Kaiwen Wei
MentalSeek-Dx: Towards Progressive Hypothetico-Deductive Reasoning for Real-world Psychiatric Diagnosis
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Mental health disorders represent a burgeoning global public health challenge. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated potential in psychiatric assessment, their clinical utility is severely constrained by benchmarks that lack ecological validity and fine-grained diagnostic supervision. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{MentalDx Bench}, the first benchmark dedicated to disorder-level psychiatric diagnosis within real-world clinical settings. Comprising 712 de-identified electronic health records annotated by board-certified psychiatrists under ICD-11 guidelines, the benchmark covers 76 disorders across 16 diagnostic categories. Evaluation of 18 LLMs reveals a critical \textit{paradigm misalignment}: strong performance at coarse diagnostic categorization contrasts with systematic failure at disorder-level diagnosis, underscoring a gap between pattern-based modeling and clinical hypothetico-deductive reasoning. In response, we propose \textbf{MentalSeek-Dx}, a medical-specialized LLM trained to internalize this clinical reasoning process through supervised trajectory construction and curriculum-based reinforcement learning. Experiments on MentalDx Bench demonstrate that MentalSeek-Dx achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance with only 14B parameters, establishing a clinically grounded framework for reliable psychiatric diagnosis.
Me-Agent: A Personalized Mobile Agent with Two-Level User Habit Learning for Enhanced Interaction
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based mobile agents have made significant performance advancements. However, these agents often follow explicit user instructions while overlooking personalized needs, leading to significant limitations for real users, particularly without personalized context: (1) inability to interpret ambiguous instructions, (2) lack of learning from user interaction history, and (3) failure to handle personalized instructions. To alleviate the above challenges, we propose Me-Agent, a learnable and memorable personalized mobile agent. Specifically, Me-Agent incorporates a two-level user habit learning approach. At the prompt level, we design a user preference learning strategy enhanced with a Personal Reward Model to improve personalization performance. At the memory level, we design a Hierarchical Preference Memory, which stores users' long-term memory and app-specific memory in different level memory. To validate the personalization capabilities of mobile agents, we introduce User FingerTip, a new benchmark featuring numerous ambiguous instructions for daily life. Extensive experiments on User FingerTip and general benchmarks demonstrate that Me-Agent achieves state-of-the-art performance in personalization while maintaining competitive instruction execution performance.
Do Models Hear Like Us? Probing the Representational Alignment of Audio LLMs and Naturalistic EEG
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Audio Large Language Models (Audio LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities in integrating speech perception with language understanding. However, whether their internal representations align with human neural dynamics during naturalistic listening remains largely unexplored. In this work, we systematically examine layer-wise representational alignment between 12 open-source Audio LLMs and Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals across 2 datasets. Specifically, we employ 8 similarity metrics, such as Spearman-based Representational Similarity Analysis (RSA), to characterize within-sentence representational geometry. Our analysis reveals 3 key findings: (1) we observe a rank-dependence split, in which model rankings vary substantially across different similarity metrics; (2) we identify spatio-temporal alignment patterns characterized by depth-dependent alignment peaks and a pronounced increase in RSA within the 250-500 ms time window, consistent with N400-related neural dynamics; (3) we find an affective dissociation whereby negative prosody, identified using a proposed Tri-modal Neighborhood Consistency (TNC) criterion, reduces geometric similarity while enhancing covariance-based dependence. These findings provide new neurobiological insights into the representational mechanisms of Audio LLMs.
ES-Mem: Event Segmentation-Based Memory for Long-Term Dialogue Agents
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Memory is critical for dialogue agents to maintain coherence and enable continuous adaptation in long-term interactions. While existing memory mechanisms offer basic storage and retrieval capabilities, they are hindered by two primary limitations: (1) rigid memory granularity often disrupts semantic integrity, resulting in fragmented and incoherent memory units; (2) prevalent flat retrieval paradigms rely solely on surface-level semantic similarity, neglecting the structural cues of discourse required to navigate and locate specific episodic contexts. To mitigate these limitations, drawing inspiration from Event Segmentation Theory, we propose ES-Mem, a framework incorporating two core components: (1) a dynamic event segmentation module that partitions long-term interactions into semantically coherent events with distinct boundaries; (2) a hierarchical memory architecture that constructs multi-layered memories and leverages boundary semantics to anchor specific episodic memory for precise context localization. Evaluations on two memory benchmarks demonstrate that ES-Mem yields consistent performance gains over baseline methods. Furthermore, the proposed event segmentation module exhibits robust applicability on dialogue segmentation datasets.
DiffER: Diffusion Entity-Relation Modeling for Reversal Curse in Diffusion Large Language Models
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:The "reversal curse" refers to the phenomenon where large language models (LLMs) exhibit predominantly unidirectional behavior when processing logically bidirectional relationships. Prior work attributed this to autoregressive training -- predicting the next token inherently favors left-to-right information flow over genuine bidirectional knowledge associations. However, we observe that Diffusion LLMs (DLLMs), despite being trained bidirectionally, also suffer from the reversal curse. To investigate the root causes, we conduct systematic experiments on DLLMs and identify three key reasons: 1) entity fragmentation during training, 2) data asymmetry, and 3) missing entity relations. Motivated by the analysis of these reasons, we propose Diffusion Entity-Relation Modeling (DiffER), which addresses the reversal curse through entity-aware training and balanced data construction. Specifically, DiffER introduces whole-entity masking, which mitigates entity fragmentation by predicting complete entities in a single step. DiffER further employs distribution-symmetric and relation-enhanced data construction strategies to alleviate data asymmetry and missing relations. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DiffER effectively alleviates the reversal curse in Diffusion LLMs, offering new perspectives for future research.
ReasonTabQA: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Table Question Answering from Real World Industrial Scenarios
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly catalyzed table-based question answering (TableQA). However, existing TableQA benchmarks often overlook the intricacies of industrial scenarios, which are characterized by multi-table structures, nested headers, and massive scales. These environments demand robust table reasoning through deep structured inference, presenting a significant challenge that remains inadequately addressed by current methodologies. To bridge this gap, we present ReasonTabQA, a large-scale bilingual benchmark encompassing 1,932 tables across 30 industry domains such as energy and automotive. ReasonTabQA provides high-quality annotations for both final answers and explicit reasoning chains, supporting both thinking and no-thinking paradigms. Furthermore, we introduce TabCodeRL, a reinforcement learning method that leverages table-aware verifiable rewards to guide the generation of logical reasoning paths. Extensive experiments on ReasonTabQA and 4 TableQA datasets demonstrate that while TabCodeRL yields substantial performance gains on open-source LLMs, the persistent performance gap on ReasonTabQA underscores the inherent complexity of real-world industrial TableQA.
T2R-bench: A Benchmark for Generating Article-Level Reports from Real World Industrial Tables
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Extensive research has been conducted to explore the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in table reasoning. However, the essential task of transforming tables information into reports remains a significant challenge for industrial applications. This task is plagued by two critical issues: 1) the complexity and diversity of tables lead to suboptimal reasoning outcomes; and 2) existing table benchmarks lack the capacity to adequately assess the practical application of this task. To fill this gap, we propose the table-to-report task and construct a bilingual benchmark named T2R-bench, where the key information flow from the tables to the reports for this task. The benchmark comprises 457 industrial tables, all derived from real-world scenarios and encompassing 19 industry domains as well as 4 types of industrial tables. Furthermore, we propose an evaluation criteria to fairly measure the quality of report generation. The experiments on 25 widely-used LLMs reveal that even state-of-the-art models like Deepseek-R1 only achieves performance with 62.71 overall score, indicating that LLMs still have room for improvement on T2R-bench. Source code and data will be available after acceptance.
MIRAGE: Scaling Test-Time Inference with Parallel Graph-Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning Chains
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) have shown significant progress in test-time scaling through chain-of-thought prompting. Current approaches like search-o1 integrate retrieval augmented generation (RAG) into multi-step reasoning processes but rely on a single, linear reasoning chain while incorporating unstructured textual information in a flat, context-agnostic manner. As a result, these approaches can lead to error accumulation throughout the reasoning chain, which significantly limits its effectiveness in medical question-answering (QA) tasks where both accuracy and traceability are critical requirements. To address these challenges, we propose MIRAGE (Multi-chain Inference with Retrieval-Augmented Graph Exploration), a novel test-time scalable reasoning framework that performs dynamic multi-chain inference over structured medical knowledge graphs. Specifically, MIRAGE 1) decomposes complex queries into entity-grounded sub-questions, 2) executes parallel inference chains, 3) retrieves evidence adaptively via neighbor expansion and multi-hop traversal, and 4) integrates answers using cross-chain verification to resolve contradictions. Experiments on three medical QA benchmarks (GenMedGPT-5k, CMCQA, and ExplainCPE) show that MIRAGE consistently outperforms GPT-4o, Tree-of-Thought variants, and other retrieval-augmented baselines in both automatic and human evaluations. Additionally, MIRAGE improves interpretability by generating explicit reasoning chains that trace each factual claim to concrete chains within the knowledge graph, making it well-suited for complex medical reasoning scenarios. The code will be available for further research.
RingMo-Agent: A Unified Remote Sensing Foundation Model for Multi-Platform and Multi-Modal Reasoning
Jul 28, 2025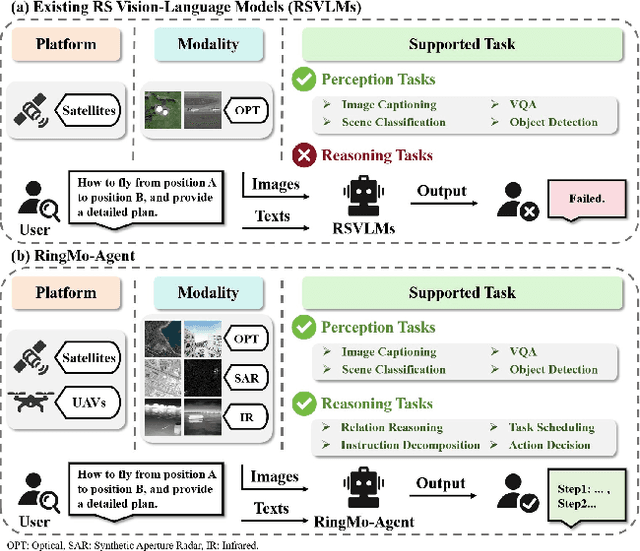
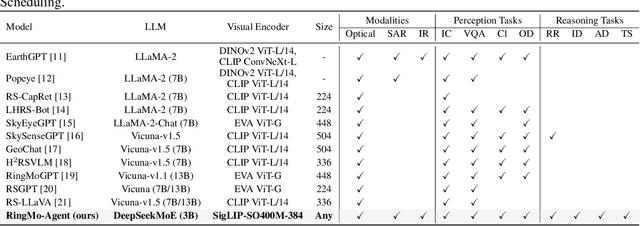
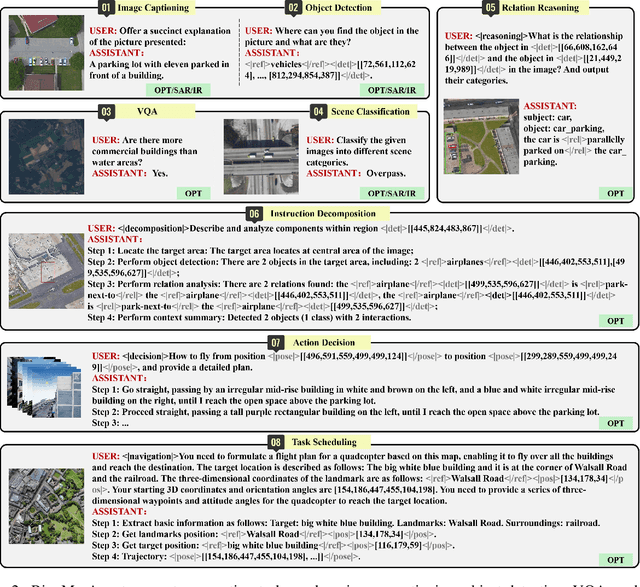
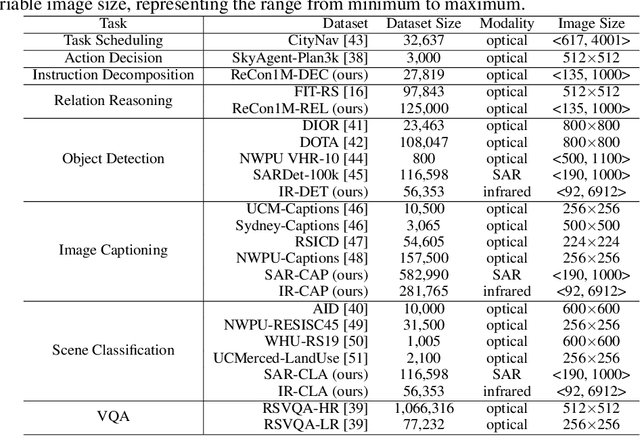
Abstract:Remote sensing (RS) images from multiple modalities and platforms exhibit diverse details due to differences in sensor characteristics and imaging perspectives. Existing vision-language research in RS largely relies on relatively homogeneous data sources. Moreover, they still remain limited to conventional visual perception tasks such as classification or captioning. As a result, these methods fail to serve as a unified and standalone framework capable of effectively handling RS imagery from diverse sources in real-world applications. To address these issues, we propose RingMo-Agent, a model designed to handle multi-modal and multi-platform data that performs perception and reasoning tasks based on user textual instructions. Compared with existing models, RingMo-Agent 1) is supported by a large-scale vision-language dataset named RS-VL3M, comprising over 3 million image-text pairs, spanning optical, SAR, and infrared (IR) modalities collected from both satellite and UAV platforms, covering perception and challenging reasoning tasks; 2) learns modality adaptive representations by incorporating separated embedding layers to construct isolated features for heterogeneous modalities and reduce cross-modal interference; 3) unifies task modeling by introducing task-specific tokens and employing a token-based high-dimensional hidden state decoding mechanism designed for long-horizon spatial tasks. Extensive experiments on various RS vision-language tasks demonstrate that RingMo-Agent not only proves effective in both visual understanding and sophisticated analytical tasks, but also exhibits strong generalizability across different platforms and sensing modalities.
FLEKE: Federated Locate-then-Edit Knowledge Editing
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Locate-then-Edit Knowledge Editing (LEKE) is a key technique for updating large language models (LLMs) without full retraining. However, existing methods assume a single-user setting and become inefficient in real-world multi-client scenarios, where decentralized organizations (e.g., hospitals, financial institutions) independently update overlapping knowledge, leading to redundant mediator knowledge vector (MKV) computations and privacy concerns. To address these challenges, we introduce Federated Locate-then-Edit Knowledge Editing (FLEKE), a novel task that enables multiple clients to collaboratively perform LEKE while preserving privacy and reducing computational overhead. To achieve this, we propose FedEdit, a two-stage framework that optimizes MKV selection and reuse. In the first stage, clients locally apply LEKE and upload the computed MKVs. In the second stage, rather than relying solely on server-based MKV sharing, FLEKE allows clients retrieve relevant MKVs based on cosine similarity, enabling knowledge re-edit and minimizing redundant computations. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that FedEdit retains over 96% of the performance of non-federated LEKE while significantly outperforming a FedAvg-based baseline by approximately twofold. Besides, we find that MEMIT performs more consistently than PMET in the FLEKE task with our FedEdit framework. Our code is available at https://github.com/zongkaiz/FLEKE.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge