Wen Gao
SoftSignSGD(S3): An Enhanced Optimizer for Practical DNN Training and Loss Spikes Minimization Beyond Adam
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Adam has proven remarkable successful in training deep neural networks, but the mechanisms underlying its empirical successes and limitations remain underexplored. In this study, we demonstrate that the effectiveness of Adam stems largely from its similarity to SignSGD in robustly handling large gradient fluctuations, yet it is also vulnerable to destabilizing loss spikes due to its uncontrolled update scaling. To enhance the advantage of Adam and mitigate its limitation, we propose SignSoftSGD (S3), a novel optimizer with three key innovations. \emph{First}, S3 generalizes the sign-like update by employing a flexible $p$-th order momentum ($p \geq 1$) in the denominator, departing from the conventional second-order momentum (variance) preconditioning. This design enables enhanced performance while achieving stable training even with aggressive learning rates. \emph{Second}, S3 minimizes the occurrences of loss spikes through unified exponential moving average coefficients for numerator and denominator momenta, which inherently bound updates to $[-1, 1]$ and simplify hyperparameter tuning. \emph{Third}, S3 incorporates an equivalent Nesterov's accelerated gradient(NAG) module, accelerating convergence without memory overhead. Theoretically, we prove that S3 achieves the optimal convergence rate of $O\left(\frac{1}{T^{\sfrac{1}{4}}}\right)$ for general nonconvex stochastic optimization under weak assumptions. Extensive experiments across a range of vision and language tasks show that \textsf{\small S3} not only converges more rapidly and improves performance but also rarely experiences loss spikes, even with a \textbf{$\bm{10 \times}$} larger learning rate. In fact, S3 delivers performance comparable to or better than AdamW with \textbf{$2 \times$} the training steps, establishing its efficacy in both efficiency and final task performance.
TinySplat: Feedforward Approach for Generating Compact 3D Scene Representation
Jun 11, 2025



Abstract:The recent development of feedforward 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) presents a new paradigm to reconstruct 3D scenes. Using neural networks trained on large-scale multi-view datasets, it can directly infer 3DGS representations from sparse input views. Although the feedforward approach achieves high reconstruction speed, it still suffers from the substantial storage cost of 3D Gaussians. Existing 3DGS compression methods relying on scene-wise optimization are not applicable due to architectural incompatibilities. To overcome this limitation, we propose TinySplat, a complete feedforward approach for generating compact 3D scene representations. Built upon standard feedforward 3DGS methods, TinySplat integrates a training-free compression framework that systematically eliminates key sources of redundancy. Specifically, we introduce View-Projection Transformation (VPT) to reduce geometric redundancy by projecting geometric parameters into a more compact space. We further present Visibility-Aware Basis Reduction (VABR), which mitigates perceptual redundancy by aligning feature energy along dominant viewing directions via basis transformation. Lastly, spatial redundancy is addressed through an off-the-shelf video codec. Comprehensive experimental results on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that TinySplat achieves over 100x compression for 3D Gaussian data generated by feedforward methods. Compared to the state-of-the-art compression approach, we achieve comparable quality with only 6% of the storage size. Meanwhile, our compression framework requires only 25% of the encoding time and 1% of the decoding time.
Emerging Advances in Learned Video Compression: Models, Systems and Beyond
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Video compression is a fundamental topic in the visual intelligence, bridging visual signal sensing/capturing and high-level visual analytics. The broad success of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has enriched the horizon of video compression into novel paradigms by leveraging end-to-end optimized neural models. In this survey, we first provide a comprehensive and systematic overview of recent literature on end-to-end optimized learned video coding, covering the spectrum of pioneering efforts in both uni-directional and bi-directional prediction based compression model designation. We further delve into the optimization techniques employed in learned video compression (LVC), emphasizing their technical innovations, advantages. Some standardization progress is also reported. Furthermore, we investigate the system design and hardware implementation challenges of the LVC inclusively. Finally, we present the extensive simulation results to demonstrate the superior compression performance of LVC models, addressing the question that why learned codecs and AI-based video technology would have with broad impact on future visual intelligence research.
A Joint Visual Compression and Perception Framework for Neuralmorphic Spiking Camera
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:The advent of neuralmorphic spike cameras has garnered significant attention for their ability to capture continuous motion with unparalleled temporal resolution.However, this imaging attribute necessitates considerable resources for binary spike data storage and transmission.In light of compression and spike-driven intelligent applications, we present the notion of Spike Coding for Intelligence (SCI), wherein spike sequences are compressed and optimized for both bit-rate and task performance.Drawing inspiration from the mammalian vision system, we propose a dual-pathway architecture for separate processing of spatial semantics and motion information, which is then merged to produce features for compression.A refinement scheme is also introduced to ensure consistency between decoded features and motion vectors.We further propose a temporal regression approach that integrates various motion dynamics, capitalizing on the advancements in warping and deformation simultaneously.Comprehensive experiments demonstrate our scheme achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance for spike compression and analysis.We achieve an average 17.25% BD-rate reduction compared to SOTA codecs and a 4.3% accuracy improvement over SpiReco for spike-based classification, with 88.26% complexity reduction and 42.41% inference time saving on the encoding side.
OpenEarthSensing: Large-Scale Fine-Grained Benchmark for Open-World Remote Sensing
Feb 28, 2025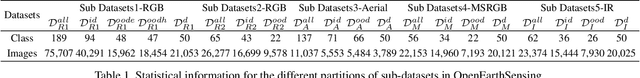
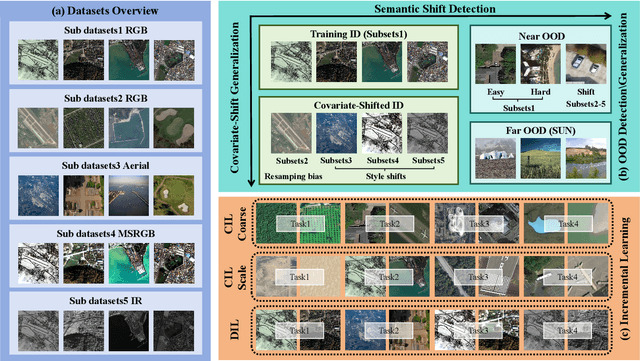
Abstract:In open-world remote sensing, deployed models must continuously adapt to a steady influx of new data, which often exhibits various shifts compared to what the model encountered during the training phase. To effectively handle the new data, models are required to detect semantic shifts, adapt to covariate shifts, and continuously update themselves. These challenges give rise to a variety of open-world tasks. However, existing open-world remote sensing studies typically train and test within a single dataset to simulate open-world conditions. Currently, there is a lack of large-scale benchmarks capable of evaluating multiple open-world tasks. In this paper, we introduce OpenEarthSensing, a large-scale fine-grained benchmark for open-world remote sensing. OpenEarthSensing includes 189 scene and objects categories, covering the vast majority of potential semantic shifts that may occur in the real world. Additionally, OpenEarthSensing encompasses five data domains with significant covariate shifts, including two RGB satellite domians, one RGB aerial domian, one MS RGB domian, and one infrared domian. The various domains provide a more comprehensive testbed for evaluating the generalization performance of open-world models. We conduct the baseline evaluation of current mainstream open-world tasks and methods on OpenEarthSensing, demonstrating that it serves as a challenging benchmark for open-world remote sensing.
CALLIC: Content Adaptive Learning for Lossless Image Compression
Dec 23, 2024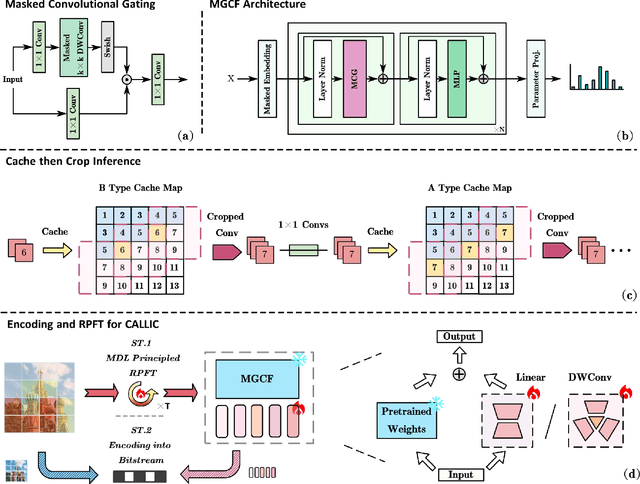
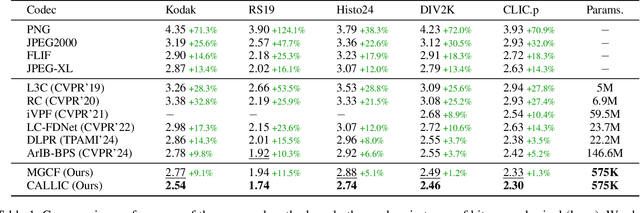
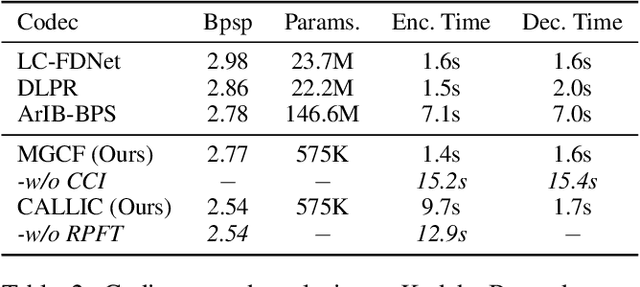
Abstract:Learned lossless image compression has achieved significant advancements in recent years. However, existing methods often rely on training amortized generative models on massive datasets, resulting in sub-optimal probability distribution estimation for specific testing images during encoding process. To address this challenge, we explore the connection between the Minimum Description Length (MDL) principle and Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning (PETL), leading to the development of a novel content-adaptive approach for learned lossless image compression, dubbed CALLIC. Specifically, we first propose a content-aware autoregressive self-attention mechanism by leveraging convolutional gating operations, termed Masked Gated ConvFormer (MGCF), and pretrain MGCF on training dataset. Cache then Crop Inference (CCI) is proposed to accelerate the coding process. During encoding, we decompose pre-trained layers, including depth-wise convolutions, using low-rank matrices and then adapt the incremental weights on testing image by Rate-guided Progressive Fine-Tuning (RPFT). RPFT fine-tunes with gradually increasing patches that are sorted in descending order by estimated entropy, optimizing learning process and reducing adaptation time. Extensive experiments across diverse datasets demonstrate that CALLIC sets a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) for learned lossless image compression.
Predicting Satisfied User and Machine Ratio for Compressed Images: A Unified Approach
Dec 23, 2024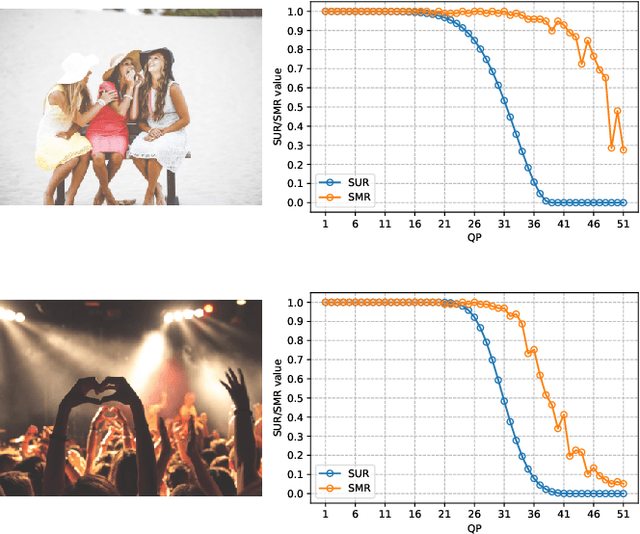
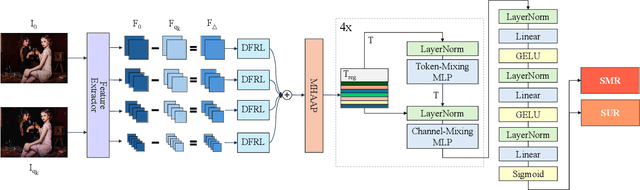
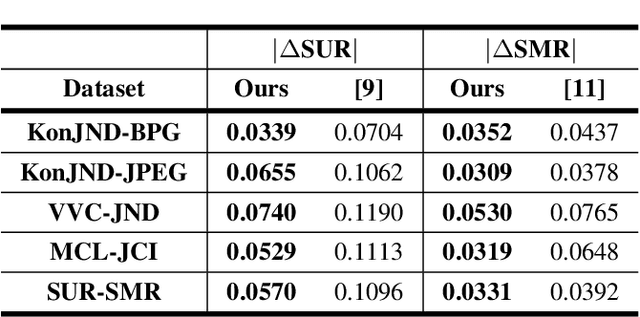
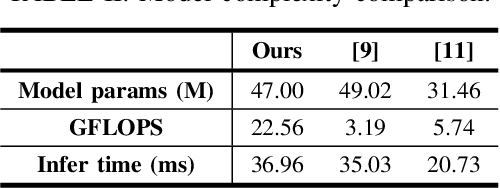
Abstract:Nowadays, high-quality images are pursued by both humans for better viewing experience and by machines for more accurate visual analysis. However, images are usually compressed before being consumed, decreasing their quality. It is meaningful to predict the perceptual quality of compressed images for both humans and machines, which guides the optimization for compression. In this paper, we propose a unified approach to address this. Specifically, we create a deep learning-based model to predict Satisfied User Ratio (SUR) and Satisfied Machine Ratio (SMR) of compressed images simultaneously. We first pre-train a feature extractor network on a large-scale SMR-annotated dataset with human perception-related quality labels generated by diverse image quality models, which simulates the acquisition of SUR labels. Then, we propose an MLP-Mixer-based network to predict SUR and SMR by leveraging and fusing the extracted multi-layer features. We introduce a Difference Feature Residual Learning (DFRL) module to learn more discriminative difference features. We further use a Multi-Head Attention Aggregation and Pooling (MHAAP) layer to aggregate difference features and reduce their redundancy. Experimental results indicate that the proposed model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art SUR and SMR prediction methods. Moreover, our joint learning scheme of human and machine perceptual quality prediction tasks is effective at improving the performance of both.
Image-based Freeform Handwriting Authentication with Energy-oriented Self-Supervised Learning
Aug 19, 2024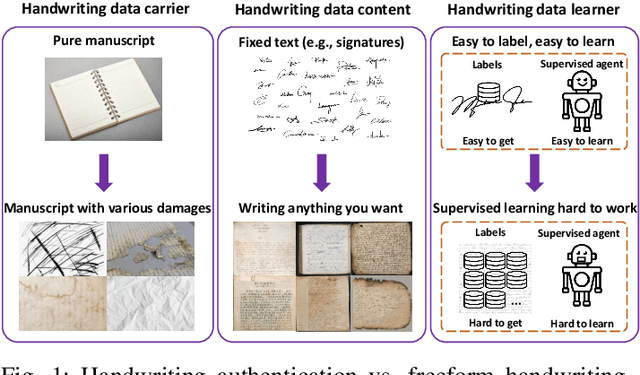
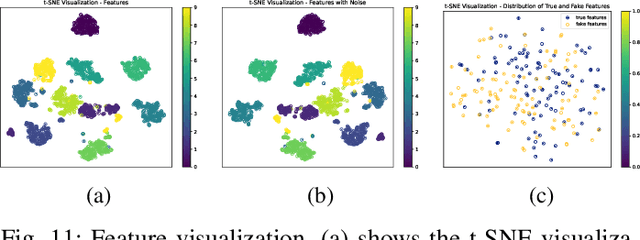

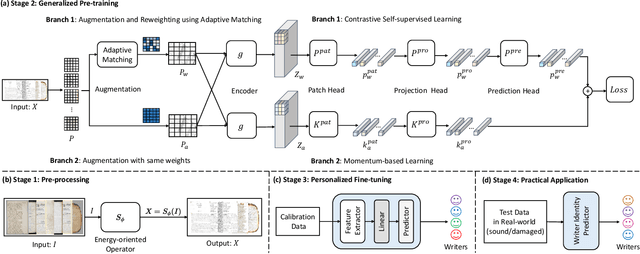
Abstract:Freeform handwriting authentication verifies a person's identity from their writing style and habits in messy handwriting data. This technique has gained widespread attention in recent years as a valuable tool for various fields, e.g., fraud prevention and cultural heritage protection. However, it still remains a challenging task in reality due to three reasons: (i) severe damage, (ii) complex high-dimensional features, and (iii) lack of supervision. To address these issues, we propose SherlockNet, an energy-oriented two-branch contrastive self-supervised learning framework for robust and fast freeform handwriting authentication. It consists of four stages: (i) pre-processing: converting manuscripts into energy distributions using a novel plug-and-play energy-oriented operator to eliminate the influence of noise; (ii) generalized pre-training: learning general representation through two-branch momentum-based adaptive contrastive learning with the energy distributions, which handles the high-dimensional features and spatial dependencies of handwriting; (iii) personalized fine-tuning: calibrating the learned knowledge using a small amount of labeled data from downstream tasks; and (iv) practical application: identifying individual handwriting from scrambled, missing, or forged data efficiently and conveniently. Considering the practicality, we construct EN-HA, a novel dataset that simulates data forgery and severe damage in real applications. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on six benchmark datasets including our EN-HA, and the results prove the robustness and efficiency of SherlockNet.
Aligning Cyber Space with Physical World: A Comprehensive Survey on Embodied AI
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:Embodied Artificial Intelligence (Embodied AI) is crucial for achieving Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and serves as a foundation for various applications that bridge cyberspace and the physical world. Recently, the emergence of Multi-modal Large Models (MLMs) and World Models (WMs) have attracted significant attention due to their remarkable perception, interaction, and reasoning capabilities, making them a promising architecture for the brain of embodied agents. However, there is no comprehensive survey for Embodied AI in the era of MLMs. In this survey, we give a comprehensive exploration of the latest advancements in Embodied AI. Our analysis firstly navigates through the forefront of representative works of embodied robots and simulators, to fully understand the research focuses and their limitations. Then, we analyze four main research targets: 1) embodied perception, 2) embodied interaction, 3) embodied agent, and 4) sim-to-real adaptation, covering the state-of-the-art methods, essential paradigms, and comprehensive datasets. Additionally, we explore the complexities of MLMs in virtual and real embodied agents, highlighting their significance in facilitating interactions in dynamic digital and physical environments. Finally, we summarize the challenges and limitations of embodied AI and discuss their potential future directions. We hope this survey will serve as a foundational reference for the research community and inspire continued innovation. The associated project can be found at https://github.com/HCPLab-SYSU/Embodied_AI_Paper_List.
Understanding is Compression
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:We have previously shown all understanding or learning are compression, under reasonable assumptions. In principle, better understanding of data should improve data compression. Traditional compression methodologies focus on encoding frequencies or some other computable properties of data. Large language models approximate the uncomputable Solomonoff distribution, opening up a whole new avenue to justify our theory. Under the new uncomputable paradigm, we present LMCompress based on the understanding of data using large models. LMCompress has significantly better lossless compression ratios than all other lossless data compression methods, doubling the compression ratios of JPEG-XL for images, FLAC for audios and H264 for videos, and tripling or quadrupling the compression ratio of bz2 for texts. The better a large model understands the data, the better LMCompress compresses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge