Xiao Zhu
CHARM: Calibrating Reward Models With Chatbot Arena Scores
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Reward models (RMs) play a crucial role in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback by serving as proxies for human preferences in aligning large language models. In this paper, we identify a model preference bias in RMs, where they systematically assign disproportionately high scores to responses from certain policy models. This bias distorts ranking evaluations and leads to unfair judgments. To address this issue, we propose a calibration method named CHatbot Arena calibrated Reward Modeling (CHARM) that leverages Elo scores from the Chatbot Arena leaderboard to mitigate RM overvaluation. We also introduce a Mismatch Degree metric to measure this preference bias. Our approach is computationally efficient, requiring only a small preference dataset for continued training of the RM. We conduct extensive experiments on reward model benchmarks and human preference alignment. Results demonstrate that our calibrated RMs (1) achieve improved evaluation accuracy on RM-Bench and the Chat-Hard domain of RewardBench, and (2) exhibit a stronger correlation with human preferences by producing scores more closely aligned with Elo rankings. By mitigating model preference bias, our method provides a generalizable and efficient solution for building fairer and more reliable reward models.
Robust UAV Jittering and Task Scheduling in Mobile Edge Computing with Data Compression
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Data compression technology is able to reduce data size, which can be applied to lower the cost of task offloading in mobile edge computing (MEC). This paper addresses the practical challenges for robust trajectory and scheduling optimization based on data compression in the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-assisted MEC, aiming to minimize the sum energy cost of terminal users while maintaining robust performance during UAV flight. Considering the non-convexity of the problem and the dynamic nature of the scenario, the optimization problem is reformulated as a Markov decision process. Then, a randomized ensembled double Q-learning (REDQ) algorithm is adopted to solve the issue. The algorithm allows for higher feasible update-to-data ratio, enabling more effective learning from observed data. The simulation results show that the proposed scheme effectively reduces the energy consumption while ensuring flight robustness. Compared to the PPO and A2C algorithms, energy consumption is reduced by approximately $21.9\%$ and $35.4\%$, respectively. This method demonstrates significant advantages in complex environments and holds great potential for practical applications.
A large language model-type architecture for high-dimensional molecular potential energy surfaces
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:Computing high dimensional potential surfaces for molecular and materials systems is considered to be a great challenge in computational chemistry with potential impact in a range of areas including fundamental prediction of reaction rates. In this paper we design and discuss an algorithm that has similarities to large language models in generative AI and natural language processing. Specifically, we represent a molecular system as a graph which contains a set of nodes, edges, faces etc. Interactions between these sets, which represent molecular subsystems in our case, are used to construct the potential energy surface for a reasonably sized chemical system with 51 dimensions. Essentially a family of neural networks that pertain to the graph-based subsystems, get the job done for this 51 dimensional system. We then ask if this same family of lower-dimensional neural networks can be transformed to provide accurate predictions for a 186 dimensional potential surface. We find that our algorithm does provide reasonably accurate results for this larger dimensional problem with sub-kcal/mol accuracy for the higher dimensional potential surface problem.
GLBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Graph with Large Language Models
Jul 11, 2024



Abstract:The emergence of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized the way we interact with graphs, leading to a new paradigm called GraphLLM. Despite the rapid development of GraphLLM methods in recent years, the progress and understanding of this field remain unclear due to the lack of a benchmark with consistent experimental protocols. To bridge this gap, we introduce GLBench, the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating GraphLLM methods in both supervised and zero-shot scenarios. GLBench provides a fair and thorough evaluation of different categories of GraphLLM methods, along with traditional baselines such as graph neural networks. Through extensive experiments on a collection of real-world datasets with consistent data processing and splitting strategies, we have uncovered several key findings. Firstly, GraphLLM methods outperform traditional baselines in supervised settings, with LLM-as-enhancers showing the most robust performance. However, using LLMs as predictors is less effective and often leads to uncontrollable output issues. We also notice that no clear scaling laws exist for current GraphLLM methods. In addition, both structures and semantics are crucial for effective zero-shot transfer, and our proposed simple baseline can even outperform several models tailored for zero-shot scenarios. The data and code of the benchmark can be found at https://github.com/NineAbyss/GLBench.
Why Deep Models Often cannot Beat Non-deep Counterparts on Molecular Property Prediction?
Jun 30, 2023Abstract:Molecular property prediction (MPP) is a crucial task in the drug discovery pipeline, which has recently gained considerable attention thanks to advances in deep neural networks. However, recent research has revealed that deep models struggle to beat traditional non-deep ones on MPP. In this study, we benchmark 12 representative models (3 non-deep models and 9 deep models) on 14 molecule datasets. Through the most comprehensive study to date, we make the following key observations: \textbf{(\romannumeral 1)} Deep models are generally unable to outperform non-deep ones; \textbf{(\romannumeral 2)} The failure of deep models on MPP cannot be solely attributed to the small size of molecular datasets. What matters is the irregular molecule data pattern; \textbf{(\romannumeral 3)} In particular, tree models using molecular fingerprints as inputs tend to perform better than other competitors. Furthermore, we conduct extensive empirical investigations into the unique patterns of molecule data and inductive biases of various models underlying these phenomena.
A Closed-Loop Perception, Decision-Making and Reasoning Mechanism for Human-Like Navigation
Jul 25, 2022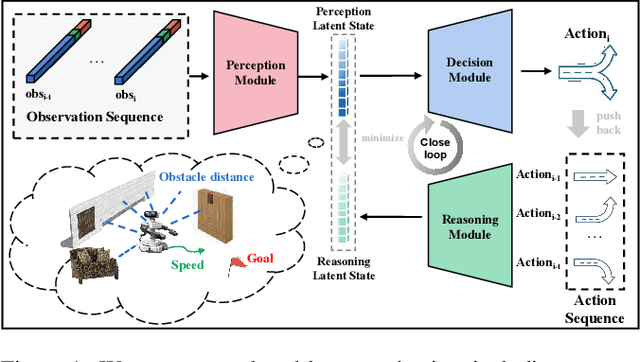
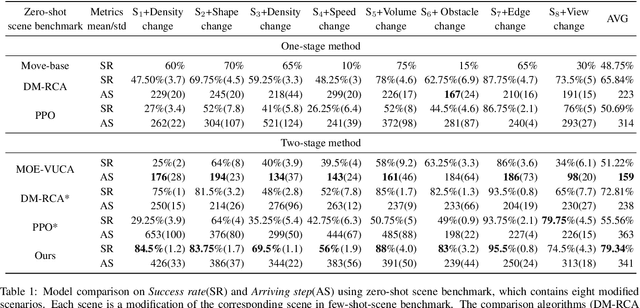
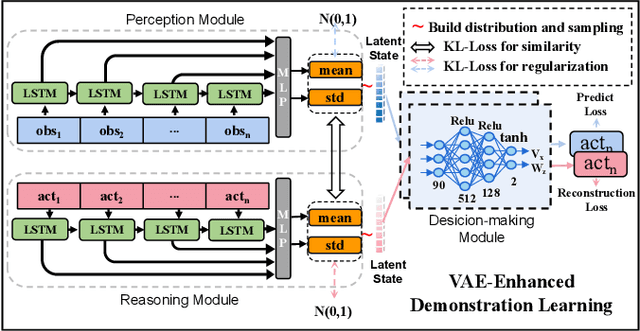

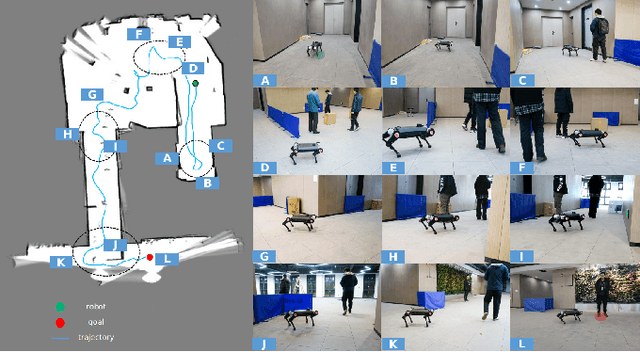
Abstract:Reliable navigation systems have a wide range of applications in robotics and autonomous driving. Current approaches employ an open-loop process that converts sensor inputs directly into actions. However, these open-loop schemes are challenging to handle complex and dynamic real-world scenarios due to their poor generalization. Imitating human navigation, we add a reasoning process to convert actions back to internal latent states, forming a two-stage closed loop of perception, decision-making, and reasoning. Firstly, VAE-Enhanced Demonstration Learning endows the model with the understanding of basic navigation rules. Then, two dual processes in RL-Enhanced Interaction Learning generate reward feedback for each other and collectively enhance obstacle avoidance capability. The reasoning model can substantially promote generalization and robustness, and facilitate the deployment of the algorithm to real-world robots without elaborate transfers. Experiments show our method is more adaptable to novel scenarios compared with state-of-the-art approaches.
FIND:Explainable Framework for Meta-learning
May 20, 2022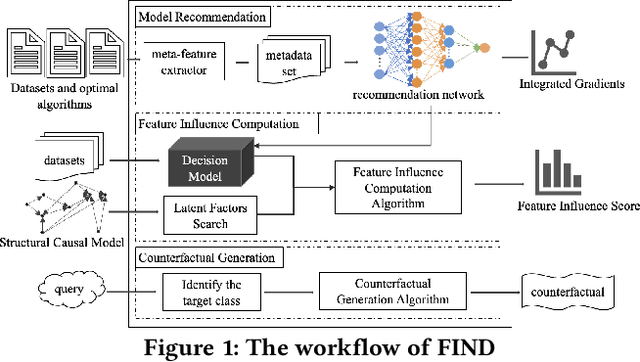

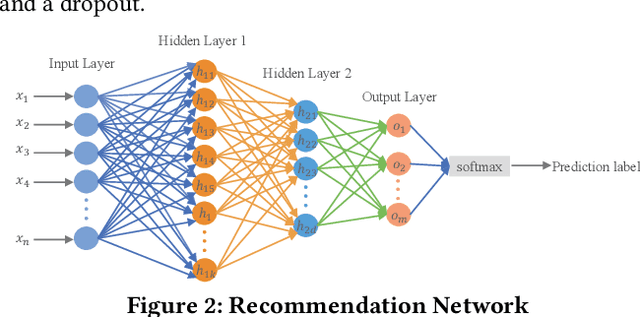
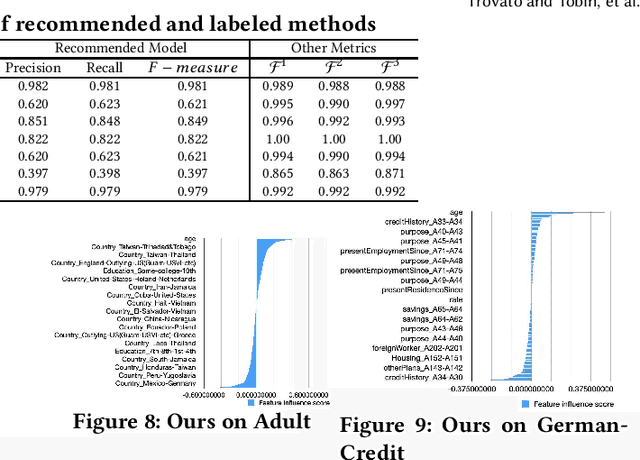
Abstract:Meta-learning is used to efficiently enable the automatic selection of machine learning models by combining data and prior knowledge. Since the traditional meta-learning technique lacks explainability, as well as shortcomings in terms of transparency and fairness, achieving explainability for meta-learning is crucial. This paper proposes FIND, an interpretable meta-learning framework that not only can explain the recommendation results of meta-learning algorithm selection, but also provide a more complete and accurate explanation of the recommendation algorithm's performance on specific datasets combined with business scenarios. The validity and correctness of this framework have been demonstrated by extensive experiments.
Learning to Navigate in a VUCA Environment: Hierarchical Multi-expert Approach
Nov 16, 2021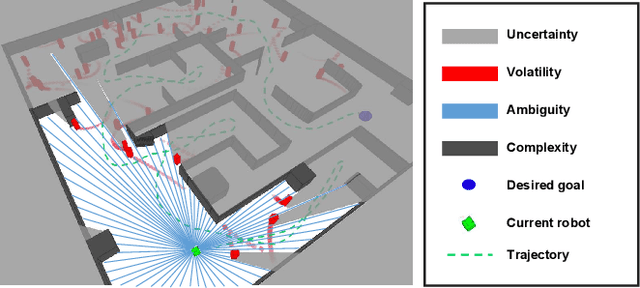
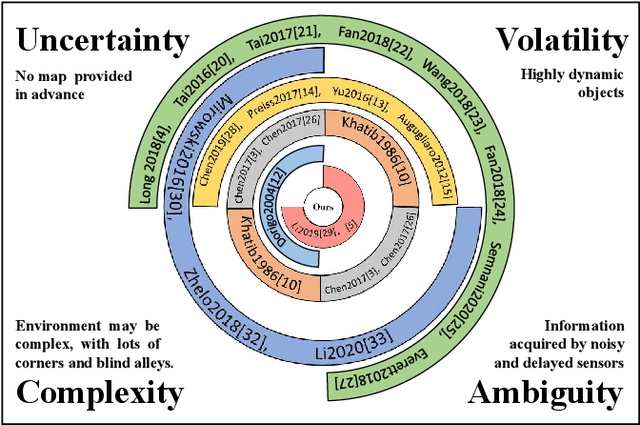
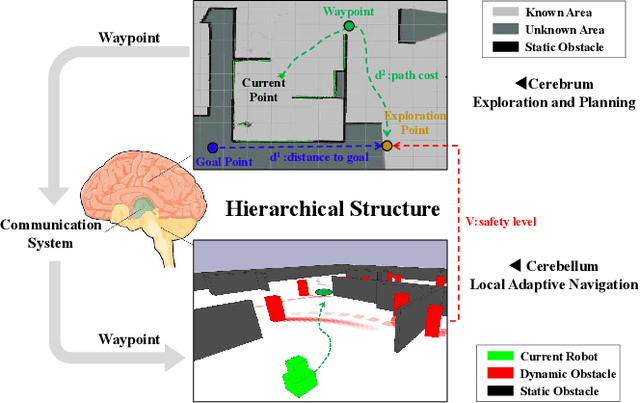
Abstract:Despite decades of efforts, robot navigation in a real scenario with volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity (VUCA for short), remains a challenging topic. Inspired by the central nervous system (CNS), we propose a hierarchical multi-expert learning framework for autonomous navigation in a VUCA environment. With a heuristic exploration mechanism considering target location, path cost, and safety level, the upper layer performs simultaneous map exploration and route-planning to avoid trapping in a blind alley, similar to the cerebrum in the CNS. Using a local adaptive model fusing multiple discrepant strategies, the lower layer pursuits a balance between collision-avoidance and go-straight strategies, acting as the cerebellum in the CNS. We conduct simulation and real-world experiments on multiple platforms, including legged and wheeled robots. Experimental results demonstrate our algorithm outperforms the existing methods in terms of task achievement, time efficiency, and security.
Privacy-Preserving Recommender Systems Challenge on Twitter's Home Timeline
Apr 28, 2020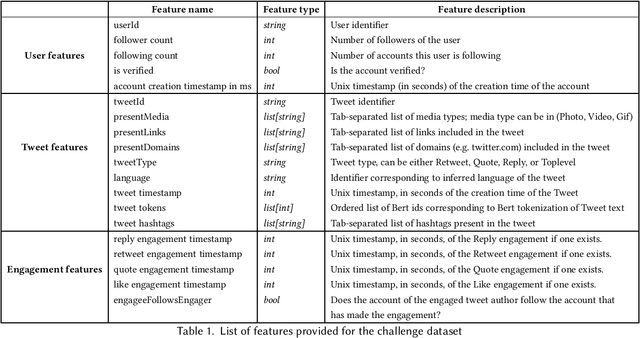
Abstract:Recommender systems constitute the core engine of most social network platforms nowadays, aiming to maximize user satisfaction along with other key business objectives. Twitter is no exception. Despite the fact that Twitter data has been extensively used to understand socioeconomic and political phenomena and user behaviour, the implicit feedback provided by users on Tweets through their engagements on the Home Timeline has only been explored to a limited extent. At the same time, there is a lack of large-scale public social network datasets that would enable the scientific community to both benchmark and build more powerful and comprehensive models that tailor content to user interests. By releasing an original dataset of 160 million Tweets along with engagement information, Twitter aims to address exactly that. During this release, special attention is drawn on maintaining compliance with existing privacy laws. Apart from user privacy, this paper touches on the key challenges faced by researchers and professionals striving to predict user engagements. It further describes the key aspects of the RecSys 2020 Challenge that was organized by ACM RecSys in partnership with Twitter using this dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge