Zi-ang Cao
CHIP: Adaptive Compliance for Humanoid Control through Hindsight Perturbation
Dec 16, 2025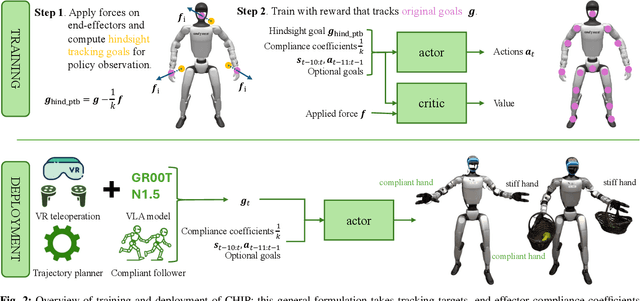
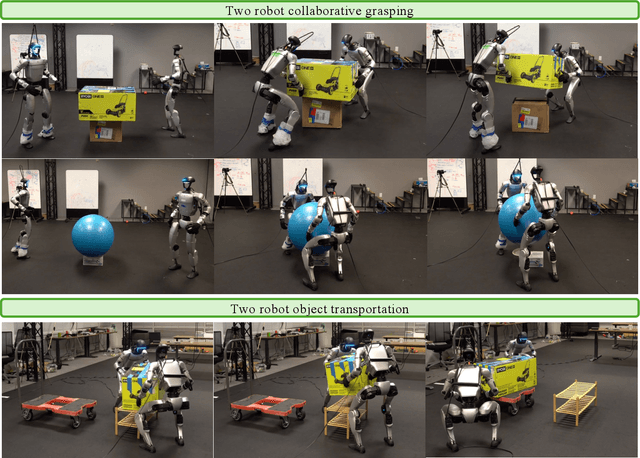
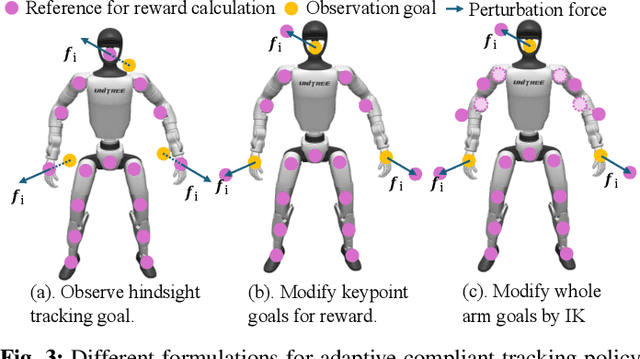
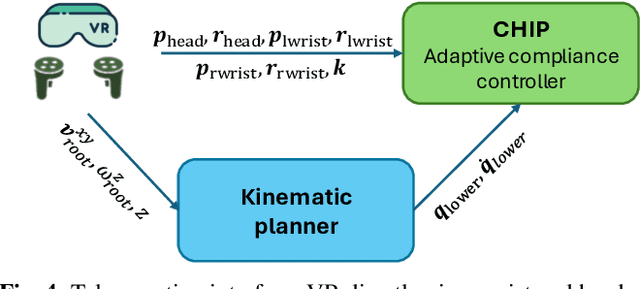

Abstract:Recent progress in humanoid robots has unlocked agile locomotion skills, including backflipping, running, and crawling. Yet it remains challenging for a humanoid robot to perform forceful manipulation tasks such as moving objects, wiping, and pushing a cart. We propose adaptive Compliance Humanoid control through hIsight Perturbation (CHIP), a plug-and-play module that enables controllable end-effector stiffness while preserving agile tracking of dynamic reference motions. CHIP is easy to implement and requires neither data augmentation nor additional reward tuning. We show that a generalist motion-tracking controller trained with CHIP can perform a diverse set of forceful manipulation tasks that require different end-effector compliance, such as multi-robot collaboration, wiping, box delivery, and door opening.
TWIST: Teleoperated Whole-Body Imitation System
May 05, 2025Abstract:Teleoperating humanoid robots in a whole-body manner marks a fundamental step toward developing general-purpose robotic intelligence, with human motion providing an ideal interface for controlling all degrees of freedom. Yet, most current humanoid teleoperation systems fall short of enabling coordinated whole-body behavior, typically limiting themselves to isolated locomotion or manipulation tasks. We present the Teleoperated Whole-Body Imitation System (TWIST), a system for humanoid teleoperation through whole-body motion imitation. We first generate reference motion clips by retargeting human motion capture data to the humanoid robot. We then develop a robust, adaptive, and responsive whole-body controller using a combination of reinforcement learning and behavior cloning (RL+BC). Through systematic analysis, we demonstrate how incorporating privileged future motion frames and real-world motion capture (MoCap) data improves tracking accuracy. TWIST enables real-world humanoid robots to achieve unprecedented, versatile, and coordinated whole-body motor skills--spanning whole-body manipulation, legged manipulation, locomotion, and expressive movement--using a single unified neural network controller. Our project website: https://humanoid-teleop.github.io
Unpacking Failure Modes of Generative Policies: Runtime Monitoring of Consistency and Progress
Oct 06, 2024
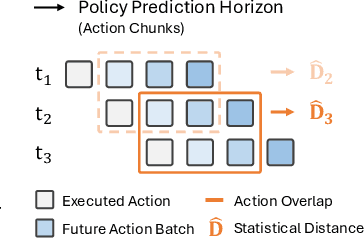

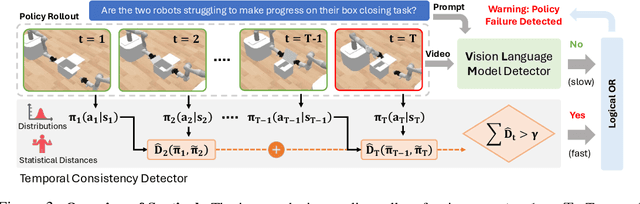
Abstract:Robot behavior policies trained via imitation learning are prone to failure under conditions that deviate from their training data. Thus, algorithms that monitor learned policies at test time and provide early warnings of failure are necessary to facilitate scalable deployment. We propose Sentinel, a runtime monitoring framework that splits the detection of failures into two complementary categories: 1) Erratic failures, which we detect using statistical measures of temporal action consistency, and 2) task progression failures, where we use Vision Language Models (VLMs) to detect when the policy confidently and consistently takes actions that do not solve the task. Our approach has two key strengths. First, because learned policies exhibit diverse failure modes, combining complementary detectors leads to significantly higher accuracy at failure detection. Second, using a statistical temporal action consistency measure ensures that we quickly detect when multimodal, generative policies exhibit erratic behavior at negligible computational cost. In contrast, we only use VLMs to detect failure modes that are less time-sensitive. We demonstrate our approach in the context of diffusion policies trained on robotic mobile manipulation domains in both simulation and the real world. By unifying temporal consistency detection and VLM runtime monitoring, Sentinel detects 18% more failures than using either of the two detectors alone and significantly outperforms baselines, thus highlighting the importance of assigning specialized detectors to complementary categories of failure. Qualitative results are made available at https://sites.google.com/stanford.edu/sentinel.
EquiBot: SIM(3)-Equivariant Diffusion Policy for Generalizable and Data Efficient Learning
Jul 01, 2024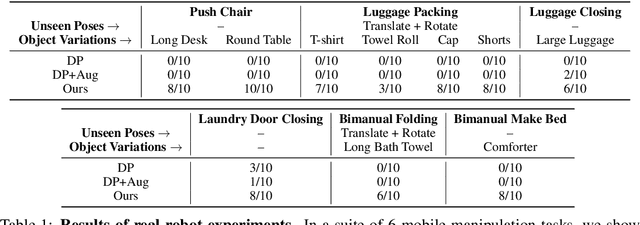
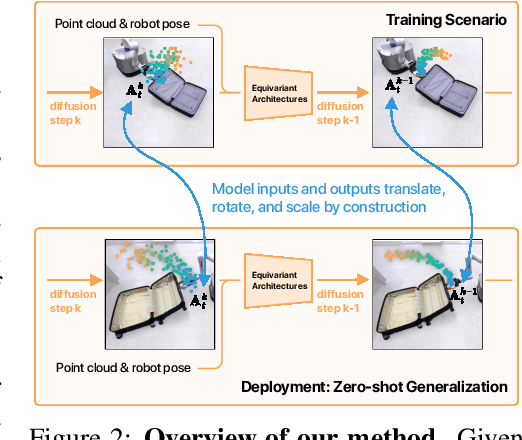
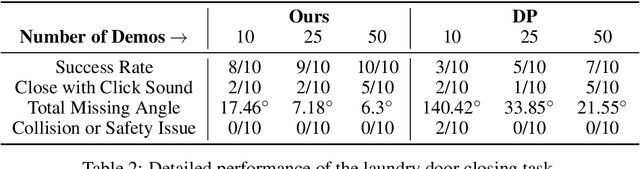

Abstract:Building effective imitation learning methods that enable robots to learn from limited data and still generalize across diverse real-world environments is a long-standing problem in robot learning. We propose EquiBot, a robust, data-efficient, and generalizable approach for robot manipulation task learning. Our approach combines SIM(3)-equivariant neural network architectures with diffusion models. This ensures that our learned policies are invariant to changes in scale, rotation, and translation, enhancing their applicability to unseen environments while retaining the benefits of diffusion-based policy learning such as multi-modality and robustness. We show in a suite of 6 simulation tasks that our proposed method reduces the data requirements and improves generalization to novel scenarios. In the real world, we show with in total 10 variations of 6 mobile manipulation tasks that our method can easily generalize to novel objects and scenes after learning from just 5 minutes of human demonstrations in each task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge