Yulia Tsvetkov
MentorCollab: Selective Large-to-Small Inference-Time Guidance for Efficient Reasoning
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) achieve strong performance by producing long chains of thought, but their inference costs are high and often generate redundant reasoning. Small language models (SLMs) are far more efficient, yet struggle on multi-step reasoning tasks. A natural idea is to let a large model guide a small one at inference time as a mentor, yet existing collaboration methods often promote imitation, resulting in verbose reasoning without consistent error correction. We propose MentorCollab, an inference-time collaboration method in which an LRM selectively and sparsely guides an SLM, rather than taking over generation. At randomly sampled token positions, we probe for divergences between the two models and use a lightweight verifier to decide whether the SLM should follow a short lookahead segment from its mentor or continue on its own. Across 15 SLM--LRM pairs and 3 domains (math reasoning, general knowledge, and commonsense reasoning), our method improves performance in 12 settings, with average gains of 3.0% and up to 8.0%, while adopting only having 18.4% tokens generated by the expensive mentor model on average. We find that short segments and selective probing are sufficient for effective collaboration. Our results show that selective inference-time guidance restores large-model reasoning ability without substantial inference overhead.
Among Us: Measuring and Mitigating Malicious Contributions in Model Collaboration Systems
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Language models (LMs) are increasingly used in collaboration: multiple LMs trained by different parties collaborate through routing systems, multi-agent debate, model merging, and more. Critical safety risks remain in this decentralized paradigm: what if some of the models in multi-LLM systems are compromised or malicious? We first quantify the impact of malicious models by engineering four categories of malicious LMs, plug them into four types of popular model collaboration systems, and evaluate the compromised system across 10 datasets. We find that malicious models have a severe impact on the multi-LLM systems, especially for reasoning and safety domains where performance is lowered by 7.12% and 7.94% on average. We then propose mitigation strategies to alleviate the impact of malicious components, by employing external supervisors that oversee model collaboration to disable/mask them out to reduce their influence. On average, these strategies recover 95.31% of the initial performance, while making model collaboration systems fully resistant to malicious models remains an open research question.
The Single-Multi Evolution Loop for Self-Improving Model Collaboration Systems
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Model collaboration -- systems where multiple language models (LMs) collaborate -- combines the strengths of diverse models with cost in loading multiple LMs. We improve efficiency while preserving the strengths of collaboration by distilling collaborative patterns into a single model, where the model is trained on the outputs of the model collaboration system. At inference time, only the distilled model is employed: it imitates the collaboration while only incurring the cost of a single model. Furthermore, we propose the single-multi evolution loop: multiple LMs collaborate, each distills from the collaborative outputs, and these post-distillation improved LMs collaborate again, forming a collective evolution ecosystem where models evolve and self-improve by interacting with an environment of other models. Extensive experiments with 7 collaboration strategies and 15 tasks (QA, reasoning, factuality, etc.) demonstrate that: 1) individual models improve by 8.0% on average, absorbing the strengths of collaboration while reducing the cost to a single model; 2) the collaboration also benefits from the stronger and more synergistic LMs after distillation, improving over initial systems without evolution by 14.9% on average. Analysis reveals that the single-multi evolution loop outperforms various existing evolutionary AI methods, is compatible with diverse model/collaboration/distillation settings, and helps solve problems where the initial model/system struggles to.
Privasis: Synthesizing the Largest "Public" Private Dataset from Scratch
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Research involving privacy-sensitive data has always been constrained by data scarcity, standing in sharp contrast to other areas that have benefited from data scaling. This challenge is becoming increasingly urgent as modern AI agents--such as OpenClaw and Gemini Agent--are granted persistent access to highly sensitive personal information. To tackle this longstanding bottleneck and the rising risks, we present Privasis (i.e., privacy oasis), the first million-scale fully synthetic dataset entirely built from scratch--an expansive reservoir of texts with rich and diverse private information--designed to broaden and accelerate research in areas where processing sensitive social data is inevitable. Compared to existing datasets, Privasis, comprising 1.4 million records, offers orders-of-magnitude larger scale with quality, and far greater diversity across various document types, including medical history, legal documents, financial records, calendars, and text messages with a total of 55.1 million annotated attributes such as ethnicity, date of birth, workplace, etc. We leverage Privasis to construct a parallel corpus for text sanitization with our pipeline that decomposes texts and applies targeted sanitization. Our compact sanitization models (<=4B) trained on this dataset outperform state-of-the-art large language models, such as GPT-5 and Qwen-3 235B. We plan to release data, models, and code to accelerate future research on privacy-sensitive domains and agents.
BASS: Benchmarking Audio LMs for Musical Structure and Semantic Reasoning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Music understanding is a complex task that often requires reasoning over both structural and semantic elements of audio. We introduce BASS, designed to evaluate music understanding and reasoning in audio language models across four broad categories: structural segmentation, lyric transcription, musicological analysis, and artist collaboration. BASS comprises 2658 questions spanning 12 tasks, 1993 unique songs and covering over 138 hours of music from a wide range of genres and tracks, crafted to assess musicological knowledge and reasoning in real-world scenarios. We evaluate 14 open-source and frontier multimodal LMs, finding that even state-of-the-art models struggle on higher-level reasoning tasks such as structural segmentation and artist collaboration, while performing best on lyric transcription. Our analysis reveals that current models leverage linguistic priors effectively but remain limited in reasoning over musical structure, vocal, and musicological attributes. BASS provides an evaluation framework with widespread applications in music recommendation and search and has the potential to guide the development of audio LMs.
MoCo: A One-Stop Shop for Model Collaboration Research
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Advancing beyond single monolithic language models (LMs), recent research increasingly recognizes the importance of model collaboration, where multiple LMs collaborate, compose, and complement each other. Existing research on this topic has mostly been disparate and disconnected, from different research communities, and lacks rigorous comparison. To consolidate existing research and establish model collaboration as a school of thought, we present MoCo: a one-stop Python library of executing, benchmarking, and comparing model collaboration algorithms at scale. MoCo features 26 model collaboration methods, spanning diverse levels of cross-model information exchange such as routing, text, logit, and model parameters. MoCo integrates 25 evaluation datasets spanning reasoning, QA, code, safety, and more, while users could flexibly bring their own data. Extensive experiments with MoCo demonstrate that most collaboration strategies outperform models without collaboration in 61.0% of (model, data) settings on average, with the most effective methods outperforming by up to 25.8%. We further analyze the scaling of model collaboration strategies, the training/inference efficiency of diverse methods, highlight that the collaborative system solves problems where single LMs struggle, and discuss future work in model collaboration, all made possible by MoCo. We envision MoCo as a valuable toolkit to facilitate and turbocharge the quest for an open, modular, decentralized, and collaborative AI future.
RLVE: Scaling Up Reinforcement Learning for Language Models with Adaptive Verifiable Environments
Nov 10, 2025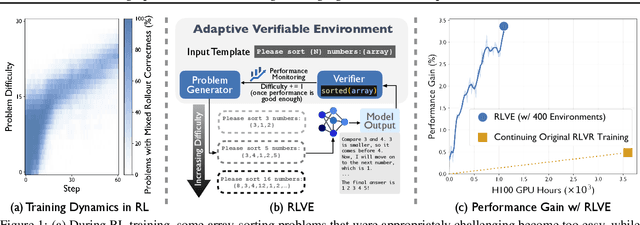

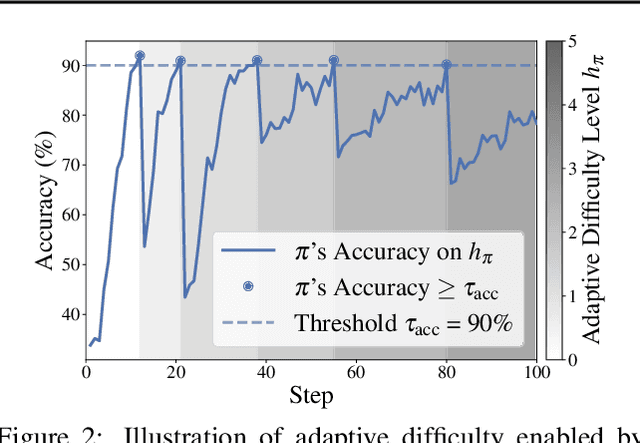
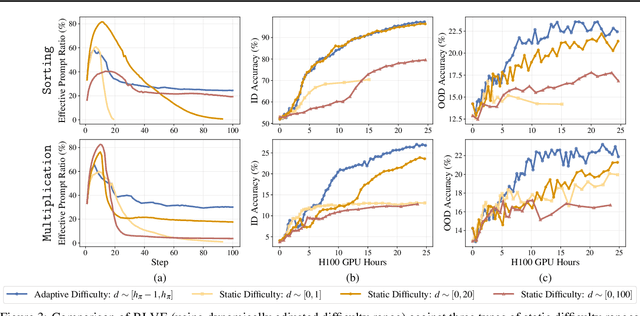
Abstract:We introduce Reinforcement Learning (RL) with Adaptive Verifiable Environments (RLVE), an approach using verifiable environments that procedurally generate problems and provide algorithmically verifiable rewards, to scale up RL for language models (LMs). RLVE enables each verifiable environment to dynamically adapt its problem difficulty distribution to the policy model's capabilities as training progresses. In contrast, static data distributions often lead to vanishing learning signals when problems are either too easy or too hard for the policy. To implement RLVE, we create RLVE-Gym, a large-scale suite of 400 verifiable environments carefully developed through manual environment engineering. Using RLVE-Gym, we show that environment scaling, i.e., expanding the collection of training environments, consistently improves generalizable reasoning capabilities. RLVE with joint training across all 400 environments in RLVE-Gym yields a 3.37% absolute average improvement across six reasoning benchmarks, starting from one of the strongest 1.5B reasoning LMs. By comparison, continuing this LM's original RL training yields only a 0.49% average absolute gain despite using over 3x more compute. We release our code publicly.
Artificial Hivemind: The Open-Ended Homogeneity of Language Models (and Beyond)
Oct 27, 2025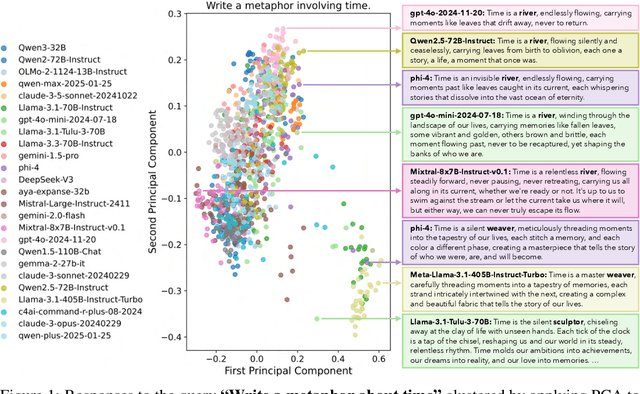
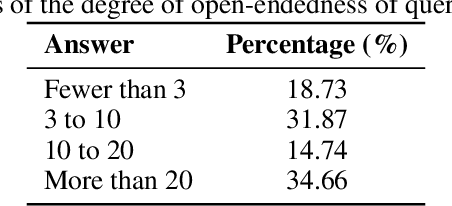
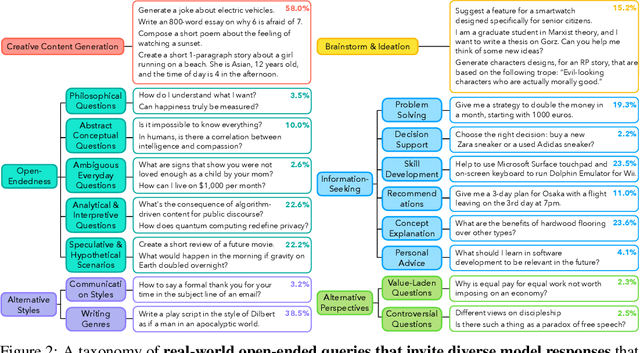

Abstract:Language models (LMs) often struggle to generate diverse, human-like creative content, raising concerns about the long-term homogenization of human thought through repeated exposure to similar outputs. Yet scalable methods for evaluating LM output diversity remain limited, especially beyond narrow tasks such as random number or name generation, or beyond repeated sampling from a single model. We introduce Infinity-Chat, a large-scale dataset of 26K diverse, real-world, open-ended user queries that admit a wide range of plausible answers with no single ground truth. We introduce the first comprehensive taxonomy for characterizing the full spectrum of open-ended prompts posed to LMs, comprising 6 top-level categories (e.g., brainstorm & ideation) that further breaks down to 17 subcategories. Using Infinity-Chat, we present a large-scale study of mode collapse in LMs, revealing a pronounced Artificial Hivemind effect in open-ended generation of LMs, characterized by (1) intra-model repetition, where a single model consistently generates similar responses, and more so (2) inter-model homogeneity, where different models produce strikingly similar outputs. Infinity-Chat also includes 31,250 human annotations, across absolute ratings and pairwise preferences, with 25 independent human annotations per example. This enables studying collective and individual-specific human preferences in response to open-ended queries. Our findings show that LMs, reward models, and LM judges are less well calibrated to human ratings on model generations that elicit differing idiosyncratic annotator preferences, despite maintaining comparable overall quality. Overall, INFINITY-CHAT presents the first large-scale resource for systematically studying real-world open-ended queries to LMs, revealing critical insights to guide future research for mitigating long-term AI safety risks posed by the Artificial Hivemind.
PrefPalette: Personalized Preference Modeling with Latent Attributes
Jul 17, 2025



Abstract:Personalizing AI systems requires understanding not just what users prefer, but the reasons that underlie those preferences - yet current preference models typically treat human judgment as a black box. We introduce PrefPalette, a framework that decomposes preferences into attribute dimensions and tailors its preference prediction to distinct social community values in a human-interpretable manner. PrefPalette operationalizes a cognitive science principle known as multi-attribute decision making in two ways: (1) a scalable counterfactual attribute synthesis step that involves generating synthetic training data to isolate for individual attribute effects (e.g., formality, humor, cultural values), and (2) attention-based preference modeling that learns how different social communities dynamically weight these attributes. This approach moves beyond aggregate preference modeling to capture the diverse evaluation frameworks that drive human judgment. When evaluated on 45 social communities from the online platform Reddit, PrefPalette outperforms GPT-4o by 46.6% in average prediction accuracy. Beyond raw predictive improvements, PrefPalette also shed light on intuitive, community-specific profiles: scholarly communities prioritize verbosity and stimulation, conflict-oriented communities value sarcasm and directness, and support-based communities emphasize empathy. By modeling the attribute-mediated structure of human judgment, PrefPalette delivers both superior preference modeling and transparent, interpretable insights, and serves as a first step toward more trustworthy, value-aware personalized applications.
Spurious Rewards: Rethinking Training Signals in RLVR
Jun 12, 2025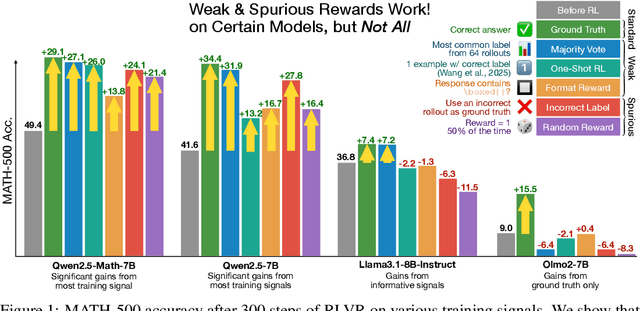
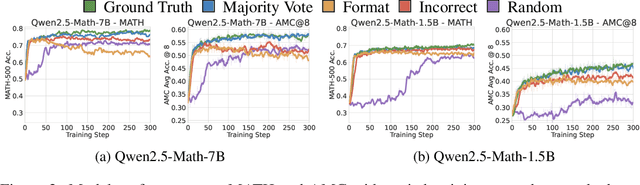
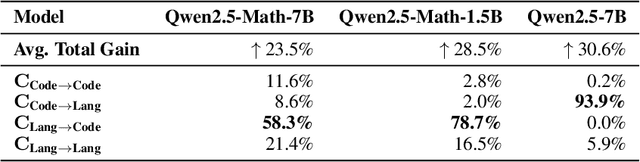
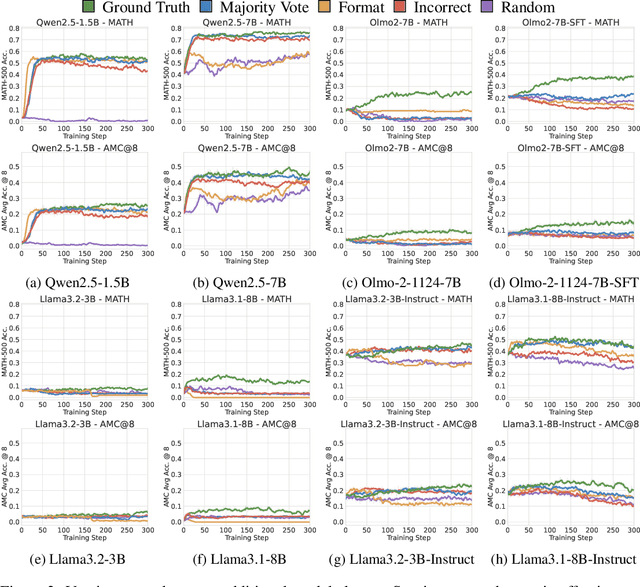
Abstract:We show that reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) can elicit strong mathematical reasoning in certain models even with spurious rewards that have little, no, or even negative correlation with the correct answer. For example, RLVR improves MATH-500 performance for Qwen2.5-Math-7B in absolute points by 21.4% (random reward), 13.8% (format reward), 24.1% (incorrect label), 26.0% (1-shot RL), and 27.1% (majority voting) -- nearly matching the 29.1% gained with ground truth rewards. However, the spurious rewards that work for Qwen often fail to yield gains with other model families like Llama3 or OLMo2. In particular, we find code reasoning -- thinking in code without actual code execution -- to be a distinctive Qwen2.5-Math behavior that becomes significantly more frequent after RLVR, from 65% to over 90%, even with spurious rewards. Overall, we hypothesize that, given the lack of useful reward signal, RLVR must somehow be surfacing useful reasoning representations learned during pretraining, although the exact mechanism remains a topic for future work. We suggest that future RLVR research should possibly be validated on diverse models rather than a single de facto choice, as we show that it is easy to get significant performance gains on Qwen models even with completely spurious reward signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge