Yuhan Li
Unlocking the Potentials of Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Diffusion Language Models
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Language Models (DLMs) have recently demonstrated remarkable capabilities in natural language processing tasks. However, the potential of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which shows great successes for enhancing large language models (LLMs), has not been well explored, due to the fundamental difference between LLM and DLM decoding. To fill this critical gap, we systematically test the performance of DLMs within the RAG framework. Our findings reveal that DLMs coupled with RAG show promising potentials with stronger dependency on contextual information, but suffer from limited generation precision. We identify a key underlying issue: Response Semantic Drift (RSD), where the generated answer progressively deviates from the query's original semantics, leading to low precision content. We trace this problem to the denoising strategies in DLMs, which fail to maintain semantic alignment with the query throughout the iterative denoising process. To address this, we propose Semantic-Preserving REtrieval-Augmented Diffusion (SPREAD), a novel framework that introduces a query-relevance-guided denoising strategy. By actively guiding the denoising trajectory, SPREAD ensures the generation remains anchored to the query's semantics and effectively suppresses drift. Experimental results demonstrate that SPREAD significantly enhances the precision and effectively mitigates RSD of generated answers within the RAG framework.
SafeLoad: Efficient Admission Control Framework for Identifying Memory-Overloading Queries in Cloud Data Warehouses
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Memory overload is a common form of resource exhaustion in cloud data warehouses. When database queries fail due to memory overload, it not only wastes critical resources such as CPU time but also disrupts the execution of core business processes, as memory-overloading (MO) queries are typically part of complex workflows. If such queries are identified in advance and scheduled to memory-rich serverless clusters, it can prevent resource wastage and query execution failure. Therefore, cloud data warehouses desire an admission control framework with high prediction precision, interpretability, efficiency, and adaptability to effectively identify MO queries. However, existing admission control frameworks primarily focus on scenarios like SLA satisfaction and resource isolation, with limited precision in identifying MO queries. Moreover, there is a lack of publicly available MO-labeled datasets with workloads for training and benchmarking. To tackle these challenges, we propose SafeLoad, the first query admission control framework specifically designed to identify MO queries. Alongside, we release SafeBench, an open-source, industrial-scale benchmark for this task, which includes 150 million real queries. SafeLoad first filters out memory-safe queries using the interpretable discriminative rule. It then applies a hybrid architecture that integrates both a global model and cluster-level models, supplemented by a misprediction correction module to identify MO queries. Additionally, a self-tuning quota management mechanism dynamically adjusts prediction quotas per cluster to improve precision. Experimental results show that SafeLoad achieves state-of-the-art prediction performance with low online and offline time overhead. Specifically, SafeLoad improves precision by up to 66% over the best baseline and reduces wasted CPU time by up to 8.09x compared to scenarios without SafeLoad.
UniAct: Unified Motion Generation and Action Streaming for Humanoid Robots
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:A long-standing objective in humanoid robotics is the realization of versatile agents capable of following diverse multimodal instructions with human-level flexibility. Despite advances in humanoid control, bridging high-level multimodal perception with whole-body execution remains a significant bottleneck. Existing methods often struggle to translate heterogeneous instructions -- such as language, music, and trajectories -- into stable, real-time actions. Here we show that UniAct, a two-stage framework integrating a fine-tuned MLLM with a causal streaming pipeline, enables humanoid robots to execute multimodal instructions with sub-500 ms latency. By unifying inputs through a shared discrete codebook via FSQ, UniAct ensures cross-modal alignment while constraining motions to a physically grounded manifold. This approach yields a 19% improvement in the success rate of zero-shot tracking of imperfect reference motions. We validate UniAct on UniMoCap, our 20-hour humanoid motion benchmark, demonstrating robust generalization across diverse real-world scenarios. Our results mark a critical step toward responsive, general-purpose humanoid assistants capable of seamless interaction through unified perception and control.
ClothHMR: 3D Mesh Recovery of Humans in Diverse Clothing from Single Image
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:With 3D data rapidly emerging as an important form of multimedia information, 3D human mesh recovery technology has also advanced accordingly. However, current methods mainly focus on handling humans wearing tight clothing and perform poorly when estimating body shapes and poses under diverse clothing, especially loose garments. To this end, we make two key insights: (1) tailoring clothing to fit the human body can mitigate the adverse impact of clothing on 3D human mesh recovery, and (2) utilizing human visual information from large foundational models can enhance the generalization ability of the estimation. Based on these insights, we propose ClothHMR, to accurately recover 3D meshes of humans in diverse clothing. ClothHMR primarily consists of two modules: clothing tailoring (CT) and FHVM-based mesh recovering (MR). The CT module employs body semantic estimation and body edge prediction to tailor the clothing, ensuring it fits the body silhouette. The MR module optimizes the initial parameters of the 3D human mesh by continuously aligning the intermediate representations of the 3D mesh with those inferred from the foundational human visual model (FHVM). ClothHMR can accurately recover 3D meshes of humans wearing diverse clothing, precisely estimating their body shapes and poses. Experimental results demonstrate that ClothHMR significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods across benchmark datasets and in-the-wild images. Additionally, a web application for online fashion and shopping powered by ClothHMR is developed, illustrating that ClothHMR can effectively serve real-world usage scenarios. The code and model for ClothHMR are available at: \url{https://github.com/starVisionTeam/ClothHMR}.
OT-ALD: Aligning Latent Distributions with Optimal Transport for Accelerated Image-to-Image Translation
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The Dual Diffusion Implicit Bridge (DDIB) is an emerging image-to-image (I2I) translation method that preserves cycle consistency while achieving strong flexibility. It links two independently trained diffusion models (DMs) in the source and target domains by first adding noise to a source image to obtain a latent code, then denoising it in the target domain to generate the translated image. However, this method faces two key challenges: (1) low translation efficiency, and (2) translation trajectory deviations caused by mismatched latent distributions. To address these issues, we propose a novel I2I translation framework, OT-ALD, grounded in optimal transport (OT) theory, which retains the strengths of DDIB-based approach. Specifically, we compute an OT map from the latent distribution of the source domain to that of the target domain, and use the mapped distribution as the starting point for the reverse diffusion process in the target domain. Our error analysis confirms that OT-ALD eliminates latent distribution mismatches. Moreover, OT-ALD effectively balances faster image translation with improved image quality. Experiments on four translation tasks across three high-resolution datasets show that OT-ALD improves sampling efficiency by 20.29% and reduces the FID score by 2.6 on average compared to the top-performing baseline models.
GraphRAG-R1: Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Process-Constrained Reinforcement Learning
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation (GraphRAG) has shown great effectiveness in enhancing the reasoning abilities of LLMs by leveraging graph structures for knowledge representation and modeling complex real-world relationships. However, existing GraphRAG methods still face significant bottlenecks when handling complex problems that require multi-hop reasoning, as their query and retrieval phases are largely based on pre-defined heuristics and do not fully utilize the reasoning potentials of LLMs. To address this problem, we propose GraphRAG-R1, an adaptive GraphRAG framework by training LLMs with process-constrained outcome-based reinforcement learning (RL) to enhance the multi-hop reasoning ability. Our method can decompose complex problems, autonomously invoke retrieval tools to acquire necessary information, and perform effective reasoning. Specifically, we utilize a modified version of Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) that supports rollout-with-thinking capability. Next, we design two process-constrained reward functions. To handle the shallow retrieval problem, we design a Progressive Retrieval Attenuation (PRA) reward to encourage essential retrievals. Then, to handle the over-thinking problem, we design Cost-Aware F1 (CAF) reward to balance the model performance with computational costs. We further design a phase-dependent training strategy, containing three training stages corresponding to cold start and these two rewards. Lastly, our method adopts a hybrid graph-textual retrieval to improve the reasoning capacity. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that GraphRAG-R1 boosts LLM capabilities in solving complex reasoning problems compared to state-of-the-art GraphRAG methods on both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets. Furthermore, our framework can be flexibly integrated with various existing retrieval methods, consistently delivering performance improvements.
ACM-UNet: Adaptive Integration of CNNs and Mamba for Efficient Medical Image Segmentation
May 30, 2025Abstract:The U-shaped encoder-decoder architecture with skip connections has become a prevailing paradigm in medical image segmentation due to its simplicity and effectiveness. While many recent works aim to improve this framework by designing more powerful encoders and decoders, employing advanced convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for local feature extraction, Transformers or state space models (SSMs) such as Mamba for global context modeling, or hybrid combinations of both, these methods often struggle to fully utilize pretrained vision backbones (e.g., ResNet, ViT, VMamba) due to structural mismatches. To bridge this gap, we introduce ACM-UNet, a general-purpose segmentation framework that retains a simple UNet-like design while effectively incorporating pretrained CNNs and Mamba models through a lightweight adapter mechanism. This adapter resolves architectural incompatibilities and enables the model to harness the complementary strengths of CNNs and SSMs-namely, fine-grained local detail extraction and long-range dependency modeling. Additionally, we propose a hierarchical multi-scale wavelet transform module in the decoder to enhance feature fusion and reconstruction fidelity. Extensive experiments on the Synapse and ACDC benchmarks demonstrate that ACM-UNet achieves state-of-the-art performance while remaining computationally efficient. Notably, it reaches 85.12% Dice Score and 13.89mm HD95 on the Synapse dataset with 17.93G FLOPs, showcasing its effectiveness and scalability. Code is available at: https://github.com/zyklcode/ACM-UNet.
Can LLMs Alleviate Catastrophic Forgetting in Graph Continual Learning? A Systematic Study
May 24, 2025Abstract:Nowadays, real-world data, including graph-structure data, often arrives in a streaming manner, which means that learning systems need to continuously acquire new knowledge without forgetting previously learned information. Although substantial existing works attempt to address catastrophic forgetting in graph machine learning, they are all based on training from scratch with streaming data. With the rise of pretrained models, an increasing number of studies have leveraged their strong generalization ability for continual learning. Therefore, in this work, we attempt to answer whether large language models (LLMs) can mitigate catastrophic forgetting in Graph Continual Learning (GCL). We first point out that current experimental setups for GCL have significant flaws, as the evaluation stage may lead to task ID leakage. Then, we evaluate the performance of LLMs in more realistic scenarios and find that even minor modifications can lead to outstanding results. Finally, based on extensive experiments, we propose a simple-yet-effective method, Simple Graph Continual Learning (SimGCL), that surpasses the previous state-of-the-art GNN-based baseline by around 20% under the rehearsal-free constraint. To facilitate reproducibility, we have developed an easy-to-use benchmark LLM4GCL for training and evaluating existing GCL methods. The code is available at: https://github.com/ZhixunLEE/LLM4GCL.
Reinforcement Learning with Continuous Actions Under Unmeasured Confounding
May 01, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of offline policy learning in reinforcement learning with continuous action spaces when unmeasured confounders are present. While most existing research focuses on policy evaluation within partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs) and assumes discrete action spaces, we advance this field by establishing a novel identification result to enable the nonparametric estimation of policy value for a given target policy under an infinite-horizon framework. Leveraging this identification, we develop a minimax estimator and introduce a policy-gradient-based algorithm to identify the in-class optimal policy that maximizes the estimated policy value. Furthermore, we provide theoretical results regarding the consistency, finite-sample error bound, and regret bound of the resulting optimal policy. Extensive simulations and a real-world application using the German Family Panel data demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methodology.
StyleLoco: Generative Adversarial Distillation for Natural Humanoid Robot Locomotion
Mar 19, 2025
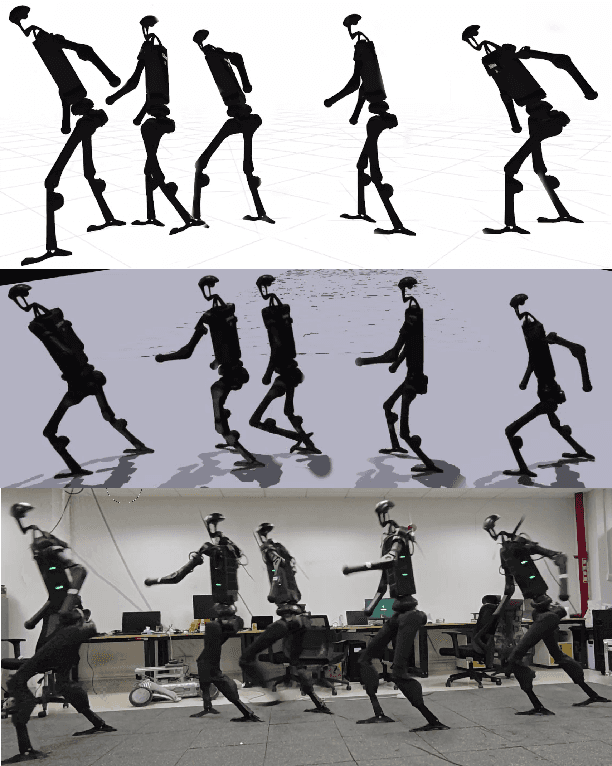
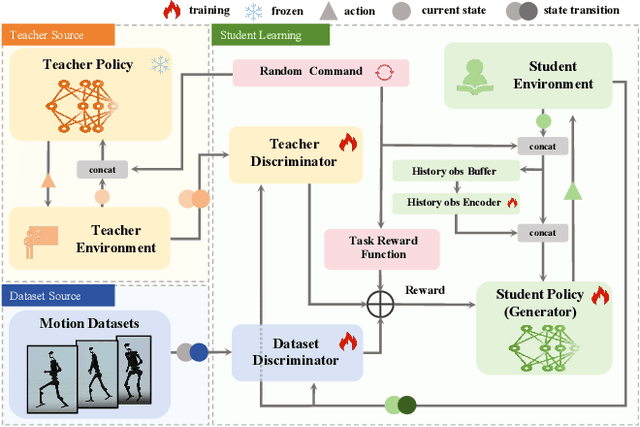

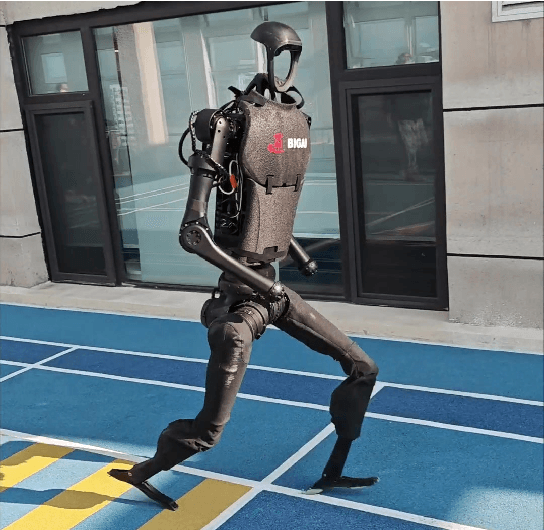
Abstract:Humanoid robots are anticipated to acquire a wide range of locomotion capabilities while ensuring natural movement across varying speeds and terrains. Existing methods encounter a fundamental dilemma in learning humanoid locomotion: reinforcement learning with handcrafted rewards can achieve agile locomotion but produces unnatural gaits, while Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning (GAIL) with motion capture data yields natural movements but suffers from unstable training processes and restricted agility. Integrating these approaches proves challenging due to the inherent heterogeneity between expert policies and human motion datasets. To address this, we introduce StyleLoco, a novel two-stage framework that bridges this gap through a Generative Adversarial Distillation (GAD) process. Our framework begins by training a teacher policy using reinforcement learning to achieve agile and dynamic locomotion. It then employs a multi-discriminator architecture, where distinct discriminators concurrently extract skills from both the teacher policy and motion capture data. This approach effectively combines the agility of reinforcement learning with the natural fluidity of human-like movements while mitigating the instability issues commonly associated with adversarial training. Through extensive simulation and real-world experiments, we demonstrate that StyleLoco enables humanoid robots to perform diverse locomotion tasks with the precision of expertly trained policies and the natural aesthetics of human motion, successfully transferring styles across different movement types while maintaining stable locomotion across a broad spectrum of command inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge