Kabir Ahuja
BLAB: Brutally Long Audio Bench
May 05, 2025Abstract:Developing large audio language models (LMs) capable of understanding diverse spoken interactions is essential for accommodating the multimodal nature of human communication and can increase the accessibility of language technologies across different user populations. Recent work on audio LMs has primarily evaluated their performance on short audio segments, typically under 30 seconds, with limited exploration of long-form conversational speech segments that more closely reflect natural user interactions with these models. We introduce Brutally Long Audio Bench (BLAB), a challenging long-form audio benchmark that evaluates audio LMs on localization, duration estimation, emotion, and counting tasks using audio segments averaging 51 minutes in length. BLAB consists of 833+ hours of diverse, full-length audio clips, each paired with human-annotated, text-based natural language questions and answers. Our audio data were collected from permissively licensed sources and underwent a human-assisted filtering process to ensure task compliance. We evaluate six open-source and proprietary audio LMs on BLAB and find that all of them, including advanced models such as Gemini 2.0 Pro and GPT-4o, struggle with the tasks in BLAB. Our comprehensive analysis reveals key insights into the trade-offs between task difficulty and audio duration. In general, we find that audio LMs struggle with long-form speech, with performance declining as duration increases. They perform poorly on localization, temporal reasoning, counting, and struggle to understand non-phonemic information, relying more on prompts than audio content. BLAB serves as a challenging evaluation framework to develop audio LMs with robust long-form audio understanding capabilities.
Finding Flawed Fictions: Evaluating Complex Reasoning in Language Models via Plot Hole Detection
Apr 16, 2025
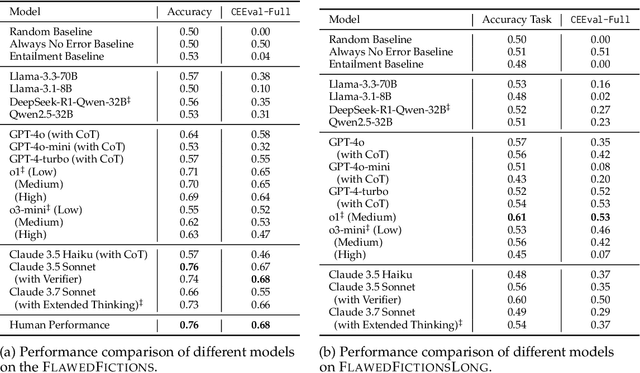

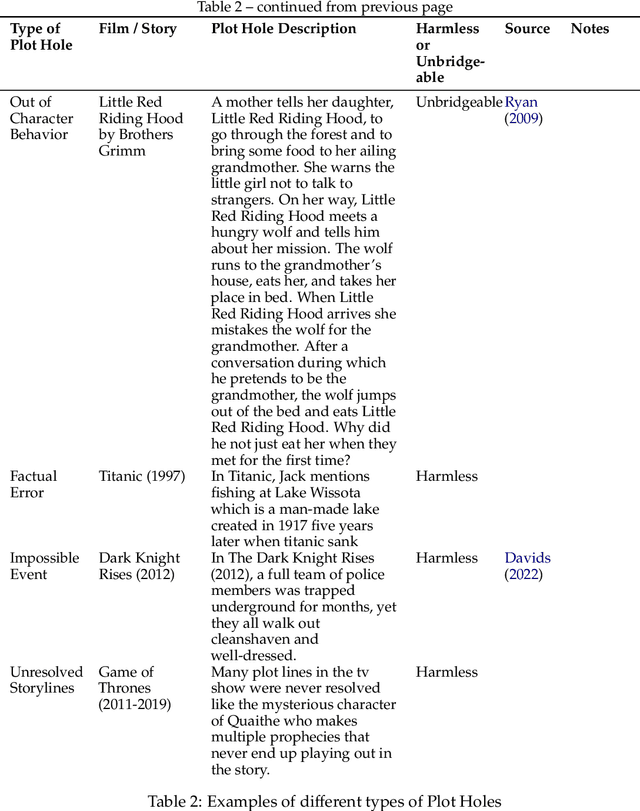
Abstract:Stories are a fundamental aspect of human experience. Engaging deeply with stories and spotting plot holes -- inconsistencies in a storyline that break the internal logic or rules of a story's world -- requires nuanced reasoning skills, including tracking entities and events and their interplay, abstract thinking, pragmatic narrative understanding, commonsense and social reasoning, and theory of mind. As Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly generate, interpret, and modify text, rigorously assessing their narrative consistency and deeper language understanding becomes critical. However, existing benchmarks focus mainly on surface-level comprehension. In this work, we propose plot hole detection in stories as a proxy to evaluate language understanding and reasoning in LLMs. We introduce FlawedFictionsMaker, a novel algorithm to controllably and carefully synthesize plot holes in human-written stories. Using this algorithm, we construct a benchmark to evaluate LLMs' plot hole detection abilities in stories -- FlawedFictions -- , which is robust to contamination, with human filtering ensuring high quality. We find that state-of-the-art LLMs struggle in accurately solving FlawedFictions regardless of the reasoning effort allowed, with performance significantly degrading as story length increases. Finally, we show that LLM-based story summarization and story generation are prone to introducing plot holes, with more than 50% and 100% increases in plot hole detection rates with respect to human-written originals.
Bridging the Gap: Dynamic Learning Strategies for Improving Multilingual Performance in LLMs
May 28, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are at the forefront of transforming numerous domains globally. However, their inclusivity and effectiveness remain limited for non-Latin scripts and low-resource languages. This paper tackles the imperative challenge of enhancing the multilingual performance of LLMs without extensive training or fine-tuning. Through systematic investigation and evaluation of diverse languages using popular question-answering (QA) datasets, we present novel techniques that unlock the true potential of LLMs in a polyglot landscape. Our approach encompasses three key strategies that yield significant improvements in multilingual proficiency. First, by meticulously optimizing prompts tailored for polyglot LLMs, we unlock their latent capabilities, resulting in substantial performance boosts across languages. Second, we introduce a new hybrid approach that synergizes LLM Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) with multilingual embeddings and achieves improved multilingual task performance. Finally, we introduce a novel learning approach that dynamically selects the optimal prompt strategy, LLM model, and embedding model per query at run-time. This dynamic adaptation maximizes the efficacy of LLMs across languages, outperforming best static and random strategies. Additionally, our approach adapts configurations in both offline and online settings, and can seamlessly adapt to new languages and datasets, leading to substantial advancements in multilingual understanding and generation across diverse languages.
Learning Syntax Without Planting Trees: Understanding When and Why Transformers Generalize Hierarchically
Apr 25, 2024Abstract:Transformers trained on natural language data have been shown to learn its hierarchical structure and generalize to sentences with unseen syntactic structures without explicitly encoding any structural bias. In this work, we investigate sources of inductive bias in transformer models and their training that could cause such generalization behavior to emerge. We extensively experiment with transformer models trained on multiple synthetic datasets and with different training objectives and show that while other objectives e.g. sequence-to-sequence modeling, prefix language modeling, often failed to lead to hierarchical generalization, models trained with the language modeling objective consistently learned to generalize hierarchically. We then conduct pruning experiments to study how transformers trained with the language modeling objective encode hierarchical structure. When pruned, we find joint existence of subnetworks within the model with different generalization behaviors (subnetworks corresponding to hierarchical structure and linear order). Finally, we take a Bayesian perspective to further uncover transformers' preference for hierarchical generalization: We establish a correlation between whether transformers generalize hierarchically on a dataset and whether the simplest explanation of that dataset is provided by a hierarchical grammar compared to regular grammars exhibiting linear generalization.
DIALECTBENCH: A NLP Benchmark for Dialects, Varieties, and Closely-Related Languages
Mar 16, 2024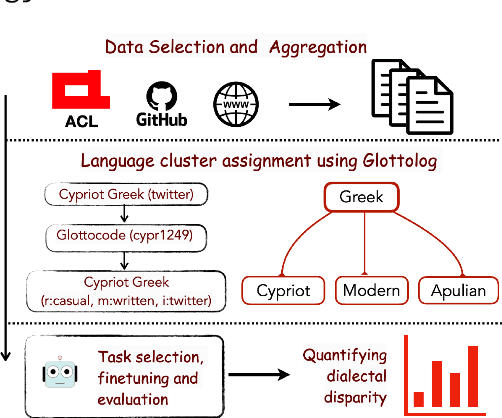
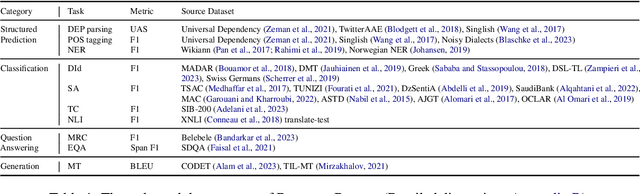
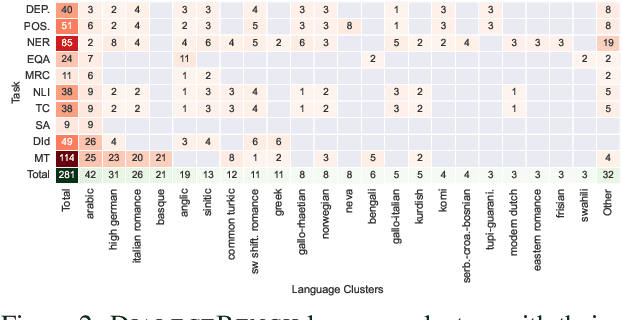
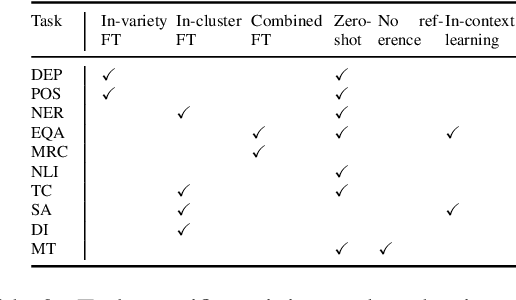
Abstract:Language technologies should be judged on their usefulness in real-world use cases. An often overlooked aspect in natural language processing (NLP) research and evaluation is language variation in the form of non-standard dialects or language varieties (hereafter, varieties). Most NLP benchmarks are limited to standard language varieties. To fill this gap, we propose DIALECTBENCH, the first-ever large-scale benchmark for NLP on varieties, which aggregates an extensive set of task-varied variety datasets (10 text-level tasks covering 281 varieties). This allows for a comprehensive evaluation of NLP system performance on different language varieties. We provide substantial evidence of performance disparities between standard and non-standard language varieties, and we also identify language clusters with large performance divergence across tasks. We believe DIALECTBENCH provides a comprehensive view of the current state of NLP for language varieties and one step towards advancing it further. Code/data: https://github.com/ffaisal93/DialectBench
MAFIA: Multi-Adapter Fused Inclusive LanguAge Models
Feb 12, 2024



Abstract:Pretrained Language Models (PLMs) are widely used in NLP for various tasks. Recent studies have identified various biases that such models exhibit and have proposed methods to correct these biases. However, most of the works address a limited set of bias dimensions independently such as gender, race, or religion. Moreover, the methods typically involve finetuning the full model to maintain the performance on the downstream task. In this work, we aim to modularly debias a pretrained language model across multiple dimensions. Previous works extensively explored debiasing PLMs using limited US-centric counterfactual data augmentation (CDA). We use structured knowledge and a large generative model to build a diverse CDA across multiple bias dimensions in a semi-automated way. We highlight how existing debiasing methods do not consider interactions between multiple societal biases and propose a debiasing model that exploits the synergy amongst various societal biases and enables multi-bias debiasing simultaneously. An extensive evaluation on multiple tasks and languages demonstrates the efficacy of our approach.
On Evaluating and Mitigating Gender Biases in Multilingual Settings
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:While understanding and removing gender biases in language models has been a long-standing problem in Natural Language Processing, prior research work has primarily been limited to English. In this work, we investigate some of the challenges with evaluating and mitigating biases in multilingual settings which stem from a lack of existing benchmarks and resources for bias evaluation beyond English especially for non-western context. In this paper, we first create a benchmark for evaluating gender biases in pre-trained masked language models by extending DisCo to different Indian languages using human annotations. We extend various debiasing methods to work beyond English and evaluate their effectiveness for SOTA massively multilingual models on our proposed metric. Overall, our work highlights the challenges that arise while studying social biases in multilingual settings and provides resources as well as mitigation techniques to take a step toward scaling to more languages.
In-Context Learning through the Bayesian Prism
Jun 08, 2023



Abstract:In-context learning is one of the surprising and useful features of large language models. How it works is an active area of research. Recently, stylized meta-learning-like setups have been devised that train these models on a sequence of input-output pairs $(x, f(x))$ from a function class using the language modeling loss and observe generalization to unseen functions from the same class. One of the main discoveries in this line of research has been that for several problems such as linear regression, trained transformers learn algorithms for learning functions in context. However, the inductive biases of these models resulting in this behavior are not clearly understood. A model with unlimited training data and compute is a Bayesian predictor: it learns the pretraining distribution. It has been shown that high-capacity transformers mimic the Bayesian predictor for linear regression. In this paper, we show empirical evidence of transformers exhibiting the behavior of this ideal learner across different linear and non-linear function classes. We also extend the previous setups to work in the multitask setting and verify that transformers can do in-context learning in this setup as well and the Bayesian perspective sheds light on this setting also. Finally, via the example of learning Fourier series, we study the inductive bias for in-context learning. We find that in-context learning may or may not have simplicity bias depending on the pretraining data distribution.
Breaking Language Barriers with a LEAP: Learning Strategies for Polyglot LLMs
May 28, 2023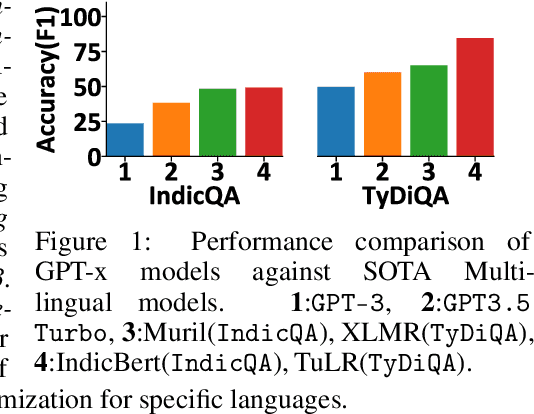
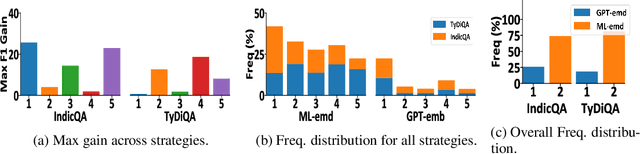
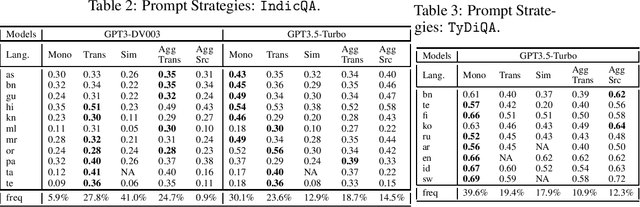
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are at the forefront of transforming numerous domains globally. However, their inclusivity and effectiveness remain limited for non-Latin scripts and low-resource languages. This paper tackles the imperative challenge of enhancing the multilingual performance of LLMs, specifically focusing on Generative models. Through systematic investigation and evaluation of diverse languages using popular question-answering (QA) datasets, we present novel techniques that unlock the true potential of LLMs in a polyglot landscape. Our approach encompasses three key strategies that yield remarkable improvements in multilingual proficiency. First, by meticulously optimizing prompts tailored for polyglot LLMs, we unlock their latent capabilities, resulting in substantial performance boosts across languages. Second, we introduce a new hybrid approach that synergizes GPT generation with multilingual embeddings and achieves significant multilingual performance improvement on critical tasks like QA and retrieval. Finally, to further propel the performance of polyglot LLMs, we introduce a novel learning algorithm that dynamically selects the optimal prompt strategy, LLM model, and embeddings per query. This dynamic adaptation maximizes the efficacy of LLMs across languages, outperforming best static and random strategies. Our results show substantial advancements in multilingual understanding and generation across a diverse range of languages.
MEGA: Multilingual Evaluation of Generative AI
Apr 03, 2023



Abstract:Generative AI models have impressive performance on many Natural Language Processing tasks such as language understanding, reasoning and language generation. One of the most important questions that is being asked by the AI community today is about the capabilities and limits of these models, and it is clear that evaluating generative AI is very challenging. Most studies on generative Large Language Models (LLMs) are restricted to English and it is unclear how capable these models are at understanding and generating other languages. We present the first comprehensive benchmarking of generative LLMs - MEGA, which evaluates models on standard NLP benchmarks, covering 8 diverse tasks and 33 typologically diverse languages. We also compare the performance of generative LLMs to State of the Art (SOTA) non-autoregressive models on these tasks to determine how well generative models perform compared to the previous generation of LLMs. We present a thorough analysis of the performance of models across languages and discuss some of the reasons why generative LLMs are currently not optimal for all languages. We create a framework for evaluating generative LLMs in the multilingual setting and provide directions for future progress in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge