Akshay Gupta
Motion Planning and Control of an Overactuated 4-Wheel Drive with Constrained Independent Steering
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses motion planning and con- trol of an overactuated 4-wheel drive train with independent steering (4WIS) where mechanical constraints prevent the wheels from executing full 360-degree rotations (swerve). The configuration space of such a robot is constrained and contains discontinuities that affect the smoothness of the robot motion. We introduce a mathematical formulation of the steering constraints and derive discontinuity planes that partition the velocity space into regions of smooth and efficient motion. We further design the motion planner for path tracking and ob- stacle avoidance that explicitly accounts for swerve constraints and the velocity transition smoothness. The motion controller uses local feedback to generate actuation from the desired velocity, while properly handling the discontinuity crossing by temporarily stopping the motion and repositioning the wheels. We implement the proposed motion planner as an extension to ROS Navigation package and evaluate the system in simulation and on a physical robot.
Building Safe GenAI Applications: An End-to-End Overview of Red Teaming for Large Language Models
Mar 05, 2025

Abstract:The rapid growth of Large Language Models (LLMs) presents significant privacy, security, and ethical concerns. While much research has proposed methods for defending LLM systems against misuse by malicious actors, researchers have recently complemented these efforts with an offensive approach that involves red teaming, i.e., proactively attacking LLMs with the purpose of identifying their vulnerabilities. This paper provides a concise and practical overview of the LLM red teaming literature, structured so as to describe a multi-component system end-to-end. To motivate red teaming we survey the initial safety needs of some high-profile LLMs, and then dive into the different components of a red teaming system as well as software packages for implementing them. We cover various attack methods, strategies for attack-success evaluation, metrics for assessing experiment outcomes, as well as a host of other considerations. Our survey will be useful for any reader who wants to rapidly obtain a grasp of the major red teaming concepts for their own use in practical applications.
The 2023 Video Similarity Dataset and Challenge
Jun 15, 2023
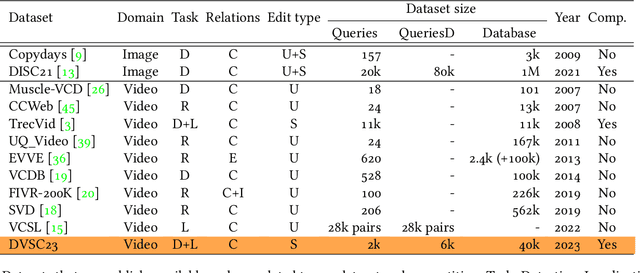
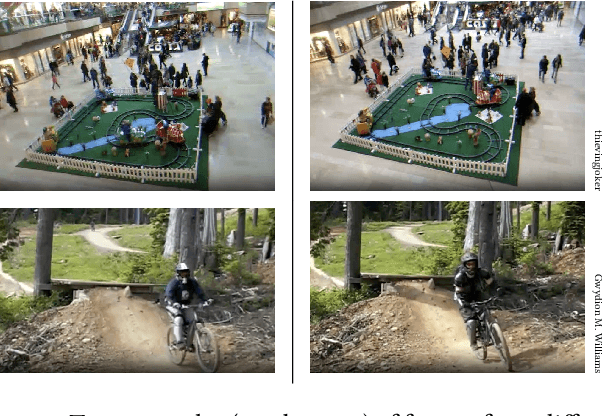
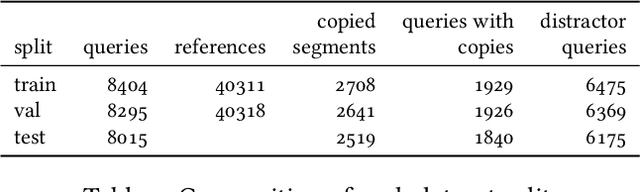
Abstract:This work introduces a dataset, benchmark, and challenge for the problem of video copy detection and localization. The problem comprises two distinct but related tasks: determining whether a query video shares content with a reference video ("detection"), and additionally temporally localizing the shared content within each video ("localization"). The benchmark is designed to evaluate methods on these two tasks, and simulates a realistic needle-in-haystack setting, where the majority of both query and reference videos are "distractors" containing no copied content. We propose a metric that reflects both detection and localization accuracy. The associated challenge consists of two corresponding tracks, each with restrictions that reflect real-world settings. We provide implementation code for evaluation and baselines. We also analyze the results and methods of the top submissions to the challenge. The dataset, baseline methods and evaluation code is publicly available and will be discussed at a dedicated CVPR'23 workshop.
MetaCon: Unified Predictive Segments System with Trillion Concept Meta-Learning
Mar 09, 2022
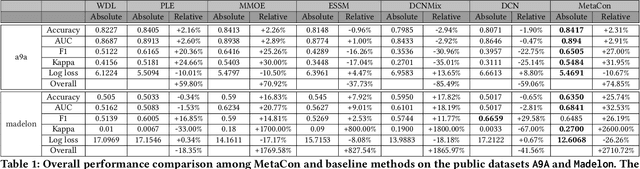
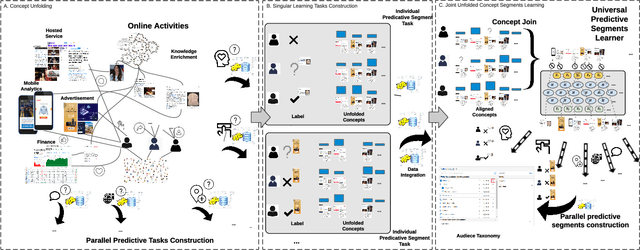
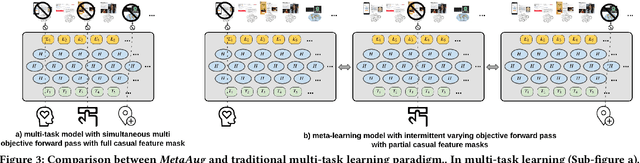
Abstract:Accurate understanding of users in terms of predicative segments play an essential role in the day to day operation of modern internet enterprises. Nevertheless, there are significant challenges that limit the quality of data, especially on long tail predictive tasks. In this work, we present MetaCon, our unified predicative segments system with scalable, trillion concepts meta learning that addresses these challenges. It builds on top of a flat concept representation that summarizes entities' heterogeneous digital footprint, jointly considers the entire spectrum of predicative tasks as a single learning task, and leverages principled meta learning approach with efficient first order meta-optimization procedure under a provable performance guarantee in order to solve the learning task. Experiments on both proprietary production datasets and public structured learning tasks demonstrate that MetaCon can lead to substantial improvements over state of the art recommendation and ranking approaches.
Learning Stance Embeddings from Signed Social Graphs
Jan 27, 2022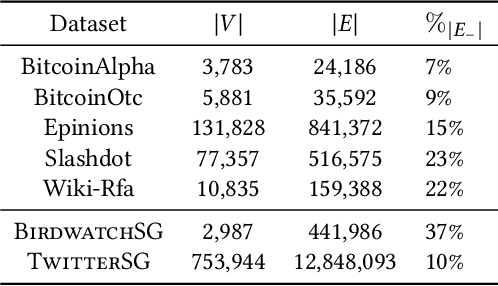
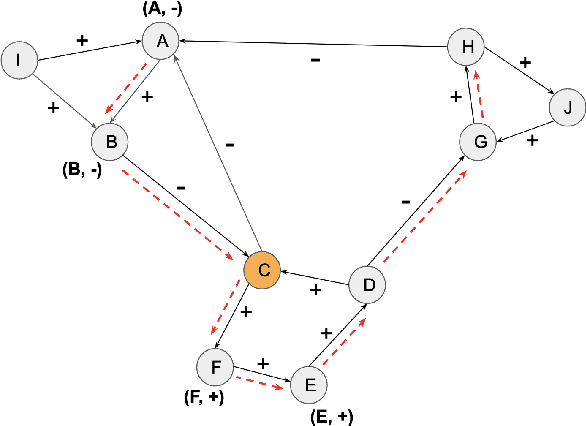
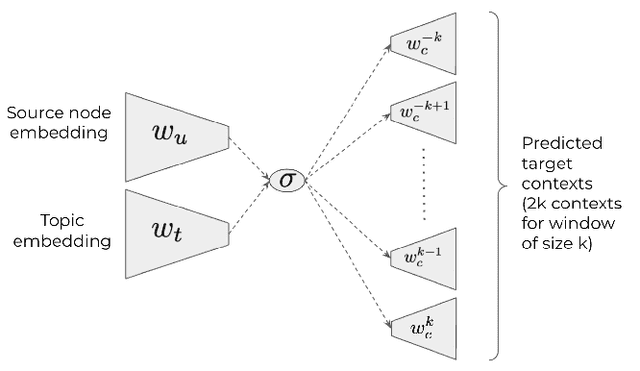
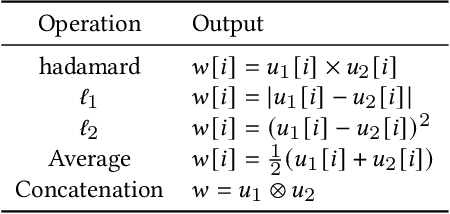
Abstract:A key challenge in social network analysis is understanding the position, or stance, of people in the graph on a large set of topics. While past work has modeled (dis)agreement in social networks using signed graphs, these approaches have not modeled agreement patterns across a range of correlated topics. For instance, disagreement on one topic may make disagreement(or agreement) more likely for related topics. We propose the Stance Embeddings Model(SEM), which jointly learns embeddings for each user and topic in signed social graphs with distinct edge types for each topic. By jointly learning user and topic embeddings, SEM is able to perform cold-start topic stance detection, predicting the stance of a user on topics for which we have not observed their engagement. We demonstrate the effectiveness of SEM using two large-scale Twitter signed graph datasets we open-source. One dataset, TwitterSG, labels (dis)agreements using engagements between users via tweets to derive topic-informed, signed edges. The other, BirdwatchSG, leverages community reports on misinformation and misleading content. On TwitterSG and BirdwatchSG, SEM shows a 39% and 26% error reduction respectively against strong baselines.
Aspect-Oriented Summarization through Query-Focused Extraction
Oct 15, 2021


Abstract:A reader interested in a particular topic might be interested in summarizing documents on that subject with a particular focus, rather than simply seeing generic summaries produced by most summarization systems. While query-focused summarization has been explored in prior work, this is often approached from the standpoint of document-specific questions or on synthetic data. Real users' needs often fall more closely into aspects, broad topics in a dataset the user is interested in rather than specific queries. In this paper, we collect a dataset of realistic aspect-oriented test cases, AspectNews, which covers different subtopics about articles in news sub-domains. We then investigate how query-focused methods, for which we can construct synthetic data, can handle this aspect-oriented setting: we benchmark extractive query-focused training schemes, and propose a contrastive augmentation approach to train the model. We evaluate on two aspect-oriented datasets and find this approach yields (a) focused summaries, better than those from a generic summarization system, which go beyond simple keyword matching; (b) a system sensitive to the choice of keywords.
Model Size Reduction Using Frequency Based Double Hashing for Recommender Systems
Jul 28, 2020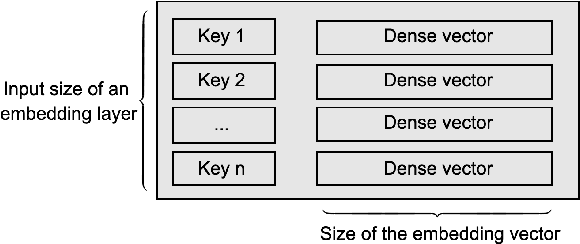
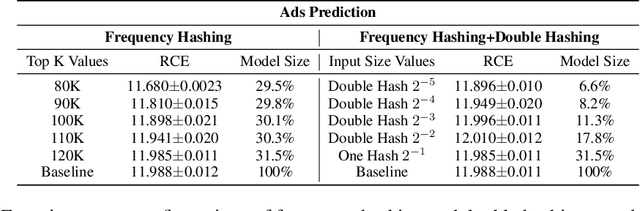
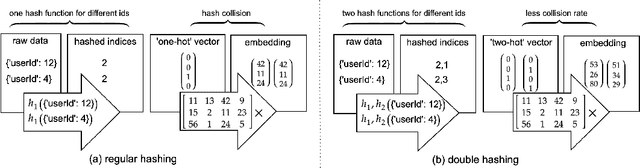
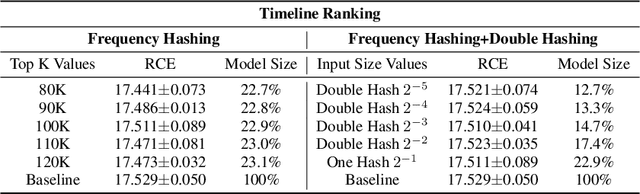
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) with sparse input features have been widely used in recommender systems in industry. These models have large memory requirements and need a huge amount of training data. The large model size usually entails a cost, in the range of millions of dollars, for storage and communication with the inference services. In this paper, we propose a hybrid hashing method to combine frequency hashing and double hashing techniques for model size reduction, without compromising performance. We evaluate the proposed models on two product surfaces. In both cases, experiment results demonstrated that we can reduce the model size by around 90 % while keeping the performance on par with the original baselines.
Privacy-Preserving Recommender Systems Challenge on Twitter's Home Timeline
Apr 28, 2020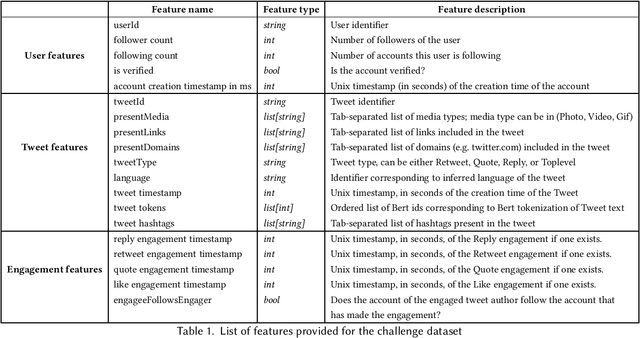
Abstract:Recommender systems constitute the core engine of most social network platforms nowadays, aiming to maximize user satisfaction along with other key business objectives. Twitter is no exception. Despite the fact that Twitter data has been extensively used to understand socioeconomic and political phenomena and user behaviour, the implicit feedback provided by users on Tweets through their engagements on the Home Timeline has only been explored to a limited extent. At the same time, there is a lack of large-scale public social network datasets that would enable the scientific community to both benchmark and build more powerful and comprehensive models that tailor content to user interests. By releasing an original dataset of 160 million Tweets along with engagement information, Twitter aims to address exactly that. During this release, special attention is drawn on maintaining compliance with existing privacy laws. Apart from user privacy, this paper touches on the key challenges faced by researchers and professionals striving to predict user engagements. It further describes the key aspects of the RecSys 2020 Challenge that was organized by ACM RecSys in partnership with Twitter using this dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge