Woong Oh Cho
Seam360GS: Seamless 360° Gaussian Splatting from Real-World Omnidirectional Images
Aug 27, 2025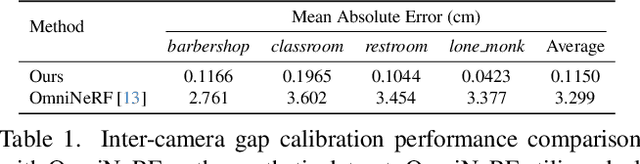
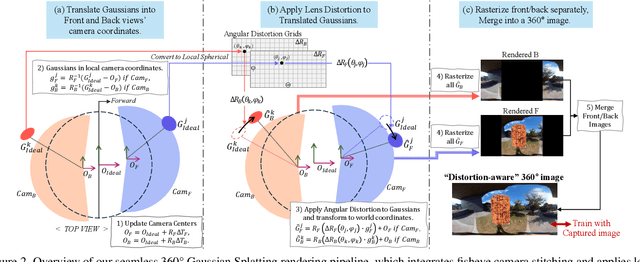
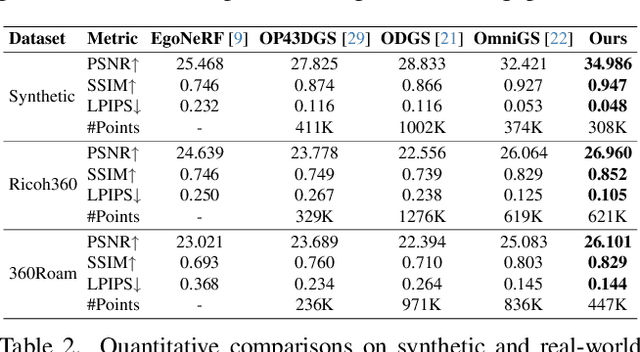

Abstract:360-degree visual content is widely shared on platforms such as YouTube and plays a central role in virtual reality, robotics, and autonomous navigation. However, consumer-grade dual-fisheye systems consistently yield imperfect panoramas due to inherent lens separation and angular distortions. In this work, we introduce a novel calibration framework that incorporates a dual-fisheye camera model into the 3D Gaussian splatting pipeline. Our approach not only simulates the realistic visual artifacts produced by dual-fisheye cameras but also enables the synthesis of seamlessly rendered 360-degree images. By jointly optimizing 3D Gaussian parameters alongside calibration variables that emulate lens gaps and angular distortions, our framework transforms imperfect omnidirectional inputs into flawless novel view synthesis. Extensive evaluations on real-world datasets confirm that our method produces seamless renderings-even from imperfect images-and outperforms existing 360-degree rendering models.
4D Scaffold Gaussian Splatting for Memory Efficient Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Nov 26, 2024



Abstract:Existing 4D Gaussian methods for dynamic scene reconstruction offer high visual fidelity and fast rendering. However, these methods suffer from excessive memory and storage demands, which limits their practical deployment. This paper proposes a 4D anchor-based framework that retains visual quality and rendering speed of 4D Gaussians while significantly reducing storage costs. Our method extends 3D scaffolding to 4D space, and leverages sparse 4D grid-aligned anchors with compressed feature vectors. Each anchor models a set of neural 4D Gaussians, each of which represent a local spatiotemporal region. In addition, we introduce a temporal coverage-aware anchor growing strategy to effectively assign additional anchors to under-reconstructed dynamic regions. Our method adjusts the accumulated gradients based on Gaussians' temporal coverage, improving reconstruction quality in dynamic regions. To reduce the number of anchors, we further present enhanced formulations of neural 4D Gaussians. These include the neural velocity, and the temporal opacity derived from a generalized Gaussian distribution. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art visual quality and 97.8% storage reduction over 4DGS.
Hierarchically Structured Neural Bones for Reconstructing Animatable Objects from Casual Videos
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:We propose a new framework for creating and easily manipulating 3D models of arbitrary objects using casually captured videos. Our core ingredient is a novel hierarchy deformation model, which captures motions of objects with a tree-structured bones. Our hierarchy system decomposes motions based on the granularity and reveals the correlations between parts without exploiting any prior structural knowledge. We further propose to regularize the bones to be positioned at the basis of motions, centers of parts, sufficiently covering related surfaces of the part. This is achieved by our bone occupancy function, which identifies whether a given 3D point is placed within the bone. Coupling the proposed components, our framework offers several clear advantages: (1) users can obtain animatable 3D models of the arbitrary objects in improved quality from their casual videos, (2) users can manipulate 3D models in an intuitive manner with minimal costs, and (3) users can interactively add or delete control points as necessary. The experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of our framework on diverse instances, in reconstruction quality, interpretability and easier manipulation. Our code is available at https://github.com/subin6/HSNB.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge