Yang Yue
Shenzhen University
Structurally Aligned Subtask-Level Memory for Software Engineering Agents
Feb 25, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential as autonomous software engineering (SWE) agents. Recent work has further explored augmenting these agents with memory mechanisms to support long-horizon reasoning. However, these approaches typically operate at a coarse instance granularity, treating the entire problem-solving episode as the atomic unit of storage and retrieval. We empirically demonstrate that instance-level memory suffers from a fundamental granularity mismatch, resulting in misguided retrieval when tasks with similar surface descriptions require distinct reasoning logic at specific stages. To address this, we propose Structurally Aligned Subtask-Level Memory, a method that aligns memory storage, retrieval, and updating with the agent's functional decomposition. Extensive experiments on SWE-bench Verified demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms both vanilla agents and strong instance-level memory baselines across diverse backbones, improving mean Pass@1 over the vanilla agent by +4.7 pp on average (e.g., +6.8 pp on Gemini 2.5 Pro). Performance gains grow with more interaction steps, showing that leveraging past experience benefits long-horizon reasoning in complex software engineering tasks.
TwinRL-VLA: Digital Twin-Driven Reinforcement Learning for Real-World Robotic Manipulation
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Despite strong generalization capabilities, Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models remain constrained by the high cost of expert demonstrations and insufficient real-world interaction. While online reinforcement learning (RL) has shown promise in improving general foundation models, applying RL to VLA manipulation in real-world settings is still hindered by low exploration efficiency and a restricted exploration space. Through systematic real-world experiments, we observe that the effective exploration space of online RL is closely tied to the data distribution of supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Motivated by this observation, we propose TwinRL, a digital twin-real-world collaborative RL framework designed to scale and guide exploration for VLA models. First, a high-fidelity digital twin is efficiently reconstructed from smartphone-captured scenes, enabling realistic bidirectional transfer between real and simulated environments. During the SFT warm-up stage, we introduce an exploration space expansion strategy using digital twins to broaden the support of the data trajectory distribution. Building on this enhanced initialization, we propose a sim-to-real guided exploration strategy to further accelerate online RL. Specifically, TwinRL performs efficient and parallel online RL in the digital twin prior to deployment, effectively bridging the gap between offline and online training stages. Subsequently, we exploit efficient digital twin sampling to identify failure-prone yet informative configurations, which are used to guide targeted human-in-the-loop rollouts on the real robot. In our experiments, TwinRL approaches 100% success in both in-distribution regions covered by real-world demonstrations and out-of-distribution regions, delivering at least a 30% speedup over prior real-world RL methods and requiring only about 20 minutes on average across four tasks.
CVE-Factory: Scaling Expert-Level Agentic Tasks for Code Security Vulnerability
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Evaluating and improving the security capabilities of code agents requires high-quality, executable vulnerability tasks. However, existing works rely on costly, unscalable manual reproduction and suffer from outdated data distributions. To address these, we present CVE-Factory, the first multi-agent framework to achieve expert-level quality in automatically transforming sparse CVE metadata into fully executable agentic tasks. Cross-validation against human expert reproductions shows that CVE-Factory achieves 95\% solution correctness and 96\% environment fidelity, confirming its expert-level quality. It is also evaluated on the latest realistic vulnerabilities and achieves a 66.2\% verified success. This automation enables two downstream contributions. First, we construct LiveCVEBench, a continuously updated benchmark of 190 tasks spanning 14 languages and 153 repositories that captures emerging threats including AI-tooling vulnerabilities. Second, we synthesize over 1,000 executable training environments, the first large-scale scaling of agentic tasks in code security. Fine-tuned Qwen3-32B improves from 5.3\% to 35.8\% on LiveCVEBench, surpassing Claude 4.5 Sonnet, with gains generalizing to Terminal Bench (12.5\% to 31.3\%). We open-source CVE-Factory, LiveCVEBench, Abacus-cve (fine-tuned model), training dataset, and leaderboard. All resources are available at https://github.com/livecvebench/CVE-Factory .
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
The Flexibility Trap: Why Arbitrary Order Limits Reasoning Potential in Diffusion Language Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) break the rigid left-to-right constraint of traditional LLMs, enabling token generation in arbitrary orders. Intuitively, this flexibility implies a solution space that strictly supersets the fixed autoregressive trajectory, theoretically unlocking superior reasoning potential for general tasks like mathematics and coding. Consequently, numerous works have leveraged reinforcement learning (RL) to elicit the reasoning capability of dLLMs. In this paper, we reveal a counter-intuitive reality: arbitrary order generation, in its current form, narrows rather than expands the reasoning boundary of dLLMs. We find that dLLMs tend to exploit this order flexibility to bypass high-uncertainty tokens that are crucial for exploration, leading to a premature collapse of the solution space. This observation challenges the premise of existing RL approaches for dLLMs, where considerable complexities, such as handling combinatorial trajectories and intractable likelihoods, are often devoted to preserving this flexibility. We demonstrate that effective reasoning is better elicited by intentionally forgoing arbitrary order and applying standard Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) instead. Our approach, JustGRPO, is minimalist yet surprisingly effective (e.g., 89.1% accuracy on GSM8K) while fully retaining the parallel decoding ability of dLLMs. Project page: https://nzl-thu.github.io/the-flexibility-trap
Co-GRPO: Co-Optimized Group Relative Policy Optimization for Masked Diffusion Model
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Recently, Masked Diffusion Models (MDMs) have shown promising potential across vision, language, and cross-modal generation. However, a notable discrepancy exists between their training and inference procedures. In particular, MDM inference is a multi-step, iterative process governed not only by the model itself but also by various schedules that dictate the token-decoding trajectory (e.g., how many tokens to decode at each step). In contrast, MDMs are typically trained using a simplified, single-step BERT-style objective that masks a subset of tokens and predicts all of them simultaneously. This step-level simplification fundamentally disconnects the training paradigm from the trajectory-level nature of inference, leaving the inference schedules never optimized during training. In this paper, we introduce Co-GRPO, which reformulates MDM generation as a unified Markov Decision Process (MDP) that jointly incorporates both the model and the inference schedule. By applying Group Relative Policy Optimization at the trajectory level, Co-GRPO cooperatively optimizes model parameters and schedule parameters under a shared reward, without requiring costly backpropagation through the multi-step generation process. This holistic optimization aligns training with inference more thoroughly and substantially improves generation quality. Empirical results across four benchmarks-ImageReward, HPS, GenEval, and DPG-Bench-demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. For more details, please refer to our project page: https://co-grpo.github.io/ .
SpatialActor: Exploring Disentangled Spatial Representations for Robust Robotic Manipulation
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Robotic manipulation requires precise spatial understanding to interact with objects in the real world. Point-based methods suffer from sparse sampling, leading to the loss of fine-grained semantics. Image-based methods typically feed RGB and depth into 2D backbones pre-trained on 3D auxiliary tasks, but their entangled semantics and geometry are sensitive to inherent depth noise in real-world that disrupts semantic understanding. Moreover, these methods focus on high-level geometry while overlooking low-level spatial cues essential for precise interaction. We propose SpatialActor, a disentangled framework for robust robotic manipulation that explicitly decouples semantics and geometry. The Semantic-guided Geometric Module adaptively fuses two complementary geometry from noisy depth and semantic-guided expert priors. Also, a Spatial Transformer leverages low-level spatial cues for accurate 2D-3D mapping and enables interaction among spatial features. We evaluate SpatialActor on multiple simulation and real-world scenarios across 50+ tasks. It achieves state-of-the-art performance with 87.4% on RLBench and improves by 13.9% to 19.4% under varying noisy conditions, showing strong robustness. Moreover, it significantly enhances few-shot generalization to new tasks and maintains robustness under various spatial perturbations. Project Page: https://shihao1895.github.io/SpatialActor
Klear-AgentForge: Forging Agentic Intelligence through Posttraining Scaling
Nov 08, 2025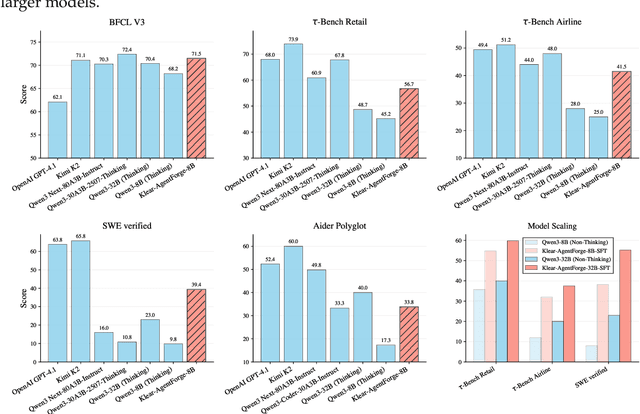
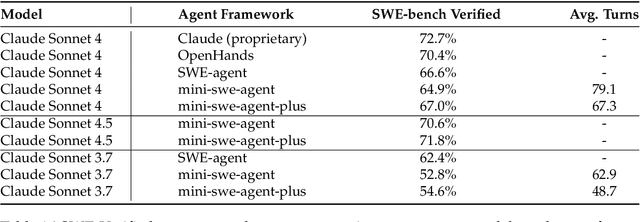
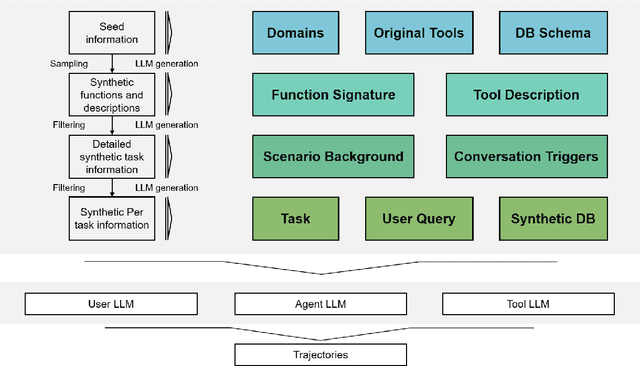
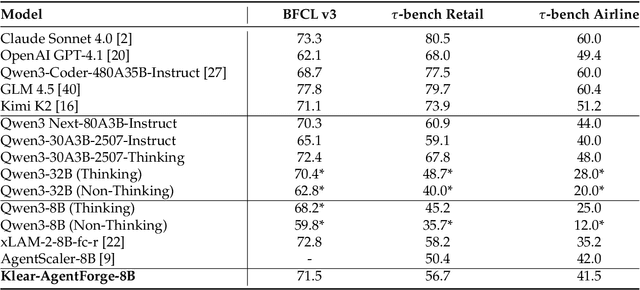
Abstract:Despite the proliferation of powerful agentic models, the lack of critical post-training details hinders the development of strong counterparts in the open-source community. In this study, we present a comprehensive and fully open-source pipeline for training a high-performance agentic model for interacting with external tools and environments, named Klear-Qwen3-AgentForge, starting from the Qwen3-8B base model. We design effective supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with synthetic data followed by multi-turn reinforcement learning (RL) to unlock the potential for multiple diverse agentic tasks. We perform exclusive experiments on various agentic benchmarks in both tool use and coding domains. Klear-Qwen3-AgentForge-8B achieves state-of-the-art performance among LLMs of similar size and remains competitive with significantly larger models.
Emulating Human-like Adaptive Vision for Efficient and Flexible Machine Visual Perception
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Human vision is highly adaptive, efficiently sampling intricate environments by sequentially fixating on task-relevant regions. In contrast, prevailing machine vision models passively process entire scenes at once, resulting in excessive resource demands scaling with spatial-temporal input resolution and model size, yielding critical limitations impeding both future advancements and real-world application. Here we introduce AdaptiveNN, a general framework aiming to drive a paradigm shift from 'passive' to 'active, adaptive' vision models. AdaptiveNN formulates visual perception as a coarse-to-fine sequential decision-making process, progressively identifying and attending to regions pertinent to the task, incrementally combining information across fixations, and actively concluding observation when sufficient. We establish a theory integrating representation learning with self-rewarding reinforcement learning, enabling end-to-end training of the non-differentiable AdaptiveNN without additional supervision on fixation locations. We assess AdaptiveNN on 17 benchmarks spanning 9 tasks, including large-scale visual recognition, fine-grained discrimination, visual search, processing images from real driving and medical scenarios, language-driven embodied AI, and side-by-side comparisons with humans. AdaptiveNN achieves up to 28x inference cost reduction without sacrificing accuracy, flexibly adapts to varying task demands and resource budgets without retraining, and provides enhanced interpretability via its fixation patterns, demonstrating a promising avenue toward efficient, flexible, and interpretable computer vision. Furthermore, AdaptiveNN exhibits closely human-like perceptual behaviors in many cases, revealing its potential as a valuable tool for investigating visual cognition. Code is available at https://github.com/LeapLabTHU/AdaptiveNN.
AR-GRPO: Training Autoregressive Image Generation Models via Reinforcement Learning
Aug 09, 2025



Abstract:Inspired by the success of reinforcement learning (RL) in refining large language models (LLMs), we propose AR-GRPO, an approach to integrate online RL training into autoregressive (AR) image generation models. We adapt the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm to refine the vanilla autoregressive models' outputs by carefully designed reward functions that evaluate generated images across multiple quality dimensions, including perceptual quality, realism, and semantic fidelity. We conduct comprehensive experiments on both class-conditional (i.e., class-to-image) and text-conditional (i.e., text-to-image) image generation tasks, demonstrating that our RL-enhanced framework significantly improves both the image quality and human preference of generated images compared to the standard AR baselines. Our results show consistent improvements across various evaluation metrics, establishing the viability of RL-based optimization for AR image generation and opening new avenues for controllable and high-quality image synthesis. The source codes and models are available at: https://github.com/Kwai-Klear/AR-GRPO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge