Sunayana Sitaram
Fluent but Culturally Distant: Can Regional Training Teach Cultural Understanding?
May 25, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are used around the world but exhibit Western cultural tendencies. To address this cultural misalignment, many countries have begun developing "regional" LLMs tailored to local communities. Yet it remains unclear whether these models merely speak the language of their users or also reflect their cultural values and practices. Using India as a case study, we evaluate five Indic and five global LLMs along two key dimensions: values (via the Inglehart-Welzel map and GlobalOpinionQA) and practices (via CulturalBench and NormAd). Across all four tasks, we find that Indic models do not align more closely with Indian cultural norms than global models. In fact, an average American person is a better proxy for Indian cultural values than any Indic model. Even prompting strategies fail to meaningfully improve alignment. Ablations show that regional fine-tuning does not enhance cultural competence and may in fact hurt it by impeding recall of existing knowledge. We trace this failure to the scarcity of high-quality, untranslated, and culturally grounded pretraining and fine-tuning data. Our study positions cultural evaluation as a first-class requirement alongside multilingual benchmarks and offers a reusable methodology for developers. We call for deeper investments in culturally representative data to build and evaluate truly sovereign LLMs.
A Multilingual, Culture-First Approach to Addressing Misgendering in LLM Applications
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Misgendering is the act of referring to someone by a gender that does not match their chosen identity. It marginalizes and undermines a person's sense of self, causing significant harm. English-based approaches have clear-cut approaches to avoiding misgendering, such as the use of the pronoun ``they''. However, other languages pose unique challenges due to both grammatical and cultural constructs. In this work we develop methodologies to assess and mitigate misgendering across 42 languages and dialects using a participatory-design approach to design effective and appropriate guardrails across all languages. We test these guardrails in a standard large language model-based application (meeting transcript summarization), where both the data generation and the annotation steps followed a human-in-the-loop approach. We find that the proposed guardrails are very effective in reducing misgendering rates across all languages in the summaries generated, and without incurring loss of quality. Our human-in-the-loop approach demonstrates a method to feasibly scale inclusive and responsible AI-based solutions across multiple languages and cultures.
Uncovering inequalities in new knowledge learning by large language models across different languages
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) gradually become integral tools for problem solving in daily life worldwide, understanding linguistic inequality is becoming increasingly important. Existing research has primarily focused on static analyses that assess the disparities in the existing knowledge and capabilities of LLMs across languages. However, LLMs are continuously evolving, acquiring new knowledge to generate up-to-date, domain-specific responses. Investigating linguistic inequalities within this dynamic process is, therefore, also essential. In this paper, we explore inequalities in new knowledge learning by LLMs across different languages and four key dimensions: effectiveness, transferability, prioritization, and robustness. Through extensive experiments under two settings (in-context learning and fine-tuning) using both proprietary and open-source models, we demonstrate that low-resource languages consistently face disadvantages across all four dimensions. By shedding light on these disparities, we aim to raise awareness of linguistic inequalities in LLMs' new knowledge learning, fostering the development of more inclusive and equitable future LLMs.
Exploring Continual Fine-Tuning for Enhancing Language Ability in Large Language Model
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:A common challenge towards the adaptability of Large Language Models (LLMs) is their ability to learn new languages over time without hampering the model's performance on languages in which the model is already proficient (usually English). Continual fine-tuning (CFT) is the process of sequentially fine-tuning an LLM to enable the model to adapt to downstream tasks with varying data distributions and time shifts. This paper focuses on the language adaptability of LLMs through CFT. We study a two-phase CFT process in which an English-only end-to-end fine-tuned LLM from Phase 1 (predominantly Task Ability) is sequentially fine-tuned on a multilingual dataset -- comprising task data in new languages -- in Phase 2 (predominantly Language Ability). We observe that the ``similarity'' of Phase 2 tasks with Phase 1 determines the LLM's adaptability. For similar phase-wise datasets, the LLM after Phase 2 does not show deterioration in task ability. In contrast, when the phase-wise datasets are not similar, the LLM's task ability deteriorates. We test our hypothesis on the open-source \mis\ and \llm\ models with multiple phase-wise dataset pairs. To address the deterioration, we analyze tailored variants of two CFT methods: layer freezing and generative replay. Our findings demonstrate their effectiveness in enhancing the language ability of LLMs while preserving task performance, in comparison to relevant baselines.
Contamination Report for Multilingual Benchmarks
Oct 21, 2024

Abstract:Benchmark contamination refers to the presence of test datasets in Large Language Model (LLM) pre-training or post-training data. Contamination can lead to inflated scores on benchmarks, compromising evaluation results and making it difficult to determine the capabilities of models. In this work, we study the contamination of popular multilingual benchmarks in LLMs that support multiple languages. We use the Black Box test to determine whether $7$ frequently used multilingual benchmarks are contaminated in $7$ popular open and closed LLMs and find that almost all models show signs of being contaminated with almost all the benchmarks we test. Our findings can help the community determine the best set of benchmarks to use for multilingual evaluation.
Exploring Pretraining via Active Forgetting for Improving Cross Lingual Transfer for Decoder Language Models
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate exceptional capabilities in a multitude of NLP tasks. However, the efficacy of such models to languages other than English is often limited. Prior works have shown that encoder-only models such as BERT or XLM-RoBERTa show impressive cross lingual transfer of their capabilities from English to other languages. In this work, we propose a pretraining strategy that uses active forgetting to achieve similar cross lingual transfer in decoder-only LLMs. We show that LLMs pretrained with active forgetting are highly effective when adapting to new and unseen languages. Through extensive experimentation, we find that LLMs pretrained with active forgetting are able to learn better multilingual representations which translates to better performance in many downstream tasks.
HEALTH-PARIKSHA: Assessing RAG Models for Health Chatbots in Real-World Multilingual Settings
Oct 17, 2024
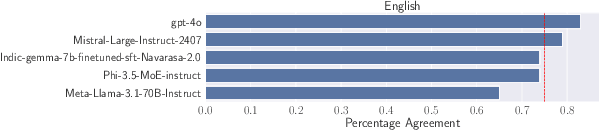
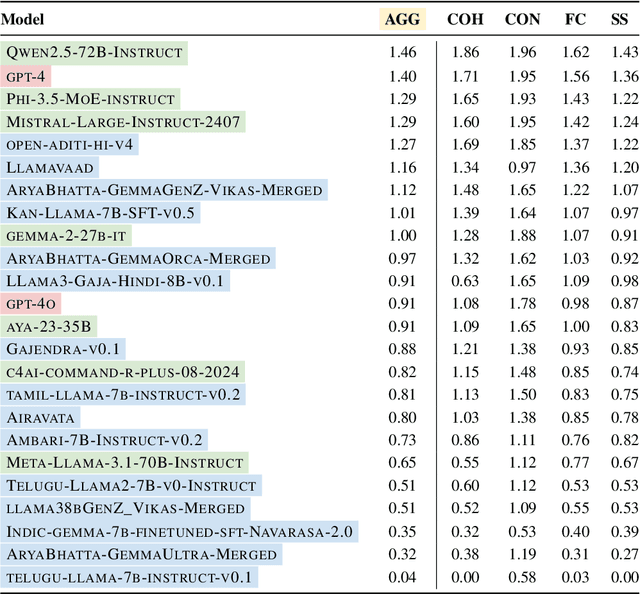
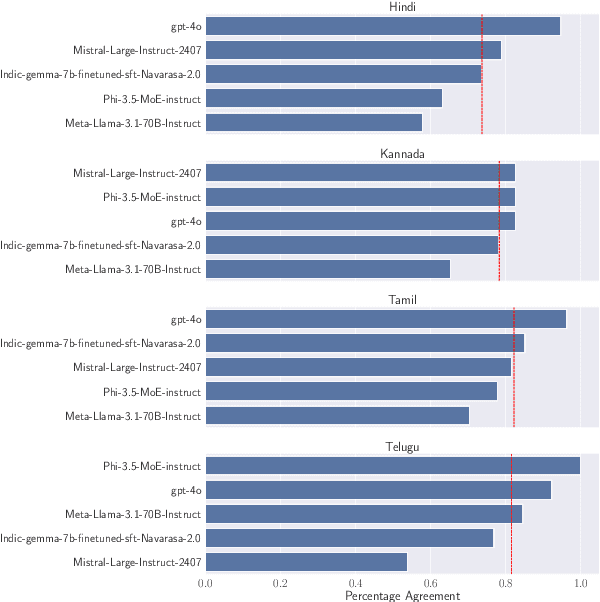
Abstract:Assessing the capabilities and limitations of large language models (LLMs) has garnered significant interest, yet the evaluation of multiple models in real-world scenarios remains rare. Multilingual evaluation often relies on translated benchmarks, which typically do not capture linguistic and cultural nuances present in the source language. This study provides an extensive assessment of 24 LLMs on real world data collected from Indian patients interacting with a medical chatbot in Indian English and 4 other Indic languages. We employ a uniform Retrieval Augmented Generation framework to generate responses, which are evaluated using both automated techniques and human evaluators on four specific metrics relevant to our application. We find that models vary significantly in their performance and that instruction tuned Indic models do not always perform well on Indic language queries. Further, we empirically show that factual correctness is generally lower for responses to Indic queries compared to English queries. Finally, our qualitative work shows that code-mixed and culturally relevant queries in our dataset pose challenges to evaluated models.
JOOCI: a Framework for Learning Comprehensive Speech Representations
Oct 14, 2024Abstract:Information in speech can be divided into two categories: what is being said (content) and how it is expressed (other). Current state-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques model speech at fixed segments, usually 10-25 ms, using a single embedding. Given the orthogonal nature of other and content information, attempting to optimize both within a single embedding results in suboptimal solutions. This approach divides the models capacity, limiting its ability to build complex hierarchical features effectively. In this work, we present an end-to-end speech representation learning framework designed to jointly optimize the other and content information (JOOCI) in speech. By using separate learnable parameters, JOOCI addresses this optimization challenge by modeling other and content information independently. Our results show that JOOCI consistently outperforms other SOTA models of similar size (100 million parameters) and pre-training data used (960 hours) by a significant margin when evaluated on a range of speech downstream tasks in the SUPERB benchmark, as shown in Table 1.
Speech Representation Learning Revisited: The Necessity of Separate Learnable Parameters and Robust Data Augmentation
Aug 20, 2024Abstract:Speech modeling methods learn one embedding for a fixed segment of speech, typically in between 10-25 ms. The information present in speech can be divided into two categories: "what is being said" (content) and "how it is expressed" (other) and these two are orthogonal in nature causing the optimization algorithm to find a sub-optimal solution if forced to optimize together. This leads to sub-optimal performance in one or all downstream tasks as shown by previous studies. Current self-supervised learning (SSL) methods such as HuBERT are very good at modeling the content information present in speech. Data augmentation improves the performance on tasks which require effective modeling of other information but this leads to a divided capacity of the model. In this work, we conduct a preliminary study to understand the importance of modeling other information using separate learnable parameters. We propose a modified version of HuBERT, termed Other HuBERT (O-HuBERT), to test our hypothesis. Our findings are twofold: first, the O-HuBERT method is able to utilize all layers to build complex features to encode other information; second, a robust data augmentation strategy is essential for learning the information required by tasks that depend on other information and to achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on the SUPERB benchmark with a similarly sized model (100 million parameters) and pre-training data (960 hours).
sPhinX: Sample Efficient Multilingual Instruction Fine-Tuning Through N-shot Guided Prompting
Jul 16, 2024Abstract:Despite the remarkable success of LLMs in English, there is a significant gap in performance in non-English languages. In order to address this, we introduce a novel recipe for creating a multilingual synthetic instruction tuning dataset, sPhinX, which is created by selectively translating instruction response pairs from English into 50 languages. We test the effectiveness of sPhinX by using it to fine-tune two state-of-the-art models, Phi-3-small and Mistral-7B and then evaluating them across a comprehensive suite of multilingual benchmarks that test reasoning, question answering, and reading comprehension. Our results show that Phi-3-small and Mistral-7B fine-tuned with sPhinX perform better on an average by 4.2%pt and 5%pt respectively as compared to the baselines. We also devise a strategy to incorporate N-shot examples in each fine-tuning sample which further boosts the performance of these models by 3%pt and 10%pt respectively. Additionally, sPhinX also outperforms other multilingual instruction tuning datasets on the same benchmarks along with being sample efficient and diverse, thereby reducing dataset creation costs. Additionally, instruction tuning with sPhinX does not lead to regression on most standard LLM benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge