Jingyuan Zhang
CVE-Factory: Scaling Expert-Level Agentic Tasks for Code Security Vulnerability
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Evaluating and improving the security capabilities of code agents requires high-quality, executable vulnerability tasks. However, existing works rely on costly, unscalable manual reproduction and suffer from outdated data distributions. To address these, we present CVE-Factory, the first multi-agent framework to achieve expert-level quality in automatically transforming sparse CVE metadata into fully executable agentic tasks. Cross-validation against human expert reproductions shows that CVE-Factory achieves 95\% solution correctness and 96\% environment fidelity, confirming its expert-level quality. It is also evaluated on the latest realistic vulnerabilities and achieves a 66.2\% verified success. This automation enables two downstream contributions. First, we construct LiveCVEBench, a continuously updated benchmark of 190 tasks spanning 14 languages and 153 repositories that captures emerging threats including AI-tooling vulnerabilities. Second, we synthesize over 1,000 executable training environments, the first large-scale scaling of agentic tasks in code security. Fine-tuned Qwen3-32B improves from 5.3\% to 35.8\% on LiveCVEBench, surpassing Claude 4.5 Sonnet, with gains generalizing to Terminal Bench (12.5\% to 31.3\%). We open-source CVE-Factory, LiveCVEBench, Abacus-cve (fine-tuned model), training dataset, and leaderboard. All resources are available at https://github.com/livecvebench/CVE-Factory .
Me-Agent: A Personalized Mobile Agent with Two-Level User Habit Learning for Enhanced Interaction
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based mobile agents have made significant performance advancements. However, these agents often follow explicit user instructions while overlooking personalized needs, leading to significant limitations for real users, particularly without personalized context: (1) inability to interpret ambiguous instructions, (2) lack of learning from user interaction history, and (3) failure to handle personalized instructions. To alleviate the above challenges, we propose Me-Agent, a learnable and memorable personalized mobile agent. Specifically, Me-Agent incorporates a two-level user habit learning approach. At the prompt level, we design a user preference learning strategy enhanced with a Personal Reward Model to improve personalization performance. At the memory level, we design a Hierarchical Preference Memory, which stores users' long-term memory and app-specific memory in different level memory. To validate the personalization capabilities of mobile agents, we introduce User FingerTip, a new benchmark featuring numerous ambiguous instructions for daily life. Extensive experiments on User FingerTip and general benchmarks demonstrate that Me-Agent achieves state-of-the-art performance in personalization while maintaining competitive instruction execution performance.
VL-RouterBench: A Benchmark for Vision-Language Model Routing
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Multi-model routing has evolved from an engineering technique into essential infrastructure, yet existing work lacks a systematic, reproducible benchmark for evaluating vision-language models (VLMs). We present VL-RouterBench to assess the overall capability of VLM routing systems systematically. The benchmark is grounded in raw inference and scoring logs from VLMs and constructs quality and cost matrices over sample-model pairs. In scale, VL-RouterBench covers 14 datasets across 3 task groups, totaling 30,540 samples, and includes 15 open-source models and 2 API models, yielding 519,180 sample-model pairs and a total input-output token volume of 34,494,977. The evaluation protocol jointly measures average accuracy, average cost, and throughput, and builds a ranking score from the harmonic mean of normalized cost and accuracy to enable comparison across router configurations and cost budgets. On this benchmark, we evaluate 10 routing methods and baselines and observe a significant routability gain, while the best current routers still show a clear gap to the ideal Oracle, indicating considerable room for improvement in router architecture through finer visual cues and modeling of textual structure. We will open-source the complete data construction and evaluation toolchain to promote comparability, reproducibility, and practical deployment in multimodal routing research.
Rethinking the Reliability of Multi-agent System: A Perspective from Byzantine Fault Tolerance
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Ensuring the reliability of agent architectures and effectively identifying problematic agents when failures occur are crucial challenges in multi-agent systems (MAS). Advances in large language models (LLMs) have established LLM-based agents as a major branch of MAS, enabling major breakthroughs in complex problem solving and world modeling. However, the reliability implications of this shift remain largely unexplored. i.e., whether substituting traditional agents with LLM-based agents can effectively enhance the reliability of MAS. In this work, we investigate and quantify the reliability of LLM-based agents from the perspective of Byzantine fault tolerance. We observe that LLM-based agents demonstrate stronger skepticism when processing erroneous message flows, a characteristic that enables them to outperform traditional agents across different topological structures. Motivated by the results of the pilot experiment, we design CP-WBFT, a confidence probe-based weighted Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus mechanism to enhance the stability of MAS with different topologies. It capitalizes on the intrinsic reflective and discriminative capabilities of LLMs by employing a probe-based, weighted information flow transmission method to improve the reliability of LLM-based agents. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CP-WBFT achieves superior performance across diverse network topologies under extreme Byzantine conditions (85.7\% fault rate). Notably, our approach surpasses traditional methods by attaining remarkable accuracy on various topologies and maintaining strong reliability in both mathematical reasoning and safety assessment tasks.
Klear-AgentForge: Forging Agentic Intelligence through Posttraining Scaling
Nov 08, 2025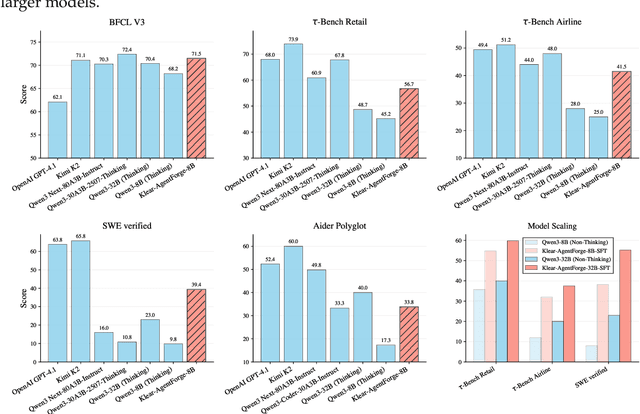
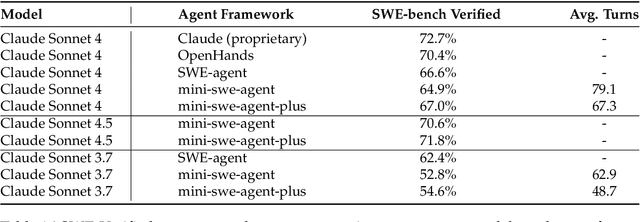
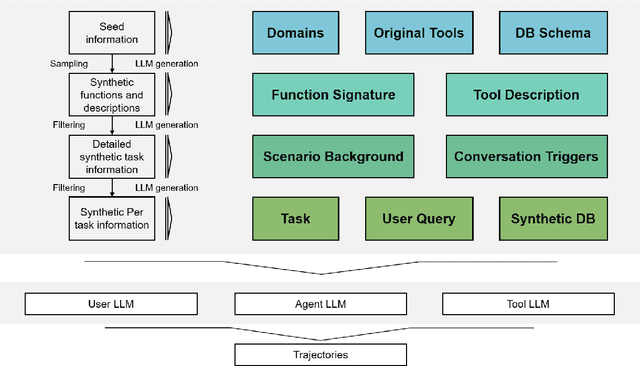
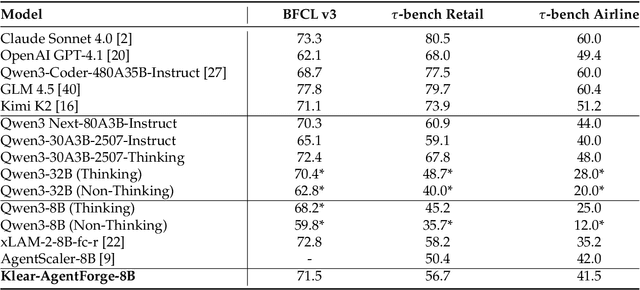
Abstract:Despite the proliferation of powerful agentic models, the lack of critical post-training details hinders the development of strong counterparts in the open-source community. In this study, we present a comprehensive and fully open-source pipeline for training a high-performance agentic model for interacting with external tools and environments, named Klear-Qwen3-AgentForge, starting from the Qwen3-8B base model. We design effective supervised fine-tuning (SFT) with synthetic data followed by multi-turn reinforcement learning (RL) to unlock the potential for multiple diverse agentic tasks. We perform exclusive experiments on various agentic benchmarks in both tool use and coding domains. Klear-Qwen3-AgentForge-8B achieves state-of-the-art performance among LLMs of similar size and remains competitive with significantly larger models.
Open Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Factual Image Generation
Oct 26, 2025



Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable progress in generating photorealistic and prompt-aligned images, but they often produce outputs that contradict verifiable knowledge, especially when prompts involve fine-grained attributes or time-sensitive events. Conventional retrieval-augmented approaches attempt to address this issue by introducing external information, yet they are fundamentally incapable of grounding generation in accurate and evolving knowledge due to their reliance on static sources and shallow evidence integration. To bridge this gap, we introduce ORIG, an agentic open multimodal retrieval-augmented framework for Factual Image Generation (FIG), a new task that requires both visual realism and factual grounding. ORIG iteratively retrieves and filters multimodal evidence from the web and incrementally integrates the refined knowledge into enriched prompts to guide generation. To support systematic evaluation, we build FIG-Eval, a benchmark spanning ten categories across perceptual, compositional, and temporal dimensions. Experiments demonstrate that ORIG substantially improves factual consistency and overall image quality over strong baselines, highlighting the potential of open multimodal retrieval for factual image generation.
Accelerating Diffusion LLM Inference via Local Determinism Propagation
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:Diffusion large language models (dLLMs) represent a significant advancement in text generation, offering parallel token decoding capabilities. However, existing open-source implementations suffer from quality-speed trade-offs that impede their practical deployment. Conservative sampling strategies typically decode only the most confident token per step to ensure quality (i.e., greedy decoding), at the cost of inference efficiency due to repeated redundant refinement iterations--a phenomenon we term delayed decoding. Through systematic analysis of dLLM decoding dynamics, we characterize this delayed decoding behavior and propose a training-free adaptive parallel decoding strategy, named LocalLeap, to address these inefficiencies. LocalLeap is built on two fundamental empirical principles: local determinism propagation centered on high-confidence anchors and progressive spatial consistency decay. By applying these principles, LocalLeap identifies anchors and performs localized relaxed parallel decoding within bounded neighborhoods, achieving substantial inference step reduction through early commitment of already-determined tokens without compromising output quality. Comprehensive evaluation on various benchmarks demonstrates that LocalLeap achieves 6.94$\times$ throughput improvements and reduces decoding steps to just 14.2\% of the original requirement, achieving these gains with negligible performance impact. The source codes are available at: https://github.com/friedrichor/LocalLeap.
MobileRAG: Enhancing Mobile Agent with Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Smartphones have become indispensable in people's daily lives, permeating nearly every aspect of modern society. With the continuous advancement of large language models (LLMs), numerous LLM-based mobile agents have emerged. These agents are capable of accurately parsing diverse user queries and automatically assisting users in completing complex or repetitive operations. However, current agents 1) heavily rely on the comprehension ability of LLMs, which can lead to errors caused by misoperations or omitted steps during tasks, 2) lack interaction with the external environment, often terminating tasks when an app cannot fulfill user queries, and 3) lack memory capabilities, requiring each instruction to reconstruct the interface and being unable to learn from and correct previous mistakes. To alleviate the above issues, we propose MobileRAG, a mobile agents framework enhanced by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which includes InterRAG, LocalRAG, and MemRAG. It leverages RAG to more quickly and accurately identify user queries and accomplish complex and long-sequence mobile tasks. Additionally, to more comprehensively assess the performance of MobileRAG, we introduce MobileRAG-Eval, a more challenging benchmark characterized by numerous complex, real-world mobile tasks that require external knowledge assistance. Extensive experimental results on MobileRAG-Eval demonstrate that MobileRAG can easily handle real-world mobile tasks, achieving 10.3\% improvement over state-of-the-art methods with fewer operational steps. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/liuxiaojieOutOfWorld/MobileRAG_arxiv
AR-GRPO: Training Autoregressive Image Generation Models via Reinforcement Learning
Aug 09, 2025



Abstract:Inspired by the success of reinforcement learning (RL) in refining large language models (LLMs), we propose AR-GRPO, an approach to integrate online RL training into autoregressive (AR) image generation models. We adapt the Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm to refine the vanilla autoregressive models' outputs by carefully designed reward functions that evaluate generated images across multiple quality dimensions, including perceptual quality, realism, and semantic fidelity. We conduct comprehensive experiments on both class-conditional (i.e., class-to-image) and text-conditional (i.e., text-to-image) image generation tasks, demonstrating that our RL-enhanced framework significantly improves both the image quality and human preference of generated images compared to the standard AR baselines. Our results show consistent improvements across various evaluation metrics, establishing the viability of RL-based optimization for AR image generation and opening new avenues for controllable and high-quality image synthesis. The source codes and models are available at: https://github.com/Kwai-Klear/AR-GRPO.
SAEL: Leveraging Large Language Models with Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts for Smart Contract Vulnerability Detection
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:With the increasing security issues in blockchain, smart contract vulnerability detection has become a research focus. Existing vulnerability detection methods have their limitations: 1) Static analysis methods struggle with complex scenarios. 2) Methods based on specialized pre-trained models perform well on specific datasets but have limited generalization capabilities. In contrast, general-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate impressive ability in adapting to new vulnerability patterns. However, they often underperform on specific vulnerability types compared to methods based on specialized pre-trained models. We also observe that explanations generated by general-purpose LLMs can provide fine-grained code understanding information, contributing to improved detection performance. Inspired by these observations, we propose SAEL, an LLM-based framework for smart contract vulnerability detection. We first design targeted prompts to guide LLMs in identifying vulnerabilities and generating explanations, which serve as prediction features. Next, we apply prompt-tuning on CodeT5 and T5 to process contract code and explanations, enhancing task-specific performance. To combine the strengths of each approach, we introduce an Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts architecture. This dynamically adjusts feature weights via a Gating Network, which selects relevant features using TopK filtering and Softmax normalization, and incorporates a Multi-Head Self-Attention mechanism to enhance cross-feature relationships. This design enables effective integration of LLM predictions, explanation features, and code features through gradient optimization. The loss function jointly considers both independent feature performance and overall weighted predictions. Experiments show that SAEL outperforms existing methods across various vulnerabilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge