Gholamreza Haffari
Monash University
Environment-Aware Code Generation: How far are We?
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has improved code generation, but most evaluations still test isolated, small-scale code (e.g., a single function) under default or unspecified software environments. As a result, it is unclear whether LLMs can reliably generate executable code tailored to a user's specific environment. We present the first systematic study of Environment-Aware Code Generation (EACG), where generated code must be functionally correct and directly executable under arbitrary software configurations. To enable realistic evaluation, we introduce VersiBCB, a benchmark that is multi-package, execution-verified, and deprecation-aware, capturing complex and evolving environments that prior datasets often overlook. Using VersiBCB, we investigate three complementary adaptation axes: data, parameters, and cache, and develop representative strategies for each. Our results show that current LLMs struggle with environment-specific code generation, while our adaptations improve environment compatibility and executability. These findings highlight key challenges and opportunities for deploying LLMs in practical software engineering workflows.
CoV: Chain-of-View Prompting for Spatial Reasoning
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Embodied question answering (EQA) in 3D environments often requires collecting context that is distributed across multiple viewpoints and partially occluded. However, most recent vision--language models (VLMs) are constrained to a fixed and finite set of input views, which limits their ability to acquire question-relevant context at inference time and hinders complex spatial reasoning. We propose Chain-of-View (CoV) prompting, a training-free, test-time reasoning framework that transforms a VLM into an active viewpoint reasoner through a coarse-to-fine exploration process. CoV first employs a View Selection agent to filter redundant frames and identify question-aligned anchor views. It then performs fine-grained view adjustment by interleaving iterative reasoning with discrete camera actions, obtaining new observations from the underlying 3D scene representation until sufficient context is gathered or a step budget is reached. We evaluate CoV on OpenEQA across four mainstream VLMs and obtain an average +11.56\% improvement in LLM-Match, with a maximum gain of +13.62\% on Qwen3-VL-Flash. CoV further exhibits test-time scaling: increasing the minimum action budget yields an additional +2.51\% average improvement, peaking at +3.73\% on Gemini-2.5-Flash. On ScanQA and SQA3D, CoV delivers strong performance (e.g., 116 CIDEr / 31.9 EM@1 on ScanQA and 51.1 EM@1 on SQA3D). Overall, these results suggest that question-aligned view selection coupled with open-view search is an effective, model-agnostic strategy for improving spatial reasoning in 3D EQA without additional training.
IntroLM: Introspective Language Models via Prefilling-Time Self-Evaluation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:A major challenge for the operation of large language models (LLMs) is how to predict whether a specific LLM will produce sufficiently high-quality output for a given query. Existing approaches rely on external classifiers, most commonly BERT based models, which suffer from limited context windows, constrained representational capacity, and additional computational overhead. We propose IntroLM, a method that enables causal language models to predict their own output quality during the prefilling phase without affecting generation using introspective tokens. By introducing token conditional LoRA that activates only for the introspective token, the model learns to predict the output quality for a given query while preserving the original backbone behavior and avoiding external evaluators. On question answering benchmarks, IntroLM applied to Qwen3 8B achieves a ROC AUC of 90 precent for success prediction, outperforming a DeBERTa classifier by 14 precent. When integrated into multi model routing systems, IntroLM achieves superior cost performance tradeoffs, reducing latency by up to 33 precent and large model usage by up to 50 precent at matched reliability.
Explain Before You Answer: A Survey on Compositional Visual Reasoning
Aug 24, 2025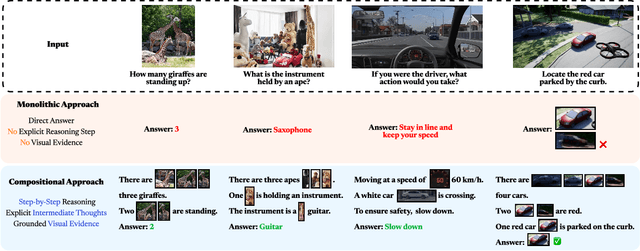
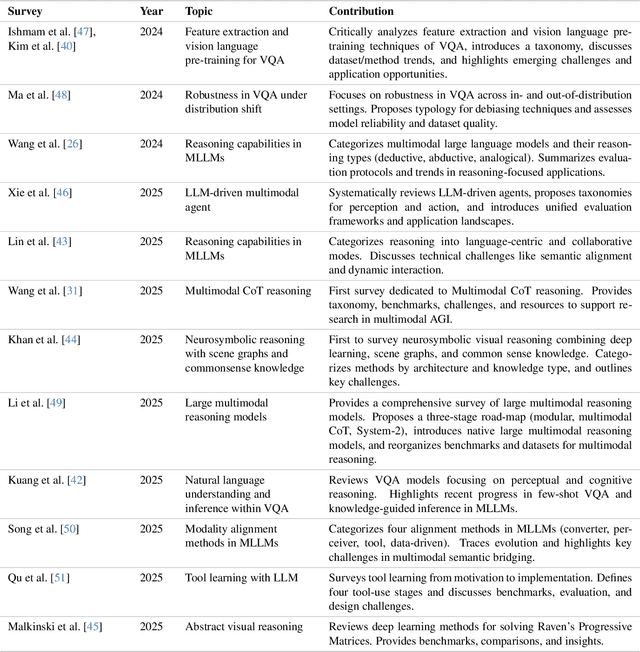
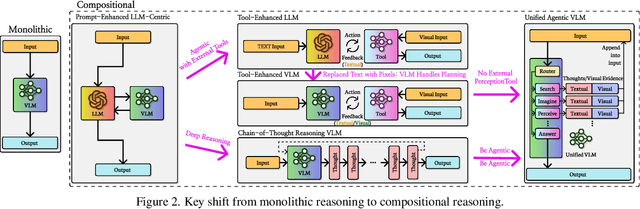
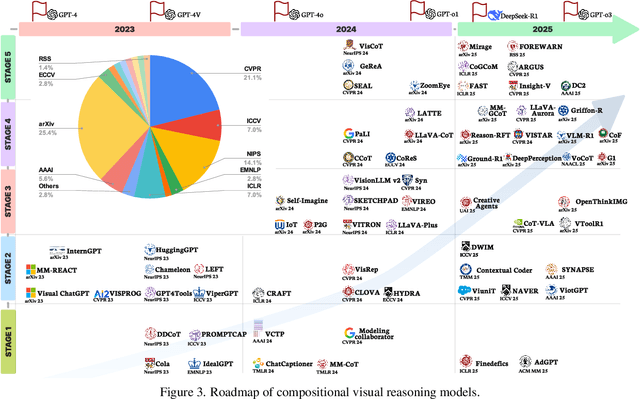
Abstract:Compositional visual reasoning has emerged as a key research frontier in multimodal AI, aiming to endow machines with the human-like ability to decompose visual scenes, ground intermediate concepts, and perform multi-step logical inference. While early surveys focus on monolithic vision-language models or general multimodal reasoning, a dedicated synthesis of the rapidly expanding compositional visual reasoning literature is still missing. We fill this gap with a comprehensive survey spanning 2023 to 2025 that systematically reviews 260+ papers from top venues (CVPR, ICCV, NeurIPS, ICML, ACL, etc.). We first formalize core definitions and describe why compositional approaches offer advantages in cognitive alignment, semantic fidelity, robustness, interpretability, and data efficiency. Next, we trace a five-stage paradigm shift: from prompt-enhanced language-centric pipelines, through tool-enhanced LLMs and tool-enhanced VLMs, to recently minted chain-of-thought reasoning and unified agentic VLMs, highlighting their architectural designs, strengths, and limitations. We then catalog 60+ benchmarks and corresponding metrics that probe compositional visual reasoning along dimensions such as grounding accuracy, chain-of-thought faithfulness, and high-resolution perception. Drawing on these analyses, we distill key insights, identify open challenges (e.g., limitations of LLM-based reasoning, hallucination, a bias toward deductive reasoning, scalable supervision, tool integration, and benchmark limitations), and outline future directions, including world-model integration, human-AI collaborative reasoning, and richer evaluation protocols. By offering a unified taxonomy, historical roadmap, and critical outlook, this survey aims to serve as a foundational reference and inspire the next generation of compositional visual reasoning research.
Physics-Grounded Motion Forecasting via Equation Discovery for Trajectory-Guided Image-to-Video Generation
Jul 09, 2025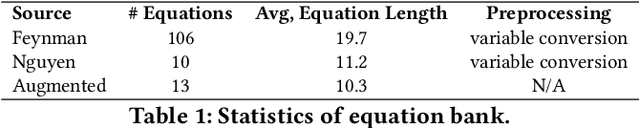
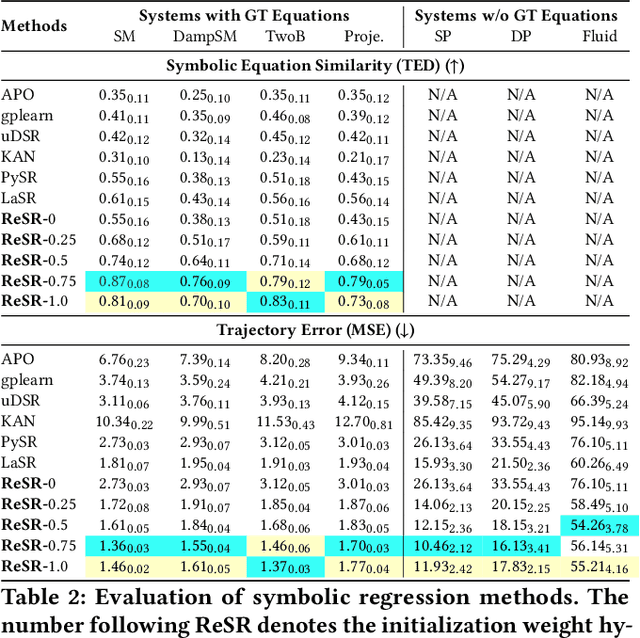
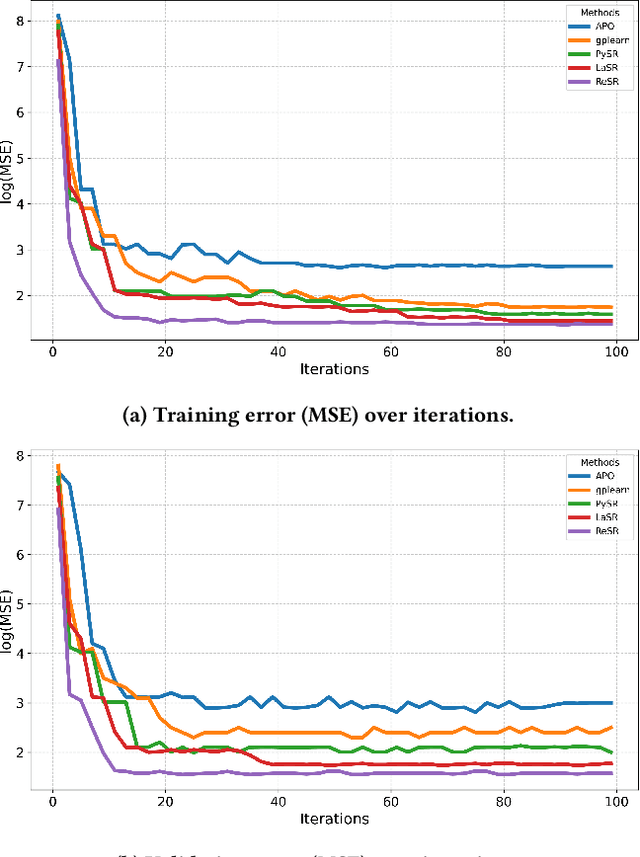
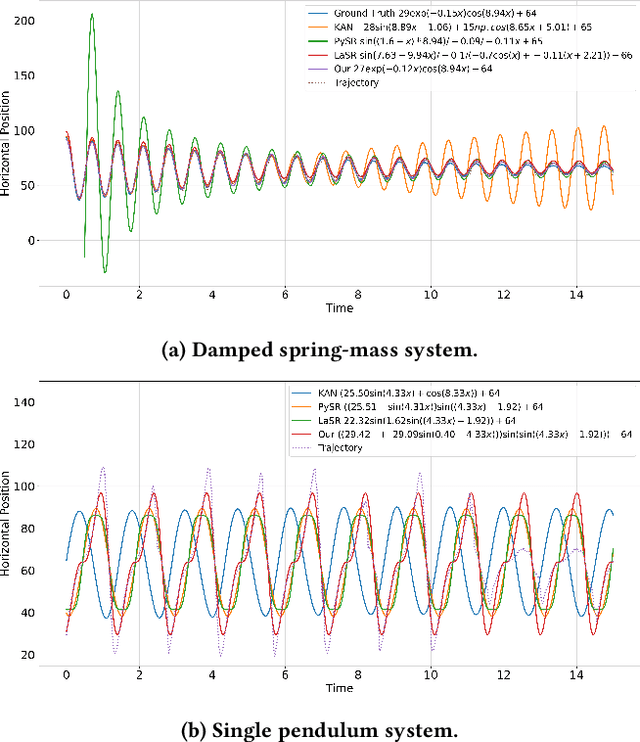
Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion-based and autoregressive video generation models have achieved remarkable visual realism. However, these models typically lack accurate physical alignment, failing to replicate real-world dynamics in object motion. This limitation arises primarily from their reliance on learned statistical correlations rather than capturing mechanisms adhering to physical laws. To address this issue, we introduce a novel framework that integrates symbolic regression (SR) and trajectory-guided image-to-video (I2V) models for physics-grounded video forecasting. Our approach extracts motion trajectories from input videos, uses a retrieval-based pre-training mechanism to enhance symbolic regression, and discovers equations of motion to forecast physically accurate future trajectories. These trajectories then guide video generation without requiring fine-tuning of existing models. Evaluated on scenarios in Classical Mechanics, including spring-mass, pendulums, and projectile motions, our method successfully recovers ground-truth analytical equations and improves the physical alignment of generated videos over baseline methods.
Table-r1: Self-supervised and Reinforcement Learning for Program-based Table Reasoning in Small Language Models
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Table reasoning (TR) requires structured reasoning over semi-structured tabular data and remains challenging, particularly for small language models (SLMs, e.g., LLaMA-8B) due to their limited capacity compared to large LMs (LLMs, e.g., GPT-4o). To narrow this gap, we explore program-based TR (P-TR), which circumvents key limitations of text-based TR (T-TR), notably in numerical reasoning, by generating executable programs. However, applying P-TR to SLMs introduces two challenges: (i) vulnerability to heterogeneity in table layouts, and (ii) inconsistency in reasoning due to limited code generation capability. We propose Table-r1, a two-stage P-TR method designed for SLMs. Stage 1 introduces an innovative self-supervised learning task, Layout Transformation Inference, to improve tabular layout generalization from a programmatic view. Stage 2 adopts a mix-paradigm variant of Group Relative Policy Optimization, enhancing P-TR consistency while allowing dynamic fallback to T-TR when needed. Experiments on four TR benchmarks demonstrate that Table-r1 outperforms all SLM-based methods, achieving at least a 15% accuracy improvement over the base model (LLaMA-8B) across all datasets and reaching performance competitive with LLMs.
FPSAttention: Training-Aware FP8 and Sparsity Co-Design for Fast Video Diffusion
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Diffusion generative models have become the standard for producing high-quality, coherent video content, yet their slow inference speeds and high computational demands hinder practical deployment. Although both quantization and sparsity can independently accelerate inference while maintaining generation quality, naively combining these techniques in existing training-free approaches leads to significant performance degradation due to the lack of joint optimization. We introduce FPSAttention, a novel training-aware co-design of FP8 quantization and sparsity for video generation, with a focus on the 3D bi-directional attention mechanism. Our approach features three key innovations: 1) A unified 3D tile-wise granularity that simultaneously supports both quantization and sparsity; 2) A denoising step-aware strategy that adapts to the noise schedule, addressing the strong correlation between quantization/sparsity errors and denoising steps; 3) A native, hardware-friendly kernel that leverages FlashAttention and is implemented with optimized Hopper architecture features for highly efficient execution. Trained on Wan2.1's 1.3B and 14B models and evaluated on the VBench benchmark, FPSAttention achieves a 7.09x kernel speedup for attention operations and a 4.96x end-to-end speedup for video generation compared to the BF16 baseline at 720p resolution-without sacrificing generation quality.
Discrete Minds in a Continuous World: Do Language Models Know Time Passes?
Jun 06, 2025



Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at temporal reasoning tasks like event ordering and duration estimation, their ability to perceive the actual passage of time remains unexplored. We investigate whether LLMs perceive the passage of time and adapt their decision-making accordingly through three complementary experiments. First, we introduce the Token-Time Hypothesis, positing that LLMs can map discrete token counts to continuous wall-clock time, and validate this through a dialogue duration judgment task. Second, we demonstrate that LLMs could use this awareness to adapt their response length while maintaining accuracy when users express urgency in question answering tasks. Finally, we develop BombRush, an interactive navigation challenge that examines how LLMs modify behavior under progressive time pressure in dynamic environments. Our findings indicate that LLMs possess certain awareness of time passage, enabling them to bridge discrete linguistic tokens and continuous physical time, though this capability varies with model size and reasoning abilities. This work establishes a theoretical foundation for enhancing temporal awareness in LLMs for time-sensitive applications.
Reshaping Representation Space to Balance the Safety and Over-rejection in Large Audio Language Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) have extended the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by enabling audio-based human interactions. However, recent research has revealed that LALMs remain vulnerable to harmful queries due to insufficient safety-alignment. Despite advances in defence measures for text and vision LLMs, effective safety-alignment strategies and audio-safety dataset specifically targeting LALMs are notably absent. Meanwhile defence measures based on Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) struggle to address safety improvement while avoiding over-rejection issues, significantly compromising helpfulness. In this work, we propose an unsupervised safety-fine-tuning strategy as remedy that reshapes model's representation space to enhance existing LALMs safety-alignment while balancing the risk of over-rejection. Our experiments, conducted across three generations of Qwen LALMs, demonstrate that our approach significantly improves LALMs safety under three modality input conditions (audio-text, text-only, and audio-only) while increasing over-rejection rate by only 0.88% on average. Warning: this paper contains harmful examples.
SituatedThinker: Grounding LLM Reasoning with Real-World through Situated Thinking
May 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) demonstrate their impressive reasoning capabilities. However, the reasoning confined to internal parametric space limits LLMs' access to real-time information and understanding of the physical world. To overcome this constraint, we introduce SituatedThinker, a novel framework that enables LLMs to ground their reasoning in real-world contexts through situated thinking, which adaptively combines both internal knowledge and external information with predefined interfaces. By utilizing reinforcement learning, SituatedThinker incentivizes deliberate reasoning with the real world to acquire information and feedback, allowing LLMs to surpass their knowledge boundaries and enhance reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate significant performance improvements on multi-hop question-answering and mathematical reasoning benchmarks. Furthermore, SituatedThinker demonstrates strong performance on unseen tasks, such as KBQA, TableQA, and text-based games, showcasing the generalizable real-world grounded reasoning capability. Our codes are available at https://github.com/jnanliu/SituatedThinker.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge