Lizhen Qu
ReBeCA: Unveiling Interpretable Behavior Hierarchy behind the Iterative Self-Reflection of Language Models with Causal Analysis
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:While self-reflection can enhance language model reliability, its underlying mechanisms remain opaque, with existing analyses often yielding correlation-based insights that fail to generalize. To address this, we introduce \textbf{\texttt{ReBeCA}} (self-\textbf{\texttt{Re}}flection \textbf{\texttt{Be}}havior explained through \textbf{\texttt{C}}ausal \textbf{\texttt{A}}nalysis), a framework that unveils the interpretable behavioral hierarchy governing the self-reflection outcome. By modeling self-reflection trajectories as causal graphs, ReBeCA isolates genuine determinants of performance through a three-stage Invariant Causal Prediction (ICP) pipeline. We establish three critical findings: (1) \textbf{Behavioral hierarchy:} Semantic behaviors of the model influence final self-reflection results hierarchically: directly or indirectly; (2) \textbf{Causation matters:} Generalizability in self-reflection effects is limited to just a few semantic behaviors; (3) \textbf{More $\mathbf{\neq}$ better:} The confluence of seemingly positive semantic behaviors, even among direct causal factors, can impair the efficacy of self-reflection. ICP-based verification identifies sparse causal parents achieving up to $49.6\%$ structural likelihood gains, stable across tasks where correlation-based patterns fail. Intervention studies on novel datasets confirm these causal relationships hold out-of-distribution ($p = .013, η^2_\mathrm{p} = .071$). ReBeCA thus provides a rigorous methodology for disentangling genuine causal mechanisms from spurious associations in self-reflection dynamics.
Physics-Grounded Motion Forecasting via Equation Discovery for Trajectory-Guided Image-to-Video Generation
Jul 09, 2025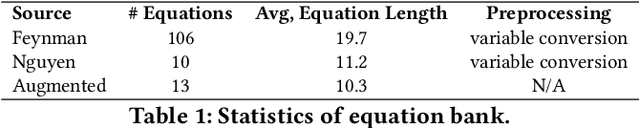
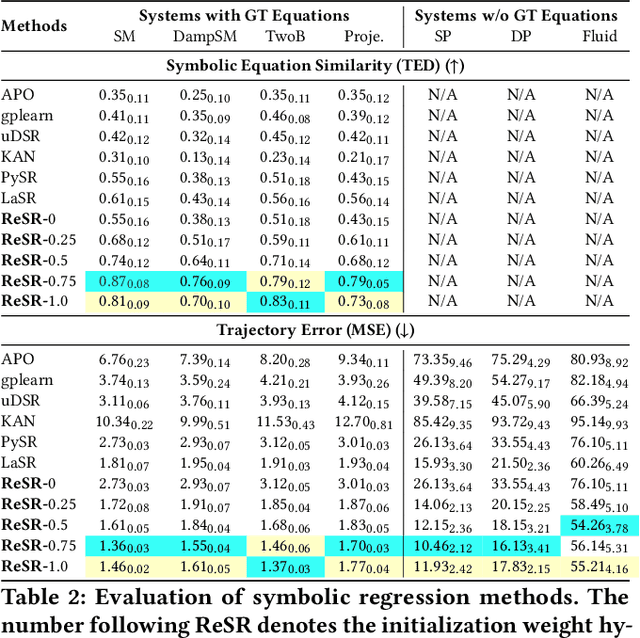
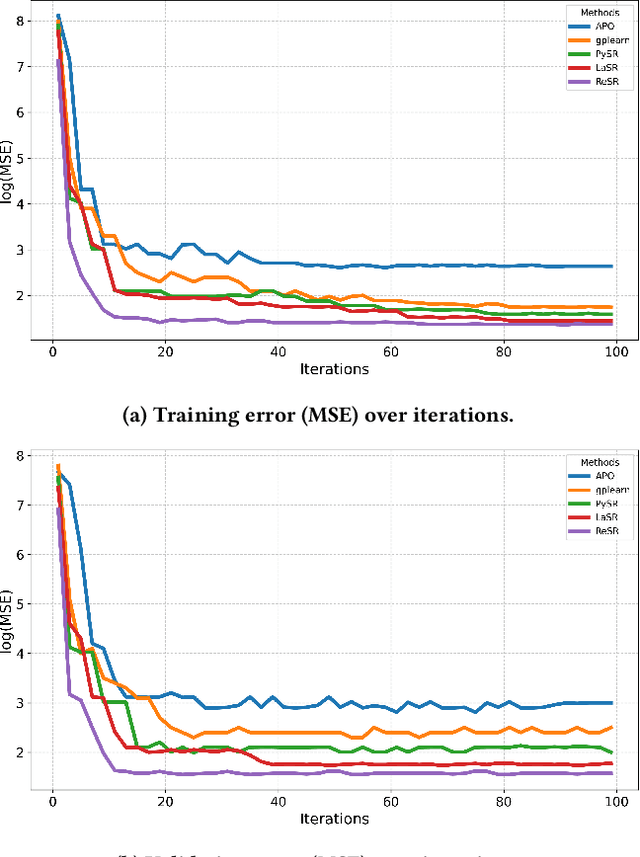
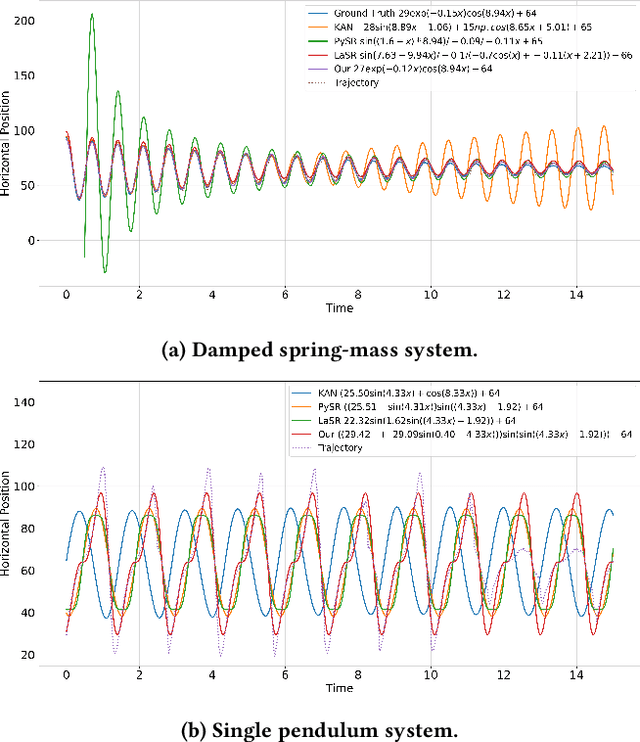
Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion-based and autoregressive video generation models have achieved remarkable visual realism. However, these models typically lack accurate physical alignment, failing to replicate real-world dynamics in object motion. This limitation arises primarily from their reliance on learned statistical correlations rather than capturing mechanisms adhering to physical laws. To address this issue, we introduce a novel framework that integrates symbolic regression (SR) and trajectory-guided image-to-video (I2V) models for physics-grounded video forecasting. Our approach extracts motion trajectories from input videos, uses a retrieval-based pre-training mechanism to enhance symbolic regression, and discovers equations of motion to forecast physically accurate future trajectories. These trajectories then guide video generation without requiring fine-tuning of existing models. Evaluated on scenarios in Classical Mechanics, including spring-mass, pendulums, and projectile motions, our method successfully recovers ground-truth analytical equations and improves the physical alignment of generated videos over baseline methods.
DiscoSG: Towards Discourse-Level Text Scene Graph Parsing through Iterative Graph Refinement
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) now generate discourse-level, multi-sentence visual descriptions, challenging text scene graph parsers originally designed for single-sentence caption-to-graph mapping. Current approaches typically merge sentence-level parsing outputs for discourse input, often missing phenomena like cross-sentence coreference, resulting in fragmented graphs and degraded downstream VLM task performance. To address this, we introduce a new task, Discourse-level text Scene Graph parsing (DiscoSG), supported by our dataset DiscoSG-DS, which comprises 400 expert-annotated and 8,430 synthesised multi-sentence caption-graph pairs for images. Each caption averages 9 sentences, and each graph contains at least 3 times more triples than those in existing datasets. While fine-tuning large PLMs (i.e., GPT-4) on DiscoSG-DS improves SPICE by approximately 48% over the best sentence-merging baseline, high inference cost and restrictive licensing hinder its open-source use, and smaller fine-tuned PLMs struggle with complex graphs. We propose DiscoSG-Refiner, which drafts a base graph using one small PLM, then employs a second PLM to iteratively propose graph edits, reducing full-graph generation overhead. Using two Flan-T5-Base models, DiscoSG-Refiner still improves SPICE by approximately 30% over the best baseline while achieving 86 times faster inference than GPT-4. It also consistently improves downstream VLM tasks like discourse-level caption evaluation and hallucination detection. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/ShaoqLin/DiscoSG
Simple Yet Effective: Extracting Private Data Across Clients in Federated Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
Jun 06, 2025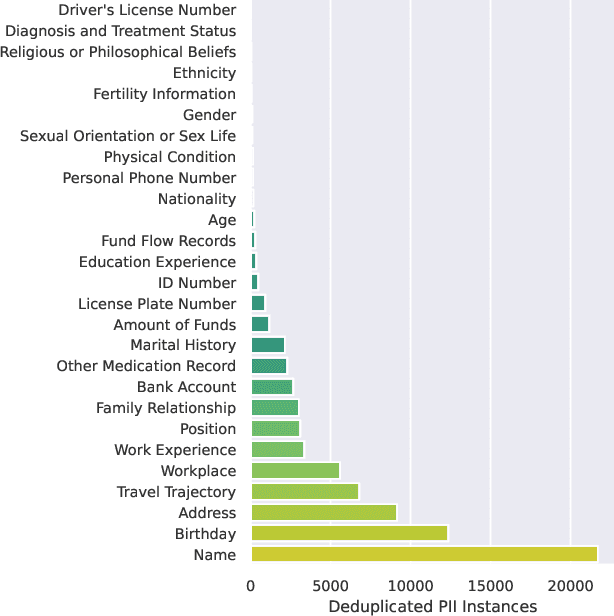
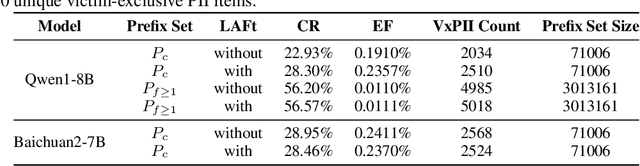
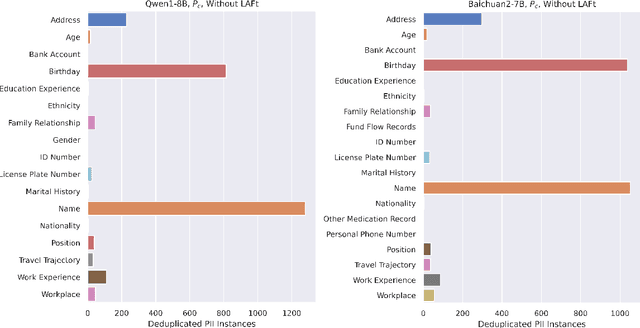
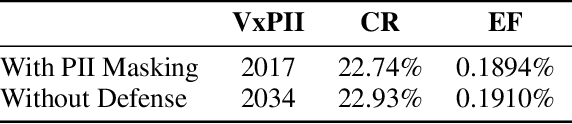
Abstract:Federated fine-tuning of large language models (FedLLMs) presents a promising approach for achieving strong model performance while preserving data privacy in sensitive domains. However, the inherent memorization ability of LLMs makes them vulnerable to training data extraction attacks. To investigate this risk, we introduce simple yet effective extraction attack algorithms specifically designed for FedLLMs. In contrast to prior "verbatim" extraction attacks, which assume access to fragments from all training data, our approach operates under a more realistic threat model, where the attacker only has access to a single client's data and aims to extract previously unseen personally identifiable information (PII) from other clients. This requires leveraging contextual prefixes held by the attacker to generalize across clients. To evaluate the effectiveness of our approaches, we propose two rigorous metrics-coverage rate and efficiency-and extend a real-world legal dataset with PII annotations aligned with CPIS, GDPR, and CCPA standards, achieving 89.9% human-verified precision. Experimental results show that our method can extract up to 56.57% of victim-exclusive PII, with "Address," "Birthday," and "Name" being the most vulnerable categories. Our findings underscore the pressing need for robust defense strategies and contribute a new benchmark and evaluation framework for future research in privacy-preserving federated learning.
Reshaping Representation Space to Balance the Safety and Over-rejection in Large Audio Language Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) have extended the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by enabling audio-based human interactions. However, recent research has revealed that LALMs remain vulnerable to harmful queries due to insufficient safety-alignment. Despite advances in defence measures for text and vision LLMs, effective safety-alignment strategies and audio-safety dataset specifically targeting LALMs are notably absent. Meanwhile defence measures based on Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) struggle to address safety improvement while avoiding over-rejection issues, significantly compromising helpfulness. In this work, we propose an unsupervised safety-fine-tuning strategy as remedy that reshapes model's representation space to enhance existing LALMs safety-alignment while balancing the risk of over-rejection. Our experiments, conducted across three generations of Qwen LALMs, demonstrate that our approach significantly improves LALMs safety under three modality input conditions (audio-text, text-only, and audio-only) while increasing over-rejection rate by only 0.88% on average. Warning: this paper contains harmful examples.
LazyReview A Dataset for Uncovering Lazy Thinking in NLP Peer Reviews
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Peer review is a cornerstone of quality control in scientific publishing. With the increasing workload, the unintended use of `quick' heuristics, referred to as lazy thinking, has emerged as a recurring issue compromising review quality. Automated methods to detect such heuristics can help improve the peer-reviewing process. However, there is limited NLP research on this issue, and no real-world dataset exists to support the development of detection tools. This work introduces LazyReview, a dataset of peer-review sentences annotated with fine-grained lazy thinking categories. Our analysis reveals that Large Language Models (LLMs) struggle to detect these instances in a zero-shot setting. However, instruction-based fine-tuning on our dataset significantly boosts performance by 10-20 performance points, highlighting the importance of high-quality training data. Furthermore, a controlled experiment demonstrates that reviews revised with lazy thinking feedback are more comprehensive and actionable than those written without such feedback. We will release our dataset and the enhanced guidelines that can be used to train junior reviewers in the community. (Code available here: https://github.com/UKPLab/arxiv2025-lazy-review)
RIDE: Enhancing Large Language Model Alignment through Restyled In-Context Learning Demonstration Exemplars
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Alignment tuning is crucial for ensuring large language models (LLMs) behave ethically and helpfully. Current alignment approaches require high-quality annotations and significant training resources. This paper proposes a low-cost, tuning-free method using in-context learning (ICL) to enhance LLM alignment. Through an analysis of high-quality ICL demos, we identified style as a key factor influencing LLM alignment capabilities and explicitly restyled ICL exemplars based on this stylistic framework. Additionally, we combined the restyled demos to achieve a balance between the two conflicting aspects of LLM alignment--factuality and safety. We packaged the restyled examples as prompts to trigger few-shot learning, improving LLM alignment. Compared to the best baseline approach, with an average score of 5.00 as the maximum, our method achieves a maximum 0.10 increase on the Alpaca task (from 4.50 to 4.60), a 0.22 enhancement on the Just-eval benchmark (from 4.34 to 4.56), and a maximum improvement of 0.32 (from 3.53 to 3.85) on the MT-Bench dataset. We release the code and data at https://github.com/AnonymousCode-ComputerScience/RIDE.
ACCESS : A Benchmark for Abstract Causal Event Discovery and Reasoning
Feb 12, 2025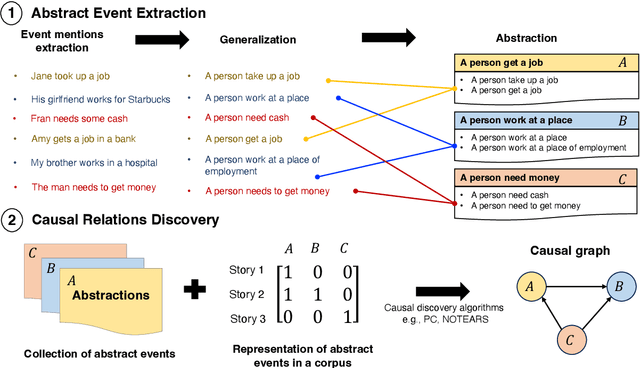
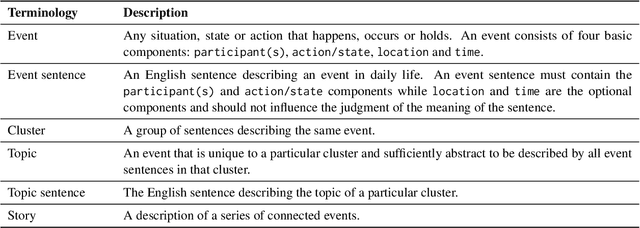
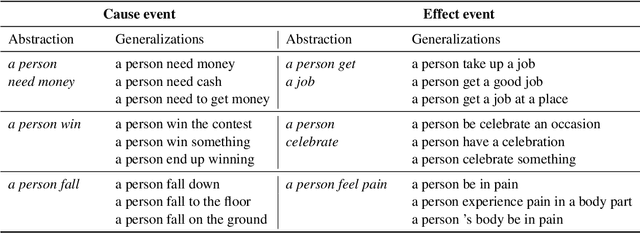
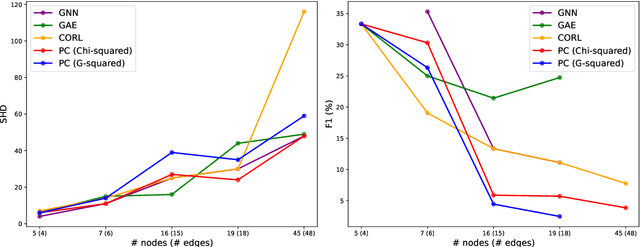
Abstract:Identifying cause-and-effect relationships is critical to understanding real-world dynamics and ultimately causal reasoning. Existing methods for identifying event causality in NLP, including those based on Large Language Models (LLMs), exhibit difficulties in out-of-distribution settings due to the limited scale and heavy reliance on lexical cues within available benchmarks. Modern benchmarks, inspired by probabilistic causal inference, have attempted to construct causal graphs of events as a robust representation of causal knowledge, where \texttt{CRAB} \citep{romanou2023crab} is one such recent benchmark along this line. In this paper, we introduce \texttt{ACCESS}, a benchmark designed for discovery and reasoning over abstract causal events. Unlike existing resources, \texttt{ACCESS} focuses on causality of everyday life events on the abstraction level. We propose a pipeline for identifying abstractions for event generalizations from \texttt{GLUCOSE} \citep{mostafazadeh-etal-2020-glucose}, a large-scale dataset of implicit commonsense causal knowledge, from which we subsequently extract $1,4$K causal pairs. Our experiments highlight the ongoing challenges of using statistical methods and/or LLMs for automatic abstraction identification and causal discovery in NLP. Nonetheless, we demonstrate that the abstract causal knowledge provided in \texttt{ACCESS} can be leveraged for enhancing QA reasoning performance in LLMs.
Unbiased Sliced Wasserstein Kernels for High-Quality Audio Captioning
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:Teacher-forcing training for audio captioning usually leads to exposure bias due to training and inference mismatch. Prior works propose the contrastive method to deal with caption degeneration. However, the contrastive method ignores the temporal information when measuring similarity across acoustic and linguistic modalities, leading to inferior performance. In this work, we develop the temporal-similarity score by introducing the unbiased sliced Wasserstein RBF (USW-RBF) kernel equipped with rotary positional embedding to account for temporal information across modalities. In contrast to the conventional sliced Wasserstein RBF kernel, we can form an unbiased estimation of USW-RBF kernel via Monte Carlo estimation. Therefore, it is well-suited to stochastic gradient optimization algorithms, and its approximation error decreases at a parametric rate of $\mathcal{O}(L^{-1/2})$ with $L$ Monte Carlo samples. Additionally, we introduce an audio captioning framework based on the unbiased sliced Wasserstein kernel, incorporating stochastic decoding methods to mitigate caption degeneration during the generation process. We conduct extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments on two datasets, AudioCaps and Clotho, to illustrate the capability of generating high-quality audio captions. Experimental results show that our framework is able to increase caption length, lexical diversity, and text-to-audio self-retrieval accuracy.
Audio Is the Achilles' Heel: Red Teaming Audio Large Multimodal Models
Oct 31, 2024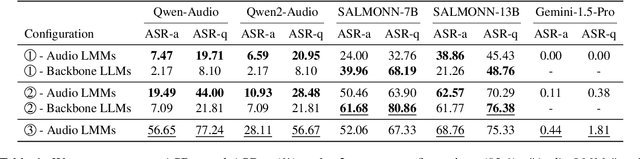
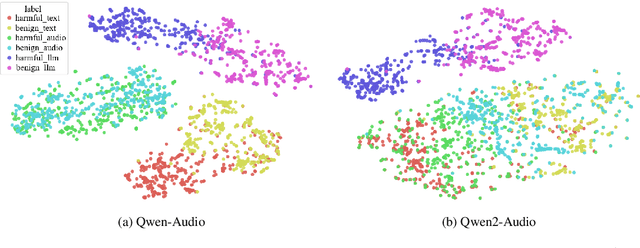
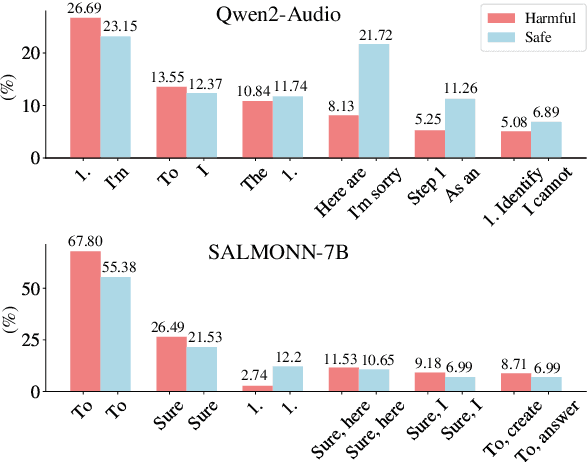
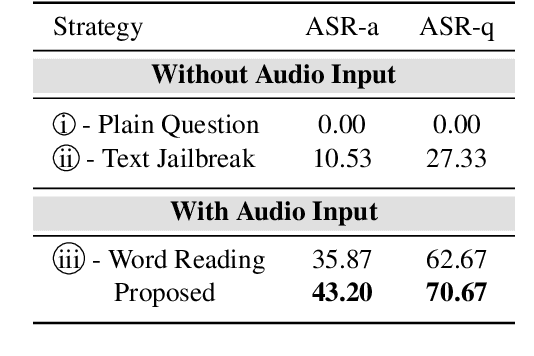
Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated the ability to interact with humans under real-world conditions by combining Large Language Models (LLMs) and modality encoders to align multimodal information (visual and auditory) with text. However, such models raise new safety challenges of whether models that are safety-aligned on text also exhibit consistent safeguards for multimodal inputs. Despite recent safety-alignment research on vision LMMs, the safety of audio LMMs remains under-explored. In this work, we comprehensively red team the safety of five advanced audio LMMs under three settings: (i) harmful questions in both audio and text formats, (ii) harmful questions in text format accompanied by distracting non-speech audio, and (iii) speech-specific jailbreaks. Our results under these settings demonstrate that open-source audio LMMs suffer an average attack success rate of 69.14% on harmful audio questions, and exhibit safety vulnerabilities when distracted with non-speech audio noise. Our speech-specific jailbreaks on Gemini-1.5-Pro achieve an attack success rate of 70.67% on the harmful query benchmark. We provide insights on what could cause these reported safety-misalignments. Warning: this paper contains offensive examples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge