Marco Pavone
Sanford University and
Graph Neural Model Predictive Control for High-Dimensional Systems
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:The control of high-dimensional systems, such as soft robots, requires models that faithfully capture complex dynamics while remaining computationally tractable. This work presents a framework that integrates Graph Neural Network (GNN)-based dynamics models with structure-exploiting Model Predictive Control to enable real-time control of high-dimensional systems. By representing the system as a graph with localized interactions, the GNN preserves sparsity, while a tailored condensing algorithm eliminates state variables from the control problem, ensuring efficient computation. The complexity of our condensing algorithm scales linearly with the number of system nodes, and leverages Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) parallelization to achieve real-time performance. The proposed approach is validated in simulation and experimentally on a physical soft robotic trunk. Results show that our method scales to systems with up to 1,000 nodes at 100 Hz in closed-loop, and demonstrates real-time reference tracking on hardware with sub-centimeter accuracy, outperforming baselines by 63.6%. Finally, we show the capability of our method to achieve effective full-body obstacle avoidance.
Scaling Verification Can Be More Effective than Scaling Policy Learning for Vision-Language-Action Alignment
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:The long-standing vision of general-purpose robots hinges on their ability to understand and act upon natural language instructions. Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have made remarkable progress toward this goal, yet their generated actions can still misalign with the given instructions. In this paper, we investigate test-time verification as a means to shrink the "intention-action gap.'' We first characterize the test-time scaling law for embodied instruction following and demonstrate that jointly scaling the number of rephrased instructions and generated actions greatly increases test-time sample diversity, often recovering correct actions more efficiently than scaling each dimension independently. To capitalize on these scaling laws, we present CoVer, a contrastive verifier for vision-language-action alignment, and show that our architecture scales gracefully with additional computational resources and data. We then introduce "boot-time compute" and a hierarchical verification inference pipeline for VLAs. At deployment, our framework precomputes a diverse set of rephrased instructions from a Vision-Language-Model (VLM), repeatedly generates action candidates for each instruction, and then uses a verifier to select the optimal high-level prompt and low-level action chunks. Compared to scaling policy pre-training on the same data, our verification approach yields 22% gains in-distribution and 13% out-of-distribution on the SIMPLER benchmark, with a further 45% improvement in real-world experiments. On the PolaRiS benchmark, CoVer achieves 14% gains in task progress and 9% in success rate.
Self-Supervised Bootstrapping of Action-Predictive Embodied Reasoning
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Embodied Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning has significantly enhanced Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, yet current methods rely on rigid templates to specify reasoning primitives (e.g., objects in the scene, high-level plans, structural affordances). These templates can force policies to process irrelevant information that distracts from critical action-prediction signals. This creates a bottleneck: without successful policies, we cannot verify reasoning quality; without quality reasoning, we cannot build robust policies. We introduce R&B-EnCoRe, which enables models to bootstrap embodied reasoning from internet-scale knowledge through self-supervised refinement. By treating reasoning as a latent variable within importance-weighted variational inference, models can generate and distill a refined reasoning training dataset of embodiment-specific strategies without external rewards, verifiers, or human annotation. We validate R&B-EnCoRe across manipulation (Franka Panda in simulation, WidowX in hardware), legged navigation (bipedal, wheeled, bicycle, quadruped), and autonomous driving embodiments using various VLA architectures with 1B, 4B, 7B, and 30B parameters. Our approach achieves 28% gains in manipulation success, 101% improvement in navigation scores, and 21% reduction in collision-rate metric over models that indiscriminately reason about all available primitives. R&B-EnCoRe enables models to distill reasoning that is predictive of successful control, bypassing manual annotation engineering while grounding internet-scale knowledge in physical execution.
Accelerating Structured Chain-of-Thought in Autonomous Vehicles
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning enhances the decision-making capabilities of vision-language-action models in autonomous driving, but its autoregressive nature introduces significant inference latency, making it impractical for real-time applications. To address this, we introduce FastDriveCoT, a novel parallel decoding method that accelerates template-structured CoT. Our approach decomposes the reasoning process into a dependency graph of distinct sub-tasks, such as identifying critical objects and summarizing traffic rules, some of which can be generated in parallel. By generating multiple independent reasoning steps concurrently within a single forward pass, we significantly reduce the number of sequential computations. Experiments demonstrate a 3-4$\times$ speedup in CoT generation and a substantial reduction in end-to-end latency across various model architectures, all while preserving the original downstream task improvements brought by incorporating CoT reasoning.
Text-Guided Layer Fusion Mitigates Hallucination in Multimodal LLMs
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) typically rely on a single late-layer feature from a frozen vision encoder, leaving the encoder's rich hierarchy of visual cues under-utilized. MLLMs still suffer from visually ungrounded hallucinations, often relying on language priors rather than image evidence. While many prior mitigation strategies operate on the text side, they leave the visual representation unchanged and do not exploit the rich hierarchy of features encoded across vision layers. Existing multi-layer fusion methods partially address this limitation but remain static, applying the same layer mixture regardless of the query. In this work, we introduce TGIF (Text-Guided Inter-layer Fusion), a lightweight module that treats encoder layers as depth-wise "experts" and predicts a prompt-dependent fusion of visual features. TGIF follows the principle of direct external fusion, requires no vision-encoder updates, and adds minimal overhead. Integrated into LLaVA-1.5-7B, TGIF provides consistent improvements across hallucination, OCR, and VQA benchmarks, while preserving or improving performance on ScienceQA, GQA, and MMBench. These results suggest that query-conditioned, hierarchy-aware fusion is an effective way to strengthen visual grounding and reduce hallucination in modern MLLMs.
Counterfactual VLA: Self-Reflective Vision-Language-Action Model with Adaptive Reasoning
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Recent reasoning-augmented Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have improved the interpretability of end-to-end autonomous driving by generating intermediate reasoning traces. Yet these models primarily describe what they perceive and intend to do, rarely questioning whether their planned actions are safe or appropriate. This work introduces Counterfactual VLA (CF-VLA), a self-reflective VLA framework that enables the model to reason about and revise its planned actions before execution. CF-VLA first generates time-segmented meta-actions that summarize driving intent, and then performs counterfactual reasoning conditioned on both the meta-actions and the visual context. This step simulates potential outcomes, identifies unsafe behaviors, and outputs corrected meta-actions that guide the final trajectory generation. To efficiently obtain such self-reflective capabilities, we propose a rollout-filter-label pipeline that mines high-value scenes from a base (non-counterfactual) VLA's rollouts and labels counterfactual reasoning traces for subsequent training rounds. Experiments on large-scale driving datasets show that CF-VLA improves trajectory accuracy by up to 17.6%, enhances safety metrics by 20.5%, and exhibits adaptive thinking: it only enables counterfactual reasoning in challenging scenarios. By transforming reasoning traces from one-shot descriptions to causal self-correction signals, CF-VLA takes a step toward self-reflective autonomous driving agents that learn to think before they act.
Towards Efficient and Effective Multi-Camera Encoding for End-to-End Driving
Dec 12, 2025Abstract:We present Flex, an efficient and effective scene encoder that addresses the computational bottleneck of processing high-volume multi-camera data in end-to-end autonomous driving. Flex employs a small set of learnable scene tokens to jointly encode information from all image tokens across different cameras and timesteps. By design, our approach is geometry-agnostic, learning a compact scene representation directly from data without relying on the explicit 3D inductive biases, such as Bird-Eye-View (BEV), occupancy or tri-plane representations, which are common in prior work. This holistic encoding strategy aggressively compresses the visual input for the downstream Large Language Model (LLM) based policy model. Evaluated on a large-scale proprietary dataset of 20,000 driving hours, our Flex achieves 2.2x greater inference throughput while improving driving performance by a large margin compared to state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, we show that these compact scene tokens develop an emergent capability for scene decomposition without any explicit supervision. Our findings challenge the prevailing assumption that 3D priors are necessary, demonstrating that a data-driven, joint encoding strategy offers a more scalable, efficient and effective path for future autonomous driving systems.
Latent Chain-of-Thought World Modeling for End-to-End Driving
Dec 11, 2025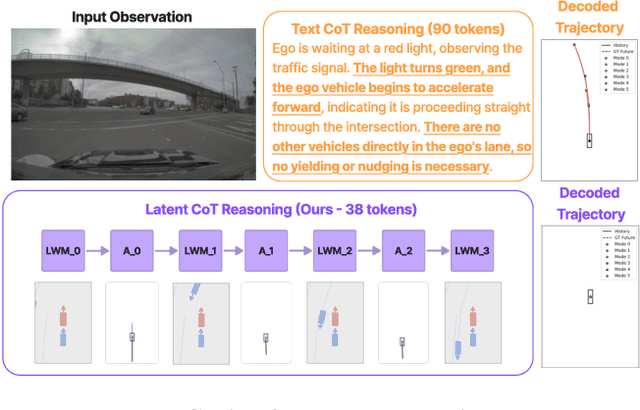
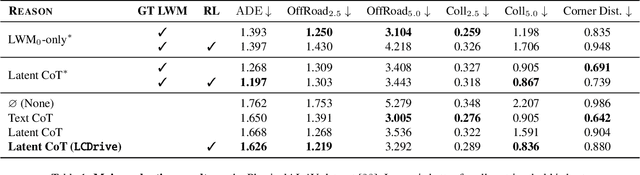
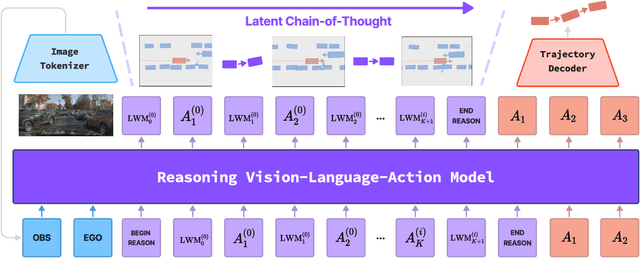
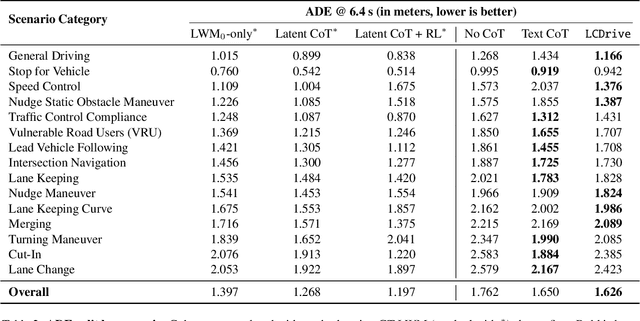
Abstract:Recent Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models for autonomous driving explore inference-time reasoning as a way to improve driving performance and safety in challenging scenarios. Most prior work uses natural language to express chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning before producing driving actions. However, text may not be the most efficient representation for reasoning. In this work, we present Latent-CoT-Drive (LCDrive): a model that expresses CoT in a latent language that captures possible outcomes of the driving actions being considered. Our approach unifies CoT reasoning and decision making by representing both in an action-aligned latent space. Instead of natural language, the model reasons by interleaving (1) action-proposal tokens, which use the same vocabulary as the model's output actions; and (2) world model tokens, which are grounded in a learned latent world model and express future outcomes of these actions. We cold start latent CoT by supervising the model's action proposals and world model tokens based on ground-truth future rollouts of the scene. We then post-train with closed-loop reinforcement learning to strengthen reasoning capabilities. On a large-scale end-to-end driving benchmark, LCDrive achieves faster inference, better trajectory quality, and larger improvements from interactive reinforcement learning compared to both non-reasoning and text-reasoning baselines.
FoundationMotion: Auto-Labeling and Reasoning about Spatial Movement in Videos
Dec 11, 2025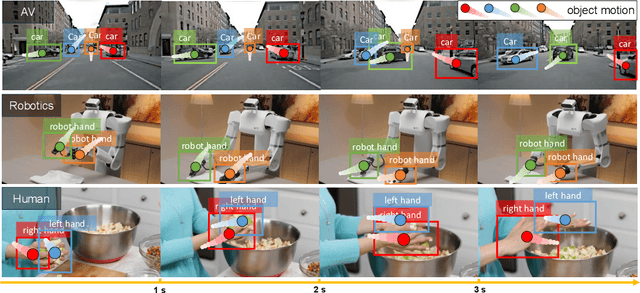
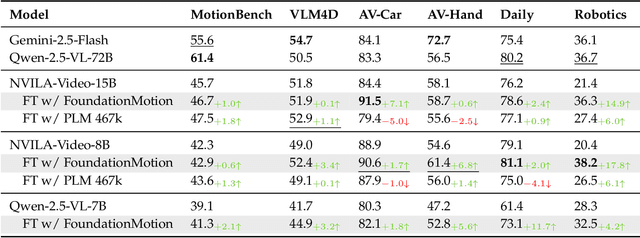
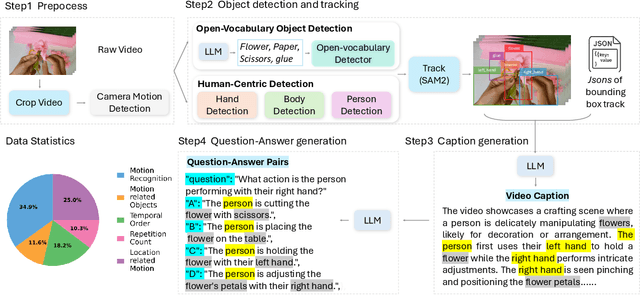
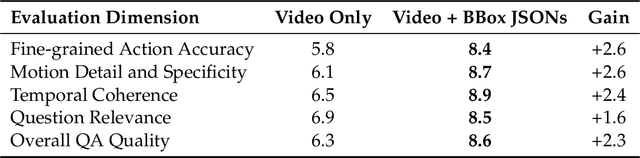
Abstract:Motion understanding is fundamental to physical reasoning, enabling models to infer dynamics and predict future states. However, state-of-the-art models still struggle on recent motion benchmarks, primarily due to the scarcity of large-scale, fine-grained motion datasets. Existing motion datasets are often constructed from costly manual annotation, severely limiting scalability. To address this challenge, we introduce FoundationMotion, a fully automated data curation pipeline that constructs large-scale motion datasets. Our approach first detects and tracks objects in videos to extract their trajectories, then leverages these trajectories and video frames with Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate fine-grained captions and diverse question-answer pairs about motion and spatial reasoning. Using datasets produced by this pipeline, we fine-tune open-source models including NVILA-Video-15B and Qwen2.5-7B, achieving substantial improvements in motion understanding without compromising performance on other tasks. Notably, our models outperform strong closed-source baselines like Gemini-2.5 Flash and large open-source models such as Qwen2.5-VL-72B across diverse motion understanding datasets and benchmarks. FoundationMotion thus provides a scalable solution for curating fine-grained motion datasets that enable effective fine-tuning of diverse models to enhance motion understanding and spatial reasoning capabilities.
Semantic Trajectory Generation for Goal-Oriented Spacecraft Rendezvous
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Reliable real-time trajectory generation is essential for future autonomous spacecraft. While recent progress in nonconvex guidance and control is paving the way for onboard autonomous trajectory optimization, these methods still rely on extensive expert input (e.g., waypoints, constraints, mission timelines, etc.), which limits the operational scalability in real rendezvous missions. This paper introduces SAGES (Semantic Autonomous Guidance Engine for Space), a trajectory-generation framework that translates natural-language commands into spacecraft trajectories that reflect high-level intent while respecting nonconvex constraints. Experiments in two settings -- fault-tolerant proximity operations with continuous-time constraint enforcement and a free-flying robotic platform -- demonstrate that SAGES reliably produces trajectories aligned with human commands, achieving over 90% semantic-behavioral consistency across diverse behavior modes. Ultimately, this work marks an initial step toward language-conditioned, constraint-aware spacecraft trajectory generation, enabling operators to interactively guide both safety and behavior through intuitive natural-language commands with reduced expert burden.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge