Seon Joo Kim
Global Geometry Is Not Enough for Vision Representations
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:A common assumption in representation learning is that globally well-distributed embeddings support robust and generalizable representations. This focus has shaped both training objectives and evaluation protocols, implicitly treating global geometry as a proxy for representational competence. While global geometry effectively encodes which elements are present, it is often insensitive to how they are composed. We investigate this limitation by testing the ability of geometric metrics to predict compositional binding across 21 vision encoders. We find that standard geometry-based statistics exhibit near-zero correlation with compositional binding. In contrast, functional sensitivity, as measured by the input-output Jacobian, reliably tracks this capability. We further provide an analytic account showing that this disparity arises from objective design, as existing losses explicitly constrain embedding geometry but leave the local input-output mapping unconstrained. These results suggest that global embedding geometry captures only a partial view of representational competence and establish functional sensitivity as a critical complementary axis for modeling composite structure.
Seam360GS: Seamless 360° Gaussian Splatting from Real-World Omnidirectional Images
Aug 27, 2025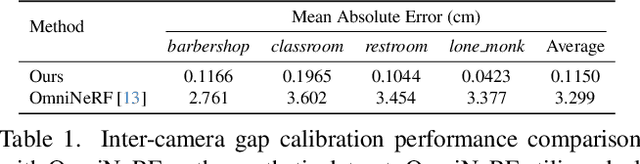
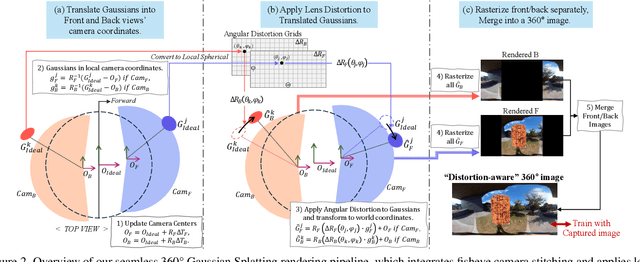
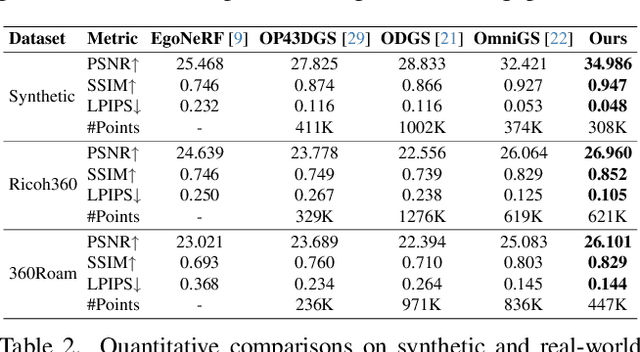

Abstract:360-degree visual content is widely shared on platforms such as YouTube and plays a central role in virtual reality, robotics, and autonomous navigation. However, consumer-grade dual-fisheye systems consistently yield imperfect panoramas due to inherent lens separation and angular distortions. In this work, we introduce a novel calibration framework that incorporates a dual-fisheye camera model into the 3D Gaussian splatting pipeline. Our approach not only simulates the realistic visual artifacts produced by dual-fisheye cameras but also enables the synthesis of seamlessly rendered 360-degree images. By jointly optimizing 3D Gaussian parameters alongside calibration variables that emulate lens gaps and angular distortions, our framework transforms imperfect omnidirectional inputs into flawless novel view synthesis. Extensive evaluations on real-world datasets confirm that our method produces seamless renderings-even from imperfect images-and outperforms existing 360-degree rendering models.
Autoregressive Universal Video Segmentation Model
Aug 26, 2025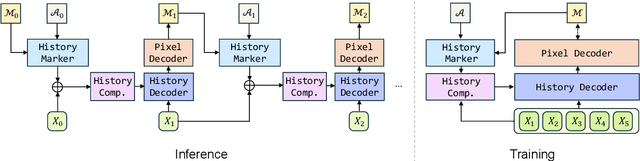
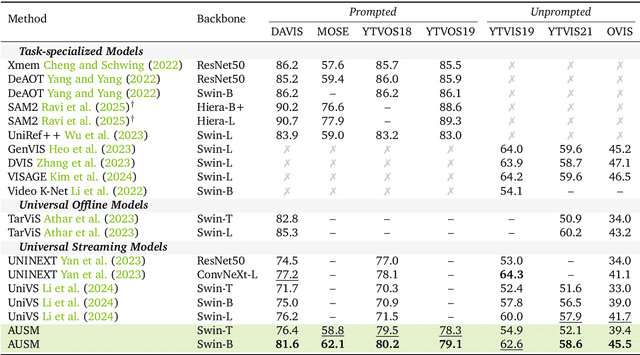
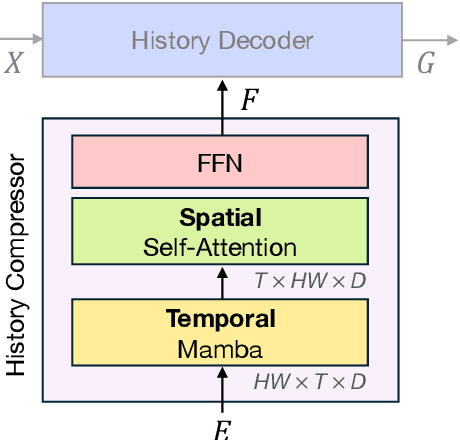

Abstract:Recent video foundation models such as SAM2 excel at prompted video segmentation by treating masks as a general-purpose primitive. However, many real-world settings require unprompted segmentation that aims to detect and track all objects in a video without external cues, leaving today's landscape fragmented across task-specific models and pipelines. We recast streaming video segmentation as sequential mask prediction, analogous to language modeling, and introduce the Autoregressive Universal Segmentation Model (AUSM), a single architecture that unifies both prompted and unprompted video segmentation. Built on recent state-space models, AUSM maintains a fixed-size spatial state and scales to video streams of arbitrary length. Furthermore, all components of AUSM are designed for parallel training across frames, yielding substantial speedups over iterative training. On standard benchmarks (DAVIS17, YouTube-VOS 2018 & 2019, MOSE, YouTube-VIS 2019 & 2021, and OVIS) AUSM outperforms prior universal streaming video segmentation methods and achieves up to 2.5x faster training on 16-frame sequences.
Unsupervised Monocular 3D Keypoint Discovery from Multi-View Diffusion Priors
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces KeyDiff3D, a framework for unsupervised monocular 3D keypoints estimation that accurately predicts 3D keypoints from a single image. While previous methods rely on manual annotations or calibrated multi-view images, both of which are expensive to collect, our method enables monocular 3D keypoints estimation using only a collection of single-view images. To achieve this, we leverage powerful geometric priors embedded in a pretrained multi-view diffusion model. In our framework, this model generates multi-view images from a single image, serving as a supervision signal to provide 3D geometric cues to our model. We also use the diffusion model as a powerful 2D multi-view feature extractor and construct 3D feature volumes from its intermediate representations. This transforms implicit 3D priors learned by the diffusion model into explicit 3D features. Beyond accurate keypoints estimation, we further introduce a pipeline that enables manipulation of 3D objects generated by the diffusion model. Experimental results on diverse aspects and datasets, including Human3.6M, Stanford Dogs, and several in-the-wild and out-of-domain datasets, highlight the effectiveness of our method in terms of accuracy, generalization, and its ability to enable manipulation of 3D objects generated by the diffusion model from a single image.
Multi-Granular Spatio-Temporal Token Merging for Training-Free Acceleration of Video LLMs
Jul 10, 2025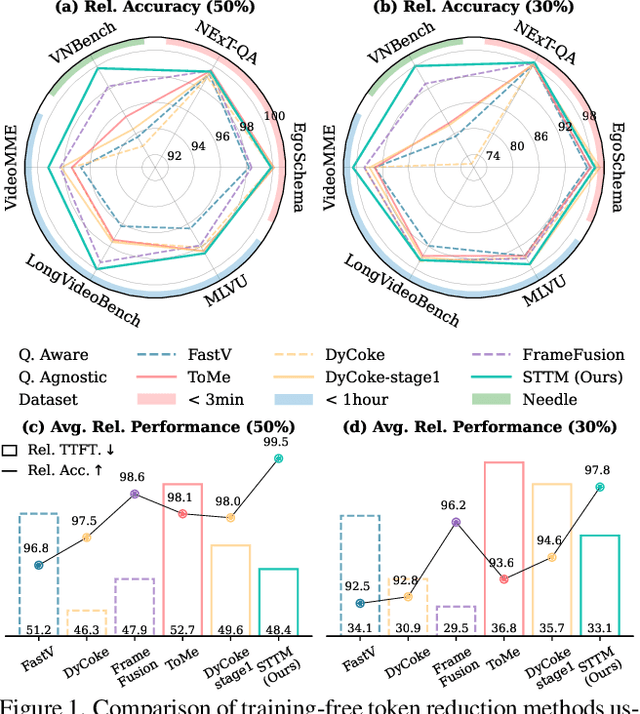

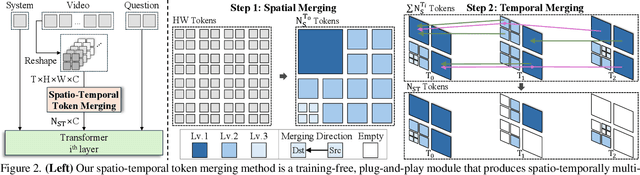

Abstract:Video large language models (LLMs) achieve strong video understanding by leveraging a large number of spatio-temporal tokens, but suffer from quadratic computational scaling with token count. To address this, we propose a training-free spatio-temporal token merging method, named STTM. Our key insight is to exploit local spatial and temporal redundancy in video data which has been overlooked in prior work. STTM first transforms each frame into multi-granular spatial tokens using a coarse-to-fine search over a quadtree structure, then performs directed pairwise merging across the temporal dimension. This decomposed merging approach outperforms existing token reduction methods across six video QA benchmarks. Notably, STTM achieves a 2$\times$ speed-up with only a 0.5% accuracy drop under a 50% token budget, and a 3$\times$ speed-up with just a 2% drop under a 30% budget. Moreover, STTM is query-agnostic, allowing KV cache reuse across different questions for the same video. The project page is available at https://www.jshyun.me/projects/sttm.
ORIDa: Object-centric Real-world Image Composition Dataset
Jun 10, 2025
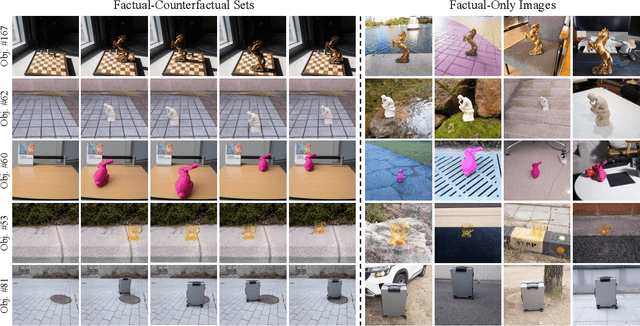
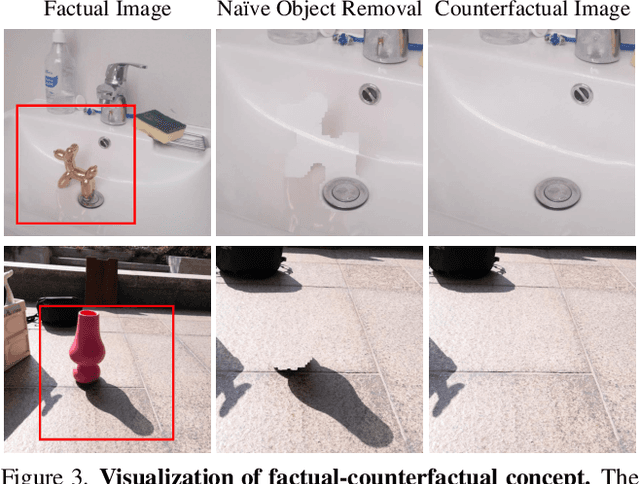

Abstract:Object compositing, the task of placing and harmonizing objects in images of diverse visual scenes, has become an important task in computer vision with the rise of generative models. However, existing datasets lack the diversity and scale required to comprehensively explore real-world scenarios. We introduce ORIDa (Object-centric Real-world Image Composition Dataset), a large-scale, real-captured dataset containing over 30,000 images featuring 200 unique objects, each of which is presented across varied positions and scenes. ORIDa has two types of data: factual-counterfactual sets and factual-only scenes. The factual-counterfactual sets consist of four factual images showing an object in different positions within a scene and a single counterfactual (or background) image of the scene without the object, resulting in five images per scene. The factual-only scenes include a single image containing an object in a specific context, expanding the variety of environments. To our knowledge, ORIDa is the first publicly available dataset with its scale and complexity for real-world image composition. Extensive analysis and experiments highlight the value of ORIDa as a resource for advancing further research in object compositing.
Bayesian Neural Scaling Laws Extrapolation with Prior-Fitted Networks
May 29, 2025



Abstract:Scaling has been a major driver of recent advancements in deep learning. Numerous empirical studies have found that scaling laws often follow the power-law and proposed several variants of power-law functions to predict the scaling behavior at larger scales. However, existing methods mostly rely on point estimation and do not quantify uncertainty, which is crucial for real-world applications involving decision-making problems such as determining the expected performance improvements achievable by investing additional computational resources. In this work, we explore a Bayesian framework based on Prior-data Fitted Networks (PFNs) for neural scaling law extrapolation. Specifically, we design a prior distribution that enables the sampling of infinitely many synthetic functions resembling real-world neural scaling laws, allowing our PFN to meta-learn the extrapolation. We validate the effectiveness of our approach on real-world neural scaling laws, comparing it against both the existing point estimation methods and Bayesian approaches. Our method demonstrates superior performance, particularly in data-limited scenarios such as Bayesian active learning, underscoring its potential for reliable, uncertainty-aware extrapolation in practical applications.
UniSkill: Imitating Human Videos via Cross-Embodiment Skill Representations
May 15, 2025Abstract:Mimicry is a fundamental learning mechanism in humans, enabling individuals to learn new tasks by observing and imitating experts. However, applying this ability to robots presents significant challenges due to the inherent differences between human and robot embodiments in both their visual appearance and physical capabilities. While previous methods bridge this gap using cross-embodiment datasets with shared scenes and tasks, collecting such aligned data between humans and robots at scale is not trivial. In this paper, we propose UniSkill, a novel framework that learns embodiment-agnostic skill representations from large-scale cross-embodiment video data without any labels, enabling skills extracted from human video prompts to effectively transfer to robot policies trained only on robot data. Our experiments in both simulation and real-world environments show that our cross-embodiment skills successfully guide robots in selecting appropriate actions, even with unseen video prompts. The project website can be found at: https://kimhanjung.github.io/UniSkill.
CCMNet: Leveraging Calibrated Color Correction Matrices for Cross-Camera Color Constancy
Apr 10, 2025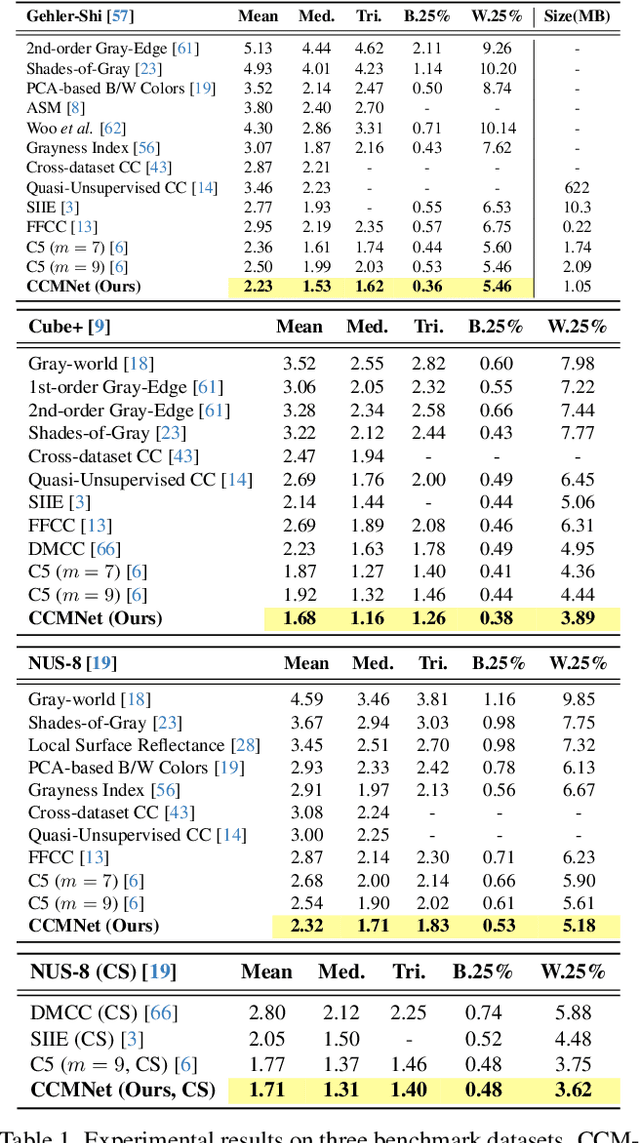
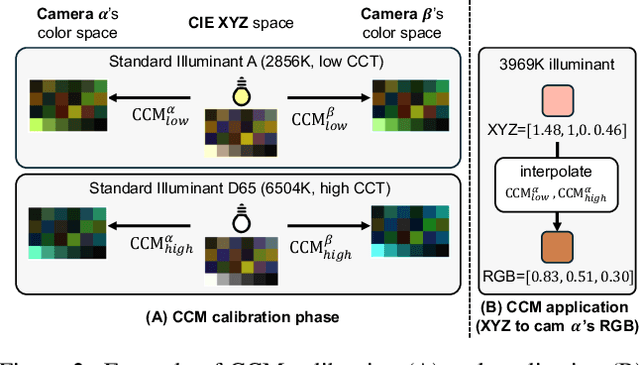
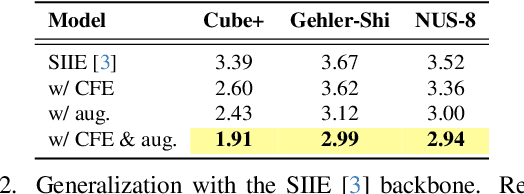
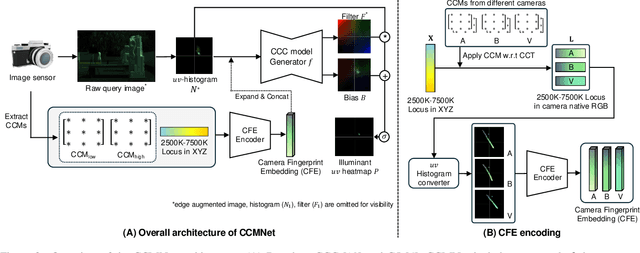
Abstract:Computational color constancy, or white balancing, is a key module in a camera's image signal processor (ISP) that corrects color casts from scene lighting. Because this operation occurs in the camera-specific raw color space, white balance algorithms must adapt to different cameras. This paper introduces a learning-based method for cross-camera color constancy that generalizes to new cameras without retraining. Our method leverages pre-calibrated color correction matrices (CCMs) available on ISPs that map the camera's raw color space to a standard space (e.g., CIE XYZ). Our method uses these CCMs to transform predefined illumination colors (i.e., along the Planckian locus) into the test camera's raw space. The mapped illuminants are encoded into a compact camera fingerprint embedding (CFE) that enables the network to adapt to unseen cameras. To prevent overfitting due to limited cameras and CCMs during training, we introduce a data augmentation technique that interpolates between cameras and their CCMs. Experimental results across multiple datasets and backbones show that our method achieves state-of-the-art cross-camera color constancy while remaining lightweight and relying only on data readily available in camera ISPs.
Representing 3D Shapes With 64 Latent Vectors for 3D Diffusion Models
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Constructing a compressed latent space through a variational autoencoder (VAE) is the key for efficient 3D diffusion models. This paper introduces COD-VAE, a VAE that encodes 3D shapes into a COmpact set of 1D latent vectors without sacrificing quality. COD-VAE introduces a two-stage autoencoder scheme to improve compression and decoding efficiency. First, our encoder block progressively compresses point clouds into compact latent vectors via intermediate point patches. Second, our triplane-based decoder reconstructs dense triplanes from latent vectors instead of directly decoding neural fields, significantly reducing computational overhead of neural fields decoding. Finally, we propose uncertainty-guided token pruning, which allocates resources adaptively by skipping computations in simpler regions and improves the decoder efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that COD-VAE achieves 16x compression compared to the baseline while maintaining quality. This enables 20.8x speedup in generation, highlighting that a large number of latent vectors is not a prerequisite for high-quality reconstruction and generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge