Wenxuan Ding
Among Us: Measuring and Mitigating Malicious Contributions in Model Collaboration Systems
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Language models (LMs) are increasingly used in collaboration: multiple LMs trained by different parties collaborate through routing systems, multi-agent debate, model merging, and more. Critical safety risks remain in this decentralized paradigm: what if some of the models in multi-LLM systems are compromised or malicious? We first quantify the impact of malicious models by engineering four categories of malicious LMs, plug them into four types of popular model collaboration systems, and evaluate the compromised system across 10 datasets. We find that malicious models have a severe impact on the multi-LLM systems, especially for reasoning and safety domains where performance is lowered by 7.12% and 7.94% on average. We then propose mitigation strategies to alleviate the impact of malicious components, by employing external supervisors that oversee model collaboration to disable/mask them out to reduce their influence. On average, these strategies recover 95.31% of the initial performance, while making model collaboration systems fully resistant to malicious models remains an open research question.
MoCo: A One-Stop Shop for Model Collaboration Research
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Advancing beyond single monolithic language models (LMs), recent research increasingly recognizes the importance of model collaboration, where multiple LMs collaborate, compose, and complement each other. Existing research on this topic has mostly been disparate and disconnected, from different research communities, and lacks rigorous comparison. To consolidate existing research and establish model collaboration as a school of thought, we present MoCo: a one-stop Python library of executing, benchmarking, and comparing model collaboration algorithms at scale. MoCo features 26 model collaboration methods, spanning diverse levels of cross-model information exchange such as routing, text, logit, and model parameters. MoCo integrates 25 evaluation datasets spanning reasoning, QA, code, safety, and more, while users could flexibly bring their own data. Extensive experiments with MoCo demonstrate that most collaboration strategies outperform models without collaboration in 61.0% of (model, data) settings on average, with the most effective methods outperforming by up to 25.8%. We further analyze the scaling of model collaboration strategies, the training/inference efficiency of diverse methods, highlight that the collaborative system solves problems where single LMs struggle, and discuss future work in model collaboration, all made possible by MoCo. We envision MoCo as a valuable toolkit to facilitate and turbocharge the quest for an open, modular, decentralized, and collaborative AI future.
Do Images Speak Louder than Words? Investigating the Effect of Textual Misinformation in VLMs
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown strong multimodal reasoning capabilities on Visual-Question-Answering (VQA) benchmarks. However, their robustness against textual misinformation remains under-explored. While existing research has studied the effect of misinformation in text-only domains, it is not clear how VLMs arbitrate between contradictory information from different modalities. To bridge the gap, we first propose the CONTEXT-VQA (i.e., Conflicting Text) dataset, consisting of image-question pairs together with systematically generated persuasive prompts that deliberately conflict with visual evidence. Then, a thorough evaluation framework is designed and executed to benchmark the susceptibility of various models to these conflicting multimodal inputs. Comprehensive experiments over 11 state-of-the-art VLMs reveal that these models are indeed vulnerable to misleading textual prompts, often overriding clear visual evidence in favor of the conflicting text, and show an average performance drop of over 48.2% after only one round of persuasive conversation. Our findings highlight a critical limitation in current VLMs and underscore the need for improved robustness against textual manipulation.
SPARTA ALIGNMENT: Collectively Aligning Multiple Language Models through Combat
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:We propose SPARTA ALIGNMENT, an algorithm to collectively align multiple LLMs through competition and combat. To complement a single model's lack of diversity in generation and biases in evaluation, multiple LLMs form a "sparta tribe" to compete against each other in fulfilling instructions while serving as judges for the competition of others. For each iteration, one instruction and two models are selected for a duel, the other models evaluate the two responses, and their evaluation scores are aggregated through a adapted elo-ranking based reputation system, where winners/losers of combat gain/lose weight in evaluating others. The peer-evaluated combat results then become preference pairs where the winning response is preferred over the losing one, and all models learn from these preferences at the end of each iteration. SPARTA ALIGNMENT enables the self-evolution of multiple LLMs in an iterative and collective competition process. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SPARTA ALIGNMENT outperforms initial models and 4 self-alignment baselines across 10 out of 12 tasks and datasets with 7.0% average improvement. Further analysis reveals that SPARTA ALIGNMENT generalizes more effectively to unseen tasks and leverages the expertise diversity of participating models to produce more logical, direct and informative outputs.
ChartMuseum: Testing Visual Reasoning Capabilities of Large Vision-Language Models
May 19, 2025Abstract:Chart understanding presents a unique challenge for large vision-language models (LVLMs), as it requires the integration of sophisticated textual and visual reasoning capabilities. However, current LVLMs exhibit a notable imbalance between these skills, falling short on visual reasoning that is difficult to perform in text. We conduct a case study using a synthetic dataset solvable only through visual reasoning and show that model performance degrades significantly with increasing visual complexity, while human performance remains robust. We then introduce ChartMuseum, a new Chart Question Answering (QA) benchmark containing 1,162 expert-annotated questions spanning multiple reasoning types, curated from real-world charts across 184 sources, specifically built to evaluate complex visual and textual reasoning. Unlike prior chart understanding benchmarks -- where frontier models perform similarly and near saturation -- our benchmark exposes a substantial gap between model and human performance, while effectively differentiating model capabilities: although humans achieve 93% accuracy, the best-performing model Gemini-2.5-Pro attains only 63.0%, and the leading open-source LVLM Qwen2.5-VL-72B-Instruct achieves only 38.5%. Moreover, on questions requiring primarily visual reasoning, all models experience a 35%-55% performance drop from text-reasoning-heavy question performance. Lastly, our qualitative error analysis reveals specific categories of visual reasoning that are challenging for current LVLMs.
RankAlign: A Ranking View of the Generator-Validator Gap in Large Language Models
Apr 15, 2025



Abstract:Although large language models (LLMs) have become generally more capable and accurate across many tasks, some fundamental sources of unreliability remain in their behavior. One key limitation is their inconsistency at reporting the the same information when prompts are changed. In this paper, we consider the discrepancy between a model's generated answer and their own verification of that answer, the generator-validator gap. We define this gap in a more stringent way than prior work: we expect correlation of scores from a generator and a validator over the entire set of candidate answers. We show that according to this measure, a large gap exists in various settings, including question answering, lexical semantics tasks, and next-word prediction. We then propose RankAlign, a ranking-based training method, and show that it significantly closes the gap by 31.8% on average, surpassing all baseline methods. Moreover, this approach generalizes well to out-of-domain tasks and lexical items.
When One LLM Drools, Multi-LLM Collaboration Rules
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:This position paper argues that in many realistic (i.e., complex, contextualized, subjective) scenarios, one LLM is not enough to produce a reliable output. We challenge the status quo of relying solely on a single general-purpose LLM and argue for multi-LLM collaboration to better represent the extensive diversity of data, skills, and people. We first posit that a single LLM underrepresents real-world data distributions, heterogeneous skills, and pluralistic populations, and that such representation gaps cannot be trivially patched by further training a single LLM. We then organize existing multi-LLM collaboration methods into a hierarchy, based on the level of access and information exchange, ranging from API-level, text-level, logit-level, to weight-level collaboration. Based on these methods, we highlight how multi-LLM collaboration addresses challenges that a single LLM struggles with, such as reliability, democratization, and pluralism. Finally, we identify the limitations of existing multi-LLM methods and motivate future work. We envision multi-LLM collaboration as an essential path toward compositional intelligence and collaborative AI development.
Varying Shades of Wrong: Aligning LLMs with Wrong Answers Only
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:In the absence of abundant reliable annotations for challenging tasks and contexts, how can we expand the frontier of LLM capabilities with potentially wrong answers? We focus on two research questions: (1) Can LLMs generate reliable preferences among wrong options? And if so, (2) Would alignment with such wrong-over-wrong preferences be helpful? We employ methods based on self-consistency, token probabilities, and LLM-as-a-judge to elicit wrong-over-wrong preferences, and fine-tune language models with preference optimization approaches using these synthesized preferences. Extensive experiments with seven LLMs and eight datasets demonstrate that (1) LLMs do have preliminary capability in distinguishing various shades of wrong, achieving up to 20.9% higher performance than random guess; (2) Alignment with wrong-over-wrong preferences helps LLMs to produce less wrong and sometimes even outright correct answers, while overall improving model calibration.
Teaching LLMs to Abstain across Languages via Multilingual Feedback
Jun 22, 2024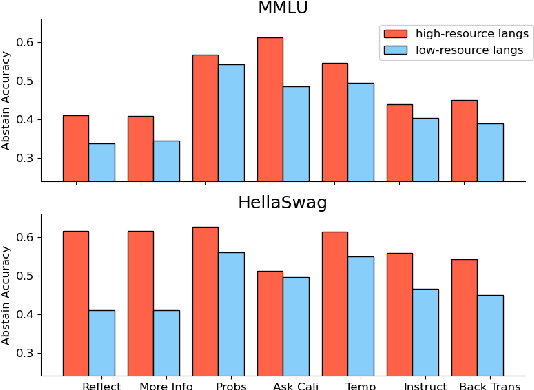
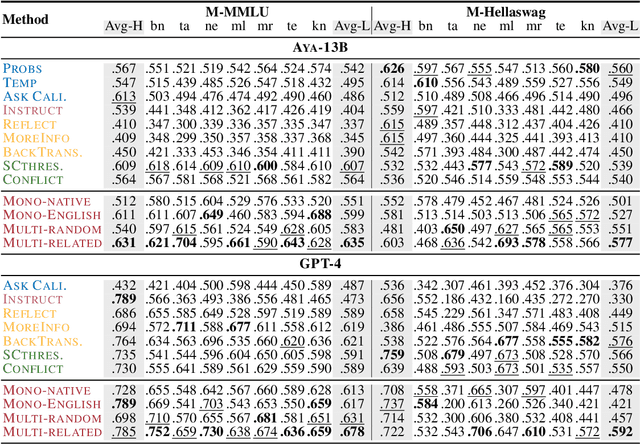
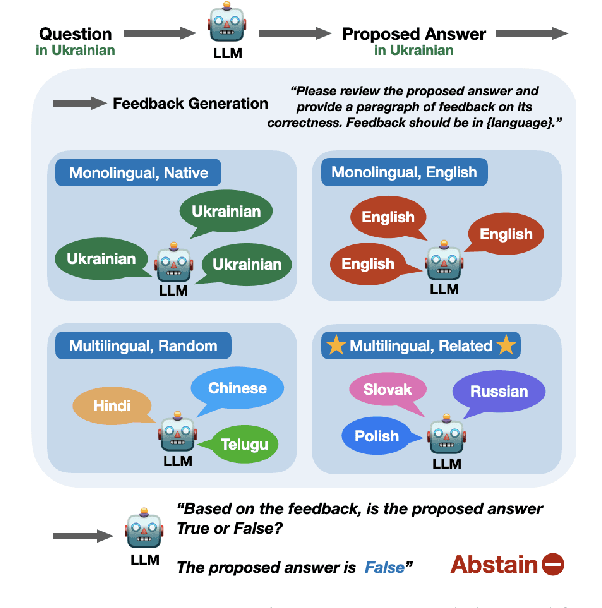
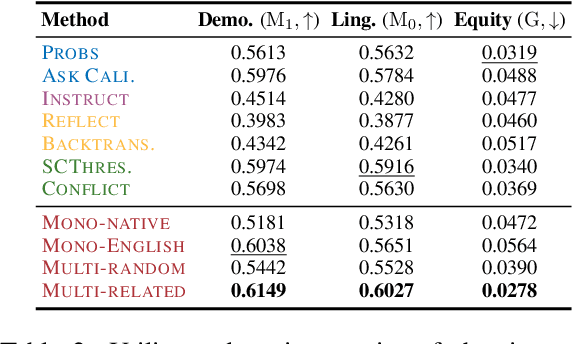
Abstract:Multilingual LLMs often have knowledge disparities across languages, with larger gaps in under-resourced languages. Teaching LLMs to abstain in the face of knowledge gaps is thus a promising strategy to mitigate hallucinations in multilingual settings. However, previous studies on LLM abstention primarily focus on English; we find that directly applying existing solutions beyond English results in up to 20.5% performance gaps between high and low-resource languages, potentially due to LLMs' drop in calibration and reasoning beyond a few resource-rich languages. To this end, we propose strategies to enhance LLM abstention by learning from multilingual feedback, where LLMs self-reflect on proposed answers in one language by generating multiple feedback items in related languages: we show that this helps identifying the knowledge gaps across diverse languages, cultures, and communities. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our multilingual feedback approach outperforms various strong baselines, achieving up to 9.2% improvement for low-resource languages across three black-box and open models on three datasets, featuring open-book, closed-book, and commonsense QA. Further analysis reveals that multilingual feedback is both an effective and a more equitable abstain strategy to serve diverse language speakers, and cultural factors have great impact on language selection and LLM abstention behavior, highlighting future directions for multilingual and multi-cultural reliable language modeling.
On the Role of Entity and Event Level Conceptualization in Generalizable Reasoning: A Survey of Tasks, Methods, Applications, and Future Directions
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:Entity- and event-level conceptualization, as fundamental elements of human cognition, plays a pivotal role in generalizable reasoning. This process involves abstracting specific instances into higher-level concepts and forming abstract knowledge that can be applied in unfamiliar or novel situations, which can enhance models' inferential capabilities and support the effective transfer of knowledge across various domains. Despite its significance, there is currently a lack of a systematic overview that comprehensively examines existing works in the definition, execution, and application of conceptualization to enhance reasoning tasks. In this paper, we address this gap by presenting the first comprehensive survey of 150+ papers, categorizing various definitions, resources, methods, and downstream applications related to conceptualization into a unified taxonomy, with a focus on the entity and event levels. Furthermore, we shed light on potential future directions in this field and hope to garner more attention from the community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge