Michael S. Brown
Generating the Past, Present and Future from a Motion-Blurred Image
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:We seek to answer the question: what can a motion-blurred image reveal about a scene's past, present, and future? Although motion blur obscures image details and degrades visual quality, it also encodes information about scene and camera motion during an exposure. Previous techniques leverage this information to estimate a sharp image from an input blurry one, or to predict a sequence of video frames showing what might have occurred at the moment of image capture. However, they rely on handcrafted priors or network architectures to resolve ambiguities in this inverse problem, and do not incorporate image and video priors on large-scale datasets. As such, existing methods struggle to reproduce complex scene dynamics and do not attempt to recover what occurred before or after an image was taken. Here, we introduce a new technique that repurposes a pre-trained video diffusion model trained on internet-scale datasets to recover videos revealing complex scene dynamics during the moment of capture and what might have occurred immediately into the past or future. Our approach is robust and versatile; it outperforms previous methods for this task, generalizes to challenging in-the-wild images, and supports downstream tasks such as recovering camera trajectories, object motion, and dynamic 3D scene structure. Code and data are available at https://blur2vid.github.io
* Code and data are available at https://blur2vid.github.io
Modular Neural Image Signal Processing
Dec 09, 2025
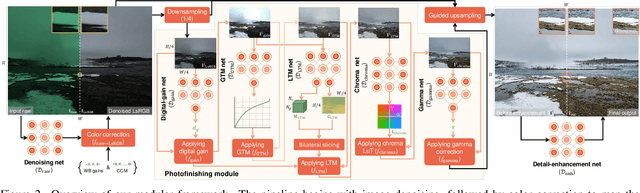
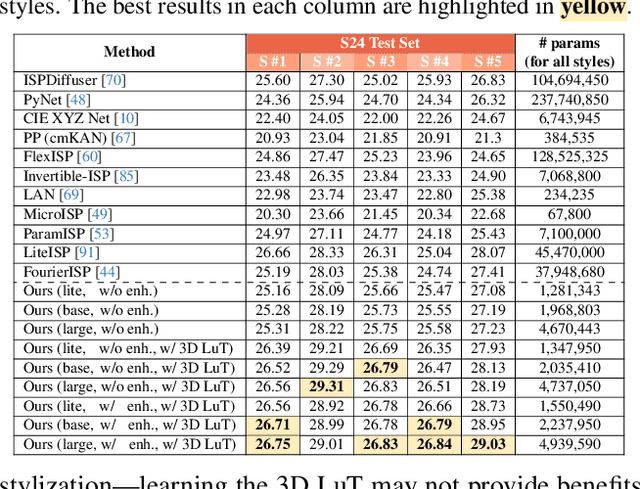
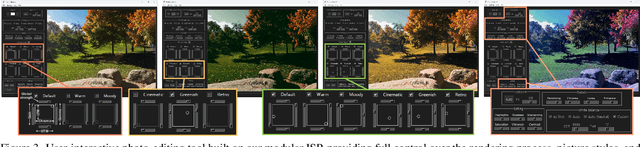
Abstract:This paper presents a modular neural image signal processing (ISP) framework that processes raw inputs and renders high-quality display-referred images. Unlike prior neural ISP designs, our method introduces a high degree of modularity, providing full control over multiple intermediate stages of the rendering process.~This modular design not only achieves high rendering accuracy but also improves scalability, debuggability, generalization to unseen cameras, and flexibility to match different user-preference styles. To demonstrate the advantages of this design, we built a user-interactive photo-editing tool that leverages our neural ISP to support diverse editing operations and picture styles. The tool is carefully engineered to take advantage of the high-quality rendering of our neural ISP and to enable unlimited post-editable re-rendering. Our method is a fully learning-based framework with variants of different capacities, all of moderate size (ranging from ~0.5 M to ~3.9 M parameters for the entire pipeline), and consistently delivers competitive qualitative and quantitative results across multiple test sets. Watch the supplemental video at: https://youtu.be/ByhQjQSjxVM
Evaluating Low-Light Image Enhancement Across Multiple Intensity Levels
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Imaging in low-light environments is challenging due to reduced scene radiance, which leads to elevated sensor noise and reduced color saturation. Most learning-based low-light enhancement methods rely on paired training data captured under a single low-light condition and a well-lit reference. The lack of radiance diversity limits our understanding of how enhancement techniques perform across varying illumination intensities. We introduce the Multi-Illumination Low-Light (MILL) dataset, containing images captured at diverse light intensities under controlled conditions with fixed camera settings and precise illuminance measurements. MILL enables comprehensive evaluation of enhancement algorithms across variable lighting conditions. We benchmark several state-of-the-art methods and reveal significant performance variations across intensity levels. Leveraging the unique multi-illumination structure of our dataset, we propose improvements that enhance robustness across diverse illumination scenarios. Our modifications achieve up to 10 dB PSNR improvement for DSLR and 2 dB for the smartphone on Full HD images.
Improved Mapping Between Illuminations and Sensors for RAW Images
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:RAW images are unprocessed camera sensor output with sensor-specific RGB values based on the sensor's color filter spectral sensitivities. RAW images also incur strong color casts due to the sensor's response to the spectral properties of scene illumination. The sensor- and illumination-specific nature of RAW images makes it challenging to capture RAW datasets for deep learning methods, as scenes need to be captured for each sensor and under a wide range of illumination. Methods for illumination augmentation for a given sensor and the ability to map RAW images between sensors are important for reducing the burden of data capture. To explore this problem, we introduce the first-of-its-kind dataset comprising carefully captured scenes under a wide range of illumination. Specifically, we use a customized lightbox with tunable illumination spectra to capture several scenes with different cameras. Our illumination and sensor mapping dataset has 390 illuminations, four cameras, and 18 scenes. Using this dataset, we introduce a lightweight neural network approach for illumination and sensor mapping that outperforms competing methods. We demonstrate the utility of our approach on the downstream task of training a neural ISP. Link to project page: https://github.com/SamsungLabs/illum-sensor-mapping.
Spectral Sensitivity Estimation with an Uncalibrated Diffraction Grating
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a practical and accurate calibration method for camera spectral sensitivity using a diffraction grating. Accurate calibration of camera spectral sensitivity is crucial for various computer vision tasks, including color correction, illumination estimation, and material analysis. Unlike existing approaches that require specialized narrow-band filters or reference targets with known spectral reflectances, our method only requires an uncalibrated diffraction grating sheet, readily available off-the-shelf. By capturing images of the direct illumination and its diffracted pattern through the grating sheet, our method estimates both the camera spectral sensitivity and the diffraction grating parameters in a closed-form manner. Experiments on synthetic and real-world data demonstrate that our method outperforms conventional reference target-based methods, underscoring its effectiveness and practicality.
Learning Camera-Agnostic White-Balance Preferences
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:The image signal processor (ISP) pipeline in modern cameras consists of several modules that transform raw sensor data into visually pleasing images in a display color space. Among these, the auto white balance (AWB) module is essential for compensating for scene illumination. However, commercial AWB systems often strive to compute aesthetic white-balance preferences rather than accurate neutral color correction. While learning-based methods have improved AWB accuracy, they typically struggle to generalize across different camera sensors -- an issue for smartphones with multiple cameras. Recent work has explored cross-camera AWB, but most methods remain focused on achieving neutral white balance. In contrast, this paper is the first to address aesthetic consistency by learning a post-illuminant-estimation mapping that transforms neutral illuminant corrections into aesthetically preferred corrections in a camera-agnostic space. Once trained, our mapping can be applied after any neutral AWB module to enable consistent and stylized color rendering across unseen cameras. Our proposed model is lightweight -- containing only $\sim$500 parameters -- and runs in just 0.024 milliseconds on a typical flagship mobile CPU. Evaluated on a dataset of 771 smartphone images from three different cameras, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance while remaining fully compatible with existing cross-camera AWB techniques, introducing minimal computational and memory overhead.
CCMNet: Leveraging Calibrated Color Correction Matrices for Cross-Camera Color Constancy
Apr 10, 2025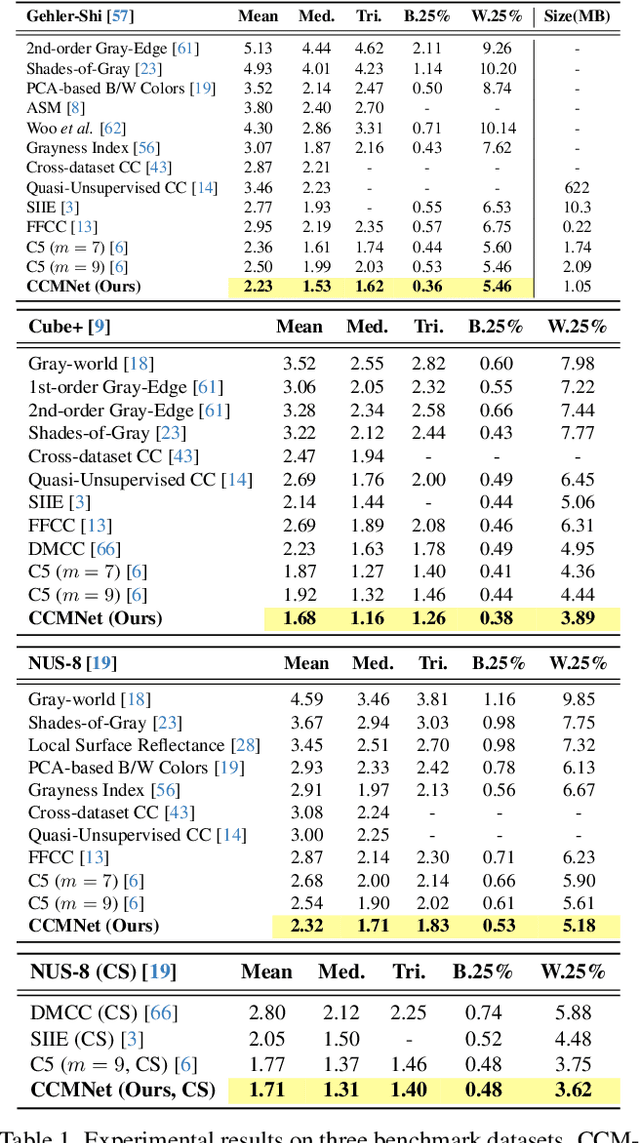
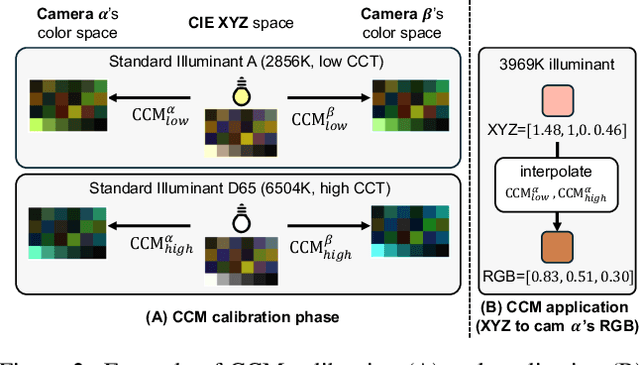
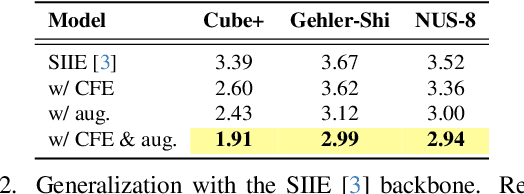
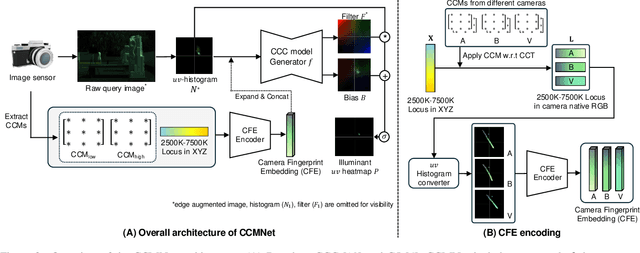
Abstract:Computational color constancy, or white balancing, is a key module in a camera's image signal processor (ISP) that corrects color casts from scene lighting. Because this operation occurs in the camera-specific raw color space, white balance algorithms must adapt to different cameras. This paper introduces a learning-based method for cross-camera color constancy that generalizes to new cameras without retraining. Our method leverages pre-calibrated color correction matrices (CCMs) available on ISPs that map the camera's raw color space to a standard space (e.g., CIE XYZ). Our method uses these CCMs to transform predefined illumination colors (i.e., along the Planckian locus) into the test camera's raw space. The mapped illuminants are encoded into a compact camera fingerprint embedding (CFE) that enables the network to adapt to unseen cameras. To prevent overfitting due to limited cameras and CCMs during training, we introduce a data augmentation technique that interpolates between cameras and their CCMs. Experimental results across multiple datasets and backbones show that our method achieves state-of-the-art cross-camera color constancy while remaining lightweight and relying only on data readily available in camera ISPs.
Time-Aware Auto White Balance in Mobile Photography
Apr 08, 2025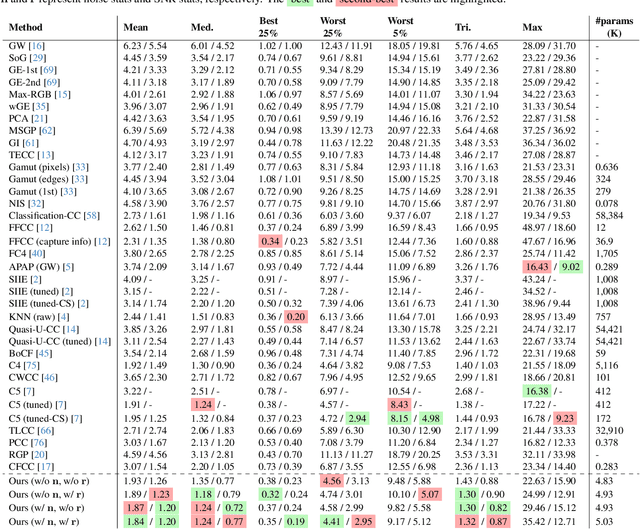
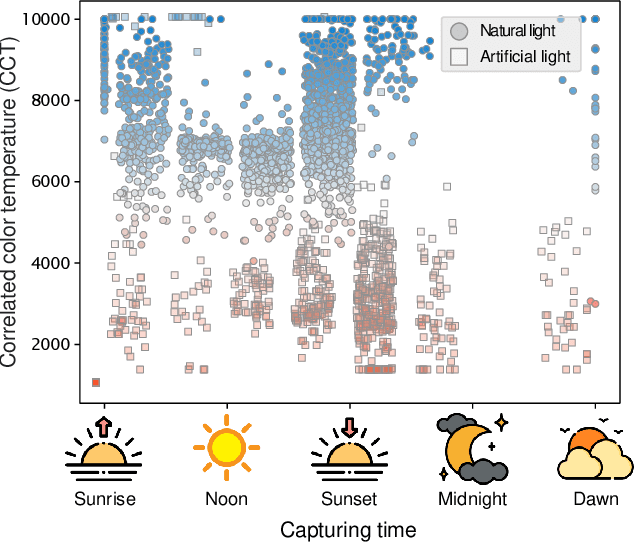
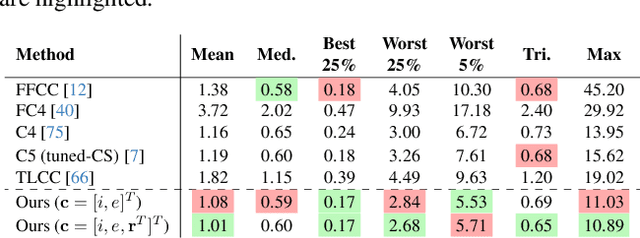
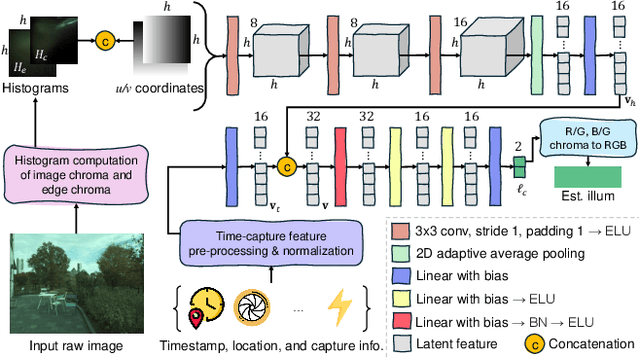
Abstract:Cameras rely on auto white balance (AWB) to correct undesirable color casts caused by scene illumination and the camera's spectral sensitivity. This is typically achieved using an illuminant estimator that determines the global color cast solely from the color information in the camera's raw sensor image. Mobile devices provide valuable additional metadata-such as capture timestamp and geolocation-that offers strong contextual clues to help narrow down the possible illumination solutions. This paper proposes a lightweight illuminant estimation method that incorporates such contextual metadata, along with additional capture information and image colors, into a compact model (~5K parameters), achieving promising results, matching or surpassing larger models. To validate our method, we introduce a dataset of 3,224 smartphone images with contextual metadata collected at various times of day and under diverse lighting conditions. The dataset includes ground-truth illuminant colors, determined using a color chart, and user-preferred illuminants validated through a user study, providing a comprehensive benchmark for AWB evaluation.
Examining Joint Demosaicing and Denoising for Single-, Quad-, and Nona-Bayer Patterns
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Camera sensors have color filters arranged in a mosaic layout, traditionally following the Bayer pattern. Demosaicing is a critical step camera hardware applies to obtain a full-channel RGB image. Many smartphones now have multiple sensors with different patterns, such as Quad-Bayer or Nona-Bayer. Most modern deep network-based models perform joint demosaicing and denoising with the current strategy of training a separate network per pattern. Relying on individual models per pattern requires additional memory overhead and makes it challenging to switch quickly between cameras. In this work, we are interested in analyzing strategies for joint demosaicing and denoising for the three main mosaic layouts (1x1 Single-Bayer, 2x2 Quad-Bayer, and 3x3 Nona-Bayer). We found that concatenating a three-channel mosaic embedding to the input image and training with a unified demosaicing architecture yields results that outperform existing Quad-Bayer and Nona-Bayer models and are comparable to Single-Bayer models. Additionally, we describe a maskout strategy that enhances the model performance and facilitates dead pixel correction -- a step often overlooked by existing AI-based demosaicing models. As part of this effort, we captured a new demosaicing dataset of 638 RAW images that contain challenging scenes with patches annotated for training, validation, and testing.
Revisiting Image Fusion for Multi-Illuminant White-Balance Correction
Mar 18, 2025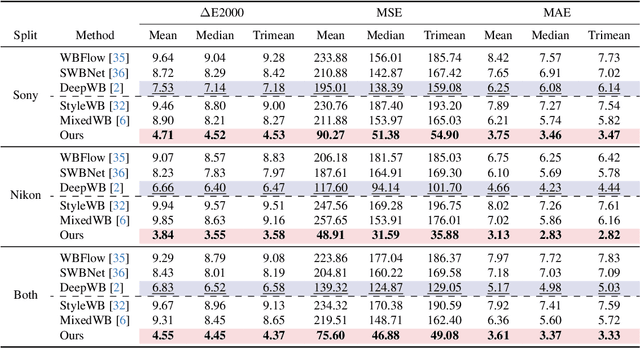
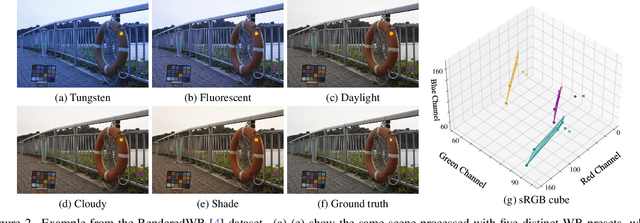
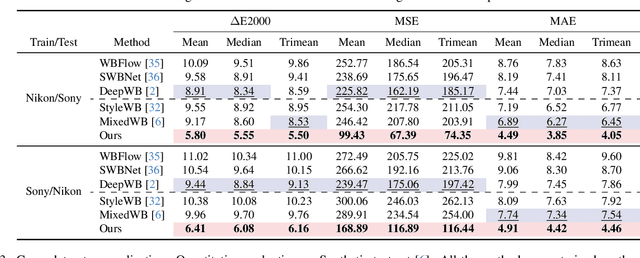
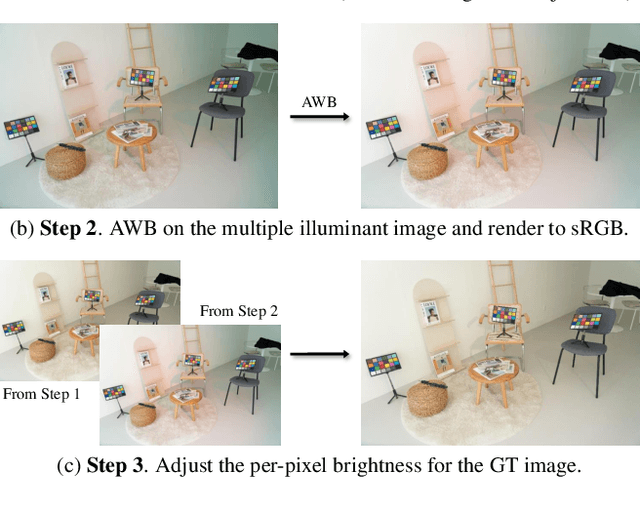
Abstract:White balance (WB) correction in scenes with multiple illuminants remains a persistent challenge in computer vision. Recent methods explored fusion-based approaches, where a neural network linearly blends multiple sRGB versions of an input image, each processed with predefined WB presets. However, we demonstrate that these methods are suboptimal for common multi-illuminant scenarios. Additionally, existing fusion-based methods rely on sRGB WB datasets lacking dedicated multi-illuminant images, limiting both training and evaluation. To address these challenges, we introduce two key contributions. First, we propose an efficient transformer-based model that effectively captures spatial dependencies across sRGB WB presets, substantially improving upon linear fusion techniques. Second, we introduce a large-scale multi-illuminant dataset comprising over 16,000 sRGB images rendered with five different WB settings, along with WB-corrected images. Our method achieves up to 100\% improvement over existing techniques on our new multi-illuminant image fusion dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge