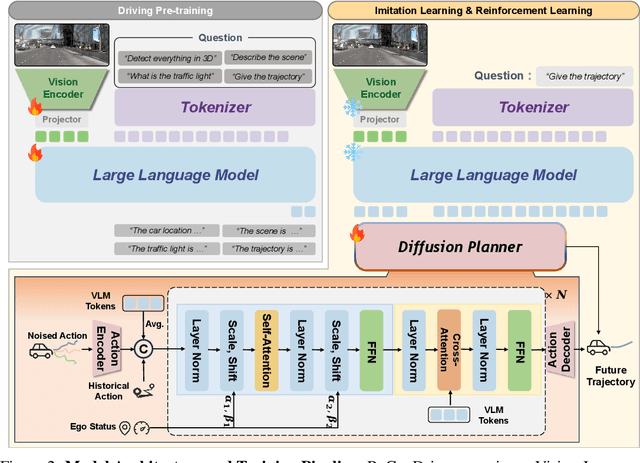
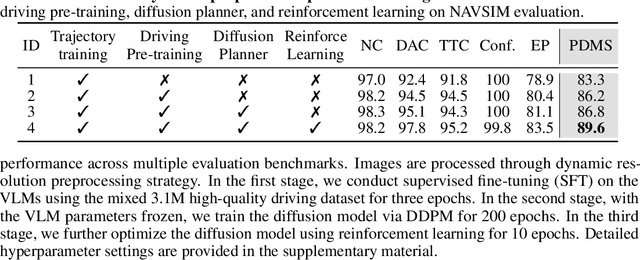
Abstract:Although end-to-end autonomous driving has made remarkable progress, its performance degrades significantly in rare and long-tail scenarios. Recent approaches attempt to address this challenge by leveraging the rich world knowledge of Vision-Language Models (VLMs), but these methods suffer from several limitations: (1) a significant domain gap between the pre-training data of VLMs and real-world driving data, (2) a dimensionality mismatch between the discrete language space and the continuous action space, and (3) imitation learning tends to capture the average behavior present in the dataset, which may be suboptimal even dangerous. In this paper, we propose ReCogDrive, an autonomous driving system that integrates VLMs with diffusion planner, which adopts a three-stage paradigm for training. In the first stage, we use a large-scale driving question-answering datasets to train the VLMs, mitigating the domain discrepancy between generic content and real-world driving scenarios. In the second stage, we employ a diffusion-based planner to perform imitation learning, mapping representations from the latent language space to continuous driving actions. Finally, we fine-tune the diffusion planner using reinforcement learning with NAVSIM non-reactive simulator, enabling the model to generate safer, more human-like driving trajectories. We evaluate our approach on the planning-oriented NAVSIM benchmark, achieving a PDMS of 89.6 and setting a new state-of-the-art that surpasses the previous vision-only SOTA by 5.6 PDMS.
Towards Fast, Memory-based and Data-Efficient Vision-Language Policy
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) pretrained on Internet-scale vision-language data have demonstrated the potential to transfer their knowledge to robotic learning. However, the existing paradigm encounters three critical challenges: (1) expensive inference cost resulting from large-scale model parameters, (2) frequent domain shifts caused by mismatched data modalities, and (3) limited capacity to handle past or future experiences. In this work, we propose LiteVLP, a lightweight, memory-based, and general-purpose vision-language policy generation model. LiteVLP is built upon a pre-trained 1B-parameter VLM and fine-tuned on a tiny-scale and conversation-style robotic dataset. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that LiteVLP outperforms state-of-the-art vision-language policy on VIMA-Bench, with minimal training time. Furthermore, LiteVLP exhibits superior inference speed while maintaining exceptional high accuracy. In long-horizon manipulation tasks, LiteVLP also shows remarkable memory ability, outperforming the best-performing baseline model by 18.8%. These results highlight LiteVLP as a promising model to integrating the intelligence of VLMs into robotic learning.
DiffusionDrive: Truncated Diffusion Model for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Nov 22, 2024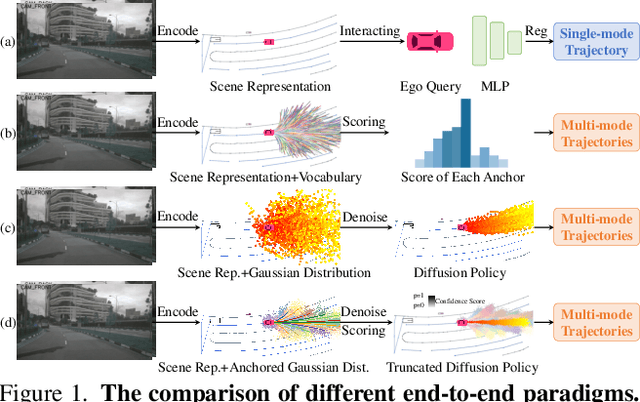
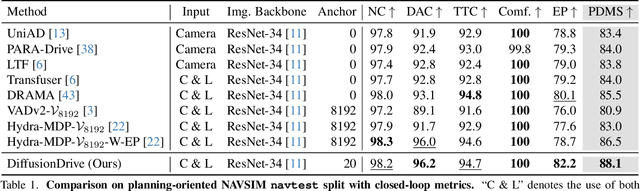
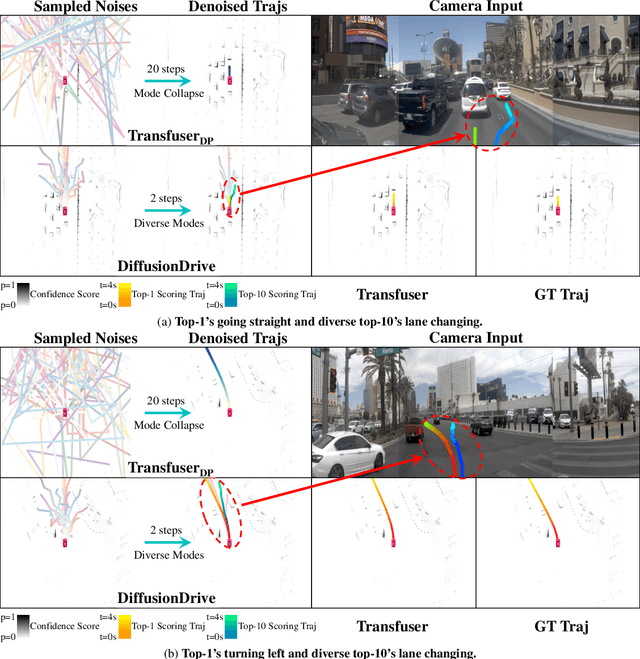
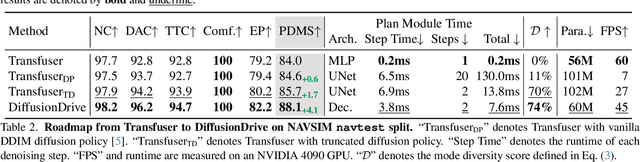
Abstract:Recently, the diffusion model has emerged as a powerful generative technique for robotic policy learning, capable of modeling multi-mode action distributions. Leveraging its capability for end-to-end autonomous driving is a promising direction. However, the numerous denoising steps in the robotic diffusion policy and the more dynamic, open-world nature of traffic scenes pose substantial challenges for generating diverse driving actions at a real-time speed. To address these challenges, we propose a novel truncated diffusion policy that incorporates prior multi-mode anchors and truncates the diffusion schedule, enabling the model to learn denoising from anchored Gaussian distribution to the multi-mode driving action distribution. Additionally, we design an efficient cascade diffusion decoder for enhanced interaction with conditional scene context. The proposed model, DiffusionDrive, demonstrates 10$\times$ reduction in denoising steps compared to vanilla diffusion policy, delivering superior diversity and quality in just 2 steps. On the planning-oriented NAVSIM dataset, with the aligned ResNet-34 backbone, DiffusionDrive achieves 88.1 PDMS without bells and whistles, setting a new record, while running at a real-time speed of 45 FPS on an NVIDIA 4090. Qualitative results on challenging scenarios further confirm that DiffusionDrive can robustly generate diverse plausible driving actions. Code and model will be available at https://github.com/hustvl/DiffusionDrive.
M3Bench: Benchmarking Whole-body Motion Generation for Mobile Manipulation in 3D Scenes
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:We propose M^3Bench, a new benchmark of whole-body motion generation for mobile manipulation tasks. Given a 3D scene context, M^3Bench requires an embodied agent to understand its configuration, environmental constraints and task objectives, then generate coordinated whole-body motion trajectories for object rearrangement tasks. M^3Bench features 30k object rearrangement tasks across 119 diverse scenes, providing expert demonstrations generated by our newly developed M^3BenchMaker. This automatic data generation tool produces coordinated whole-body motion trajectories from high-level task instructions, requiring only basic scene and robot information. Our benchmark incorporates various task splits to assess generalization across different dimensions and leverages realistic physics simulation for trajectory evaluation. Through extensive experimental analyses, we reveal that state-of-the-art models still struggle with coordinated base-arm motion while adhering to environment-context and task-specific constraints, highlighting the need to develop new models that address this gap. Through M^3Bench, we aim to facilitate future robotics research towards more adaptive and capable mobile manipulation in diverse, real-world environments.
M2Diffuser: Diffusion-based Trajectory Optimization for Mobile Manipulation in 3D Scenes
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models have opened new avenues for research into embodied AI agents and robotics. Despite significant achievements in complex robotic locomotion and skills, mobile manipulation-a capability that requires the coordination of navigation and manipulation-remains a challenge for generative AI techniques. This is primarily due to the high-dimensional action space, extended motion trajectories, and interactions with the surrounding environment. In this paper, we introduce M2Diffuser, a diffusion-based, scene-conditioned generative model that directly generates coordinated and efficient whole-body motion trajectories for mobile manipulation based on robot-centric 3D scans. M2Diffuser first learns trajectory-level distributions from mobile manipulation trajectories provided by an expert planner. Crucially, it incorporates an optimization module that can flexibly accommodate physical constraints and task objectives, modeled as cost and energy functions, during the inference process. This enables the reduction of physical violations and execution errors at each denoising step in a fully differentiable manner. Through benchmarking on three types of mobile manipulation tasks across over 20 scenes, we demonstrate that M2Diffuser outperforms state-of-the-art neural planners and successfully transfers the generated trajectories to a real-world robot. Our evaluations underscore the potential of generative AI to enhance the generalization of traditional planning and learning-based robotic methods, while also highlighting the critical role of enforcing physical constraints for safe and robust execution.
M${}^{3}$Bench: Benchmarking Whole-body Motion Generation for Mobile Manipulation in 3D Scenes
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:We propose M^3Bench, a new benchmark for whole-body motion generation for mobile manipulation tasks. Given a 3D scene context, M^3Bench requires an embodied agent to understand its configuration, environmental constraints and task objectives, then generate coordinated whole-body motion trajectories for object rearrangement tasks. M^3Bench features 30k object rearrangement tasks across 119 diverse scenes, providing expert demonstrations generated by our newly developed M^3BenchMaker. This automatic data generation tool produces coordinated whole-body motion trajectories from high-level task instructions, requiring only basic scene and robot information. Our benchmark incorporates various task splits to assess generalization across different dimensions and leverages realistic physics simulation for trajectory evaluation. Through extensive experimental analyses, we reveal that state-of-the-art models still struggle with coordinated base-arm motion while adhering to environment-context and task-specific constraints, highlighting the need to develop new models that address this gap. Through M^3Bench, we aim to facilitate future robotics research towards more adaptive and capable mobile manipulation in diverse, real-world environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge