Yanjie Ze
ResMimic: From General Motion Tracking to Humanoid Whole-body Loco-Manipulation via Residual Learning
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Humanoid whole-body loco-manipulation promises transformative capabilities for daily service and warehouse tasks. While recent advances in general motion tracking (GMT) have enabled humanoids to reproduce diverse human motions, these policies lack the precision and object awareness required for loco-manipulation. To this end, we introduce ResMimic, a two-stage residual learning framework for precise and expressive humanoid control from human motion data. First, a GMT policy, trained on large-scale human-only motion, serves as a task-agnostic base for generating human-like whole-body movements. An efficient but precise residual policy is then learned to refine the GMT outputs to improve locomotion and incorporate object interaction. To further facilitate efficient training, we design (i) a point-cloud-based object tracking reward for smoother optimization, (ii) a contact reward that encourages accurate humanoid body-object interactions, and (iii) a curriculum-based virtual object controller to stabilize early training. We evaluate ResMimic in both simulation and on a real Unitree G1 humanoid. Results show substantial gains in task success, training efficiency, and robustness over strong baselines. Videos are available at https://resmimic.github.io/ .
Retargeting Matters: General Motion Retargeting for Humanoid Motion Tracking
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Humanoid motion tracking policies are central to building teleoperation pipelines and hierarchical controllers, yet they face a fundamental challenge: the embodiment gap between humans and humanoid robots. Current approaches address this gap by retargeting human motion data to humanoid embodiments and then training reinforcement learning (RL) policies to imitate these reference trajectories. However, artifacts introduced during retargeting, such as foot sliding, self-penetration, and physically infeasible motion are often left in the reference trajectories for the RL policy to correct. While prior work has demonstrated motion tracking abilities, they often require extensive reward engineering and domain randomization to succeed. In this paper, we systematically evaluate how retargeting quality affects policy performance when excessive reward tuning is suppressed. To address issues that we identify with existing retargeting methods, we propose a new retargeting method, General Motion Retargeting (GMR). We evaluate GMR alongside two open-source retargeters, PHC and ProtoMotions, as well as with a high-quality closed-source dataset from Unitree. Using BeyondMimic for policy training, we isolate retargeting effects without reward tuning. Our experiments on a diverse subset of the LAFAN1 dataset reveal that while most motions can be tracked, artifacts in retargeted data significantly reduce policy robustness, particularly for dynamic or long sequences. GMR consistently outperforms existing open-source methods in both tracking performance and faithfulness to the source motion, achieving perceptual fidelity and policy success rates close to the closed-source baseline. Website: https://jaraujo98.github.io/retargeting_matters. Code: https://github.com/YanjieZe/GMR.
4D Visual Pre-training for Robot Learning
Aug 24, 2025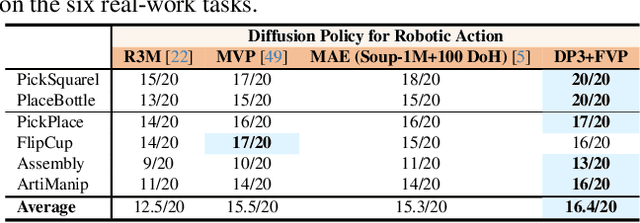
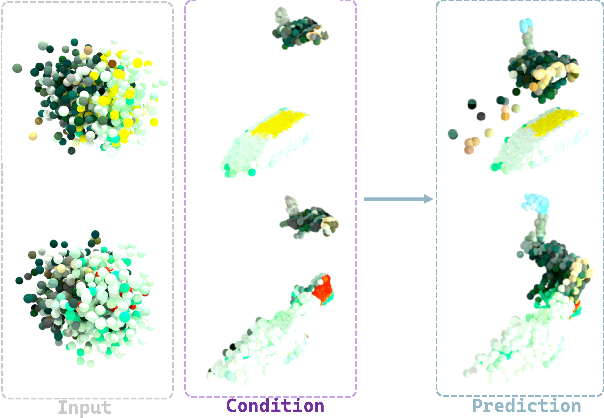
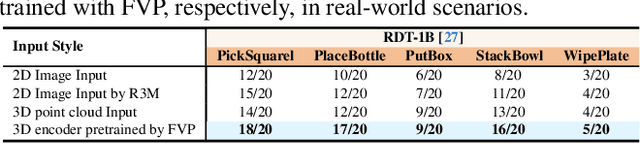
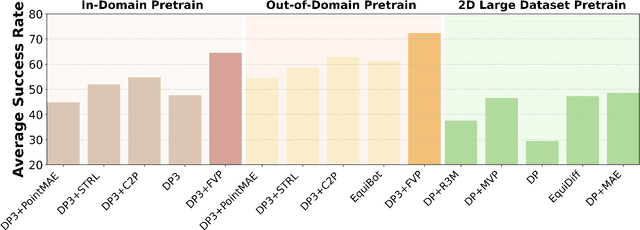
Abstract:General visual representations learned from web-scale datasets for robotics have achieved great success in recent years, enabling data-efficient robot learning on manipulation tasks; yet these pre-trained representations are mostly on 2D images, neglecting the inherent 3D nature of the world. However, due to the scarcity of large-scale 3D data, it is still hard to extract a universal 3D representation from web datasets. Instead, we are seeking a general visual pre-training framework that could improve all 3D representations as an alternative. Our framework, called FVP, is a novel 4D Visual Pre-training framework for real-world robot learning. FVP frames the visual pre-training objective as a next-point-cloud-prediction problem, models the prediction model as a diffusion model, and pre-trains the model on the larger public datasets directly. Across twelve real-world manipulation tasks, FVP boosts the average success rate of 3D Diffusion Policy (DP3) for these tasks by 28%. The FVP pre-trained DP3 achieves state-of-the-art performance across imitation learning methods. Moreover, the efficacy of FVP adapts across various point cloud encoders and datasets. Finally, we apply FVP to the RDT-1B, a larger Vision-Language-Action robotic model, enhancing its performance on various robot tasks. Our project page is available at: https://4d- visual-pretraining.github.io/.
TWIST: Teleoperated Whole-Body Imitation System
May 05, 2025Abstract:Teleoperating humanoid robots in a whole-body manner marks a fundamental step toward developing general-purpose robotic intelligence, with human motion providing an ideal interface for controlling all degrees of freedom. Yet, most current humanoid teleoperation systems fall short of enabling coordinated whole-body behavior, typically limiting themselves to isolated locomotion or manipulation tasks. We present the Teleoperated Whole-Body Imitation System (TWIST), a system for humanoid teleoperation through whole-body motion imitation. We first generate reference motion clips by retargeting human motion capture data to the humanoid robot. We then develop a robust, adaptive, and responsive whole-body controller using a combination of reinforcement learning and behavior cloning (RL+BC). Through systematic analysis, we demonstrate how incorporating privileged future motion frames and real-world motion capture (MoCap) data improves tracking accuracy. TWIST enables real-world humanoid robots to achieve unprecedented, versatile, and coordinated whole-body motor skills--spanning whole-body manipulation, legged manipulation, locomotion, and expressive movement--using a single unified neural network controller. Our project website: https://humanoid-teleop.github.io
X-Capture: An Open-Source Portable Device for Multi-Sensory Learning
Apr 03, 2025



Abstract:Understanding objects through multiple sensory modalities is fundamental to human perception, enabling cross-sensory integration and richer comprehension. For AI and robotic systems to replicate this ability, access to diverse, high-quality multi-sensory data is critical. Existing datasets are often limited by their focus on controlled environments, simulated objects, or restricted modality pairings. We introduce X-Capture, an open-source, portable, and cost-effective device for real-world multi-sensory data collection, capable of capturing correlated RGBD images, tactile readings, and impact audio. With a build cost under $1,000, X-Capture democratizes the creation of multi-sensory datasets, requiring only consumer-grade tools for assembly. Using X-Capture, we curate a sample dataset of 3,000 total points on 500 everyday objects from diverse, real-world environments, offering both richness and variety. Our experiments demonstrate the value of both the quantity and the sensory breadth of our data for both pretraining and fine-tuning multi-modal representations for object-centric tasks such as cross-sensory retrieval and reconstruction. X-Capture lays the groundwork for advancing human-like sensory representations in AI, emphasizing scalability, accessibility, and real-world applicability.
BEHAVIOR Robot Suite: Streamlining Real-World Whole-Body Manipulation for Everyday Household Activities
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Real-world household tasks present significant challenges for mobile manipulation robots. An analysis of existing robotics benchmarks reveals that successful task performance hinges on three key whole-body control capabilities: bimanual coordination, stable and precise navigation, and extensive end-effector reachability. Achieving these capabilities requires careful hardware design, but the resulting system complexity further complicates visuomotor policy learning. To address these challenges, we introduce the BEHAVIOR Robot Suite (BRS), a comprehensive framework for whole-body manipulation in diverse household tasks. Built on a bimanual, wheeled robot with a 4-DoF torso, BRS integrates a cost-effective whole-body teleoperation interface for data collection and a novel algorithm for learning whole-body visuomotor policies. We evaluate BRS on five challenging household tasks that not only emphasize the three core capabilities but also introduce additional complexities, such as long-range navigation, interaction with articulated and deformable objects, and manipulation in confined spaces. We believe that BRS's integrated robotic embodiment, data collection interface, and learning framework mark a significant step toward enabling real-world whole-body manipulation for everyday household tasks. BRS is open-sourced at https://behavior-robot-suite.github.io/
Learning Smooth Humanoid Locomotion through Lipschitz-Constrained Policies
Oct 15, 2024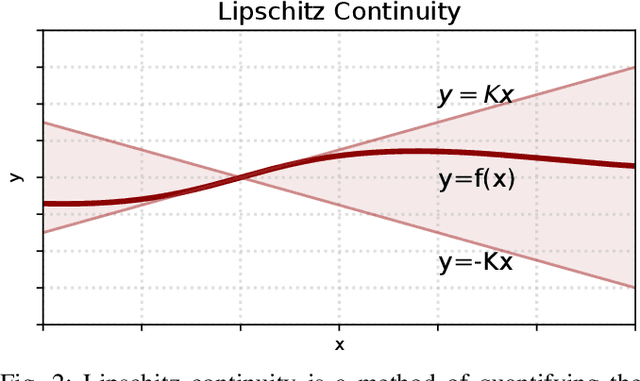
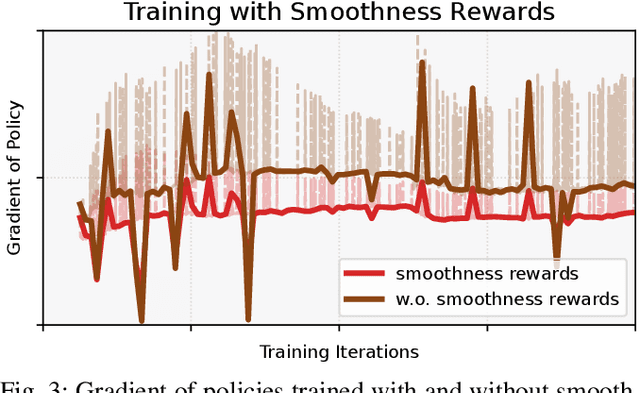
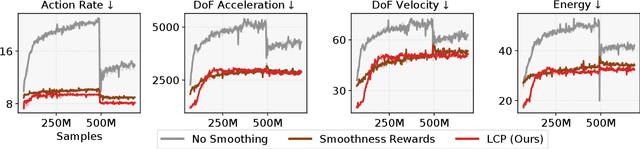
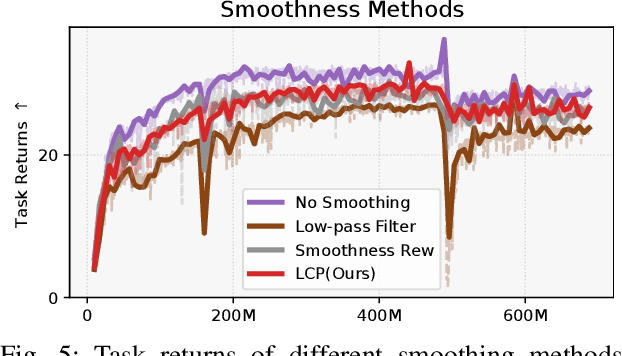
Abstract:Reinforcement learning combined with sim-to-real transfer offers a general framework for developing locomotion controllers for legged robots. To facilitate successful deployment in the real world, smoothing techniques, such as low-pass filters and smoothness rewards, are often employed to develop policies with smooth behaviors. However, because these techniques are non-differentiable and usually require tedious tuning of a large set of hyperparameters, they tend to require extensive manual tuning for each robotic platform. To address this challenge and establish a general technique for enforcing smooth behaviors, we propose a simple and effective method that imposes a Lipschitz constraint on a learned policy, which we refer to as Lipschitz-Constrained Policies (LCP). We show that the Lipschitz constraint can be implemented in the form of a gradient penalty, which provides a differentiable objective that can be easily incorporated with automatic differentiation frameworks. We demonstrate that LCP effectively replaces the need for smoothing rewards or low-pass filters and can be easily integrated into training frameworks for many distinct humanoid robots. We extensively evaluate LCP in both simulation and real-world humanoid robots, producing smooth and robust locomotion controllers. All simulation and deployment code, along with complete checkpoints, is available on our project page: https://lipschitz-constrained-policy.github.io.
Generalizable Humanoid Manipulation with Improved 3D Diffusion Policies
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Humanoid robots capable of autonomous operation in diverse environments have long been a goal for roboticists. However, autonomous manipulation by humanoid robots has largely been restricted to one specific scene, primarily due to the difficulty of acquiring generalizable skills. Recent advances in 3D visuomotor policies, such as the 3D Diffusion Policy (DP3), have shown promise in extending these capabilities to wilder environments. However, 3D visuomotor policies often rely on camera calibration and point-cloud segmentation, which present challenges for deployment on mobile robots like humanoids. In this work, we introduce the Improved 3D Diffusion Policy (iDP3), a novel 3D visuomotor policy that eliminates these constraints by leveraging egocentric 3D visual representations. We demonstrate that iDP3 enables a full-sized humanoid robot to autonomously perform skills in diverse real-world scenarios, using only data collected in the lab. Videos are available at: https://humanoid-manipulation.github.io
Catch It! Learning to Catch in Flight with Mobile Dexterous Hands
Sep 16, 2024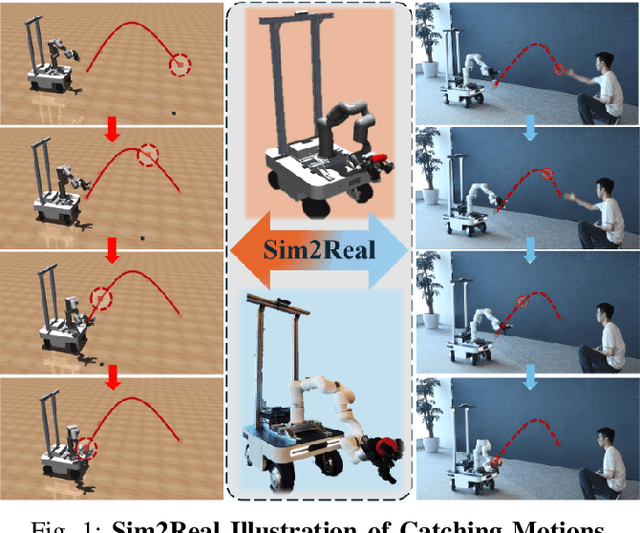

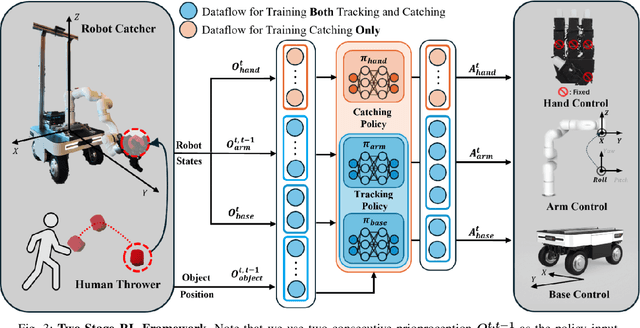
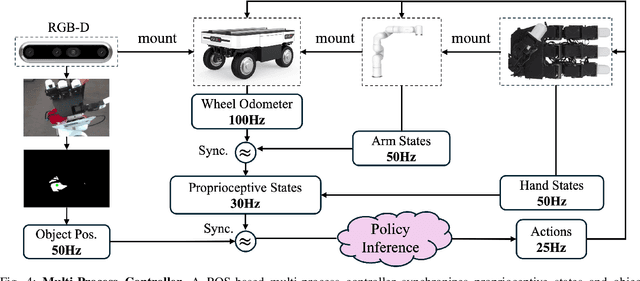
Abstract:Catching objects in flight (i.e., thrown objects) is a common daily skill for humans, yet it presents a significant challenge for robots. This task requires a robot with agile and accurate motion, a large spatial workspace, and the ability to interact with diverse objects. In this paper, we build a mobile manipulator composed of a mobile base, a 6-DoF arm, and a 12-DoF dexterous hand to tackle such a challenging task. We propose a two-stage reinforcement learning framework to efficiently train a whole-body-control catching policy for this high-DoF system in simulation. The objects' throwing configurations, shapes, and sizes are randomized during training to enhance policy adaptivity to various trajectories and object characteristics in flight. The results show that our trained policy catches diverse objects with randomly thrown trajectories, at a high success rate of about 80\% in simulation, with a significant improvement over the baselines. The policy trained in simulation can be directly deployed in the real world with onboard sensing and computation, which achieves catching sandbags in various shapes, randomly thrown by humans. Our project page is available at https://mobile-dex-catch.github.io/.
Learning Visual Quadrupedal Loco-Manipulation from Demonstrations
Mar 29, 2024



Abstract:Quadruped robots are progressively being integrated into human environments. Despite the growing locomotion capabilities of quadrupedal robots, their interaction with objects in realistic scenes is still limited. While additional robotic arms on quadrupedal robots enable manipulating objects, they are sometimes redundant given that a quadruped robot is essentially a mobile unit equipped with four limbs, each possessing 3 degrees of freedom (DoFs). Hence, we aim to empower a quadruped robot to execute real-world manipulation tasks using only its legs. We decompose the loco-manipulation process into a low-level reinforcement learning (RL)-based controller and a high-level Behavior Cloning (BC)-based planner. By parameterizing the manipulation trajectory, we synchronize the efforts of the upper and lower layers, thereby leveraging the advantages of both RL and BC. Our approach is validated through simulations and real-world experiments, demonstrating the robot's ability to perform tasks that demand mobility and high precision, such as lifting a basket from the ground while moving, closing a dishwasher, pressing a button, and pushing a door. Project website: https://zhengmaohe.github.io/leg-manip
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge