Yue Yu
TranX-Adapter: Bridging Artifacts and Semantics within MLLMs for Robust AI-generated Image Detection
Feb 25, 2026Abstract:Rapid advances in AI-generated image (AIGI) technology enable highly realistic synthesis, threatening public information integrity and security. Recent studies have demonstrated that incorporating texture-level artifact features alongside semantic features into multimodal large language models (MLLMs) can enhance their AIGI detection capability. However, our preliminary analyses reveal that artifact features exhibit high intra-feature similarity, leading to an almost uniform attention map after the softmax operation. This phenomenon causes attention dilution, thereby hindering effective fusion between semantic and artifact features. To overcome this limitation, we propose a lightweight fusion adapter, TranX-Adapter, which integrates a Task-aware Optimal-Transport Fusion that leverages the Jensen-Shannon divergence between artifact and semantic prediction probabilities as a cost matrix to transfer artifact information into semantic features, and an X-Fusion that employs cross-attention to transfer semantic information into artifact features. Experiments on standard AIGI detection benchmarks upon several advanced MLLMs, show that our TranX-Adapter brings consistent and significant improvements (up to +6% accuracy).
Advancing Open-source World Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:We present LingBot-World, an open-sourced world simulator stemming from video generation. Positioned as a top-tier world model, LingBot-World offers the following features. (1) It maintains high fidelity and robust dynamics in a broad spectrum of environments, including realism, scientific contexts, cartoon styles, and beyond. (2) It enables a minute-level horizon while preserving contextual consistency over time, which is also known as "long-term memory". (3) It supports real-time interactivity, achieving a latency of under 1 second when producing 16 frames per second. We provide public access to the code and model in an effort to narrow the divide between open-source and closed-source technologies. We believe our release will empower the community with practical applications across areas like content creation, gaming, and robot learning.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Coding in a Bubble? Evaluating LLMs in Resolving Context Adaptation Bugs During Code Adaptation
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Code adaptation is a fundamental but challenging task in software development, requiring developers to modify existing code for new contexts. A key challenge is to resolve Context Adaptation Bugs (CtxBugs), which occurs when code correct in its original context violates constraints in the target environment. Unlike isolated bugs, CtxBugs cannot be resolved through local fixes and require cross-context reasoning to identify semantic mismatches. Overlooking them may lead to critical failures in adaptation. Although Large Language Models (LLMs) show great potential in automating code-related tasks, their ability to resolve CtxBugs remains a significant and unexplored obstacle to their practical use in code adaptation. To bridge this gap, we propose CtxBugGen, a novel framework for generating CtxBugs to evaluate LLMs. Its core idea is to leverage LLMs' tendency to generate plausible but context-free code when contextual constraints are absent. The framework generates CtxBugs through a four-step process to ensure their relevance and validity: (1) Adaptation Task Selection, (2) Task-specific Perturbation,(3) LLM-based Variant Generation and (4) CtxBugs Identification. Based on the benchmark constructed by CtxBugGen, we conduct an empirical study with four state-of-the-art LLMs. Our results reveal their unsatisfactory performance in CtxBug resolution. The best performing LLM, Kimi-K2, achieves 55.93% on Pass@1 and resolves just 52.47% of CtxBugs. The presence of CtxBugs degrades LLMs' adaptation performance by up to 30%. Failure analysis indicates that LLMs often overlook CtxBugs and replicate them in their outputs. Our study highlights a critical weakness in LLMs' cross-context reasoning and emphasize the need for new methods to enhance their context awareness for reliable code adaptation.
AdaptEval: A Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models on Code Snippet Adaptation
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have automated various software engineering tasks, with benchmarks emerging to evaluate their capabilities. However, for adaptation, a critical activity during code reuse, there is no benchmark to assess LLMs' performance, leaving their practical utility in this area unclear. To fill this gap, we propose AdaptEval, a benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs on code snippet adaptation. Unlike existing benchmarks, AdaptEval incorporates the following three distinctive features: First, Practical Context. Tasks in AdaptEval are derived from developers' practices, preserving rich contextual information from Stack Overflow and GitHub communities. Second, Multi-granularity Annotation. Each task is annotated with requirements at both task and adaptation levels, supporting the evaluation of LLMs across diverse adaptation scenarios. Third, Fine-grained Evaluation. AdaptEval includes a two-tier testing framework combining adaptation-level and function-level tests, which enables evaluating LLMs' performance across various individual adaptations. Based on AdaptEval, we conduct the first empirical study to evaluate six instruction-tuned LLMs and especially three reasoning LLMs on code snippet adaptation. Experimental results demonstrate that AdaptEval enables the assessment of LLMs' adaptation capabilities from various perspectives. It also provides critical insights into their current limitations, particularly their struggle to follow explicit instructions. We hope AdaptEval can facilitate further investigation and enhancement of LLMs' capabilities in code snippet adaptation, supporting their real-world applications.
MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
Transform and Entropy Coding in AV2
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:AV2 is the successor to the AV1 royalty-free video coding standard developed by the Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia). Its primary objective is to deliver substantial compression gains and subjective quality improvements while maintaining low-complexity encoder and decoder operations. This paper describes the transform, quantization and entropy coding design in AV2, including redesigned transform kernels and data-driven transforms, expanded transform partitioning, and a mode & coefficient dependent transform signaling. AV2 introduces several new coding tools including Intra/Inter Secondary Transforms (IST), Trellis Coded Quantization (TCQ), Adaptive Transform Coding (ATC), Probability Adaptation Rate Adjustment (PARA), Forward Skip Coding (FSC), Cross Chroma Component Transforms (CCTX), Parity Hiding (PH) tools and improved lossless coding. These advances enable AV2 to deliver the highest quality video experience for video applications at a significantly reduced bitrate.
MiMo-Audio: Audio Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Existing audio language models typically rely on task-specific fine-tuning to accomplish particular audio tasks. In contrast, humans are able to generalize to new audio tasks with only a few examples or simple instructions. GPT-3 has shown that scaling next-token prediction pretraining enables strong generalization capabilities in text, and we believe this paradigm is equally applicable to the audio domain. By scaling MiMo-Audio's pretraining data to over one hundred million of hours, we observe the emergence of few-shot learning capabilities across a diverse set of audio tasks. We develop a systematic evaluation of these capabilities and find that MiMo-Audio-7B-Base achieves SOTA performance on both speech intelligence and audio understanding benchmarks among open-source models. Beyond standard metrics, MiMo-Audio-7B-Base generalizes to tasks absent from its training data, such as voice conversion, style transfer, and speech editing. MiMo-Audio-7B-Base also demonstrates powerful speech continuation capabilities, capable of generating highly realistic talk shows, recitations, livestreaming and debates. At the post-training stage, we curate a diverse instruction-tuning corpus and introduce thinking mechanisms into both audio understanding and generation. MiMo-Audio-7B-Instruct achieves open-source SOTA on audio understanding benchmarks (MMSU, MMAU, MMAR, MMAU-Pro), spoken dialogue benchmarks (Big Bench Audio, MultiChallenge Audio) and instruct-TTS evaluations, approaching or surpassing closed-source models. Model checkpoints and full evaluation suite are available at https://github.com/XiaomiMiMo/MiMo-Audio.
The World is Your Canvas: Painting Promptable Events with Reference Images, Trajectories, and Text
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:We present WorldCanvas, a framework for promptable world events that enables rich, user-directed simulation by combining text, trajectories, and reference images. Unlike text-only approaches and existing trajectory-controlled image-to-video methods, our multimodal approach combines trajectories -- encoding motion, timing, and visibility -- with natural language for semantic intent and reference images for visual grounding of object identity, enabling the generation of coherent, controllable events that include multi-agent interactions, object entry/exit, reference-guided appearance and counterintuitive events. The resulting videos demonstrate not only temporal coherence but also emergent consistency, preserving object identity and scene despite temporary disappearance. By supporting expressive world events generation, WorldCanvas advances world models from passive predictors to interactive, user-shaped simulators. Our project page is available at: https://worldcanvas.github.io/.
Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Holistic Design of Catalysts Tailored for Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Growth
Dec 18, 2025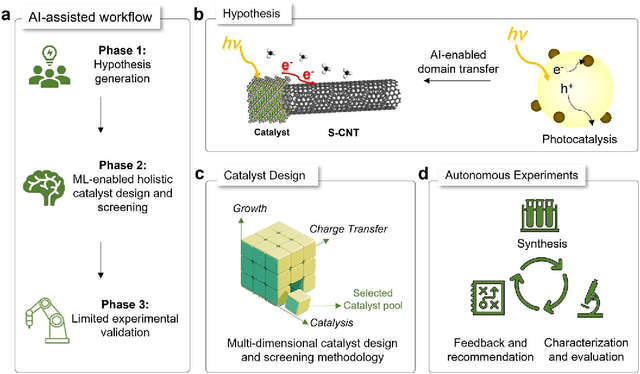
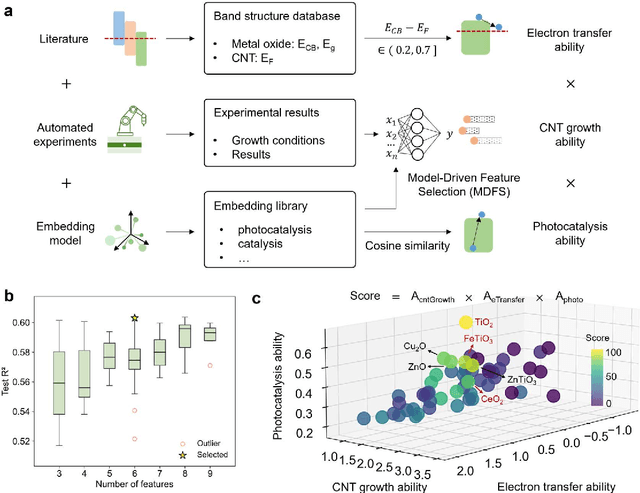
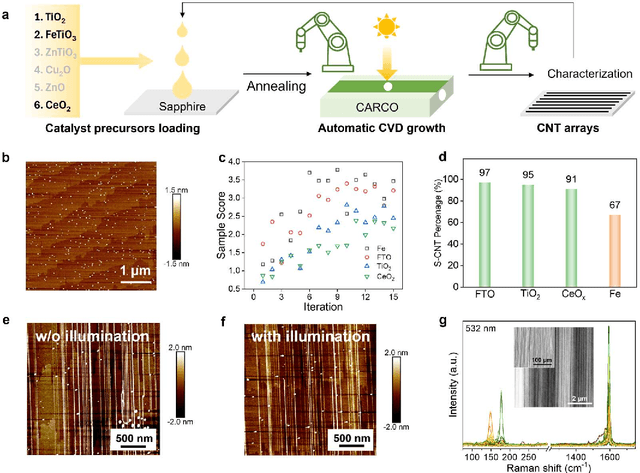
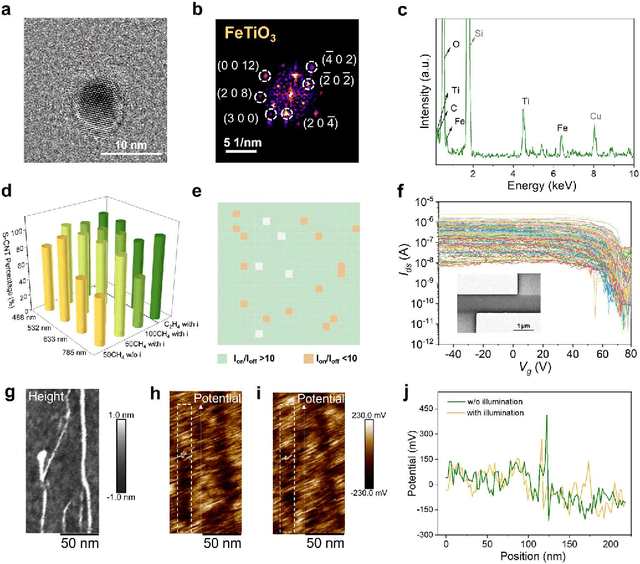
Abstract:Catalyst design is crucial for materials synthesis, especially for complex reaction networks. Strategies like collaborative catalytic systems and multifunctional catalysts are effective but face challenges at the nanoscale. Carbon nanotube synthesis contains complicated nanoscale catalytic reactions, thus achieving high-density, high-quality semiconducting CNTs demands innovative catalyst design. In this work, we present a holistic framework integrating machine learning into traditional catalyst design for semiconducting CNT synthesis. It combines knowledge-based insights with data-driven techniques. Three key components, including open-access electronic structure databases for precise physicochemical descriptors, pre-trained natural language processing-based embedding model for higher-level abstractions, and physical - driven predictive models based on experiment data, are utilized. Through this framework, a new method for selective semiconducting CNT synthesis via catalyst - mediated electron injection, tuned by light during growth, is proposed. 54 candidate catalysts are screened, and three with high potential are identified. High-throughput experiments validate the predictions, with semiconducting selectivity exceeding 91% and the FeTiO3 catalyst reaching 98.6%. This approach not only addresses semiconducting CNT synthesis but also offers a generalizable methodology for global catalyst design and nanomaterials synthesis, advancing materials science in precise control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge