Jihan Yao
MoCo: A One-Stop Shop for Model Collaboration Research
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Advancing beyond single monolithic language models (LMs), recent research increasingly recognizes the importance of model collaboration, where multiple LMs collaborate, compose, and complement each other. Existing research on this topic has mostly been disparate and disconnected, from different research communities, and lacks rigorous comparison. To consolidate existing research and establish model collaboration as a school of thought, we present MoCo: a one-stop Python library of executing, benchmarking, and comparing model collaboration algorithms at scale. MoCo features 26 model collaboration methods, spanning diverse levels of cross-model information exchange such as routing, text, logit, and model parameters. MoCo integrates 25 evaluation datasets spanning reasoning, QA, code, safety, and more, while users could flexibly bring their own data. Extensive experiments with MoCo demonstrate that most collaboration strategies outperform models without collaboration in 61.0% of (model, data) settings on average, with the most effective methods outperforming by up to 25.8%. We further analyze the scaling of model collaboration strategies, the training/inference efficiency of diverse methods, highlight that the collaborative system solves problems where single LMs struggle, and discuss future work in model collaboration, all made possible by MoCo. We envision MoCo as a valuable toolkit to facilitate and turbocharge the quest for an open, modular, decentralized, and collaborative AI future.
MMMG: a Comprehensive and Reliable Evaluation Suite for Multitask Multimodal Generation
May 23, 2025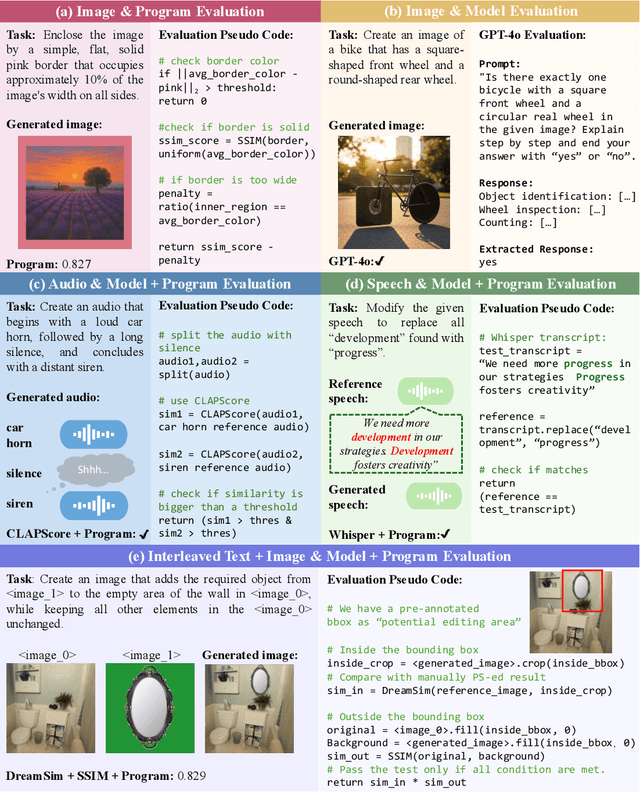
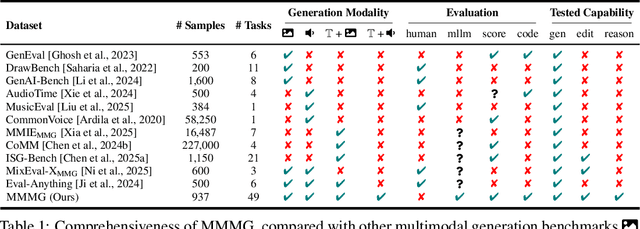
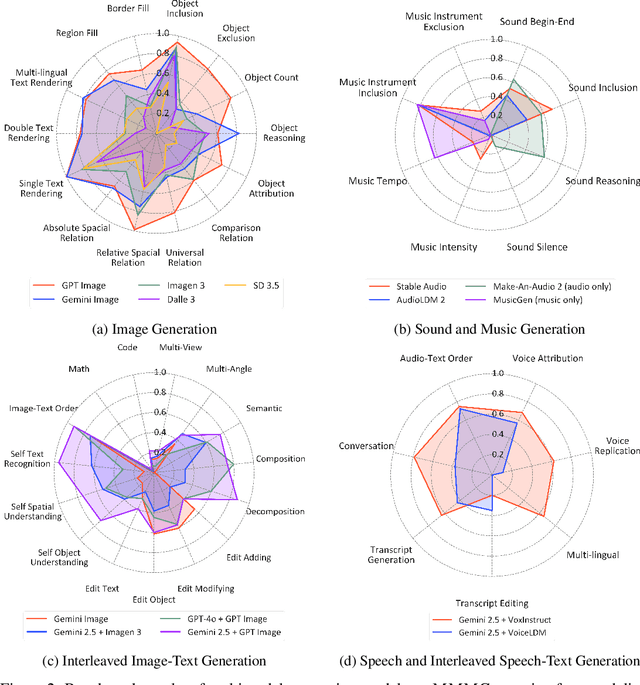
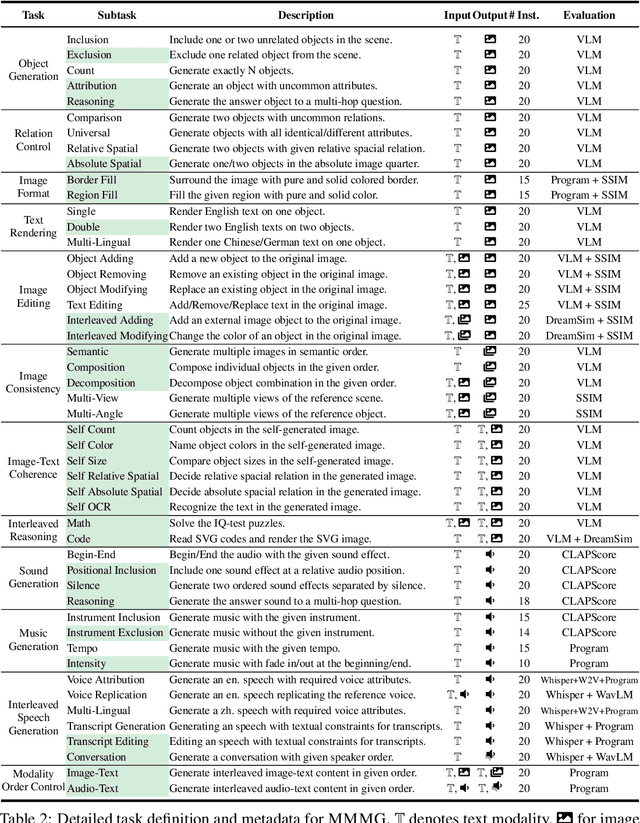
Abstract:Automatically evaluating multimodal generation presents a significant challenge, as automated metrics often struggle to align reliably with human evaluation, especially for complex tasks that involve multiple modalities. To address this, we present MMMG, a comprehensive and human-aligned benchmark for multimodal generation across 4 modality combinations (image, audio, interleaved text and image, interleaved text and audio), with a focus on tasks that present significant challenges for generation models, while still enabling reliable automatic evaluation through a combination of models and programs. MMMG encompasses 49 tasks (including 29 newly developed ones), each with a carefully designed evaluation pipeline, and 937 instructions to systematically assess reasoning, controllability, and other key capabilities of multimodal generation models. Extensive validation demonstrates that MMMG is highly aligned with human evaluation, achieving an average agreement of 94.3%. Benchmarking results on 24 multimodal generation models reveal that even though the state-of-the-art model, GPT Image, achieves 78.3% accuracy for image generation, it falls short on multimodal reasoning and interleaved generation. Furthermore, results suggest considerable headroom for improvement in audio generation, highlighting an important direction for future research.
Varying Shades of Wrong: Aligning LLMs with Wrong Answers Only
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:In the absence of abundant reliable annotations for challenging tasks and contexts, how can we expand the frontier of LLM capabilities with potentially wrong answers? We focus on two research questions: (1) Can LLMs generate reliable preferences among wrong options? And if so, (2) Would alignment with such wrong-over-wrong preferences be helpful? We employ methods based on self-consistency, token probabilities, and LLM-as-a-judge to elicit wrong-over-wrong preferences, and fine-tune language models with preference optimization approaches using these synthesized preferences. Extensive experiments with seven LLMs and eight datasets demonstrate that (1) LLMs do have preliminary capability in distinguishing various shades of wrong, achieving up to 20.9% higher performance than random guess; (2) Alignment with wrong-over-wrong preferences helps LLMs to produce less wrong and sometimes even outright correct answers, while overall improving model calibration.
Know Your Limits: A Survey of Abstention in Large Language Models
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:Abstention, the refusal of large language models (LLMs) to provide an answer, is increasingly recognized for its potential to mitigate hallucinations and enhance safety in LLM systems. In this survey, we introduce a framework to examine abstention from three perspectives: the query, the model, and human values. We organize the literature on abstention methods, benchmarks, and evaluation metrics using this framework, and discuss merits and limitations of prior work. We further identify and motivate areas for future work, centered around whether abstention can be achieved as a meta-capability that transcends specific tasks or domains, while still providing opportunities to optimize abstention abilities based on context.
The Art of Refusal: A Survey of Abstention in Large Language Models
Jul 25, 2024



Abstract:Abstention, the refusal of large language models (LLMs) to provide an answer, is increasingly recognized for its potential to mitigate hallucinations and enhance safety in building LLM systems. In this survey, we introduce a framework to examine abstention behavior from three perspectives: the query, the model, and human values. We review the literature on abstention methods (categorized based on the development stages of LLMs), benchmarks, and evaluation metrics, and discuss the merits and limitations of prior work. We further identify and motivate areas for future research, such as encouraging the study of abstention as a meta-capability across tasks and customizing abstention abilities based on context. In doing so, we aim to broaden the scope and impact of abstention methodologies in AI systems.
Developing a Framework for Auditing Large Language Models Using Human-in-the-Loop
Feb 16, 2024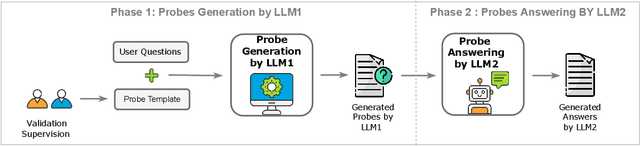
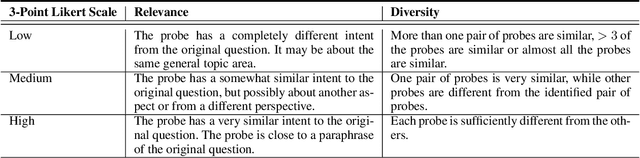

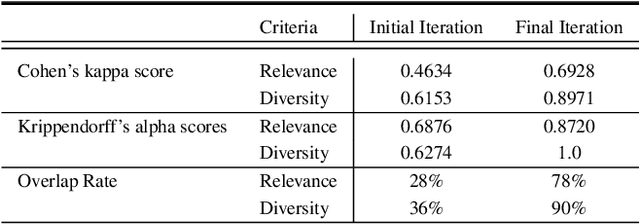
Abstract:As LLMs become more pervasive across various users and scenarios, identifying potential issues when using these models becomes essential. Examples include bias, inconsistencies, and hallucination. Although auditing the LLM for these problems is desirable, it is far from being easy or solved. An effective method is to probe the LLM using different versions of the same question. This could expose inconsistencies in its knowledge or operation, indicating potential for bias or hallucination. However, to operationalize this auditing method at scale, we need an approach to create those probes reliably and automatically. In this paper we propose an automatic and scalable solution, where one uses a different LLM along with human-in-the-loop. This approach offers verifiability and transparency, while avoiding circular reliance on the same LLMs, and increasing scientific rigor and generalizability. Specifically, we present a novel methodology with two phases of verification using humans: standardized evaluation criteria to verify responses, and a structured prompt template to generate desired probes. Experiments on a set of questions from TruthfulQA dataset show that we can generate a reliable set of probes from one LLM that can be used to audit inconsistencies in a different LLM. The criteria for generating and applying auditing probes is generalizable to various LLMs regardless of the underlying structure or training mechanism.
POTEC: Off-Policy Learning for Large Action Spaces via Two-Stage Policy Decomposition
Feb 09, 2024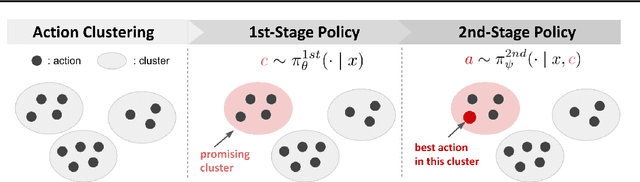
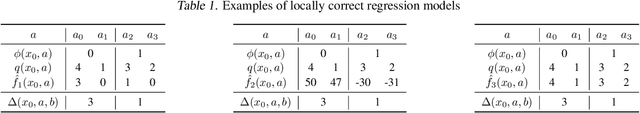
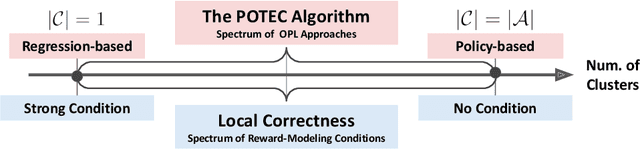
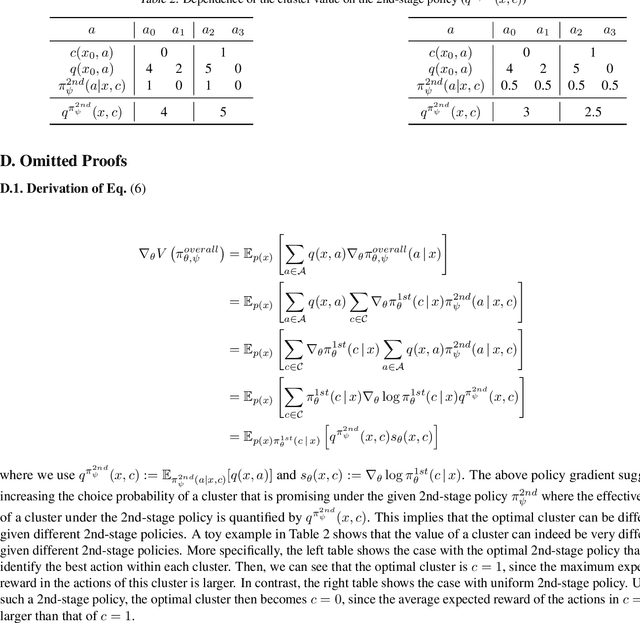
Abstract:We study off-policy learning (OPL) of contextual bandit policies in large discrete action spaces where existing methods -- most of which rely crucially on reward-regression models or importance-weighted policy gradients -- fail due to excessive bias or variance. To overcome these issues in OPL, we propose a novel two-stage algorithm, called Policy Optimization via Two-Stage Policy Decomposition (POTEC). It leverages clustering in the action space and learns two different policies via policy- and regression-based approaches, respectively. In particular, we derive a novel low-variance gradient estimator that enables to learn a first-stage policy for cluster selection efficiently via a policy-based approach. To select a specific action within the cluster sampled by the first-stage policy, POTEC uses a second-stage policy derived from a regression-based approach within each cluster. We show that a local correctness condition, which only requires that the regression model preserves the relative expected reward differences of the actions within each cluster, ensures that our policy-gradient estimator is unbiased and the second-stage policy is optimal. We also show that POTEC provides a strict generalization of policy- and regression-based approaches and their associated assumptions. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that POTEC provides substantial improvements in OPL effectiveness particularly in large and structured action spaces.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge