Greg Durrett
Calibrate-Then-Act: Cost-Aware Exploration in LLM Agents
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:LLMs are increasingly being used for complex problems which are not necessarily resolved in a single response, but require interacting with an environment to acquire information. In these scenarios, LLMs must reason about inherent cost-uncertainty tradeoffs in when to stop exploring and commit to an answer. For instance, on a programming task, an LLM should test a generated code snippet if it is uncertain about the correctness of that code; the cost of writing a test is nonzero, but typically lower than the cost of making a mistake. In this work, we show that we can induce LLMs to explicitly reason about balancing these cost-uncertainty tradeoffs, then perform more optimal environment exploration. We formalize multiple tasks, including information retrieval and coding, as sequential decision-making problems under uncertainty. Each problem has latent environment state that can be reasoned about via a prior which is passed to the LLM agent. We introduce a framework called Calibrate-Then-Act (CTA), where we feed the LLM this additional context to enable it to act more optimally. This improvement is preserved even under RL training of both the baseline and CTA. Our results on information-seeking QA and on a simplified coding task show that making cost-benefit tradeoffs explicit with CTA can help agents discover more optimal decision-making strategies.
PropMEND: Hypernetworks for Knowledge Propagation in LLMs
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Knowledge editing techniques for large language models (LLMs) can inject knowledge that is later reproducible verbatim, but they fall short on propagating that knowledge: models cannot answer questions that require reasoning with the injected knowledge. We present a hypernetwork-based approach for knowledge propagation, named PropMEND, where we meta-learn how to modify gradients of a language modeling loss to encourage injected information to propagate. Our approach extends the meta-objective of MEND [29] so that gradient updates on knowledge are transformed to enable answering multi-hop questions involving that knowledge. We show improved performance on the RippleEdit dataset, showing almost 2x accuracy on challenging multi-hop questions whose answers are not explicitly stated in the injected fact. We further introduce a new dataset, Controlled RippleEdit, to evaluate the generalization of our hypernetwork, testing knowledge propagation along relations and entities unseen during hypernetwork training. PropMEND still outperforms existing approaches in unseen entity-relation pairs, yet the performance gap decreases substantially, suggesting future work in propagating knowledge to a wide range of relations.
Causal Graph based Event Reasoning using Semantic Relation Experts
Jun 07, 2025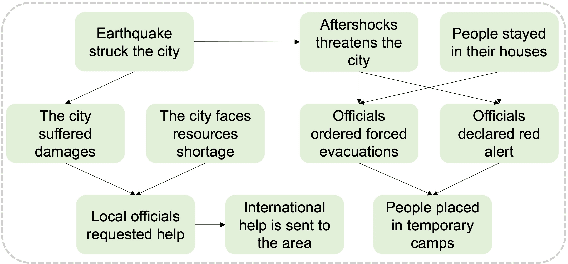
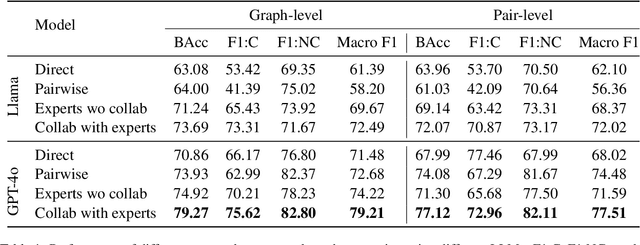
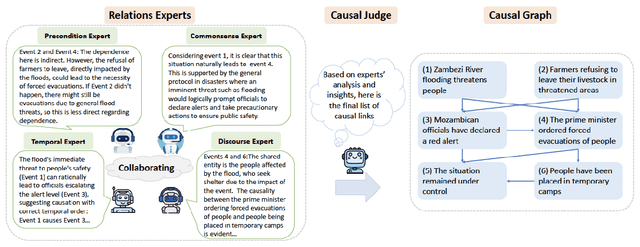
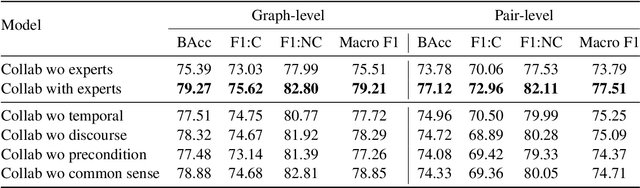
Abstract:Understanding how events in a scenario causally connect with each other is important for effectively modeling and reasoning about events. But event reasoning remains a difficult challenge, and despite recent advances, Large Language Models (LLMs) still struggle to accurately identify causal connections between events. This struggle leads to poor performance on deeper reasoning tasks like event forecasting and timeline understanding. To address this challenge, we investigate the generation of causal event graphs (e.g., A enables B) as a parallel mechanism to help LLMs explicitly represent causality during inference. This paper evaluates both how to generate correct graphs as well as how graphs can assist reasoning. We propose a collaborative approach to causal graph generation where we use LLMs to simulate experts that focus on specific semantic relations. The experts engage in multiple rounds of discussions which are then consolidated by a final expert. Then, to demonstrate the utility of causal graphs, we use them on multiple downstream applications, and also introduce a new explainable event prediction task that requires a causal chain of events in the explanation. These explanations are more informative and coherent than baseline generations. Finally, our overall approach not finetuned on any downstream task, achieves competitive results with state-of-the-art models on both forecasting and next event prediction tasks.
SPARTA ALIGNMENT: Collectively Aligning Multiple Language Models through Combat
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:We propose SPARTA ALIGNMENT, an algorithm to collectively align multiple LLMs through competition and combat. To complement a single model's lack of diversity in generation and biases in evaluation, multiple LLMs form a "sparta tribe" to compete against each other in fulfilling instructions while serving as judges for the competition of others. For each iteration, one instruction and two models are selected for a duel, the other models evaluate the two responses, and their evaluation scores are aggregated through a adapted elo-ranking based reputation system, where winners/losers of combat gain/lose weight in evaluating others. The peer-evaluated combat results then become preference pairs where the winning response is preferred over the losing one, and all models learn from these preferences at the end of each iteration. SPARTA ALIGNMENT enables the self-evolution of multiple LLMs in an iterative and collective competition process. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SPARTA ALIGNMENT outperforms initial models and 4 self-alignment baselines across 10 out of 12 tasks and datasets with 7.0% average improvement. Further analysis reveals that SPARTA ALIGNMENT generalizes more effectively to unseen tasks and leverages the expertise diversity of participating models to produce more logical, direct and informative outputs.
OpenThoughts: Data Recipes for Reasoning Models
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Reasoning models have made rapid progress on many benchmarks involving math, code, and science. Yet, there are still many open questions about the best training recipes for reasoning since state-of-the-art models often rely on proprietary datasets with little to no public information available. To address this, the goal of the OpenThoughts project is to create open-source datasets for training reasoning models. After initial explorations, our OpenThoughts2-1M dataset led to OpenThinker2-32B, the first model trained on public reasoning data to match DeepSeek-R1-Distill-32B on standard reasoning benchmarks such as AIME and LiveCodeBench. We then improve our dataset further by systematically investigating each step of our data generation pipeline with 1,000+ controlled experiments, which led to OpenThoughts3. Scaling the pipeline to 1.2M examples and using QwQ-32B as teacher yields our OpenThoughts3-7B model, which achieves state-of-the-art results: 53% on AIME 2025, 51% on LiveCodeBench 06/24-01/25, and 54% on GPQA Diamond - improvements of 15.3, 17.2, and 20.5 percentage points compared to the DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B. All of our datasets and models are available on https://openthoughts.ai.
Learning Composable Chains-of-Thought
May 28, 2025Abstract:A common approach for teaching large language models (LLMs) to reason is to train on chain-of-thought (CoT) traces of in-distribution reasoning problems, but such annotated data is costly to obtain for every problem of interest. We want reasoning models to generalize beyond their training distribution, and ideally to generalize compositionally: combine atomic reasoning skills to solve harder, unseen reasoning tasks. We take a step towards compositional generalization of reasoning skills when addressing a target compositional task that has no labeled CoT data. We find that simply training models on CoT data of atomic tasks leads to limited generalization, but minimally modifying CoT formats of constituent atomic tasks to be composable can lead to improvements. We can train "atomic CoT" models on the atomic tasks with Composable CoT data and combine them with multitask learning or model merging for better zero-shot performance on the target compositional task. Such a combined model can be further bootstrapped on a small amount of compositional data using rejection sampling fine-tuning (RFT). Results on string operations and natural language skill compositions show that training LLMs on Composable CoT outperforms multitask learning and continued fine-tuning baselines within a given training data budget.
AstroVisBench: A Code Benchmark for Scientific Computing and Visualization in Astronomy
May 28, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are being explored for applications in scientific research, including their capabilities to synthesize literature, answer research questions, generate research ideas, and even conduct computational experiments. Ultimately, our goal is for these to help scientists derive novel scientific insights. In many areas of science, such insights often arise from processing and visualizing data to understand its patterns. However, evaluating whether an LLM-mediated scientific workflow produces outputs conveying the correct scientific insights is challenging to evaluate and has not been addressed in past work. We introduce AstroVisBench, the first benchmark for both scientific computing and visualization in the astronomy domain. AstroVisBench judges a language model's ability to both (1) create astronomy-specific workflows to process and analyze data and (2) visualize the results of these workflows through complex plots. Our evaluation of visualizations uses a novel LLM-as-a-judge workflow, which is validated against annotation by five professional astronomers. Using AstroVisBench we present an evaluation of state-of-the-art language models, showing a significant gap in their ability to engage in astronomy research as useful assistants. This evaluation provides a strong end-to-end evaluation for AI scientists that offers a path forward for the development of visualization-based workflows, which are central to a broad range of domains from physics to biology.
CLEVER: A Curated Benchmark for Formally Verified Code Generation
May 21, 2025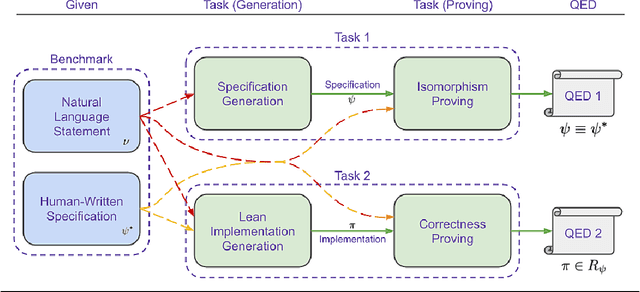
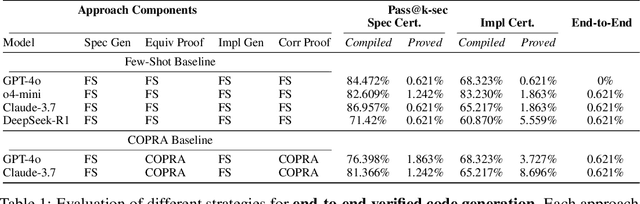

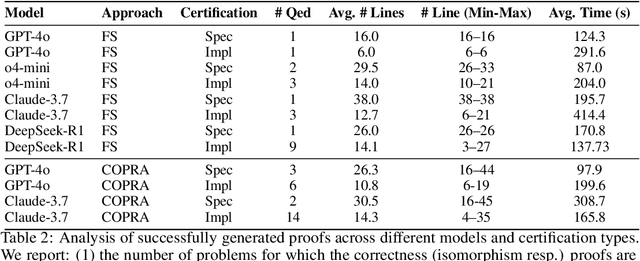
Abstract:We introduce ${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$, a high-quality, curated benchmark of 161 problems for end-to-end verified code generation in Lean. Each problem consists of (1) the task of generating a specification that matches a held-out ground-truth specification, and (2) the task of generating a Lean implementation that provably satisfies this specification. Unlike prior benchmarks, ${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$ avoids test-case supervision, LLM-generated annotations, and specifications that leak implementation logic or allow vacuous solutions. All outputs are verified post-hoc using Lean's type checker to ensure machine-checkable correctness. We use ${\rm C{\small LEVER}}$ to evaluate several few-shot and agentic approaches based on state-of-the-art language models. These methods all struggle to achieve full verification, establishing it as a challenging frontier benchmark for program synthesis and formal reasoning. Our benchmark can be found on GitHub(https://github.com/trishullab/clever) as well as HuggingFace(https://huggingface.co/datasets/amitayusht/clever). All our evaluation code is also available online(https://github.com/trishullab/clever-prover).
ChartMuseum: Testing Visual Reasoning Capabilities of Large Vision-Language Models
May 19, 2025Abstract:Chart understanding presents a unique challenge for large vision-language models (LVLMs), as it requires the integration of sophisticated textual and visual reasoning capabilities. However, current LVLMs exhibit a notable imbalance between these skills, falling short on visual reasoning that is difficult to perform in text. We conduct a case study using a synthetic dataset solvable only through visual reasoning and show that model performance degrades significantly with increasing visual complexity, while human performance remains robust. We then introduce ChartMuseum, a new Chart Question Answering (QA) benchmark containing 1,162 expert-annotated questions spanning multiple reasoning types, curated from real-world charts across 184 sources, specifically built to evaluate complex visual and textual reasoning. Unlike prior chart understanding benchmarks -- where frontier models perform similarly and near saturation -- our benchmark exposes a substantial gap between model and human performance, while effectively differentiating model capabilities: although humans achieve 93% accuracy, the best-performing model Gemini-2.5-Pro attains only 63.0%, and the leading open-source LVLM Qwen2.5-VL-72B-Instruct achieves only 38.5%. Moreover, on questions requiring primarily visual reasoning, all models experience a 35%-55% performance drop from text-reasoning-heavy question performance. Lastly, our qualitative error analysis reveals specific categories of visual reasoning that are challenging for current LVLMs.
CRUST-Bench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for C-to-safe-Rust Transpilation
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:C-to-Rust transpilation is essential for modernizing legacy C code while enhancing safety and interoperability with modern Rust ecosystems. However, no dataset currently exists for evaluating whether a system can transpile C into safe Rust that passes a set of test cases. We introduce CRUST-Bench, a dataset of 100 C repositories, each paired with manually-written interfaces in safe Rust as well as test cases that can be used to validate correctness of the transpilation. By considering entire repositories rather than isolated functions, CRUST-Bench captures the challenges of translating complex projects with dependencies across multiple files. The provided Rust interfaces provide explicit specifications that ensure adherence to idiomatic, memory-safe Rust patterns, while the accompanying test cases enforce functional correctness. We evaluate state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) on this task and find that safe and idiomatic Rust generation is still a challenging problem for various state-of-the-art methods and techniques. We also provide insights into the errors LLMs usually make in transpiling code from C to safe Rust. The best performing model, OpenAI o1, is able to solve only 15 tasks in a single-shot setting. Improvements on CRUST-Bench would lead to improved transpilation systems that can reason about complex scenarios and help in migrating legacy codebases from C into languages like Rust that ensure memory safety. You can find the dataset and code at https://github.com/anirudhkhatry/CRUST-bench.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge