Zhaoya Gong
Peking University
Uncovering inequalities in new knowledge learning by large language models across different languages
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) gradually become integral tools for problem solving in daily life worldwide, understanding linguistic inequality is becoming increasingly important. Existing research has primarily focused on static analyses that assess the disparities in the existing knowledge and capabilities of LLMs across languages. However, LLMs are continuously evolving, acquiring new knowledge to generate up-to-date, domain-specific responses. Investigating linguistic inequalities within this dynamic process is, therefore, also essential. In this paper, we explore inequalities in new knowledge learning by LLMs across different languages and four key dimensions: effectiveness, transferability, prioritization, and robustness. Through extensive experiments under two settings (in-context learning and fine-tuning) using both proprietary and open-source models, we demonstrate that low-resource languages consistently face disadvantages across all four dimensions. By shedding light on these disparities, we aim to raise awareness of linguistic inequalities in LLMs' new knowledge learning, fostering the development of more inclusive and equitable future LLMs.
Research on Foundation Model for Spatial Data Intelligence: China's 2024 White Paper on Strategic Development of Spatial Data Intelligence
May 30, 2024Abstract:This report focuses on spatial data intelligent large models, delving into the principles, methods, and cutting-edge applications of these models. It provides an in-depth discussion on the definition, development history, current status, and trends of spatial data intelligent large models, as well as the challenges they face. The report systematically elucidates the key technologies of spatial data intelligent large models and their applications in urban environments, aerospace remote sensing, geography, transportation, and other scenarios. Additionally, it summarizes the latest application cases of spatial data intelligent large models in themes such as urban development, multimodal systems, remote sensing, smart transportation, and resource environments. Finally, the report concludes with an overview and outlook on the development prospects of spatial data intelligent large models.
PlanGPT: Enhancing Urban Planning with Tailored Language Model and Efficient Retrieval
Feb 29, 2024
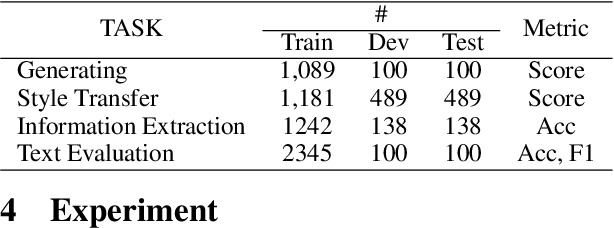
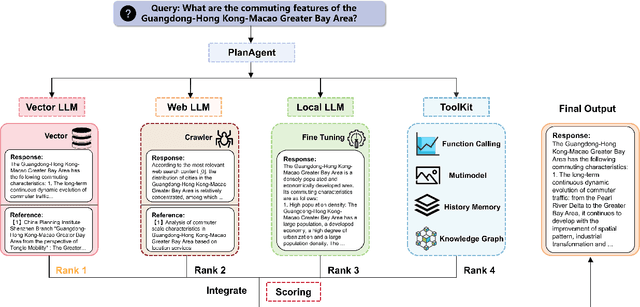
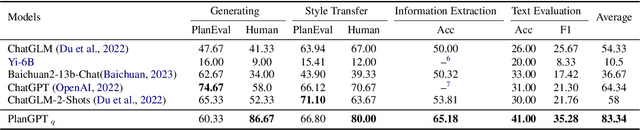
Abstract:In the field of urban planning, general-purpose large language models often struggle to meet the specific needs of planners. Tasks like generating urban planning texts, retrieving related information, and evaluating planning documents pose unique challenges. To enhance the efficiency of urban professionals and overcome these obstacles, we introduce PlanGPT, the first specialized Large Language Model tailored for urban and spatial planning. Developed through collaborative efforts with institutions like the Chinese Academy of Urban Planning, PlanGPT leverages a customized local database retrieval framework, domain-specific fine-tuning of base models, and advanced tooling capabilities. Empirical tests demonstrate that PlanGPT has achieved advanced performance, delivering responses of superior quality precisely tailored to the intricacies of urban planning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge