Sukai Huang
MATA: A Trainable Hierarchical Automaton System for Multi-Agent Visual Reasoning
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Recent vision-language models have strong perceptual ability but their implicit reasoning is hard to explain and easily generates hallucinations on complex queries. Compositional methods improve interpretability, but most rely on a single agent or hand-crafted pipeline and cannot decide when to collaborate across complementary agents or compete among overlapping ones. We introduce MATA (Multi-Agent hierarchical Trainable Automaton), a multi-agent system presented as a hierarchical finite-state automaton for visual reasoning whose top-level transitions are chosen by a trainable hyper agent. Each agent corresponds to a state in the hyper automaton, and runs a small rule-based sub-automaton for reliable micro-control. All agents read and write a shared memory, yielding transparent execution history. To supervise the hyper agent's transition policy, we build transition-trajectory trees and transform to memory-to-next-state pairs, forming the MATA-SFT-90K dataset for supervised finetuning (SFT). The finetuned LLM as the transition policy understands the query and the capacity of agents, and it can efficiently choose the optimal agent to solve the task. Across multiple visual reasoning benchmarks, MATA achieves the state-of-the-art results compared with monolithic and compositional baselines. The code and dataset are available at https://github.com/ControlNet/MATA.
Explain Before You Answer: A Survey on Compositional Visual Reasoning
Aug 24, 2025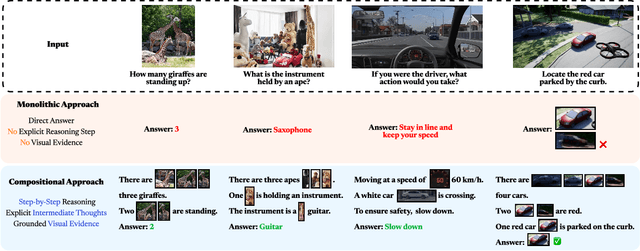
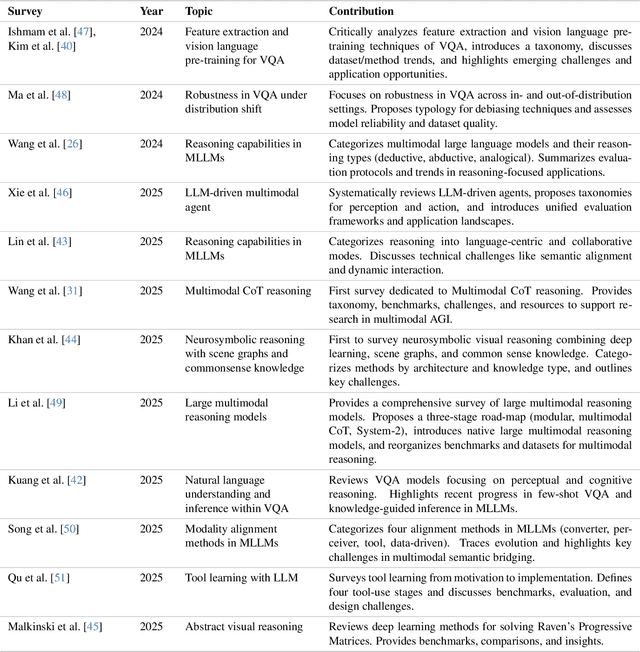
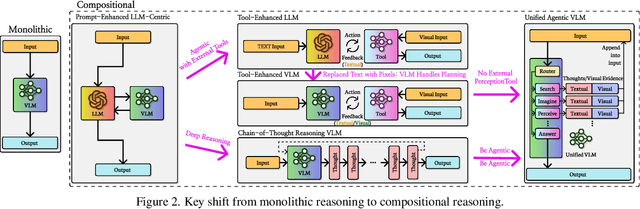
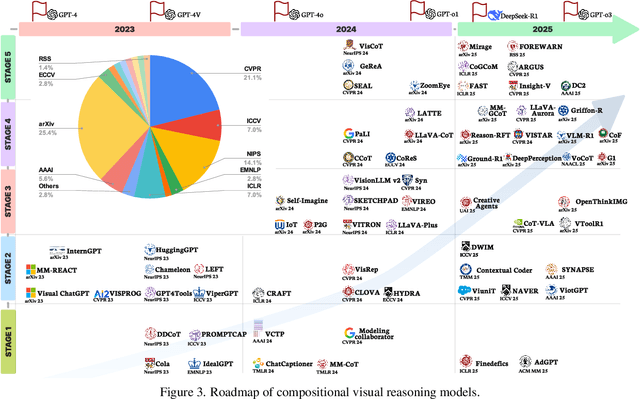
Abstract:Compositional visual reasoning has emerged as a key research frontier in multimodal AI, aiming to endow machines with the human-like ability to decompose visual scenes, ground intermediate concepts, and perform multi-step logical inference. While early surveys focus on monolithic vision-language models or general multimodal reasoning, a dedicated synthesis of the rapidly expanding compositional visual reasoning literature is still missing. We fill this gap with a comprehensive survey spanning 2023 to 2025 that systematically reviews 260+ papers from top venues (CVPR, ICCV, NeurIPS, ICML, ACL, etc.). We first formalize core definitions and describe why compositional approaches offer advantages in cognitive alignment, semantic fidelity, robustness, interpretability, and data efficiency. Next, we trace a five-stage paradigm shift: from prompt-enhanced language-centric pipelines, through tool-enhanced LLMs and tool-enhanced VLMs, to recently minted chain-of-thought reasoning and unified agentic VLMs, highlighting their architectural designs, strengths, and limitations. We then catalog 60+ benchmarks and corresponding metrics that probe compositional visual reasoning along dimensions such as grounding accuracy, chain-of-thought faithfulness, and high-resolution perception. Drawing on these analyses, we distill key insights, identify open challenges (e.g., limitations of LLM-based reasoning, hallucination, a bias toward deductive reasoning, scalable supervision, tool integration, and benchmark limitations), and outline future directions, including world-model integration, human-AI collaborative reasoning, and richer evaluation protocols. By offering a unified taxonomy, historical roadmap, and critical outlook, this survey aims to serve as a foundational reference and inspire the next generation of compositional visual reasoning research.
Chasing Progress, Not Perfection: Revisiting Strategies for End-to-End LLM Plan Generation
Dec 14, 2024Abstract:The capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to plan remains a topic of debate. Some critics argue that strategies to boost LLMs' reasoning skills are ineffective in planning tasks, while others report strong outcomes merely from training models on a planning corpus. This study reassesses recent strategies by developing an end-to-end LLM planner and employing diverse metrics for a thorough evaluation. We find that merely fine-tuning LLMs on a corpus of planning instances does not lead to robust planning skills, as indicated by poor performance on out-of-distribution test sets. At the same time, we find that various strategies, including Chain-of-Thought, do enhance the probability of a plan being executable. This indicates progress towards better plan quality, despite not directly enhancing the final validity rate. Among the strategies we evaluated, reinforcement learning with our novel `Longest Contiguous Common Subsequence' reward emerged as the most effective, contributing to both plan validity and executability. Overall, our research addresses key misconceptions in the LLM-planning literature; we validate incremental progress in plan executability, although plan validity remains a challenge. Hence, future strategies should focus on both these aspects, drawing insights from our findings.
Overcoming Reward Model Noise in Instruction-Guided Reinforcement Learning
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) have gained traction as auxiliary reward models to provide more informative reward signals in sparse reward environments. However, our work reveals a critical vulnerability of this method: a small amount of noise in the reward signal can severely degrade agent performance. In challenging environments with sparse rewards, we show that reinforcement learning agents using VLM-based reward models without proper noise handling perform worse than agents relying solely on exploration-driven methods. We hypothesize that false positive rewards -- where the reward model incorrectly assigns rewards to trajectories that do not fulfill the given instruction -- are more detrimental to learning than false negatives. Our analysis confirms this hypothesis, revealing that the widely used cosine similarity metric, when applied to comparing agent trajectories and language instructions, is prone to generating false positive reward signals. To address this, we introduce BiMI (Binary Mutual Information), a novel noise-resilient reward function. Our experiments demonstrate that, BiMI significantly boosts the agent performance, with an average improvement ratio of 44.5\% across diverse environments with learned, non-oracle VLMs, thereby making VLM-based reward models practical for real-world applications.
Planning in the Dark: LLM-Symbolic Planning Pipeline without Experts
Sep 24, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in solving natural language-described planning tasks, but their direct use often leads to inconsistent reasoning and hallucination. While hybrid LLM-symbolic planning pipelines have emerged as a more robust alternative, they typically require extensive expert intervention to refine and validate generated action schemas. It not only limits scalability but also introduces a potential for biased interpretation, as a single expert's interpretation of ambiguous natural language descriptions might not align with the user's actual intent. To address this, we propose a novel approach that constructs an action schema library to generate multiple candidates, accounting for the diverse possible interpretations of natural language descriptions. We further introduce a semantic validation and ranking module that automatically filter and rank the generated schemas and plans without expert-in-the-loop. The experiments showed our pipeline maintains superiority in planning over the direct LLM planning approach. These findings demonstrate the feasibility of a fully automated end-to-end LLM-symbolic planner that requires no expert intervention, opening up the possibility for a broader audience to engage with AI planning with less prerequisite of domain expertise.
A Reminder of its Brittleness: Language Reward Shaping May Hinder Learning for Instruction Following Agents
May 26, 2023Abstract:Teaching agents to follow complex written instructions has been an important yet elusive goal. One technique for improving learning efficiency is language reward shaping (LRS), which is used in reinforcement learning (RL) to reward actions that represent progress towards a sparse reward. We argue that the apparent success of LRS is brittle, and prior positive findings can be attributed to weak RL baselines. Specifically, we identified suboptimal LRS designs that reward partially matched trajectories, and we characterised a novel type of reward perturbation that addresses this issue based on the concept of loosening task constraints. We provided theoretical and empirical evidence that agents trained using LRS rewards converge more slowly compared to pure RL agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge