Yu-Chiang Frank Wang
MV-SAM: Multi-view Promptable Segmentation using Pointmap Guidance
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Promptable segmentation has emerged as a powerful paradigm in computer vision, enabling users to guide models in parsing complex scenes with prompts such as clicks, boxes, or textual cues. Recent advances, exemplified by the Segment Anything Model (SAM), have extended this paradigm to videos and multi-view images. However, the lack of 3D awareness often leads to inconsistent results, necessitating costly per-scene optimization to enforce 3D consistency. In this work, we introduce MV-SAM, a framework for multi-view segmentation that achieves 3D consistency using pointmaps -- 3D points reconstructed from unposed images by recent visual geometry models. Leveraging the pixel-point one-to-one correspondence of pointmaps, MV-SAM lifts images and prompts into 3D space, eliminating the need for explicit 3D networks or annotated 3D data. Specifically, MV-SAM extends SAM by lifting image embeddings from its pretrained encoder into 3D point embeddings, which are decoded by a transformer using cross-attention with 3D prompt embeddings. This design aligns 2D interactions with 3D geometry, enabling the model to implicitly learn consistent masks across views through 3D positional embeddings. Trained on the SA-1B dataset, our method generalizes well across domains, outperforming SAM2-Video and achieving comparable performance with per-scene optimization baselines on NVOS, SPIn-NeRF, ScanNet++, uCo3D, and DL3DV benchmarks. Code will be released.
Advancing Structured Priors for Sparse-Voxel Surface Reconstruction
Jan 25, 2026Abstract:Reconstructing accurate surfaces with radiance fields has progressed rapidly, yet two promising explicit representations, 3D Gaussian Splatting and sparse-voxel rasterization, exhibit complementary strengths and weaknesses. 3D Gaussian Splatting converges quickly and carries useful geometric priors, but surface fidelity is limited by its point-like parameterization. Sparse-voxel rasterization provides continuous opacity fields and crisp geometry, but its typical uniform dense-grid initialization slows convergence and underutilizes scene structure. We combine the advantages of both by introducing a voxel initialization method that places voxels at plausible locations and with appropriate levels of detail, yielding a strong starting point for per-scene optimization. To further enhance depth consistency without blurring edges, we propose refined depth geometry supervision that converts multi-view cues into direct per-ray depth regularization. Experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate improvements over prior methods in geometric accuracy, better fine-structure recovery, and more complete surfaces, while maintaining fast convergence.
GaussExplorer: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Embodied Exploration and Reasoning
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:We present GaussExplorer, a framework for embodied exploration and reasoning built on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). While prior approaches to language-embedded 3DGS have made meaningful progress in aligning simple text queries with Gaussian embeddings, they are generally optimized for relatively simple queries and struggle to interpret more complex, compositional language queries. Alternative studies based on object-centric RGB-D structured memories provide spatial grounding but are constrained by pre-fixed viewpoints. To address these issues, GaussExplorer introduces Vision-Language Models (VLMs) on top of 3DGS to enable question-driven exploration and reasoning within 3D scenes. We first identify pre-captured images that are most correlated with the query question, and subsequently adjust them into novel viewpoints to more accurately capture visual information for better reasoning by VLMs. Experiments show that ours outperforms existing methods on several benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of integrating VLM-based reasoning with 3DGS for embodied tasks.
Speech-Hands: A Self-Reflection Voice Agentic Approach to Speech Recognition and Audio Reasoning with Omni Perception
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We introduce a voice-agentic framework that learns one critical omni-understanding skill: knowing when to trust itself versus when to consult external audio perception. Our work is motivated by a crucial yet counterintuitive finding: naively fine-tuning an omni-model on both speech recognition and external sound understanding tasks often degrades performance, as the model can be easily misled by noisy hypotheses. To address this, our framework, Speech-Hands, recasts the problem as an explicit self-reflection decision. This learnable reflection primitive proves effective in preventing the model from being derailed by flawed external candidates. We show that this agentic action mechanism generalizes naturally from speech recognition to complex, multiple-choice audio reasoning. Across the OpenASR leaderboard, Speech-Hands consistently outperforms strong baselines by 12.1% WER on seven benchmarks. The model also achieves 77.37% accuracy and high F1 on audio QA decisions, showing robust generalization and reliability across diverse audio question answering datasets. By unifying perception and decision-making, our work offers a practical path toward more reliable and resilient audio intelligence.
OpenVoxel: Training-Free Grouping and Captioning Voxels for Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Understanding
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:We propose OpenVoxel, a training-free algorithm for grouping and captioning sparse voxels for the open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding tasks. Given the sparse voxel rasterization (SVR) model obtained from multi-view images of a 3D scene, our OpenVoxel is able to produce meaningful groups that describe different objects in the scene. Also, by leveraging powerful Vision Language Models (VLMs) and Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), our OpenVoxel successfully build an informative scene map by captioning each group, enabling further 3D scene understanding tasks such as open-vocabulary segmentation (OVS) or referring expression segmentation (RES). Unlike previous methods, our method is training-free and does not introduce embeddings from a CLIP/BERT text encoder. Instead, we directly proceed with text-to-text search using MLLMs. Through extensive experiments, our method demonstrates superior performance compared to recent studies, particularly in complex referring expression segmentation (RES) tasks. The code will be open.
Fast-ThinkAct: Efficient Vision-Language-Action Reasoning via Verbalizable Latent Planning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) tasks require reasoning over complex visual scenes and executing adaptive actions in dynamic environments. While recent studies on reasoning VLAs show that explicit chain-of-thought (CoT) can improve generalization, they suffer from high inference latency due to lengthy reasoning traces. We propose Fast-ThinkAct, an efficient reasoning framework that achieves compact yet performant planning through verbalizable latent reasoning. Fast-ThinkAct learns to reason efficiently with latent CoTs by distilling from a teacher, driven by a preference-guided objective to align manipulation trajectories that transfers both linguistic and visual planning capabilities for embodied control. This enables reasoning-enhanced policy learning that effectively connects compact reasoning to action execution. Extensive experiments across diverse embodied manipulation and reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that Fast-ThinkAct achieves strong performance with up to 89.3\% reduced inference latency over state-of-the-art reasoning VLAs, while maintaining effective long-horizon planning, few-shot adaptation, and failure recovery.
TA-Prompting: Enhancing Video Large Language Models for Dense Video Captioning via Temporal Anchors
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Dense video captioning aims to interpret and describe all temporally localized events throughout an input video. Recent state-of-the-art methods leverage large language models (LLMs) to provide detailed moment descriptions for video data. However, existing VideoLLMs remain challenging in identifying precise event boundaries in untrimmed videos, causing the generated captions to be not properly grounded. In this paper, we propose TA-Prompting, which enhances VideoLLMs via Temporal Anchors that learn to precisely localize events and prompt the VideoLLMs to perform temporal-aware video event understanding. During inference, in order to properly determine the output caption sequence from an arbitrary number of events presented within a video, we introduce an event coherent sampling strategy to select event captions with sufficient coherence across temporal events and cross-modal similarity with the given video. Through extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, we show that our TA-Prompting is favorable against state-of-the-art VideoLLMs, yielding superior performance on dense video captioning and temporal understanding tasks including moment retrieval and temporalQA.
* 8 pages for main paper (exclude citation pages), 6 pages for appendix, totally 10 figures 7 tables and 2 algorithms. The paper is accepted by WACV 2026
Masking Teacher and Reinforcing Student for Distilling Vision-Language Models
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Large-scale vision-language models (VLMs) have recently achieved remarkable multimodal understanding, but their massive size makes them impractical for deployment on mobile or edge devices. This raises the need for compact yet capable VLMs that can efficiently learn from powerful large teachers. However, distilling knowledge from a large teacher to a small student remains challenging due to their large size gap: the student often fails to reproduce the teacher's complex, high-dimensional representations, leading to unstable learning and degraded performance. To address this, we propose Masters (Masking Teacher and Reinforcing Student), a mask-progressive reinforcement learning (RL) distillation framework. Masters first masks non-dominant weights of the teacher to reduce unnecessary complexity, then progressively restores the teacher by gradually increasing its capacity during training. This strategy allows the student to learn richer representations from the teacher in a smooth and stable manner. To further refine knowledge transfer, Masters integrates an offline RL stage with two complementary rewards: an accuracy reward that measures the correctness of the generated responses, and a distillation reward that quantifies the ease of transferring responses from teacher to student. Unlike online think-answer RL paradigms that are computationally expensive and generate lengthy responses, our offline RL leverages pre-generated responses from masked teachers. These provide rich yet efficient guidance, enabling students to achieve strong performance without requiring the think-answer process.
4D-RGPT: Toward Region-level 4D Understanding via Perceptual Distillation
Dec 22, 2025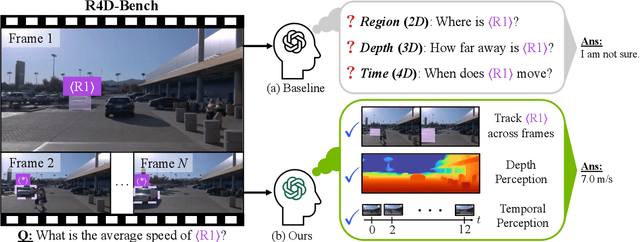
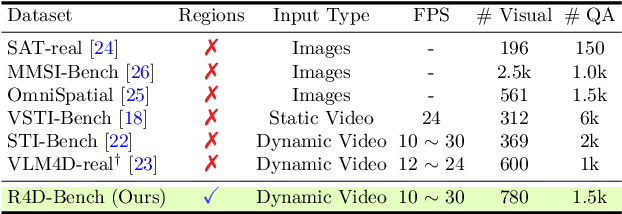
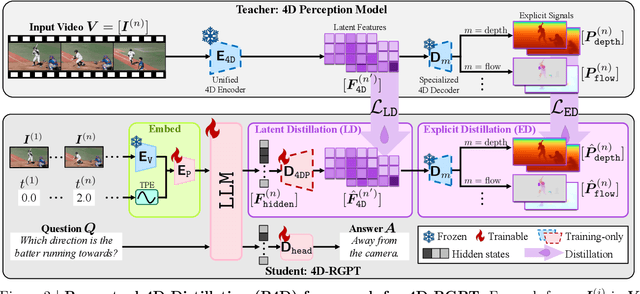
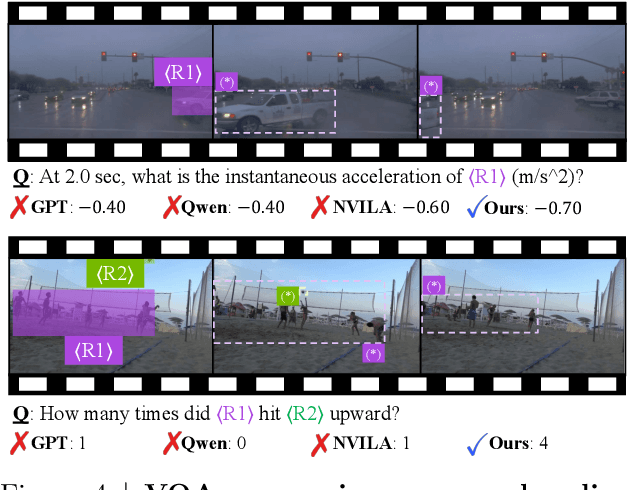
Abstract:Despite advances in Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), their ability to reason over 3D structures and temporal dynamics remains limited, constrained by weak 4D perception and temporal understanding. Existing 3D and 4D Video Question Answering (VQA) benchmarks also emphasize static scenes and lack region-level prompting. We tackle these issues by introducing: (a) 4D-RGPT, a specialized MLLM designed to capture 4D representations from video inputs with enhanced temporal perception; (b) Perceptual 4D Distillation (P4D), a training framework that transfers 4D representations from a frozen expert model into 4D-RGPT for comprehensive 4D perception; and (c) R4D-Bench, a benchmark for depth-aware dynamic scenes with region-level prompting, built via a hybrid automated and human-verified pipeline. Our 4D-RGPT achieves notable improvements on both existing 4D VQA benchmarks and the proposed R4D-Bench benchmark.
Zoom-Zero: Reinforced Coarse-to-Fine Video Understanding via Temporal Zoom-in
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Grounded video question answering (GVQA) aims to localize relevant temporal segments in videos and generate accurate answers to a given question; however, large video-language models (LVLMs) exhibit limited temporal awareness. Although existing approaches based on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) attempt to improve temporal grounding, they still struggle to faithfully ground their answers in the relevant video evidence, leading to temporal mislocalization and hallucinations. In this work, we present Zoom-Zero, a coarse-to-fine framework that first localizes query-relevant segments and then temporally zooms into the most salient frames for finer-grained visual verification. Our method addresses the limits of GRPO for the GVQA task with two key innovations: (i) a zoom-in accuracy reward that validates the fidelity of temporal grounding prediction and facilitates fine-grained visual verification on grounded frames; (ii) token-selective credit assignment, which attributes rewards to the tokens responsible for temporal localization or answer generation, mitigating GRPO's issue in handling multi-faceted reward signals. Our proposed method advances grounded video question answering, improving temporal grounding by 5.2\% on NExT-GQA and 4.6\% on ReXTime, while also enhancing average answer accuracy by 2.4\%. Additionally, the coarse-to-fine zoom-in during inference further benefits long-form video understanding by preserving critical visual details without compromising global context, yielding an average improvement of 6.4\% on long-video benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge